Design Features
It is no secret that other fishermen with extensive experience, if necessary, make spinning rings with their own hands, using various hard metals and composites. But nowadays this is, rather, an exception to the rule , since on sale you can find a lot of high-quality new rings from various manufacturers. Now they are made from modern materials that must meet the following requirements:
- be durable and wear-resistant;
- have excellent corrosion resistance;
- be as light as possible, because their weight affects the weight, and, consequently, the quality characteristics of the entire rod.
The design of good rings consists of two elements: a strong, wear-resistant insert and its frame (frame), which is attached to the blank body on one or two legs. Moreover, frames on two legs only have frames on particularly strong spinning rods , and then only the first three or four rings. The remaining passage rings are mounted on one leg; modern structural materials allow this to be done without a significant reduction in their strength, but with a significant reduction in the weight of the fasteners.
A good angler should know the basic quality characteristics of frames. This:
- Number of mounting legs.
- Frame height.
- Total length.
- Frame diameter.
Nowadays, the strongest and lightest frames are made of titanium .
Modern inserts, which are in direct contact with the fishing line and are located inside the frames, are made of three materials:
- Made from aluminum oxide ( Al2O3 ).
- Made from silicon carbide ( SiC ).
- From any light metal on which a surface coating of a particularly strong alloy is applied, for example titanium nitride.
Various rings made of durable metal or porcelain , which used to be very popular, are no longer used .
You need to know that aluminum oxide rings can be used if you use regular monofilament . When using braided cords , it is better to choose a spinning rod with more wear-resistant rings .
The best rings on spinning rods
09/13/2013 admin Leave a comment
A rod without rings is not a spinning rod. Many anglers have a question about which rings are the best. Spinning guides are designed to guide the fishing line and prevent it from sagging under its own weight or sticking to the rod, but the most important purpose is to distribute the load along the whip. The material of the guide rings, their quality and correct location affect the service life of the fishing line, as well as the spinning rod as a whole. Placing the rings in the wrong place will lead to its breaking, since when casting and when fishing for fish, the rod will take on deformation loads that are contrary to the structure of the whip.
Both the casting distance and the quality of the line on the reel depend on the strength of the material from which the rings are made and the degree of its polishing. On the first spinning rods, the rings were made of steel wire. Over time, the designer introduced steel, chrome and chromium carbide rings. They are still installed on metal and fiberglass spinning rods . Such rings have a lot of disadvantages. Their frames rust, their liners wear out and crack. The low quality of such products is not justified even by their cheapness. Ceramic rings can be called a little improved.
They are inexpensive, but they are fragile and heavy. Oxide rings (made of silicon, lithium, aluminum oxide) are better quality, but they also have many disadvantages: they are difficult to polish, and sometimes they snap off. Agate rings are considered the best. In appearance and especially in price, they are more like jewelry. Therefore, not everyone can afford such luxury. However, science and production do not stand still.
And if spinning players needed rings of extreme hardness, mirror smoothness, with a minimum coefficient of friction and, most importantly, at an affordable price, then sooner or later they were bound to appear. And so it happened. “sic” rings appeared, made of silicon carbide-based material. Recently, leading companies producing high-quality fishing rods have been equipping them with just such rings.
In addition, such companies also produce unbreakable rings of the highest quality “gold germet”, although their price is very high and not every angler can afford to purchase such a purchase. Depending on its length, the rod can be installed with 4-7 guide rings, less often up to 8-9, or 11. Short rods for winter or vertical trolling are equipped with 3 rings. Theoretically, the optimal number of rings and their correct placement would make it possible to turn a spinning rod into an absolutely reliable tackle.
But in practice, it turns out, not everything is so simple. It would seem that the more rings there are. The more evenly the load is distributed along the entire length of the rod. And when fishing for large fish or when casting sharply, the elasticity and flexibility of the whip is fully used, and the strength of the fishing line becomes less important. However, increasing the number of rings, firstly, increases the weight of the tackle, thereby changing its characteristics not for the better. And secondly, it increases the friction of the fishing line in the guides and when casting, the range and accuracy decreases. And when winding, the likelihood of it breaking increases.
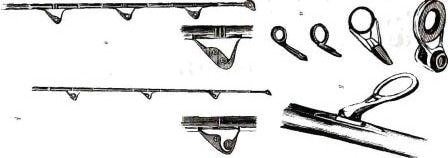
The number of rings on the whip is determined based on calculations, taking into account its properties and dimensions. The largest ring in diameter is placed closer to the butt, further, i.e. Rings are attached to the tip of the whip in decreasing order, but the frequency of their arrangement increases (to reduce the load on the tip). For the same reason, the last upper “tulip” ring should not be located at a right angle to the whip, like the previous rings, but at an angle of 110 - 125 degrees.
This position makes the rod resistant to heavy loads in the lower parts of the whip. The diameter of the rings is also a very important factor, especially when equipping rods with open spinning reels. The fact is that with such a reel, the fishing line is wound from a stationary spool, and not from a rotating drum, and running from it, the fishing line describes a complex spiral trajectory. At the same time, it should “fall” into the rings, slightly touching their walls. Otherwise, the line will break, which will inevitably lead to tangling.
Therefore, to reduce friction, it is necessary to increase the diameter of the rings, but this is irrational: the structure of the rod will deteriorate and its price will increase. This problem was solved by the appearance of rings with triangular-shaped inserts with rounded tops. Passing through such rings, the line comes into contact with the sleeve only at three points. This modification of the rings solved the problem with friction and eliminated rotational runout of the fishing line, and the weight of the rings themselves also decreases. Usually only the most massive base ring closest to the coil is triangular.
On modern spinning rods, the guide rings have become even more complex. The simplest ones include an outer frame, a plastic shock absorber and a durable, wear-resistant liner. But there are also roller, folding, and removable rings. Basically, the rings are attached to the whip using stands (legs), their number, depending on the design features, varies from two to four. The newest modern lightweight rings are equipped with more than just one particularly strong spring post.
A separate group of fishing rods is represented by spinning rods with one or two base rings or without guide rings. The line passes into the cavity of the rod through a perfectly polished Kevlar channel or through rings located in the cavity of the rod. In terms of strength, ringless fishing rods are superior to traditional spinning rods, since they evenly distribute the load on the rod along its entire length, but the casting range of bait with such gear is limited to fifteen to twenty meters. Therefore, rods without rings are used mainly when fishing with a float or swimmer.
These articles may interest you
- Why don't roaches bite, reasons?
- Winter fishing in Finland, what and how
- Lures with a rotating petal, differences and features
- Fishing on the Inya River in the Altai Territory
- Fishing on the Ob in Altai and Novosibirsk region
- Fishing on Lake Teletskoye in the Altai Mountains
- Our gear
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Recent Entries
- Fishing with dragnet
- Making Carolina rigs for pike and perch fishing
- How to equip a Volzhanka 46 Fish boat for fishing
- Winter fishing in Finland, what and how
- About setting up the jig when assembling winter tackle
- Fishing on the Tura River in winter in February
- The A-elita vent is visible from afar
- Winter lure “A-Elita” is the best of all
- How to attach a float rig to a fishing rod?
- Installation of float equipment for fly and plug fishing rods
Advanced site search
Group 1 below in site entries
What should they be?
There are several important requirements for the guides of high-quality fishing rods, each of which is determined by the declared characteristics of the form itself.
As a rule, when designing a fishing rod, the required minimum number . This setting affects the following:
- To ensure the correct distribution of the load that occurs during fishing along the length of the rod.
- To increase or decrease the possible casting distance.
- For the weight of the rod.
- To ensure that the line (cord) passes evenly along the blank, which is very important when casting.
In most cases, manufacturers, when calculating the number of guides needed, adhere to the following rule: quantity = rod length in feet - 1 . This means that if the length of the form is 7 feet (approximately 214 cm) , then it must have 6 rings , including the tulip.
The following requirements apply to the rings themselves:
- The inner surface must be well polished.
- The entire surface must be free of cracks and chips.
- Solid, wear-resistant base.
- High-quality assembly of components
- Strong attachment to the base, without gaps or play.
Particular attention should be paid to the final ring - the tulip. When fishing, it bears up to 90% of all loads , so it must have special wear resistance in all respects. If, upon inspection, you find the slightest damage (chips, roughness of the inner surface, groove), it is recommended to immediately replace it with a new one.
Interesting! Not long ago, tulips with a special “dry” profile appeared on sale. They have a high-strength insert that seems to “drench” the frame itself, thereby protecting it from contact with the cord.
The same applies to the rest of the access rings. Any deviation from the requirements placed on them can lead to damage to the fishing line (cord) and improper operation of the entire equipment, which ultimately can lead to failure in fishing.
Selecting a spinning rod. What should you consider?
Spinning rods for fishing are usually selected according to certain parameters, such as:
- manufacturer;
- model;
- length;
- fishing rod weight;
- the material from which it is made;
- as well as cost.
The length of the spinning rod can, in principle, be any - there are models from 1.5 to 4 meters long. The casting distance depends primarily on this parameter. So, for example, if you are going to fish from the shore or from a boat, then you will need a two-meter rod.
In addition, when choosing a spinning rod, it is also recommended to pay attention to the ease of assembly/disassembly of the rod. So, for example, telescopic spinning rods are convenient because they easily extend and fold inside the structure itself. But plug-in spinning rods, on the contrary, need to be constantly assembled and disassembled in parts. Both options are equally popular among fishermen, although judging by the reviews: plug-in ones are more reliable.

As for the cost of spinning rods. The price range for them is quite large - from 1,500 to 40,000 rubles and above. It is best to look at models starting from 2,500-3,000 rubles. For this price you can buy a high-quality spinning rod that will serve you for more than one season.
Of course, there are more expensive and reliable models, but if you choose your first fishing rod, there is no point in overpaying for it (since, from experience, the first few fishing rods of every novice fisherman are thrown away).
Also, you should not buy fishing rods of unknown manufacture, from unknown Chinese brands, on foreign websites, as well as in regular markets or bazaars. Despite the low price, these are all disposable products and are not designed to last long.

We've got the theory figured out well, let's now move on to the most interesting thing: the rating of the best models on the Russian market.
Types of pass rings
- BALZER SIC
SIC – with silicon carbide insert. A distinctive feature is incredible strength and wear resistance to loads and high temperatures. The only drawback is their relative fragility.
- SIH - Made from lightweight yet durable material and designed to hold maximum weight.
- LOW is a special element to protect the cord from overlapping when throwing a whip.
- With ceramic insert - designed to block a cord made of monofilament material
Types of access rings
Passage rings are divided into 2 groups: according to technical characteristics and according to the material of manufacture.
According to technical characteristics, there are the following types of throughput rings for spinning rods:
1. SIC are rings with a silicon carbide insert. They are durable, do not corrode, and are lightweight. But they have one significant drawback: the material is too fragile, the ring can break even if transported carelessly. 2. SIH - lightweight, durable rings that are resistant to corrosion. Made from steel or titanium. 3. LOW – rings that are designed to protect the cord from overlapping when casting the rod. 4. Rings with ceramic inserts are lightweight, durable, and do not corrode.
As for the material of manufacture, the passage rings can be made of:
- become; — titanium; - aluminum oxide.
When making inserts, metal ceramics coated with silicon carbide, titanium nitride, porcelain, or porcelain are often used.
The guide rings play a far from secondary role in balancing the blank, so they must meet the following characteristics:
- be hard, bending resistant; — have good thermal conductivity; — do not succumb to corrosion; — there should be no chips, cracks or other damage on the surface.
Requirements for rings
- Polished surface.
- No cracks or chips.
- Lack of roughness.
- Solid and clean base.
- Strength of the material.
Parameters taken into account:
- size;
- weight;
- diameter.
To use your fishing rod effectively and for a long time, you need to secure it.
To protect a fishing rod from breakage, there must be a precise arrangement of rings - their number depends on the length of the rod.
As you approach the end of the form, the gap between them should increase by 0.02 centimeters. Proper placement will turn the spinning rod into a reliable tackle.
How to choose good guide rings
When purchasing, pay attention to the following:
– material of manufacture – it must be one that does not corrode, does not bend or crack; – size – select rings for your type of spinning rod, line thickness and reel dimensions. Rings that are not suitable in size will lead to the blank being unbalanced; when jerking, the tip may break; – fishing technique – if you use long-distance casting techniques, then pay attention to the LOW rings, which protect the line from overlapping when casting.
Guide rings for spinning rods
So - SiC is the material of the ceramic insert in the ring - silicon carbide. What is important about rings is that they are light: the “frame” and “insert” are not thick and bulky. It’s just that the lighter they are, the more sensitive and balanced the tackle becomes. The number of rings is important - if you bought a spinning rod for a couple of hundred dollars, then “everything is as it should”, but if for a couple of thousand rubles and there are a lot of rings, then this will overload the form, and a small number will lead to breakdown. The rings perform one important function - they evenly distribute the load from the fishing line along the rod blank. A more or less decent fishing rod is equipped with aluminum oxide rings, which do an excellent job with braid. More expensive rods have “SiC” installed, but there is not much difference. The main thing when choosing a fishing rod is that the line does not give too sharp an angle when passing through the rings under load - everything should be smooth. Nowadays there are rings coated with titanium nitride - they differ from ordinary ones in their smaller size and weight, but they also “hold” the braid perfectly. Both the casting distance and the landing of fish partly depend on the rings. How many should there be on a rod? Each manufacturer has its own designs and installation methods. For us, the main thing is to see whether the rings are attached to the rod well, whether the thread is wound evenly, and whether there are any extra protruding drops of varnish. You need to check that there are no cracks, nicks or similar surprises on the rings (even a small crack can cut your fishing line or braid). There is no need to be alarmed - when using braided braids, the rings may become deformed, although this only happens on outdated models. Now they put quite acceptable rings on even the cheapest spinning rods. If the rings are made by FUJI (the name is engraved on the leg of the ring), then you can safely buy the rod.
DIY ring replacement
Replacing the ring on a spinning rod may be necessary if it has lost its working properties, is damaged, or if the frame mount is broken . In order to make a quality replacement, the angler must prepare a comfortable workplace with good lighting and the following materials:
- A set of new rings. Or one ring, if the others do not need to be changed.
- Synthetic threads of small diameter.
- A good waterproof polyurethane varnish or Flex Coat.
- Paraffin candle or lighter.
- Epoxy adhesive.
- Sandpaper.
- Magnifying glass.
- A small sharp knife.
- A little duct tape.
- Hair dryer.
- Pliers.
To hold the spinning rod in the desired position during installation, it is necessary to prepare a special stand. It can be cut from a thick cardboard box.
It is clear that in order to install new rings, you first need to remove the old ones. How to properly remove rings from a spinning rod without damaging its body? Follow the following algorithm of actions:
- Using a hairdryer, carefully heat the base of the old fastener.
- In the area of the ring's foot, use a sharp knife to cut its covering.
- Carefully unwind the old winding, simultaneously removing the old varnish and glue.
- Remove the ring.
- We finally clean the fastening area. To do this, heat it with a hairdryer and a stick, carefully scraping off all excess.
- After removing the old winding, we remove the tulip using rotational movements, grabbing it by the body with pliers.
Important! Do not allow the rod to overheat. This can lead to damage to its surface and, as a result, to a change in its operating parameters.
How to properly attach new rings to a spinning rod is shown below:
- To prepare the ring for installation, you first need to fit its foot(s) to the surface of the blank. This is done using sandpaper.
- Using electrical tape, we temporarily install the rings in their designated places. This must be done to determine the compliance of their sizes and establish correct alignment.
- The next stage is wrapping the legs with synthetic thread. This is a very painstaking and responsible moment. First you need to secure the free end of the thread to the foot, and then wind it, following each new turn closer to the base of the foot.
- For greater reliability of fastening, it is better to make the winding in two or three layers.
- Carefully coat the threads and the base of the foot with epoxy glue. It must be the right consistency in order to secure all surfaces of the thread and the base of the foot.
- After the glue has dried, coat the fasteners with varnish or Flex Coat.
- The tulip must be fastened in the same sequence, with the only difference being that before installing it, you need to use a file to adjust the inner diameter of its mounting ring to the diameter of the tip of your spinning rod.
That's it, after the glue and varnish have completely dried, your spinning rod is ready for use again. You can equip it and go fishing.
Materials
Required tools:
- New part.
- Sharpened knife.
- Adhesive base that hardens quickly.
- Epoxy-based paste kit.
- Nylon cord or braided thread (with a minimum diameter).
- Container for mixing epoxy glue.
- Rod.
- Brush (to distribute the paste evenly).
Installation
- Heat the section of the rod that is intended for wrapping the ring element (you can use a hairdryer). This will help make the area softer. If the warm-up cools down quickly, it is possible to repeat this method again during operation. The absence of softening means that a different product has been applied to the hard coating, which differs in composition from the epoxy base. In this regard, heating attempts should be excluded, as they will not be successful.
- Using the tip of a knife, make an incision on the surface of the tab of the ring element. This will prevent damage to the shape. At this stage it is necessary to remove the coating completely. If you cannot remove the entire winding with one cut, it is worth repeating the steps to achieve an optimal result.
- In order to get rid of all particles, you can use a wooden or plastic base. These elements will help remove all the winding without damaging the surface.
- Sharpen the edges of the handle. This will make it easier to wind the cord.
- When choosing a thread, you should focus on a synthetic base, the thickness of which is No. 50 according to the sewing nomenclature.
- The winding process itself consists of 2 stages: tensioning the cord and fixing it on the form. For convenience, you should use a thick cardboard box.
- Next, you need to pass the cord through a thick covering, such as a stack of paper. This will allow you to achieve the most optimal tension. To prevent the spool of thread from unwinding prematurely, you should lower it into a container.
- The cord is fixed by turning the element around the form. To do this, you need to overlap, which is the most reliable way. Secure the winding section with a piece of tape.
- This process must be repeated until the thread reaches the top.
- Place the monofilament line behind the cord before the line reaches the end approximately 4 millimeters.
- When the winding is complete, secure the cord and cut off the end.
- Thread the thread through the loop and secure it.
- Trim the excess cord and tighten the element so that unwinding is prevented.
Guide ring materials
- metal ceramics;
- silicon carbide;
- aluminium oxide.
The materials from which the guide ring inserts are made have 4 main characteristics:
- hardness;
- density;
- thermal conductivity;
- strength.
The third parameter (thermal conductivity) is important for the simple reason that due to constant friction of the fishing line, an insert with low thermal conductivity heats up quite quickly, and this can cause damage to it, as well as damage to the glue that is used to attach it.
Silicon carbide (SiC) inserts are characterized by the highest thermal conductivity.
The numbers on the ring indicate the inner diameter of the frame into which the insert is inserted. It is for this reason that rings of the same size can have different internal diameters.
The strength of the rings is increased by increasing the thickness of the insert or frame itself, but this also increases their size and weight.
Therefore, Fuji employees came up with and released the innovative “New Concept Ring”, the inserts of which are 20% thinner than any other. In addition, the internal diameter of the new rings was increased by 8%, which was achieved due to improved material quality.
How to extend the life of a spinning tulip?
The service life of a tulip (as well as all spinning rings) can be increased if they are made with more round grooves. Fishermen process the rings by rounding them. After this procedure, the line passing through the tulip at high speed does not wear out so quickly: when rubbing against the edge of the rounded ring, vibrations are transmitted to the entire rod, and not just to the tulip fastener.
Despite this, an overly rounded ring provides a high area of contact with the cord, which increases heat and wears out the line along its entire thickness, making it thinner.

Therefore, as spinners advise, it makes sense to install a tulip with a ring diameter of up to 2 cm, and reduce the holes in the middle ring to 1.2 cm.
A large tulip makes the spinning rod heavier, which is harmful not only to the quality of fishing, but also to the spinning rod itself.
Practice shows that the following set of parameters is optimal: the butt ring should be less than 1 cm, the second - 0.8 cm, the third: 0.6 cm, the fourth - 0.5 cm, the fifth 0.45 cm, tulip - 0 .8 cm.
After fishing, clean the tulip with a brush and dry it so that residual dirt and water do not cause corrosion and destroy it.
Replacing the tulip
The process of replacing a tulip is easy to use and takes place in several stages:
- Apply masking tape to the edge of the tulip. This will help the glue not to go beyond the boundaries of the planting of this element at the end of the process.
- The decorative winding is removed. In this case, the area should be cut as carefully as possible so as not to damage the foot. It is also necessary to control the heating process to prevent fire.
- After the winding is removed, you need to heat the tulip and remove it. You can use a lighter for this.
- If low-quality glue is used, you will have to cut off the tulip along with the top section.
- Clean the tackle from paste particles.
- If the coating has been removed along with the glue, apply a small layer of varnish.
- Grease the top with paste and secure the tulip.
- Leave the rod for a day for the glue to harden.
Changing a tulip in emergency conditions
Experienced fishermen understand that the most unpleasant things happen during the process. If a tulip breaks down while fishing and you don’t always want to go home or to the garage, it makes sense to carry out an emergency replacement of the tulip. To do this you will need a special repair kit consisting of:
- electrical tape;
- masking tape;
- knife;
- pliers;
- lighters;
- instant glue.

There is no point in using epoxy resin, since it takes a very long time to dry, and in extreme conditions you will not be able to do a “clean” job - there is sand, water, dust around. Silicone hotmelt adhesive is also not an option since you need electricity for it. Instant-drying ethyl acetate-based glue - “Second”, “Moment” and others - is ideal for you.
Electrical tape and masking mesh can serve as an excellent seal in case of play between the tulip and the spinning rod. Instead of varnish, you can use ethyl acetate glue; it hardens quickly and has the same properties as varnish when it dries.
The design of spinning rods and their types
A standard spinning rod consists of 3 parts:
- A fishing rod that is equipped with special guides;
- Coil;
- Fishing line.

The main element of the design is the fishing rod. It is usually slightly pointed, cone-shaped and differs among spinning rods only in length.
Most often, such structures are made of carbon or graphite material. This is because they are both light and tough. Carbon fiber and fiberglass spinning rods are also popular. But fishing rods made of composite are considered the least durable and budget models.

Another important element of such fishing rods is the reel. They can be different in design: inertial or non-inertial. Inertial ones are more popular among fishermen, since they can be repaired independently, unlike non-inertial ones, which have to be completely replaced when they fail.

The fishing line in fishing rods of this type is also special. It is the connecting link between the bait and the rod. Today, fishing rods are most often equipped with multifilament and fluorocarbon fishing lines, as well as monofilament lines.

There is another important element of spinning - bait. There may be a variety of options here, depending on what kind of fish you plan to catch, and what is easier and more understandable for the fisherman to work with. The most popular types of baits:
- Spoon;
- Vibrotail;
- Wobbler;
- Mouse;
- Spinnerbait;
- Twister and others.

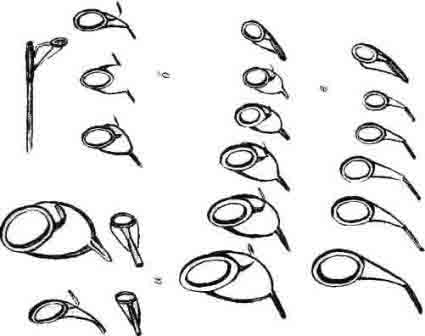
Arrangement of rings
The rings on the form must be located on the same line in order. In order to correctly position the elements, you must perform the following steps step by step:
- Traditional way.
- Use several parts to form a cone-shaped tunnel.
- The base is the leading component.
- The outermost part is considered as the top of the structure.
- New concept.
- The cone is shortened.
- The first element is shifted to the middle of the structure.
- Small parts allow the main line to pass through them.
Location Features:
- Linear arrangement.
- An average of 5-6 rings are used.
- The fewer the rings, the more the bait casting distance increases.
In order to check the reliability of the design, it is necessary to combine all elements at the same time. This will help you understand the correct fixation of the elements and detect any errors in the work.
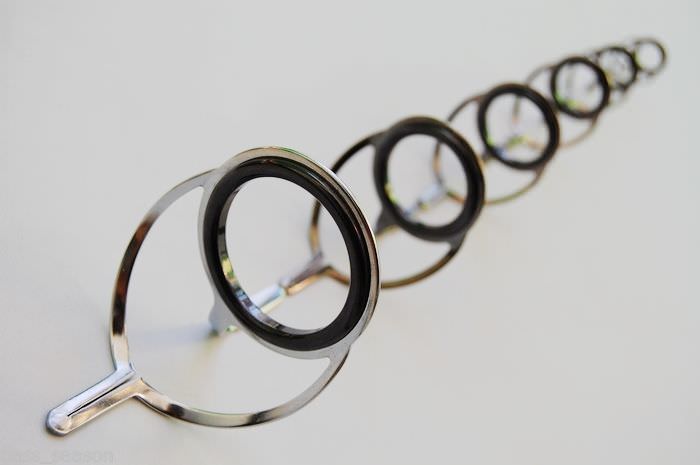

What is the FUJI KR concept ring arrangement?
KR CONCEPT or “ KR-concept ” is a set of rules and recommendations from Fuji that manufacturers of spinning rods should use to make the most of the properties of guides.
Some rules for placing guides on the rod blank were taken from the old NEW GUIDE CONCEPT (NGC). But there is one very significant difference between these two concepts. If NEW GUIDE CONCEPT is suitable for many series of guide rings intended for spinning rods, then for KR CONCEPT only rings of certain series are suitable. The KR concept arose due to the increased popularity of thin braided cords, which went well with light and small guides (Fig. 1).
Fuji Guide Rings
Currently, pass rings from the Japanese company Fuji remain, perhaps, the highest quality and most reliable of all those present on the world market. The Japanese are known for their hard work, love of experimentation and new discoveries, which is also evident in the context of making rod guides.
The titanium alloy, which is used in the production of rings, exceeds the standard by 3 times in terms of strength and resistance to physical stress, and by 6 times in terms of material fatigue.
Fuji makes inserts from various types of aluminum oxide (Alconate, Hard ring) or ultra-strong cermet Gold Cermet. The latter is coated with titanium nitride and contains a number of durable metals, including gold.
Gold Cermet is characterized not only by the high hardness of the material, its smoothness and strength, but also by its low weight.
Key Features of the FUJI KR Concept
- The height of the legs of the first rings from the reel plays an important role in this concept. In the KR concept, smaller diameter first rings from the reel are used to quickly dampen the rotating cone and better control of the line when casting. But in this case, the arc of vibration of the fishing line between the first rings increases, which theoretically can lead to the fishing line touching the blank. To prevent this, make the legs of the throughput rings higher and increase their number.
- As a result of the rapid damping of the cone, the line stops oscillating faster. This property allows us to move the Chock closer to the coil, but thereby we will need to increase the number of runners that go behind it. What are the benefits of this? With this arrangement of rings, the line is pulled out earlier into a straight line along the blank when casting. This will give us greater sensitivity of the tackle and increase casting distance and accuracy, and adding one running rod adds some power. Fuji calls this process “Rapid Choke,” which literally means “rapid choke.” To make this process more efficient, KR-series rings are designed so that the plane of the ring mandrel is at an angle of 300 to its frame.
- The displacement of relatively powerful Choke rings towards the reel leads to an increase in the load on the spinning blank in the middle part, where low-power running rods are located. To remove this “misunderstanding”, special rings of the KB series are placed in this place.
Secrets of successful fishing: Spinning rod guide sizes
Along with the number of rings on the spinning rod
Their diameter also plays an important role. One of the main functions of the first ring of the butt leg of a spinning rod is to extinguish the “breaker” of the fishing line flying out from the spool of the spinning reel. The location of this ring is approximately clear, but the diameter, taking into account the above, must be selected experimentally. In general, if the number of rings mainly depends on the length and action of the fishing rod, then the size of the rings depends on the type of reel.
So, the spinning reel requires installation
on a spinning rod with rings of huge diameter. That’s why at one time, 10-15 years ago, most companies equipped many of their own spinning rods designed for spinning reels with rings of increased diameter. Later, there was a tendency to reduce the rings, and at the moment the proportion of spinning rods with large guides is less than a few percent in the total shaft, which reflects today's views on the role of the diameter of the rings. This discussion continues to this day. But practice shows: if you check in action two spinning rods that are similar in everything, except for the diameter of the rings, then you can make sure that a spinning rod with correctly installed guide rings of increased diameter allows, under other equal criteria, to cast 5-7 m further than a spinning rod with ordinary rings.
How important are these few meters for the fisherman?
, only he himself must decide. It is difficult to find high-quality rings with a huge diameter; their cost will be comparable to the price of the spinning rod itself (if we are talking about cheap mass-produced spinning rods). It is permissible, and only in the very last case, to make the ring closest to the reel from metal wire - this ring, due to the rotational movement of the fishing line, does not wear out to the formation of grooves. But other rings, in any case, must be made of hard ceramics or an alloy with a hardness of at least 6 units on the diamond scale.
Necessary ADVICE
“FUJI” rings (if they are not fake, which, by the way, our market is flooded with) are very expensive, and it is hardly worth using them on ordinary spinning rods. A novice fisherman should not create unnecessary difficulties for himself - it is better to leave the rings as they are during the learning period. This means that the largest ring has an internal diameter of 30-32 mm, and its center is 35-37 mm away from the axis of the spinning rod. In general, for inertial reels and multipliers such characteristics of the rings are close to good, and in the case of inertial reels, the loss of several meters of casting can be more than compensated for by other methods.
What rings are used in the FUJI KR Concept
FUJI KR Concept spinning rods use three types of guide rings - KL-H, KB, KT .
KL-H guide rings (Fig. 2) are used as Butt rings to quickly dampen fishing line vibrations. The frame design is made “without corners” so that there is nothing for the fishing line to cling to. The series has a smaller insert diameter. The index “H” indicates that this ring has a high stem. Currently available sizes: 25, 20, 16, 12, 10, 8, 5.5mm.
Fig.2. Rings KL-H
KB series guide rings (Fig. 3) is to relieve the load on the blank in the middle part of the rod. To counteract the load, these rings have wide and powerful legs and a thick mandrel. The frame design is also made in a “no corners” design. Depending on the length of the spinning rod, from one to three KB series rings are used. Available in sizes 4, 4.5 mm.
Fig.3. KB rings
For running rings, KT (Fig. 4). They are characterized by very light weight due to the thin frame and mandrel. They have the same “no corners” design. Light weight allows you to relieve the thin upper part of the rod. They have sizes: 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, 8, 10mm.
Fig.4. KT rings
Device of access rings
A modern guide ring consists of two parts: a frame and an insert (Fig. 2), although even now fly fishing rod rings continue to be made from chrome-plated wire. The frame is characterized primarily by two parameters: height H and hole diameter D, where the solid insert is placed. It is accepted that diameter D is the size of the ring. Thus, size “16” is not the inner diameter of the insert, but the diameter of the frame. Due to differences in materials used, a ring of the same “official” size may have a different actual bore diameter (Figure 3).

(a)-Alconite™Fuji (New Concept insert) (b)-SiC™ Fuji (New Concept insert) (c)- Fuji “O” aluminum oxide (d)- “SiC” based on zirconium oxide (e)- “ SiC" based on silicon carbide
In addition, the frames differ in design depending on the purpose of the ring (Fig. 4, a). To describe the “tulip”, an additional parameter is used - the inner diameter of the tube with which it is attached to the glue on the tip of the rod (Fig. 4.6).
Finally, the material from which the frame is made is distinguished. The main requirement: strength, elasticity, ability to resist fatigue and corrosion. Most often this is steel of various grades. According to Fuji founder Riuichi Omura, the use of titanium frames from a functional point of view only makes sense for ultra-light class rods, where a fraction of a gram in the weight of the equipment can significantly affect the balance. The use of such rings on rods of medium and heavier classes cannot be justified from the point of view of common sense. These are advertising gimmicks that significantly increase the cost of the rod: a titanium frame ring with a SiC™ insert costs three times more than a steel frame, and the improvement in balance is so small for rods in these classes that it hardly justifies such an expense. As we will see below, other methods are used for high-quality balancing using equipment. But the main working part of the ring is the internal hard insert, the description of which takes into account the following characteristics: • hardness (Vickers) – characterizes abrasion resistance; • thermal conductivity – shows how quickly heat is removed from the place of friction of the fishing line on the surface of the insert. This characteristic is, of course, very important: if heat is removed slowly, the line will wear out faster; • bending strength – the higher it is, the greater the deformation under loads the ring can be subjected to without the risk of damaging the insert; • specific gravity (density) – determines the mass of the ring.
In addition, any insert must have a highly clean surface, as this affects the coefficient of friction of the fishing line against it.
The materials used for inserts are created based on the most optimal, from the manufacturer’s point of view, combination of these characteristics and their price. At Fuji, they are divided into three main types: • Gold Cermet™ (cermets) • SiC™ - silicon carbide (silicon carbide) • various types of aluminum oxide-based materials (Alconite™ - hardened aluminum oxide; Hardloy™ - improved aluminum oxide; " O" – aluminum oxide).
The Gold Cermet™ insert, which is considered the best in our country (apparently because it is the most expensive), has a range of applications as limited as a titanium frame. It has the highest bending strength, which makes it possible to use it for the production of very thin and, therefore, light rings. But in other parameters, such as hardness and thermal conductivity, it is two times inferior to SiC™. Yellow rings can also be found from other manufacturers, but this is not a homogeneous metal-ceramic material, unchanged in composition throughout the entire depth, like Fuji, but a thin (less than a micron) coating applied to one or another material. So, when you see such “non-Fuji” guides on a fishing rod, don’t rush to rejoice - after a while, especially if you use braided fishing line, the coating will wear off. But if underneath there is still a fairly high-quality aluminum oxide, then you shouldn’t be too upset. SiC™ – silicon carbide – quite fully meets the entire range of requirements for the insert. It has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity among all materials used today. In addition, Fuji technologies make the surface of the ring as smooth as possible. Other companies also have rings under the same name “SiC”. We should stop at two. The first is also a material based on silicon carbide. But since it is quite difficult to compete with Fuji in quality, manufacturers prefer to simplify the technology to reduce the price. As a result, the surface is not as smooth and the profile is less rounded. All this, despite comparable hardness, makes such inserts more susceptible to “sawing” after prolonged exposure, especially with braided fishing line (Fig. 5).

Another case of "SiC" is a material very similar in color to real SiC™, but its base is zirconium oxide (ZrO2). In all respects it is inferior to high-quality aluminum oxide, not to mention SiC™. In this case, the letters SiC are just a name that was chosen specifically to be “similar” to SiC™ Fuji. Among all types of aluminum oxide, until recently, Hardloy™ was the most highly valued. It has the lowest specific gravity, so the guide rings are lighter compared to rings of the same profile, but made from other types of aluminum oxide. However, thin enough inserts cannot be made from it. Fuji's most significant recent achievement has been the creation of the completely unique Alconite™ material (also based on aluminum oxide). From a consumer point of view, it is head and shoulders above all other oxides and has almost caught up with SiC™. It is this material that allows the production of high-quality inserts with the smallest profile (thinner than SiC™). Even though it is much more difficult to machine a thin surface, meaning the fabrication labor is significantly more expensive, Alconite™ is less than half the price of SiC™.