Spinning fishing is the most effective method of fishing for predatory fish. It is like an exciting game, the task of which is to outsmart the fish. The predator must believe that your bait is its prey.
A good spinning player treats the process as an art. He is well acquainted with the habits of a predator, can accurately estimate the depth, determine the hunting time, knows how to select bait taking into account environmental factors, and also knows how to choose a spinning rod that is suitable for a particular type of fishing. For a beginner, this process will seem complicated, but over time he will begin to delve into the intricacies and will definitely fall in love with this business.
Types of spinning rods
The main types of spinning rods are distinguished by the type of rod design:
- plug;
- telescopic.
Plug-in spinning rods come in two- or three-legged versions. They are made from modern high-strength materials that ensure the reliability of the tool. The advantages of the composite type of design are precise control of equipment, targeted feeding and the possibility of using lightweight equipment. The main disadvantage of plug-type spinning rods is their high cost.
The telescopic design is retractable and has several docking points, which negatively affects strength and reliability. Telescopic fishing rods are popular today due to the ability to use them in any conditions. They are compact and mobile.
There are also types of spinning rods based on fishing style:
- jig;
- twitching.
Jig is a style based on an uneven jumping liner. It allows you to catch prey close to the bottom and in the water column. The choice of spinning rod for jig fishing depends on environmental conditions. For example, for fishing from the shore you will need a rod of 2.5 m with a fast action and a weight test of 20 g. Fishing from a boat will require a shorter design that works well with dough up to 15 g.
Twitching is called fishing in river oxbows and reservoirs with abundant vegetation. It is necessary to use bell-shaped rods suitable for jerking wobblers.

Spinning rod materials
The most common materials used to make fishing rods are: carbon fiber (coal, graphite, carbon - the same), fiberglass or their composite mixtures. Often, various synthetic fibers (for example, Kevlar fibers) are added to expensive spinning rod models to give it additional strength and rigidity.
Fiberglass spinning rods are heavier and more flexible with a low elastic modulus. Coal “sticks” are relatively hard and light. Composite fishing rods are something in between.
At the moment, graphite or composite spinning rods are most widespread, and fiberglass is used only for cheap models. There are different grades of graphite materials, the most popular are IM 700, hipron, XT30, XT60, XT100, SC 42, SC 33.
Fiberglass spinning rods are cheaper, but they are usually too soft and heavy, and the rings leave much to be desired (cheap spinning rods don’t have expensive rings). Composite fishing rods are the most widespread. The price is not very high, and the quality is quite acceptable. That’s why this is the best option for a first rod.
How to choose the length of the spinning rod
Depending on the planned fishing conditions, the optimal length of the spinning rod is determined, which affects the following indicators:
- casting range and accuracy;
- comfort of using the gear;
- ability to hold large fish.
The longer the spinning rod, the further it is possible to cast. Increases the likelihood of catching large, active fish. But the rod must be in harmony with the physical characteristics of the fisherman. If it turns out to be too large, the fishing efficiency will decrease.
It is also important to consider the convenience of transporting the spinning rod. The shorter it is, the easier it is. A small rod has high sensitivity and is less tiring to work with.

To understand how to choose the length of the spinning rod, you need to consider the following recommendations:
- 1.4 – 1.8 m: ideal size for fishing from a boat in small bodies of water. Allows you to make precise casts over short distances;
- 1.8 – 2.1 m: optimal length for fishing on medium-sized rivers and lakes. Provides the opportunity to fish a wider area. Convenient for casting from overgrown shores, on shallow backwaters and mountain rivers;
- 2.1 – 2.7 m: this rod is suitable for coastal fishing. Allows you to make long casts, feel the tackle and bait when retrieving;
- 2.7 – 3.2: suitable for casting from a cliff, when trolling;
- 3.2 m or more: a spinning rod of this size is used on large bodies of water. Most often, plug-type models have this length.
Spinning rod design
The design of a spinning rod is not particularly different from the design of any fishing tackle.
1. Blank – the main part, which is made of fiberglass, carbon fiber or composite material. Expensive models use multi-layer weaving of fibers, which is responsible for the quality of the blank.
2. Guides are another important part of the fishing rod. Usually they are durable metal inserts in a frame. The frame is equipped with legs, due to which it is attached to the form. The most durable titanium frames. The rings themselves are made of aluminum oxide, silicon carbide or other high-quality alloy.
3. Handle – should be comfortable and easy to clean. Typically made from cork or neoprene. The length of the handle must match the length of the form. There are one-handed, one-and-a-half and two-handed handles.
4. Reel seat - must be reliable and strong, adapted for a multiplier or spinning reel. The design of the reel seat itself is selected depending on the fishing conditions and ease of grip.
Spinning rod materials
Today, spinning rods are made from high-strength and technologically advanced raw materials.
The following spinning rod materials are mainly used:
- fiberglass (fiberglass) - is a budget option, but has good impact resistance. The main disadvantages are heavy weight and poor balance;
- carbon (carbon fiber) is an expensive material. The rod, made of carbon, has high sensitivity, perfect balance and lightness. When working with such a spinning rod, you should avoid applying hard blows to the body and handle it carefully during and after fishing;
- composite materials - rods made from these raw materials are comparable in lightness to carbon ones, quite durable and balanced. The cost is low.

Which test to choose
The test parameter must be taken into account when choosing a spinning rod. It reflects the minimum and maximum weight of the bait used on the rod. The parameter value is indicated on the body.
Typically, the test is expressed in grams. The most common figure is 5-20g which means you should use a bait no lighter than 5g and no heavier than 20g. Weight below the minimum allowable limit will not allow you to make a good cast, and if the upper limit is exceeded, the rod experiences heavy load and may break.
Sometimes the test is expressed in ounces (Oz). One ounce is equal to 28 grams. That is, the value 1/4 - 1 Oz means that the test indicator is 7-28 rubles.

Main characteristics
Every decent fishing supply store, as a rule, can offer a wide variety of types of spinning rods. When choosing a spinning rod, experienced fishermen are primarily interested in their following quality characteristics:
- Length.
- Build.
- Test.
- Material of manufacture.
Each of these parameters is important and can become decisive for a particular fisherman.
Rod length

The choice of blank length primarily depends on the conditions in which the fishing will be carried out.
It is rational to use the shortest whips when fishing from a boat or from a bank overgrown with trees on a medium-sized body of water. In such conditions, a spinning rod with a length of 1.6 to 2.1 m will be the most convenient; it will allow you to make accurate casts and the fishing required by the fisherman.
The most practical are spinning rods with a length of 1.9 to 2.7 m . They will allow you to effectively operate the tackle in almost any fishing conditions.
Rods with a length of 3.2 m or more are used when fishing in large bodies of water , when necessary, to make long casts and amplitude, powerful hooks. For example, in sea fishing, spinning rods no shorter than 3.6 meters are used.
Tuning Characteristics
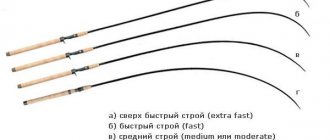
The structure of a fishing rod is very important when it is exposed to various dynamic loads, which happens when casting bait and when fishing for a trophy. In such cases, this qualitative characteristic determines the nature of the resistance of the blank, which determines its capabilities both in the range and accuracy of casting bait, and in landing large fish. The classification of spinning rods according to this parameter is as follows:
- Fastest formation (EF) . When loaded, the upper part of such forms bends. With their help you can make the most accurate casts at medium distances. They are also considered the most sensitive.
- Fast formation (F) . These rods, under load, bend in their upper third. With the proper skill, with the help of such a whip, you can make accurate casts over decent distances.
- Medium action (M) (parabolic) . Such forms are characterized by a bend in their upper half. They are considered the most versatile and practical. With their help, you can make a long cast, and they can withstand the jerks of a large trophy well.
- Slow action (S) rods have spinning rods that, under the influence of load, resist with their entire length. With their help, the longest throws are made. They are also better than other rods in softening the jerks of trophy prey.

It is important to know that determining the class by construction of telescopic spinning rods is somewhat difficult . This is a consequence of the non-uniform structure of the blank, as well as the fact that the first (thickest) knee practically does not bend.
Test
Spinning rod classes, determined depending on their test performance, show the weight of the baits that the manufacturer recommends using with them. This characteristic is often called the power of a fishing rod. It is quite conditional, but still, the classification of spinning rods according to this parameter is very similar among many well-known manufacturers. It looks something like this:
- The lightest class (UL) includes spinning rods that are designed to work with baits whose weight does not exceed 7 grams . These forms are used to catch small but very cautious fish.
- The light class (L) includes whips with a recommended lure weight of up to 14 grams.
- The medium-light class of rods (ML) allows you to use baits weighing from 7 to 20 grams . These are the most popular forms in the central part of our country. With proper skill, they can bring fish weighing up to 8 kg to the landing net.
- The middle (M) class involves the use of baits whose weight ranges from 12 to 30 grams . Such spinning rods are considered the most practical and versatile.

- Forms belonging to the medium-heavy (MH) class are designed for the use of baits weighing up to 40 grams .
- The heavy (H) class of spinning rods is designed for using baits weighing up to 55 grams . Such rods can already withstand trolling fishing.
- The heaviest (EH) class assumes that this spinning rod can easily withstand manipulation with baits whose weight exceeds 60 grams . They are often designed for bait weights from 100 to 250 grams.
The rod's test value is marked just above the handle. Some British and American companies denote it in ounces (oz). 1 ounce = 28.5 grams .
Material of manufacture
Three main materials are used to produce modern spinning rods:
- fiberglass;
- carbon fiber (carbon);
- composite
Fiberglass rods are considered the most inexpensive and unpretentious . They are quite strong, but short-lived and have a very decent weight, which is especially unpleasant during active and long-term fishing.

are the lightest, most balanced and resilient .
Their main disadvantages are high price and fragility. They require special care and withstand impacts to the body very poorly. However, due to their high performance qualities, such spinning rods are chosen by advanced fishermen and sports fishermen.
Composite material allows you to combine the main positive aspects that are inherent in rods made of fiberglass and carbon fiber. They are quite light, durable and, at the same time, not so expensive. We can say that such spinning rods are the most practical. Moreover, this characteristic fully applies to both telescopes and plug-in models.
Which system to choose
The structure of a spinning rod characterizes the degree of rigidity of the rod and its ability to bend under load. To determine the action, you need to attach a weight to the rod that is twice the maximum permissible weight of the bait. The degree of bending and shape of the body under load determines the action, the choice of which must correspond to the fishing conditions and the desired size of prey.
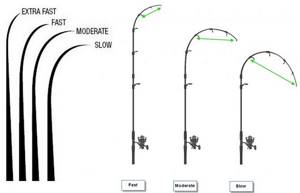
There are four types of rod action:
- very fast (Extra Fast, EF): the bend is located in the upper quarter;
- fast (Fast, F): curvature occupies the upper third;
- medium (Moderate, M): half curved;
- slow (Slow, S): curvature is observed along the entire length.
There are intermediate models on sale. For example, rods with a medium-fast Moderate-Fast action are often used.
The tuning is influenced by the thickness of the body walls, the inherent rigidity of the material and the presence of additional reinforcing elements. The indicator also depends on the type and number of throughput rings.
Classification of spinning rods
The most important parameters of a spinning rod are class, test and action.
Spinning rod class
By class, spinning rods are divided into 4 main types (not counting intermediate ones): ultra light class, light class, medium class, heavy class. The division into classes is arbitrary and may differ among different manufacturers, but one of the popular and generally accepted ones looks like this:
- ultra light class (Ultra Light) - test up to 7 g;
- light class (Light) - test from 7 to 15 g;
- middle class (Moderate) - test from 15 to 40 g;
- heavy class (Heavy) - test from 40 g and above.
UL (ultralight) is currently the most popular fishing class. Tackle of this particular class is used for catching small fish - perch, grayling, trout, ide, chub, and coastal pike. With rods of this class, thin lines (0.12-0.2 mm) and light baits weighing up to 10 grams are used (almost all spinners, small spoons, wobblers, silicone baits with light jig heads).
M - this class of fishing is widespread mainly in those regions where the pressure on water bodies is insignificant, and the fish have at least some chance of growing to a very decent size. In such places, the main trophies can be large perch and pike, sea taimen and salmon. This class is characterized by thicker forests than the previous ones (0.25-0.35 mm), the weight of the bait already reaches 40 grams, because The fishing depth and casting distance can be significant. The length of the rod is generally 2.4 - 3.3 meters.
H is the heaviest fishing class. It is used when catching large trophies, namely catfish, cod, sea taimen and other large predators. Spinning rods of this class have maximum strength. The length of rods in this class is more than 2.7 meters, the weight of the thrown bait is more than 30 grams.
Spinning test
The rod test can be determined by the inscription on it. Power is indicated in grams - in the weight of the bait being thrown. For example, “5 - 10 g.” According to the test, rods are divided into four groups:
- I - up to 10 grams;
- II - 10 - 30 grams;
- III – 30 – 60 grams
- IV - over 60 grams.
Spinning rod structure
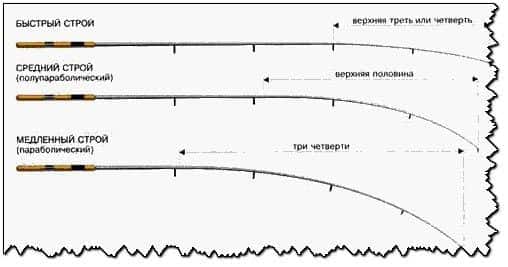
The structure of the spinning rod is the most important parameter, since the casting of the bait and the nature of the fishing depend on it. The action characterizes the type of bending of the rod under load. The most popular American tuning classification system is:
- EXTRA FAST (EF) (very fast) - the maximum bend of the rod occurs in the upper quarter of the whip
- FAST (F) (fast) - the rod bends in the upper third of the whip
- MODERATE (M) (medium) - the upper half of the whip bends
- SLOW (S) (slow) - the rod bends along its entire length.
Braided line for spinning
Various types of fishing lines are used for fishing, but the most popular is the so-called braided line for spinning. Its main advantages are low elongation and high breaking load. We will consider similar characteristics of how to choose braid for a spinning rod below.
The choice of braided fishing line is made taking into account the following characteristics:
- expected fishing conditions - for open, clean places, equipment with a thin fishing line will be sufficient, and in difficult overgrown areas, a stronger and more solid braid will be required;
- strength of the cord - here you need to use the test indicator indicated on the fishing line. It is usually expressed in kilograms or libres (1Lb is equal to 0.45 kg);
- fishing line thickness - the choice is not always clear and depends on the quality and quantity of threads. A thin braid may be stronger than a larger one;
- color of the braid - this indicator is secondary, but helps the fisherman more accurately control the localization of the bait. The choice of color depends on personal preference.

Choosing a spinning reel
A spinning reel is an important part that is involved in casting and retrieving bait. The parameters of the mechanism affect the catching of prey.
There are three types of coils:
- inertial (conducting);
- animators;
- inertialess.
And so, let's take a closer look at how to choose a spinning reel. “Inertia” are well known to older generation fishermen. They have a gear ratio of 1:1, i.e. The revolution of the spool corresponds to the turn of the line. Small reels are used in winter fishing, and medium and large ones are used for “reel” fishing, when the bait goes downstream and unwinds the line. Inertia is the main disadvantage, because the line continues to unwind for some time after the bait splashes down. In this case, the spool has to be slowed down by hand. For this reason, “inertia” is not recommended for beginners.
{banner_vnutri-kontenta-3}

The multiplier is an inertial reel equipped with a gear system, braking and line laying mechanisms. Gear ratios range from 4.1:1 to 6.3:1. The lower this indicator, the higher the traction force.

Multipliers are divided into four categories:
- light: for baits weighing 4-30g;
- medium: for casting baits weighing 6-60 g;
- heavy: allow the use of baits weighing 40-600 g;
- super-heavy: suitable for catching giant fish.
Multiplier reels have a number of disadvantages. They require open space for casting and adjustment of the braking system after each use. Multipliers are installed only on a certain type of fishing rod, in which the reel seat is equipped with a trigger that prevents the spinning rod from turning in the hands.
Spinning reels are the most popular because... At a low cost, they do their job well. They are easy to operate and do not tangle the line when casting.

Classes of spinning rods. Which spinning rod to choose?
We start dancing from the stove. If we need to fish with extremely light baits, we talk about spinning rods with minimal tests, and if, on the contrary, with the heaviest ones, we begin to adapt to this hardcore. Presumably, this is how all these classes of spinning rods appeared. As a result, modern spinning rods are divided according to a simple and understandable criterion: casting, i.e., according to the weight range of the baits for which they are intended for casting. It is customary to distinguish four main classes of fishing rods in ascending order: ultralight, light, medium and heavy. Each class has more or less clear and, importantly, generally accepted boundaries, but this results in fewer questions, not only for beginners, but also for “continuers.”
The questions that I personally have repeatedly heard from friends and acquaintances are quite specific and by no means devoid of... And they usually sound like this: “Which spinning rod should I choose for chub (asp, pike perch) on a large river (small river, lake, reservoir)? » It turns out that here a person does not have enough experience, but he has enough ingenuity - and he very reasonably wants to avoid his own full-on mistakes - and immediately make, if not the right choice, then at least a step in the right direction. There are also more serious cases when you hear, for example, a question like “why do you take two (three, five) spinning rods with you fishing?” It turns out that a person, in principle, has no understanding of why the “universal” telescopic spinning rod of the same production, which is lying on the rear shelf in the car of regular barbecue makers, is bad... All this prompted me to write this article.

Modern fishing is by no means a simple, and certainly not an easy activity from a technical point of view. And not everyone is able to try everything in it, or they don’t have the desire to do so. But, nevertheless, questions similar to those that I voiced above sooner or later arise in front of many spinning players - after all, you always want something new. As for me, fortunately, I have first-hand knowledge of spinning rods of different classes. He devoted several seasons only to ultralight, then gradually shifted his priorities towards the light class. And when he began to develop large rivers, he, willy-nilly, acquired powerful heavy-range gear. Well, as I became more interested in fishing in the vastness of large lakes and reservoirs, I returned again “to the roots” - where many people start - to the medium class. Since to this day I combine all this harmoniously and love it equally, I hope I will be able to cover all classes comprehensively, without bias towards personal preferences - and therefore more or less objectively. So, the scheme is simple: class - definition - working purpose - advantages - disadvantages - degree of universality.
The smallest and lightest spinning rods, designed for full casting of baits up to 7 g (1/4 ounce). Its working purpose is delicate catching of a wide variety of fish.
Advantages. Firstly, versatility: ultralight spinning is applicable on a wide variety of reservoirs - from small rivers to large reservoirs. Secondly, this lightest class of spinning rods is effective even in the most difficult places - such as, for example, on rivers within the city. In addition, ultralight has the most diverse species composition of possible trophies, because even non-predatory fish like roach or bleak are deliberately caught with miniature baits of this class. And, finally, ultralight is inimitable in terms of the sensations when fishing and the aesthetics of the tackle itself.
Read: Review of spinnerbaits for pike: features of the bait and fishing technique
Flaws. Due to the banal physical parameters of the baits used, the size of the average UL trophy leaves much to be desired, and often does not reach the fishing limit. Many even avoid spinning rods of this class in order to cut off obviously small fish in their catches. However, we understand that everything is relative - it happens that a fish from the “heavy” category also becomes a trophy for an ultra-lighter, and if, say, a pike up to a kilogram or a sports-sized perch dominates in a reservoir, then it is much more pleasant to catch them with an UL spinning rod, if such a task is worth it. The appearance of spinning rods of this class was predicted almost by Jules Verne, but it became possible only with the advent of new types of materials and modern methods of processing them.
This class of spinning rods is designed for fishing with baits up to 14 g (1/2 ounce). The working purpose is delicate catching of wary fish - however, with a bias towards larger bodies of water than in the ultralight. These spinning rods have some overlap with the previous class, since they can work with the same baits as ultralight. With the exception of perhaps the smallest ones, weighing less than 3 g. On the other hand, a light-class rod is already capable of fishing with fairly large and heavy lures - such as, for example, a twitching pike wobbler or a “spinner” of the third number. The range of applications for spinning rods is almost as wide as that of ultralight, but shifts towards large bodies of water - due to the useful possibility of long casts, greater deterrent resource when landing fish and the power of the gear in general.
Advantages. Versatility: light-range spinning rods are applicable on a wide variety of reservoirs, and with all this versatility, such a spinning rod, when compared with the also universal ultralight, already has enough power to, as they say, dictate something to the fish when playing. In my opinion, other things being equal, light is superior to the previous class in terms of the thrill of the bite itself. If we continue the parallel with the lightest spinning class, it should be noted that due to greater power while maintaining a similar structure, light rods can be made longer. A classic UL spinning rod is usually 1.8-2.2 m, while a light one is 2.1-2.7 m. And this, you see, is a significant advantage when casting.
Flaws. Many people dislike this class of spinning rods due to the fact that they are “converted ultralight” and “unfinished medium” - in general, neither two nor one and a half.
A class of spinning rods that are designed for fishing with baits weighing up to 21-28 g (3/4-1 ounce). Purpose: catching predatory fish on medium and large rivers, lakes, and reservoirs. Not very suitable for streams and small rivers.
Advantages. This is already quite a powerful spinning rod for targeted catching of medium or even large fish. It is still the most popular among domestic spinning fans due to a certain “versatility” that is tangible at first glance, but this is quite controversial. It is not as demanding on the quality of the rod as the junior classes, which means it is hypothetically more accessible to those who want to try spinning.
Read: Winter spinning. Secrets of successful fishing
Flaws. It is the spinning rods of this class, in my opinion, that are to blame for the emergence of myths about the existence of a “universal” fishing rod. Presumably, due to the fact that, from the point of view of the average person, they can be fished with baits that go beyond the class, both up and down - and this, it turns out, is almost the entire range of the most popular spinning lures. It turns out that I have a medium class - I have a spinning rod with which I can fish with both a miniature “zero spinner” and a full-fledged oscillating spoon, for example. Theoretically, this is absolutely accurate, but the quality of such fishing leaves much to be desired, because in the case of a miniature “spinner,” the rod is practically not involved in casting, and there are no sensors during retrieving, but in the case of a large pike “spinner,” the tackle is often already is overloaded.
These are spinning rods that are designed to work with baits from 28 g, but the upper threshold goes to infinity. However, if we talk about spinning rods for freshwater fishing in inland waters, this test usually does not exceed 120 g, and often falls within the range of 55-80 g.
Working purpose: this is quite highly specialized gear, usually applicable for jigging or trolling fishing on large rivers with great depths and in various specific areas of modern fishing such as jerking.
Advantages. First of all - power and reliability. It is the spinning rods of this class that allow you to fight with captured specimens.
Flaws. Paradoxically, this is excess power. It is clear that large catfish or pike perch are increasingly rare guests on the hook, and more often the “standard” in the form of a kilos of pike perch or pike is caught, so heavy spinning rods simply throw these guys into the boat, like a duck. In general, you can’t expect any pleasure from fighting here.
Below I will schematically describe my choice for each typical situation.
A) It is planned to fish in small river conditions. The width of the channel is up to 10 m, more often 3-4 m, the river is winding, densely overgrown with bank vegetation that interferes with casting, average depths are 1-1.5 m - ultralight and light. The logic here is simple: you need to work with miniature baits, which are best suited for such rivers, while making delicate casts in cramped conditions. Conclusion: you need a lightweight compact spinning rod. My UL rod has a length of 214 cm, and my light rod is 244 cm long - they are comfortable for catching waves in such conditions, with the only difference being that with a longer and more powerful light spinning rod it is more convenient to circle various coastal obstacles and fish in sedge thickets. In my opinion, spinning rods of other classes are not useful in these specific conditions.
B) Fishing in medium river conditions, on the upper reaches of large rivers. The width of the channel is up to 30-50 m, background depths are 1.5-2 m, there are holes up to 3-4 m. Ultralight, light and medium can be useful here, depending on the fishing objects. The most popular hunting objects in such places are pike, asp, perch, pike perch, chub, ide, and less commonly, catfish. For vagrant catfish, as well as pike and pike perch, a medium spinning rod, in my opinion, is optimal, allowing you to send a medium-sized bait far and accurately and catch, for example, with a jig, and, of course, has a decent deterrent resource in case of a bite from an outstanding fish. If we are targeting a white predator - asp and company, here I would already use a light kit, or an ultra-light class spinning rod - it all depends on the mood and activity of the fish we are looking for. If, for example, a chub aggressively attacks a microbe-class wobbler, it makes sense to increase the number of baits and try, perhaps, a crank 40-45 millimeters long - with an eye on an adult fish. And then the hands themselves will put aside the ultralight in favor of the light. However, the exact opposite happens.
Read: Fishing for chub on small rivers
C) Fishing is planned on the stream - targeting grayling, trout, dace - definitely ultralight! The water area is very miniature - a kind of river “bonsai”. Long casts are not required, but filigree precision and accuracy are required. Casting will often require wrist casts; this is where the ultra-light spinning class reveals itself in all its glory. We aim the miniature wobbler in the given square and do it silently with a short wrist throw. After which - careful winding with a reel that seems just like a toy. The process itself gives incredible pleasure to a sophisticated person - and, as if by chance, the light rod sharply bends into an arc. It's a bite! Yes, without a clear blow, but all this “lack of ringing” will be more than compensated by the subtle struggle when playing.
D) Fishing is planned on a large navigable river. The expanses of water are such that the influence of the wind is already noticeable. Depths can be in the range from 2 to 25 m, more often – 2-10 m. The predator is varied: catfish, pike, pike perch, bersh, asp, chub, ide, perch. Bonuses are possible. Heavy-class spinning rods are most applicable here. If the vector of preferences is towards asp and ide or, say, pike in the backwaters and rumbles, the medium class may be more convenient. In any case, you will need a fishing rod with a reserve of power and a longer one - with maximum range. However, no one will forbid us here, on Big Water, to fish with light or ultralight, expanding the list of trophies with sabrefish or schooling perch, but this is rather a special case. Mostly people come here for something else - deep jigging and trolling - in the hope of catching the “fish of life”.
D) A reservoir, large expanses of water, significant depths, but, however, without a noticeable current. The main determining factor here is the wind. Everything will depend on its strength and direction. Fishing most often involves jigs or jerky wobblers, hence the preference for gear. My choice here is a medium spinning rod with a dough of up to 21-28 g for jig or 32-38 g for wobbler fishing. We spin from a boat, so casting range is not as critical here as, say, in coastal fishing. And not every boat can comfortably handle fishing rods under three meters. My choice for the length of the spinning rod in these conditions is 2.4-2.7 m for jig and 2.1 m for wobbler fishing.
In general, I think the diagram is clear, and it can help a novice spinning player who is faced with choosing his working tool.
Subscribe to
our channel in Yandex Zen
Spinning baits
Selecting bait for a spinning rod is an art that requires good tackle skills and extensive fishing experience. It is necessary to take into account the behavior of the fish, terrain and weather conditions.
The modern fisherman has many different baits in his arsenal:
- spinners;
- wobblers;
- silicone;
- foam;
- other types.
Lures are made from hard materials and visually imitate the shape and color of a predator’s prey. They come in two types: rotating and oscillating. The former are suitable for catching active fish in the summer. Making noise when twisting, they attract the attention of animals in muddy water. The spoons imitate the smooth, slow movements of the prey, which ensures a good bite.
Wobblers visually resemble fry. There are many models of baits that allow you to catch any predators. When choosing wobblers, the shape, color, degree of buoyancy, vibration frequency, and depth should be taken into account. The main disadvantage of the equipment is its high grip.
Silicone baits are a wide category of baits for catching “traditional” predators: pike, pike perch, burbot, perch, etc. They are also successfully used in hunting more peaceful inhabitants of water bodies. “Silicons” imitate various objects of the underwater world and are made in edible and inedible forms. The first type includes baits additionally impregnated with attractants - substances with attractive aromas. A fish that has bitten on the “edible” holds it in its mouth. This allows you to take advantage of the moment and make a more accurate hook.

Foam rubber fish are very simple baits that are easy to make with your own hands. They are equipped with a sinker, double or triple hook. They have proven themselves well in catching passive predators in cold water. They have excellent aerodynamic properties, catchability and low cost.
In addition to the main types, there are many other baits used in special conditions. For example, spinnerbaits consist of a jig head and a spinning blade connected by wire. This design allows you to fish in an overgrown area, because hooks are eliminated as much as possible. Streamers are a device of a different nature, consisting of a long hook with synthetic feathers. They perform well where other attachments do not work.
An experienced spinning angler always has many types of bait. But throwing it into the water is not enough; you need to understand the behavior of the fish well and present the bait correctly.
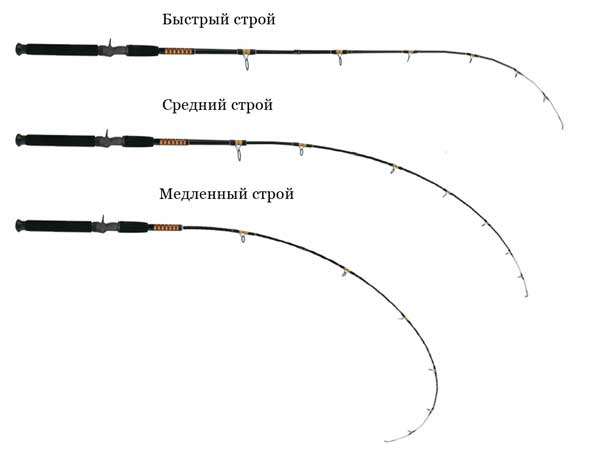
According to the nature of the formation, spinning rods are divided
1. Extra-fast (very fast system). Under load, the whip bends at the top. The most sensitive type of spinning rod, which is suitable for precise casting at medium distances. 2. Fast (fast system). When loaded, these spinning rods bend the upper third of the blank. Suitable for long casting. 3. Medium (medium tuning). They bend at the top (half). Spinning rods with medium action are considered very practical and suitable for any type of fishing. They have a good casting range and can handle heavy fish. 4. Slow (slow build). This type of rod bends under load along its entire length. Slow action spinning rods make the longest casts and are able to resist the jerks of predators.
Classification by type of action applies only to plug-type spinning rods.
Spinning fishing spots
Spinning fishing spots are public bodies of water where you can fish within the permitted time limits. But when choosing a place, you need to remember about the current prohibitions, the violation of which entails liability before the law.
Fishing is prohibited in protected areas, on the territories of fishing enterprises and at a distance of less than 500 m from hydraulic structures. Fishing on private property requires the owner's permission. Sometimes authorities impose temporary restrictions on fishing in certain bodies of water.

In addition to the rules for choosing a place, it is important to know about the prohibitions on equipment. You can use spinning rods, fishing rods, mugs, feeders and float and bottom fishing rods, but no more than 5 pieces per person. It is permissible to use other gear, provided that the total number of hooks does not exceed 10 units. The use of electrical devices, networks and various types of trap structures is strictly prohibited. In some cases, fishing with these tools is permitted with a license.
Overview of the main parameters for choosing a rod when fishing from the shore
As mentioned above, spinning is a universal tackle. However, if when fishing from a boat the set of criteria is very limited, since fishing is actually carried out in open space, then when casting from the shore, all possible influencing factors must be taken into account. It is necessary to pay attention first of all to the following characteristics:
- Coastline. It is worth carefully looking around to see how overgrown the approach to the reservoir is, whether there are bushes or trees growing along the water. It should also be remembered that spinning is a sporting tackle and the angler has to move often, so you need to study the condition of the shore along the entire expected length of the route.
- Size and nature of the reservoir. Determines how far you need to cast. Depending on the area and the presence of flow, these can be large and small rivers, streams, flowing and stagnant lakes. Also, the choice of fishing rod is influenced by the topography of the bottom and how swampy the reservoir is.
- Bait used. Everything here is quite simple, since there are several main branches of spinning tackle. This is fishing with oscillating spoons and their varieties, rotating spoons, wobblers and poppers, as well as silicone. The use of a certain type of bait determines the tactics and methods of fishing, for example, when installing a silicone fish, the angler will most likely choose jig wiring. From here the class of the rod will be determined.
- Estimated catch. It also dictates what kind of rod you need to use. For example, to catch small perches you will need lighter tackle, but if the angler is counting on catching a large specimen of pike or pike perch, the spinning rod should be much tougher.
Neglecting at least one of these factors can lead to complete discomfort during fishing and its accompaniment by constant snagging on coastal vegetation, tangling of the fishing line and, as a result, the end of fishing. In order to wisely choose a spinning rod for fishing from the shore, you need to understand the parameters described below.

Price and type of rod
Before buying a spinning blank, you need to carefully study the market, since there are a huge number of offers there. And very often you can find a budget rod within 3,000 rubles, which in its characteristics will be similar to a product produced by a famous brand and having a retail price of 30,000 rubles and above.
And yet, despite the fact that the brand is a significant, but not fundamental, circumstance, it should be noted that among both beginners and experienced fishermen, rods from Daiwa and Shimano have a good reputation; manufacturers Banax, Nissin, Tenryu are a little less known. The range of these companies is very large and allows you to choose a set of rods for the required type of fishing.
Based on their technical design, forms are divided into plug-in and telescopic. The first ones consist mainly of two parts and are connected end-to-end using a plug connection. This guarantees them high strength, uniform load distribution and, accordingly, excellent balance.
Rods of the second type are very outdated; their only advantage is their compactness during transportation, which made them popular mainly among lovers of float and bottom tackle. Accordingly, when fishing with spinning tackle from the shore, it is better to give preference to a plug form.

Primary parameters for choosing a fishing rod: test and length
These characteristics almost completely describe the fishing rod for a particular body of water. So, the length allows you to determine the casting distance, having a direct relationship - the longer, the further. The test, in turn, shows how heavy the bait can be delivered to the desired area of the reservoir and partially determines what weight of fish is expected to be caught.
Rods have a very different test, and extreme values can be from tenths to a unit of grams when fishing with ultra-light baits, and from tens to hundreds of grams when hunting fish such as taimen, salmon, catfish or very large pike using special oscillating spinners. Universal values for most reservoirs when fishing from the shore will be 7-30 grams, 5-15 grams, 5-25 grams or close to them, i.e., no more than 30 grams and lying in a wide range.
It should be remembered that it is better to choose a test with a small margin, ideally so that the mass of the bait is its average value. As an example, if you plan to cast a spinner weighing from 7 to 15 grams, then a rod test of 5-25 grams would be ideal.
We recommend reading: Features of catching and baiting bream
The choice of length is motivated not only by the casting range, but also by the nature of the shoreline of the reservoir. If the coast is clean, without high coastal vegetation, then there is the possibility of a large sweep, which allows the use of a blank length of up to 3.3 meters. As an example, these could be large lakes or reservoirs. If the reservoir is located in a wooded area and is bordered by lush vegetation, even coniferous trees, then it is best to use rods with a length of 1.8 to 2.1 meters. In general, as practice shows, even when alternating fishing on forest streams with a transition to a large forest lake with partially clear banks, a rod 2.1 meters long is quite universal.
Here you can immediately give a specific example, which may be useful to beginners. So, the intended fishing location is a small river flowing from a forest lake and flowing into a huge water area. The width of the stream does not exceed 3 meters, with riffles leading to places with a moderate current. The species of inhabited fish with prospects for catching are pike, pied trout and brown trout. Accordingly, rotating spoons weighing 6-7 grams will be used for trout, a Castmaster-type spinner weighing 13 grams for trout, and it is also possible to use a popper and wobbler weighing 15 grams for catching pike. From these considerations it is clear that a Daiwa rod with a length of 2.1 meters and a test weight from 5 to 21 grams will be universal. With its help, you can easily make both pendulum and side casts without fear of making a shore hook.

Rod build
This parameter should be displayed in a separate column, since it ultimately characterizes the form of the rod and determines what baits will be used for fishing. In fact, it indicates the information content of the tackle when casting, retrieving and retrieving, depending on the type of equipment. Despite the fact that this is a separate and very large topic, you should at least superficially study this parameter in order to correctly select a spinning rod for fishing from the shore.
The action is indicated on the form of the rod; it is convenient to divide it into three types:
- Extra fast and fast. These are rigid rods in which only the whip is used during casting, retrieving and retrieving. When fishing from the shore, it is well suited for jigging or twitching, where the sharpness of both the hook and the transfer of impulse to the bait should be maximum.
- Medium. If the angler does not fully know what kind of fish lives in the reservoir and is going to use a wide range of baits, this is the ideal rod setup. In all modes, exactly half of the form functions. It can be used with both jig baits and all spinners; landing fish is very simple, since its jerks are effectively dampened.
- Slow. As the name implies, the rod responds to the load with its entire length. This type of blank is used when fishing with large spoons and, accordingly, trophy fish. Good shock absorption allows you to effectively fight against a massive predator. Also suitable for some types of twitching.
So, as can be seen from the description, for beginners or anglers who do not have sufficient information about the reservoir, it is recommended to use a medium or, as it is called, semi-parabolic system. This rod will allow you to use a wide range of baits, provide optimal casting and comfortable fishing.
The quality of the rod blank
As mentioned above, there are a huge variety of fishing rods on the market from different manufacturers. One of the pricing factors is the material from which the form, handle and fittings are made, as well as the quality of the assembly itself. That is, with the same characteristics, a more expensive fishing rod may be more durable. However, sometimes the principle works, which is based on the fact that it is impossible to buy an exclusive product for too little a price, but for a large specific fake it is quite possible. Therefore, it is necessary to examine the rods as carefully as possible, examine the surface for chips and cracks, check the alignment of the guide rings, the integrity of the fastening, etc.
Most rod blanks are made of carbon fiber. This material is distinguished by exceptional characteristics, such as low weight and high strength, compliance with specified characteristics. The only drawback is the low resistance of the structure to impact loads due to its fragility. However, today the cost of budget products does not exceed 3,000 rubles for very decent quality and that is why it can be recommended to beginners. Fiberglass spinning rods are usually made telescopic, are obsolete, heavy and are used mainly as a unit for traveling as they take up very little space.
Guide rings on the rod blank are also made of different materials, but all-metal ones are increasingly leaving their positions, and their place is being taken by designs with various spacers made of ceramics, Teflon, etc. This innovation eliminates the unpleasant phenomenon of the fishing line rubbing against the ring material, followed by breakage and loss of valuable bait.
Recommended reading: Winter tips
Summarizing the characteristics of a spinning rod for fishing from the shore, we can highlight general tips for choosing a blank. First, the parameters and price segment are determined, from which several copies are subsequently selected, preferably from different manufacturers. Secondly, the structures are checked for integrity, there should be no chips anywhere, all surfaces must be smooth and polished, the form must be uniform and straight along its entire length. The reel holder must have a strong and reliable fastening ring, the thread is intact, the moving elements can be put on easily, but without play. The handle must be made of cork or high-quality polymer, and the location of the reel seat must be such as to maintain balance with the blank, otherwise after hundreds of casts the hand will “fall off”. The plug connection should also not have any play. Small bonuses like an eye for catching a hook will be very nice.

Do you have a FisherGoMan self-hooking fishing rod?
Yes
General recommendations for beginners
Fishing is an exciting activity, but beginners are often disappointed due to their first failures, so let’s take a closer look at the general recommendations for beginners. It is important to realize that a good result requires skills in working with equipment, understanding the behavior of fish, and experience working in a variety of conditions. Skills are acquired gradually, so the main advice is to be patient and enjoy fishing.
A general list of tips for beginners includes the following points:
- listen to the advice of experienced people;
- prepare inventory: choose the right tools, check their serviceability and functionality;
- determine the fishing location in advance and find out as much as possible about it: what kind of fish is found, what is the terrain and weather forecast;
- select bait according to the expected conditions.
By carefully planning the process and following the advice of experienced people, fishing is sure to bring results and an unforgettable experience.