The city of Kurchatov: the beginning
Before talking about the Kurchatov Reservoir, let's get to know the city itself a little better. It is located in the Kursk region, just 37 kilometers from Kursk itself. This town is very small - a little more than 38 thousand people live in it (there is a tendency for the number of residents to decrease from year to year). It is also relatively young, it was founded only in 1968, therefore, this year it will celebrate its anniversary - fifty years. Initially, on the territory of the city of Kurchatov, which, by the way, as you can easily guess, was named after the famous Russian physicist Igor Kurchatov, there were various villages. There were quite a lot of them, some gradually deteriorated and disappeared, others still held on to life. However, in the mid-sixties of the last century, when the order for the construction of the Kursk nuclear power plant was issued, a workers’ settlement was hastily built for the group of workers who arrived to build it so that they would have a place to live. This place, which appeared in 1968, was initially designed for no more than eighteen thousand people and remained nameless for some time, three years later received the name - the village of Kurchatov. And twelve years later (in 1983), the settlement, which had already grown quite large by that time, was given the status of a city.
Other Kursk news for this day
11 January 2021, 21:27
A terrible accident near Kursk: the identity of the deceased driver is being established
[/td]
January 11, 2021, 10:00 p.m.The number of coronavirus patients increased per day in 5 cities and 14 districts of the Kursk region | |
11 January 2021, 21:26The Kursk sculpture “Date” took 2nd place in the competition for the most unusual monument in Russia | January 11, 2021, 21:00A driver was injured in a collision between a VAZ and a bump stop near Kursk |
11 January 2021, 20:30An elderly man died in the Kursk region | 11 January 2021, 20:07During the New Year holidays, 209 children were born in the Kursk region |
11 January 2021, 19:16In 2021, 1,885 people were vaccinated against coronavirus in the Kursk region | 11 January 2021, 19:08At the end of the week, the Kursk region will receive a coronavirus vaccine for 1,800 people |
11 January 2021, 18:03Guys suspected of vandalism were photographed in Kursk | 11 January 2021, 17:44The Education Committee of the Kursk Region commented on the death of a teacher during a lesson |
11 January 2021, 17:33Near Kursk, a teenager fell from a 9th floor window | 11 January 2021, 15:46In Kursk, at school No. 53, a teacher died during a lesson |
11 January 2021, 15:30A resident of the Kursk region was almost crushed by a garbage container | 11 January 2021, 14:25Near Kursk, a car crashed into a truck, three were wounded |
11 January 2021, 13:18Kuryan dies after being stabbed on Christmas Day | 11 January 2021, 13:00Frosts, blizzards and snow drifts are expected in the Kursk region |
11 January 2021, 12:27A trolleybus hit a pedestrian in the center of Kursk | 11 January 2021, 12:15In Kursk, on Deriglazova Avenue, a dump of plastic canisters was removed |
January 11, 2021, 11:50Kursk rapier masters won medals at All-Russian tournaments | January 11, 2021, 11:30Firefighters rescued elderly women from Kursk |
January 11, 2021, 11:20In the Kursk region, a car hit a cyclist carrying a child | 11 January 2021, 11:07On Klykov Avenue, vandals defaced graffiti with Kursk ornaments |
11 January 2021, 10:45Near Kursk, a drunk driver rammed a police UAZ | 11 January 2021, 10:35The final vote on naming the Kursk airport has begun |
11 January 2021, 10:19The number of coronavirus tests has decreased in the Kursk region | 11 January 2021, 10:01A hotline has opened in the Kursk region to provide beneficiaries with free medicines |
11 January 2021, 09:40The Kursk sculpture “Date” may become the most unusual monument in Russia | 11 January 2021, 09:38Kursk residents can expect a 6-day work week and 3 days off in February |
11 January 2021, 09:31In the Kursk region, schools whose parents have signed a petition can be transferred to distance learning | 11 January 2021, 09:06A calendar “46 festivals of the 46th region” was released in the Kursk region |
11 January 2021, 08:57In May, construction of a road from Deriglazov Avenue to the M2 “Crimea” highway will begin in Kursk | 11 January 2021, 08:51Roman Starovoit instructed to deal with the increase in the cost of travel on minibuses in Kursk |
11 January 2021, 08:50In the Kursk region, the discharge of patients with coronavirus has decreased significantly | 11 January 2021, 08:45During the New Year holidays, the Kursk ambulance received from 600 to 800 calls per day |
11 January 2021, 08:44Three children with coronavirus are in hospital in Kursk | 11 January 2021, 08:42Another 171 cases of coronavirus were detected in the Kursk region over the past 24 hours |
11 January 2021, 08:30In the Kursk region, a house burned down in the morning, a pensioner died | 11 January 2021, 07:50A woman died in a terrible accident at a bus stop near Kursk |
| 11 January 2021, 07:30 |
City today
Today Kurchatov ranks third in size among the cities of the Kursk region. In addition, this is one of the most comfortable cities in the above-mentioned region, which has even received All-Russian awards several times for its cleanliness and beauty.
The distinctive features of this settlement are, firstly, the complete absence of the private sector in it, and secondly, the ridiculously simple layout of the streets, making Kurchatov very easy to navigate even for a person who is poorly oriented in the area.
Briefly about the main thing
The reservoir of the city of Kurchatov is also called the cooling pond of the Kursk nuclear power plant. And this pond appeared in 1976-1977 of the last century in the floodplain of the Seim River, which flows near Kurchatov. Why a cooling pond? The thing is that the main function of the Kurchatov reservoir from the moment of its launch to this day has been and remains to maintain the operation of the heat exchange equipment and protection system of the above-mentioned station. Thanks to the cooling pond, water continuously flows into the cooling systems of nuclear power plant reactors.
Kursk region
Kursk region is a federal subject in the southwest of the European part of Russia. The region is located on the East European Plain, on the southwestern slopes of the Central Russian Upland, in the forest-steppe zone. The relief of the region is erosive, highly dissected by a network of ravines and girders.
Kursk region is part of the Central Federal District. The administrative center is Kursk.
The region's territory is 29,997 km2, the population (as of January 1, 2017) is 1,122,893 people.
Surface water resources
The water bodies of the Kursk region belong to the basins of two large rivers - the Dnieper and Don (78% and 22% of the territory, respectively).
The river network of the Kursk region is represented by about 900 rivers with a total length of about 7.6 thousand km (the density of the river network is 0.25 km/km2), most of which are small rivers and streams. The rivers of the region are characterized by mixed feeding with a predominance of snow. The rivers of the Kursk region belong to the Eastern European type of water regime, they are characterized by high spring floods, summer-autumn low water, occasionally interrupted by rain floods, and low winter low water. They freeze in late November - early December, open in late March - early April. The largest rivers in the region are: in the Dnieper basin - Seim and Psel, in the Don basin - Oskol (a tributary of the Seversky Donets).
The average long-term river flow is 3.8 km3/year. In 2015, river flow in the Kursk region amounted to 2.2 km3/year, which is 42.11% lower than the long-term average. Below is the dynamics of river flow in the Kursk region from 2010 to 2015.

According to the Institute of Lake Science of the Russian Academy of Sciences, on the territory of the Kursk region there are about 1,800 lakes and artificial reservoirs with an area of about 205 km2 (lake content 0.69%), including 280 lakes with an area of more than 0.01 km2 and a number of smaller lakes, mainly floodplains . The largest lake in the region, Makovye, has an area of only 1.31 km2. Artificial reservoirs are much larger than natural ones; the largest of them are the Stary Oskol reservoir on the river. Oskol, located on the border of the Kursk and Belgorod regions, the cooling pond of the Kursk Nuclear Power Plant (a bulk reservoir on the Seim river, also the Kurchatov reservoir or the Kurchatov “sea”) and the reservoir of the Mikhailovsky Mining and Processing Plant OJSC on the river. Svape (right tributary of the Seim river).
Swamps and wetlands occupy 1.07% of the territory of the Kursk region - 321 km2.
The area and number of lakes and artificial reservoirs, swamps and wetlands are variable; they depend on natural (water regime, climatic phenomena, swamping, meandering, etc.) and anthropogenic (drainage of territories, creation of new artificial reservoirs, etc.) factors.
Groundwater resources
The forecast groundwater resources of the Kursk region are 3288 thousand m3/day (4.44% of the total volume of forecast groundwater resources in the Central Federal District and 0.38% in Russia). Groundwater reserves in the region as of January 1, 2015 amounted to 1230.6 thousand m3/day, which corresponds to a degree of knowledge of 37.4%.
According to data as of January 1, 2015, 273.1 thousand m3/day were produced and extracted from underground water bodies of the Kursk region during the year, including 215.4 thousand m3/day from the fields. The degree of development of groundwater reserves is 17.5%.
Provision of population with water resources (according to 2015 data)
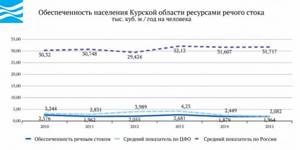
The provision of the region's population with river flow resources is 1.964 thousand m3/year per person, which is significantly lower than the Russian average (31.717 thousand m3/year per person) and comparable to the indicator of the Central Federal District (2.082 thousand m3/year per person).
The provision of predicted groundwater resources is 2.936 m3/day per person, which is lower than the Russian average (5.94 m3/day per person), but higher than the figure for the Federal District (1.894 m3/day per person).
Below is the dynamics of provision of the population of the Kursk region with river flow resources in 2010–2015.
Water use (as of 2015)
The intake of water resources from all types of natural sources in the Kursk region is 228.84 million m3, the volumes of intake from surface and underground sources are comparable (57.61% and 42.39%, respectively). Below is the dynamics of fresh water intake in the Kursk region in 2010–2015.

The total water losses during transportation in the Kursk region are 9.35 million m3 or 4.09% of taken water, which is lower than both the federal district figure (5.39%) and the Russian average (11.02%). Below is the dynamics of water losses during transportation in the Kursk region in 2010–2015.

Direct-flow water consumption amounted to 218.58 million m3. Most of the water was used for industrial, as well as drinking and domestic needs (74.27% and 20.94%, respectively), agricultural water supply and irrigation account for 1.75% and 0.2%, respectively. Below is the dynamics of water consumption in the Kursk region in 2010–2015.
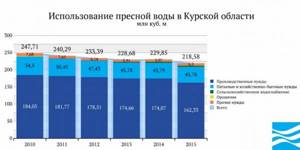
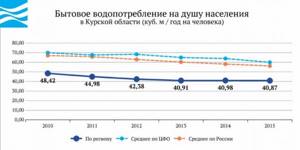
Domestic water consumption per capita in the Kursk region is 40.874 m3/year per person, which is lower than both the Russian average and the federal district indicator (56.205 59.952 m3/year per person, respectively). Below is the dynamics of domestic water consumption per capita in the region in 2010–2015.
The volume of circulating and re-sequential water consumption in the region is 6130.63 million m3 or 96.56% of the total water consumption in the region. Below is the dynamics of direct-flow and recycling and re-sequential water consumption in the region in 2010–2015.

Discharge of wastewater into water bodies of the Kursk region is 86.13 million m3, of which 86.8% is conditionally pure and standardly treated wastewater, the volume of polluted and insufficiently treated wastewater is 13.2%. The region generates 0.36% of the total volume of polluted and insufficiently treated wastewater in the Central Federal District and 0.08% in Russia. Among the regions of the federal district, the Kursk region ranks last in terms of the volume of contaminated and insufficiently treated wastewater and third in terms of the share of conditionally clean and normatively treated wastewater in the total volume of wastewater disposal after the Kostroma and Tver regions. Below is the dynamics of water disposal in the region in 2010–2015.

Water quality (based on 2014 data)
In 2014, in the centralized water supply systems of the Kursk region, non-compliance with standards for sanitary and chemical indicators was recorded in 4.5% of samples taken, and for microbiological indicators - in 1.5% of samples. In non-centralized water supply systems, the quality of 3.6% of samples for sanitary-chemical indicators and 3.6% of samples for microbiological indicators did not meet the standard. Below is the dynamics of the corresponding indicators in the region in 2010–2014.

Water management
The Kursk region is in the area of responsibility of the Don Basin Water Administration of the Federal Agency for Water Resources of Russia.
The functions of providing public services and managing federal property in the field of water resources in the region are carried out by the Water Resources Department of the Don BVU for the Kursk Region.
The powers in the field of water relations transferred to the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, the functions of providing public services and managing regional property in the field of water resources in the region are carried out by the Department of Environmental Safety and Natural Resources Management of the Kursk Region.
The state program “Reproduction and use of natural resources, environmental protection in the Kursk region” is being implemented in the region - a regional program aimed at developing a network and ensuring the functioning of specially protected natural areas of regional significance, restoration and environmental rehabilitation of water bodies, providing a favorable habitat for population, improving the system for protecting wildlife and their habitats, recycling deteriorated, prohibited pesticides and agrochemicals and other hazardous waste, major repairs of hydraulic structures that are in regional and municipal ownership, as well as abandoned hydraulic structures.
When preparing the material, data from the State reports “On the state and protection of the environment of the Russian Federation in 2015”, “On the state and use of water resources of the Russian Federation in 2015”, “On the state and use of land in the Russian Federation in 2015”, were used. “On the state and protection of the environment in the Kursk region in 2015”, collection “Regions of Russia. Socio-economic indicators. 2016". The ratings of regions for surface and underground water resources do not take into account the indicators of federal cities - Moscow, St. Petersburg and Sevastopol.
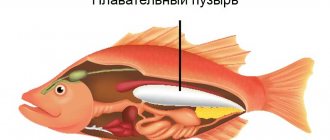
Features of the reservoir
A special feature of the reservoir is that it is home to a huge number of different species of fish. Moreover, special workshops at the Kursk Power Plant additionally breed some of the owners of gills and scales so that they carry out biological purification of water. In addition, many different birds live near the reservoir. They nest there because this local “sea” does not freeze in winter.

We will tell you in more detail about the different representatives of the animal world on the reservoir of the city of Kurchatov below, but for now it is worth adding that for the residents of the city this place has become not only an opportunity for successful fishing, but also a good rest. Fortunately, the territory allows it: the area of the Kurchatov Reservoir is almost twenty square kilometers - a very impressive figure. The depth of the “sea” near Kursk in some places reaches seventeen meters.
Free fishing in the Kursk region
In the Kursk region you can find many good places for fishing. It must be said that in the Kursk region there is no particular abundance of water resources, therefore, almost all fishing is mainly concentrated on the rivers of the Don or Dnieper basins. About 188 rivers flow through this area, with a total length of more than 10 km. And the largest of them exceed 100 km in length. These are: Psel, Tuskar, Seim, Svapa and Kshen. In addition, there are 870 lakes and about 800 artificial reservoirs.
Here are the TOP 7 best places where you can fish for free in the Kursk region:
1. River Psel

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
The Kursk region covers only the upper reaches. It originates from the village of Prigorki. Previously, there were about 50 species of fish in this tributary of the Dnieper. But the cascade of dams does not have the best effect on the ichthyofauna and hydrobiological regime.
Psel is becoming increasingly shallow, its riverbed is silting up. Fish cannot move freely upstream to spawn. The number of burbots, nose-nosed ruffes, longhorned beetles, and podusts has significantly thinned out.
Today, Kursk fishermen go to Psel for crucian carp, bream, chub, taking with them donkeys or spinning rods.
GPS coordinates: 51.08516, 35.78802
2. Seim River

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
Fishing on the main waterway of the region attracts not only Kursk residents, but also visiting anglers. The Seim is distinguished by its calm disposition, complex structure of the bottom topography, and a winding riverbed with a large number of riffles. In the lower reaches the width reaches 100 meters. The prevailing depths are 2–3 m. Some places abound in deep pools, reaching 8–10 meters.
In the upper reaches there is loach, crucian carp, and ruff. Between Chervona Sloboda and Tetkino there are promising riffles for spinning fishing for chub, perch, and rudd. In numerous backwaters you can catch pike. Mostly one-kilogram specimens are found, and specimens weighing 3–4 kg are considered a notable trophy.
Podust and ide are found in the Mutino-Putivl area. In the lower reaches, when the water recedes, there is a high probability of encountering a catfish. This fish is significantly smaller in size than the Volga monsters. Catching individuals weighing about 10 kg is a great success.
There are pike perch, but they are rare in catches. More often, the fanged one is caught on live bait during ice fishing.
Meadow and light forest areas of the Seim have easy access. Access to the wooded shores is only possible by boat.
GPS coordinates: 51.68597, 36.11533
3. River Svapa

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
Length – 197 km. It originates near the village of Podsborovka and flows into the Seim opposite the village of Zhilishche. Within the Central Russian Upland it flows between hills, agricultural lands, meadows, oak forests and pine groves. The lower part is in continuous deciduous forests. The Gnilushi reserve is also located there.
In Svapa there is a lot of bitterling, pike up to a kilogram, chub, small bersh, and medium-sized roach. Less common are bream, asp, and ide.
Working gear: spinning rod and float rod. The lower reaches of Svapa are popular with underwater hunters.
GPS coordinates: 52.22121, 35.53342
Small Pond (Paniki village)

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
This pond is located near the village of Paniki. There is a dirt road leading to this pond, which means it can be reached even after rain. In the Small Pond you can catch crucian carp, which can weigh from one kilogram. If we talk about gear, then a spinning rod is better suited for this reservoir.
GPS coordinates: 51.39788, 36.24503
Lake Malino

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
The oxbow lake on the Seim River has an elongated shape: the width of the reservoir reaches 200 m, length – 4.5 km. The southern shores are bordered by forest, the northern and western shores are surrounded by meadows.
Shallow areas of the lake are covered with water lilies and egg capsules. Floodplain meadows near the coastline turn into dense thickets of cattails and reeds. They have several exits to the water.
The reservoir is home to carp, pike, chub, perch, and roach. The lake is located in a state reserve. During spawning, you can only fish here from the shore using a float rod.
Location: Rylsky district, Kapystich village
GPS coordinates: 51.69193, 34.84194
Kursk Reservoir

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
Fishermen are drawn to this place as many varieties of fish live here, such as ruff, tilapia (a rare species of fish).
For those who want to catch big fish, it is necessary to fish at depth. For large catches, you should also purchase a boat. In this reservoir there are many reeds in which many fish live. There are different baits for fishing; corn and dough are often used.
The water in the Kursk Sea does not freeze in winter. To the delight of the surrounding birds and open water fishing enthusiasts. In addition to typical representatives of the ichthyofauna of the region, the following fish are caught in the Kurchatov Reservoir: pike perch, white and black carp, silver carp, tilapia, and carp.
In autumn, the water above the northern edges of the reservoir becomes silver from the accumulation of small roach and other small things, which serve as the main food for predatory fish. Pike are caught using live bait, spoons, wobblers and silicone.
There are fewer large pike perch, but they are still found in deep areas. Small pike perch are caught off the coast, and closer to winter they are found near pits.
Crucian carp fish guard their prey in the northern part of the reservoir, where there are many reed thickets.
Perch spots are located closer to the center of the reservoir, where there are many holes. Spinners' favorites are white and pearlescent twisters. Local humpbacks respond worse to wobblers and spoons.
Large roach hides in driftwood overgrown with mud, lying on the sandy bottom. In such places there is excellent fishing for rudd.
Breamers go by boat to the center of the reservoir, where bream hide in holes and bottom drops.
Among the baits there is no competition: dung worms, batter, maggots.
GPS coordinates: 51.6783, 35.68707
7. Lake Fitizh

Description, what kind of fish is found, how to get there:
Another Seimas oxbow stretches in a three-kilometer winding ribbon from southeast to northwest. The area of the lake is 67 hectares.
Beach lovers do not like Fitizh because of the swampy shores and muddy bottom. But fishermen come here all year round. The lake is inhabited only by pike, asp and ide, but the fish pleases with their quantity and size.
Some fisherman catch a whole bucket of ide in a day. In Fitizh he is large, but distinguished by his capriciousness. In the spring it is caught with a float rod. After spawning restrictions, it’s time for spinning and feeder.
The presence of asp in Fitizh indicates the high purity of the lake. The predator is found in deep areas. For long-distance fishing, use Bolognese rods with match tackle or parabolic spinning rods with a spinner.
Pike can be caught both in deep and shallow water using a wide variety of spinning baits. But in the summer, fishing with live bait is still more successful.
Location: Lgovsky district, village. Fitizh
GPS coordinates: 51.68573, 35.15082
Do you know any other good places for fishing in the Kursk region - write in the comments