Twitching is a special technique of fishing with wobblers, which involves jerking the bait, simulating the movement of a wounded fish fleeing from a predator.
The word twitching itself comes from the English word twitch, which is translated into Russian as twitching, twitching. When fishing by twitching, the wobbler is pulled in jerks, which are made by the end of the rod with different strength and amplitude. Twitching is used to catch a wide variety of predatory fish: pike, perch, pike perch, asp and many others. The peculiarity of twitching is that with its help you can provoke even a well-fed, passive predator to attack.
We will talk about what twitching is, its advantages and disadvantages, gear for twitching and the types of twitching wiring in this article.
What is twitching
Twitching is a technique for inserting a wobbler and is based on jerking. Twitching wiring consists of a cycle of jerks and pauses. The movements of the rod tip when jerking a wobbler can have different strength and amplitude. Pauses can also have different durations, which depend on the specific fishing conditions and the degree of activity of the predator in the reservoir.
Initially, only minnow wobblers were used for twitching fishing; now, in addition to minnow wobblers, many other types of wobblers are often used. Twitching allows you to reveal all the rich possibilities that are inherent in the design and structure of such baits as wobblers.
Over time, with the acquisition of experience, the spinning angler develops a unique, his own style of twitching, which allows him to fish in the most difficult fishing conditions.
Twitching is a universal way of catching predatory fish. By twitching you can fish in reservoirs with still water and in the current, fish in deep or shallow water, fish locally or fish in a large area, catch both active fish and fish in a passive state.
The main object of twitch fishing in our conditions is pike. Most twitching wobblers presented in fishing stores are designed specifically for catching pike in different fishing conditions. Another popular target for twitching fishing is perch, which responds well to twitching with small wobblers.

Twitching is a very dynamic, exciting and interesting method of spinning fishing, forcing the spinner to constantly experiment with wobblers and the optimal technique for wiring them. Each attack of a predator on a fisherman’s bait indicates his skill and is therefore especially valued.
A spinning fisherman fishing with twitching does not get bored with the monotony of a uniform retrieve; he needs to constantly show a creative approach to fishing, because each bait and each retrieve is absolutely unique and inimitable.
Every spinner who is serious about spinning fishing must master twitching and include it in his arsenal of fishing methods and techniques.
What is twitching wiring?
It is known that there are dozens of different ways to catch a predator using a spinning rod, but all of them are applicable to a certain type of bait. If uniform or stepwise pulling of the tackle is more suitable for spinners, and jig is more suitable for twisters and vibrotails, then for an attachment such as a wobbler, the best solution is jerking (twitching). This method consists of a series of lateral strokes of the rod, leading to jerks of the main line with short pauses.

What does twitching wiring do? Firstly, the wobbler does not sink or float, but plays in the water column. Secondly, the sharp movements of the bait are the best way to attract even an inactive predator. Thirdly, it is during the pause after the jerk that predatory fish attack most often. And simply twitching is much more effective than other methods when catching predators hunting in the middle depths.
Benefits of twitching

- One of the advantages of twitching is a wide variety of wobblers, which reveal their full potential only with twitching wiring.
- Twitching allows you to catch not only active fish, but also fish that are in a passive state.
- Twitching involves high fishing activity and a constant search for bait and the technique of retrieving it, all this does not allow the spinner to get bored.
- Twitching is a fairly universal fishing method. Twitching can be used to fish in reservoirs with both still water and currents, and to fish in great depths or areas of shallow water. By twitching you can fish at a specific point or fish a large area in search of active fish.
Disadvantages of twitching

- Twitching fishing involves purchasing specialized gear, primarily fishing rods. Universal, wide-profile spinning rods, which are common among most spinning anglers, are not very suitable for twitch fishing.
- When fishing by twitching, the bait is various wobblers, primarily minnow wobblers. The price of wobblers significantly exceeds the price of other spinning baits: rotating and oscillating spoons, especially jig baits.
- Fishing with twitching requires the angler to master the jerking technique, so it is better for novice spinning anglers to start fishing with baits that are simpler in terms of pulling technique, such as spoons or jigs, and only then begin to master the art of twitching.
Classification of twitching baits
Twitching wiring involves using exclusively wobblers as bait. Spoons, vibrating tails, twisters and jig baits are not suitable for this method of fishing. But how to choose the right nozzle, and what characteristics should it have?
For twitching, it is important to understand that all wobblers are divided by buoyancy and by the area of the front blade. The first criterion determines the ability of the bait to sink or stay afloat, and the second - to play and go deeper into the water when retrieving. According to buoyancy, wobblers are divided into:
- non-sinking (floating);
- suspenders (floating);
- drowning.
Based on the area of the front blade, all baits are classified into:
- wobblers with a small blade area (do not play when retrieved evenly and sink slowly when retrieved);
- wobblers with a large blade area (having a unique game of their own and quickly sinking when retrieved).
Twitching wobblers with a small blade requires the fisherman to individually select the intensity of jerks and the duration of pauses. This is a rather difficult process, especially for beginners.
Wobblers with a large blade, which play in the water even when the fishing line is evenly reeled in, are more versatile. And their use in combination with rhythmic and monotonous jerks is already a classic twitching wiring. For beginner spinning anglers, it is recommended to use just such attachments.
Spinning rod for twitching

The success of twitching largely depends on a properly selected spinning rod. In order for a spinning rod to be suitable for twitching, it must meet certain requirements:
Weight
Spinning rod for twitching should first of all be light. During twitch fishing, the angler’s hand holding the spinning rod is under constant tension, since it not only has to hold the rod, but also make jerking movements with it. When twitching, a wrist grip is used; the butt of the spinning rod almost never rests on the elbow. The light weight of the spinning rod allows you to twitch throughout the day without getting tired and get real pleasure from fishing. The spinning rod for twitching should be well balanced. The spaced handle is very convenient for twitching. This handle reduces the weight of the spinning rod, increases its sensitivity, and provides a more comfortable grip.
Test
The spinning rod test for twitching should correspond to the weight of the wobbler you are going to fish with. The spinning rod should not fail when performing a jerk retrieve. It’s good if the test of your spinning rod slightly (3-5 grams) exceeds the weight of the wobbler that you use for fishing. The most common among anglers are spinning rods for twitching with a top dough of 15-20 grams.
Length
The spinning rod for twitching should not be too long so that during fishing the angler can change the speed of the wobbler and the strength of the jerks. When fishing from the shore, the optimal length of a spinning rod for twitching is 2.4 m. When fishing from a boat, the optimal length of a spinning rod for twitching is 1.8-2.1 m. The most universal rod length for twitching is 2.1 meters, such a spinning rod will be felt by the angler as an extension his hands, the angler can easily change the speed of the retrieve, the frequency and amplitude of jerks and twitches.
You may be interested in: Boat motors: 15 best motors in terms of price-quality ratio
Build
Correct twitching is only possible if you have a rod that is properly selected in terms of rigidity. Only a spinning rod of the correct rigidity allows you to move the bait with jerking animation.
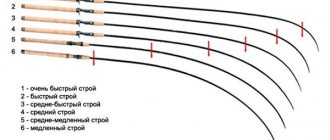
Spinning rods of medium-fast, fast, and super-fast action are suitable for twitch fishing.
- Medium-fast action - well suited for not very high-speed, soft twitching of certain models of wobblers in special fishing conditions.
- Fast action is the most universal spinning system for twitching, suitable for any body of water and any fishing conditions, provides good accuracy and casting range of the bait. Makes it possible to use both soft and aggressive, hard twitching.
- Ultra-fast action - a spinning rod system that allows you to use the toughest twitching. Less versatile compared to fast action spinning rods.
Twitch fishing gear
Rod
The peculiarity of bait wiring, which is carried out more by a fishing rod, imposes certain requirements on the spinning rods used for twitching when fishing for pike, perch, and other predators. There are basically three of them: tuning, length, test.
Rod build
For twitching, it is best to choose fast action spinning rods. It’s good to have medium-fast and super-fast action rods for certain fishing conditions, but good products are expensive and purchasing several types is expensive for the average compatriot fisherman.
Fast action in the ranking of spinning rods for twitching is exactly the golden mean that can be followed by professional fishermen and beginners who want to master twitching.
In general, the preferences for purchasing a twitching rod with a certain action are as follows:
- fast action: a universal rod that can be used for twitching on any body of water and in any conditions;
- ultra-fast action: such a spinning rod for twitching, according to reviews, is good on reservoirs with a noticeable current, when ultralight or light class tackle is used for twitching; spinning rods of this type are worth buying when you plan to twitch only with wobblers;
- medium-fast action: used when measured and smooth movement of wobblers is necessary and when the weight of the latter is 2-3 times lower than the blank test.
Rod length
This characteristic is different for fishing conditions on the shore and from a boat. In the first option, a rod must be purchased with a length of 2.2-2.0 m, in the second 2.0-1.8 m. Going beyond these intervals when choosing a spinning rod for twitching is possible, but only if it is necessary when twitching, for example , circle obstacles with bait, cast away, work in “crowded conditions,” fish in snags. But such situations are rare and only experienced twitchers can take them into account.
Rod test
Typically, a fishing rod is purchased with a test suitable for the tenacity and weight of the wobblers that are supposed to be used for twitching. And general recommendations for choosing a fishing rod that will suit most domestic reservoirs are as follows:
- when hunting mainly for pike and perch weighing up to 0.30 kg, you can purchase a spinning rod, for example, ultralight for twitching, with a dough of up to 10 g;
- if the catches are expected to contain kilogram predators, then the test should be selected up to 15 g;
- with the likelihood of frequently catching predators per kilogram, the best spinning rod for twitching
there will be a rod that has a test of 20 g and above.
Coil
For twitching fishing, an inertia-free reel with good line laying will definitely not be superfluous, otherwise, for more or less quiet twitching fishing, you will have to reduce the height of winding the cord on the reel spool. When using soft braid, an inexpensive reel, as well as a side wind, instead of the recommended 2-3 mm to the edge of the spool, it is better to leave the height at least 5 mm. By following this simple recommendation, we minimize the formation of a beard or dropping loops when casting, albeit with a slight reduction in casting distance.
fishing line
Traditionally, the jerk wiring technique in most cases involves the use of multi-filament fishing lines. The requirements for the line (braid) when fishing by twitching are extremely simple. Since when reeling it in, unlike jig fishing or fishing with spoons, there is no constant tension (low weight of baits, sagging of the cord during a pause, side wind, etc.), laying the cord on the reel is very far from ideal.
During the pause, the braid sags and during subsequent rewinding it falls on the spool rather loosely, as a result of which the dropping of loops and the formation of a beard is almost guaranteed during the subsequent cast. Soft cords are least preferred, especially those marked “PE”; the use of cords such as Power Pro or thermofusion (alloy) cords such as Fireline is more justified, these braids are less demanding on the quality of laying precisely due to their rigidity, and it is definitely easier to untangle a hard cord. But, again, we should not forget that with these braids the casting range is slightly shorter. In twitching, a thicker cord will definitely give a head start to a thin one, again due to better laying (the cord’s own weight), but we don’t cross the line of reason, if we catch perch, we still have to use the thinnest braided line.
Leashes
In twitching, leashes are used that are rigid, which prevent the tees from “clinging” to the cord when twitching. They can be wire or made of string. The only requirement for them is the length, which must exceed the size of the wobbler. It is also possible to use ordinary leashes for wobblers for twitching, but they quickly wear out, turning into a sloppy “tail”.
Twitching reel

For twitch fishing, both spinning and multiplier spinning reels are used.
When using a spinning reel, it is important that the weight of the reel is not very large. The reel should provide good balance between the reel and the spinning rod.
The main requirement for a twitching reel is the quality of line winding. The reel must properly lay the line on the reel spool. When fishing with twitching and other types of jerking, the line is wound onto the reel spool under inconsistent tension, because of this the turns can lie unevenly, fall through, or, on the contrary, form humps. On subsequent casts this may result in dropped loops and beards.

The reel should be strong enough to pull out fish weighing up to 5-8 kg. The optimal size of a spinning reel for twitching is 2500-3000 according to the Daiwa classification. The gear ratio of the coil should be in the range of 4.7-5.
Many spinning anglers use a baitcasting reel for twitching. A multiplier reel has greater durability, provides a longer casting distance, and produces a tighter line winding that guarantees no beards when casting. The disadvantage of multiplier reels is their higher cost compared to spinning reels and the need for a special type of spinning rod designed for installing multipliers.
Twitching line
Any type of fishing line can be used for twitching, including monofilament and fluorocarbon, but the main type of fishing line used for twitching is braided fishing line.
Braided fishing line has a number of advantages: lack of elongation, high breaking load, small diameter.

The use of braided fishing line allows you to have constant hard contact with the bait and produce jerky retrieves with the correct animation. In addition, braiding increases the overall sensitivity of the tackle and the quality of hooking.
The correctly selected diameter of the braided fishing line plays an important role; a fishing line with a diameter that is too large can prevent the wobbler from playing well.
The optimal diameter of a braided fishing line for twitching is 0.12 mm; the breaking load of such a fishing line will be about 10 kg. If it is possible to catch a very large pike in the reservoir where you are fishing, you can increase the diameter of the braid to 0.14 mm.
Leash for twitching

When fishing for pike by twitching, the use of a leash is mandatory. For pike fishing, hard metal leashes made of tungsten or steel are best suited. The length of the leash should be slightly longer than the length of the bait and in most cases is about 15 cm. The use of string leashes when twitching shows good results; they have sufficient rigidity and do not create snags and overlaps.
Wobblers for twitching
A wide variety of wobblers are used for twitch fishing. Wobblers for twitching can be either bladed or bladeless. There are a huge variety of types of wobblers for twitching. The angler has plenty to choose from.

The most popular among bladed wobblers for twitching are minnow wobblers. Minnows are narrow-bodied baits that resemble small fish in their shape and appearance. Most minnows do not have their own game, that is, with a uniform retrieve, they practically do not make oscillatory movements that attract a predator, but with a jerking retrieve, their behavior in the water changes, they become like a wounded fry running away from a predator.
When choosing a wobbler for twitching, an angler should be guided by the following considerations:
- The size of the wobbler for twitching depends on what kind of fish you are going to catch. For perch and small pike, the wobbler size should be from 3 to 7 cm; for catching large pike and pike perch, the optimal wobbler size is from 7 to 9 cm; for very large pikes, the wobbler size can be increased to 11-13 cm.
- The color of the wobbler is selected experimentally while fishing. When fishing in dark or muddy water, as well as when catching an active predator, you can try fishing with a wobbler with a bright, provocative coloring. When fishing in clear water and when fishing with long pauses, it is better to use a wobbler with a natural coloring, since in such fishing conditions the predator has a lot of time to examine the bait.
- The degree of buoyancy of the wobbler affects the length of pauses between jerks. For a floating wobbler, the pause lasts from the jerk of the wobbler to its ascent and complete stop. For a wobbler, the suspension pause takes the period of time from the jerk to the stop of the wobbler in the water column. The sinking wobbler is carried out either with minimal pauses or without pauses at all, since during the pause the wobbler begins to sink, which cannot but alert a cautious predator. Suspender wobblers, which are capable of hovering in the water column, are optimal for twitching fishing.
- The depth of the wobbler depends on the time of year and other fishing conditions. In summer, when fishing in ponds overgrown with aquatic vegetation and snags, the best results are shown by using surface wobblers and wobblers with a minimum degree of depth. In the fall, when predators move to deeper places and stay near the bottom, the use of wobblers with a large degree of depth is justified.
- Not all wobblers have their own game; many wobblers for twitching do not have their own game; only the skill of the fisherman can make such wobblers play. For beginner spinning anglers who are just mastering twitch fishing, it is better to choose those wobblers that have their own game, and as their skill grows, gradually switch to fishing with wobblers that require active animation of the bait by the angler.
You may be interested in: Fishing in the Moscow region
Features of twitching
Twitching
This type of wiring most fully reveals the capabilities of this class of wobblers. It is achieved through different jerks with the rod, both in strength and frequency amplitude. Jerks can be chaotic or, on the contrary, strictly measured. In accordance with this, the movements of the wobbler in the water will be completely different. Depending on this particular model, during these very jerks the wobbler may wiggle a little, that is, its own game appears, or it may not make any side fluctuations.
Standard behavior of a purely jerky wobbler: flying from side to side and slightly in a vertical plane. This type of wiring can provoke a predator, whether hungry or not. The size of the catch directly depends on how you can master this type of wiring, what variety you can give it, how lively (natural) the wiring will be.
The highest quality twitching is achieved when the spinning rod is pointed downwards (the fisherman is standing in a boat, or on some hill above the water).
The wiring varies depending on the object being fished (mainly perch or pike). This is due to the fact that perch loves high-frequency vibrations, and pike loves low-frequency vibrations.
Types of twitching

The fisherman selects the type of twitching wiring, depending on the fishing conditions:
- Season
- Weather
- Predator species
- Predator activity
- Presence and strength of current
- Degrees of buoyancy for wobblers
- Wobbler depths
When fishing by twitching, you should remember that only the rod is involved in guiding the wobbler; jerks and pulls are done with the hand
After casting the wobbler, you need to make 2-3 turns with the reel in order to drive your wobbler into the desired horizon and only after that start twitching.

The jerks are performed with the tip of the spinning rod. The jerks that an angler makes during twitching can have different strengths and amplitudes. Each wobbler model requires a different jerk force, some wobblers require a strong jerk, others a light one is enough. It is advisable to test the new wobbler in advance before fishing in order to select the jerk force required for its correct animation.
The length of pauses plays a big role in twitching. The duration of the pause during twitching can be from 2 to 40 seconds. The duration of the pause depends on the degree of activity of the predator. Short pauses are suitable for fishing in late spring, summer and early autumn, when predatory fish are in an active state. In early spring and late autumn, at low water temperatures, the predator becomes inactive; pauses should be increased to 10-30 seconds. Experienced fishermen, at the beginning of fishing, use a wobbler with short pauses, hoping to attract an active predator; at the end of fishing, they increase the duration of the pauses, hoping to provoke an attack from a predator in a passive state.

It is important that after the jerk there is some slack in the line, otherwise the stretched line will not allow the wobbler to play the way it should. In order to create the correct slack in the fishing line, the wobbler is jerked rather than pulled out in a smooth motion. After a pause, the reel handle reels out the slack line. If after a jerk there is no slack in the line, most likely the rod is too soft for twitching and should be replaced, or another wobbler should be selected for it. You can create slack in the fishing line by returning the tip of the spinning rod back to the initial position after the jerk.
When selecting twitching wiring, a simple rule applies: the more active the predator, the more aggressive the wiring!
If the bait begins to show its own game during twitching, then you need to increase the sharpness of the jerk.
Twitching can be fished in any body of water, but it will be most effective in quiet backwaters and coastal areas of lakes. Wind is the main enemy of twitching; it interferes with both casting the wobbler and controlling the retrieve.

There are three types of twitching postings:
- monotonous twitching - jerking with constant alternation of jerks and pauses
- rhythmic twitching - jerking wiring, consisting of a series of jerks and pauses that are repeated cyclically throughout the wiring
- chaotic twitching - is a jerk wiring consisting of jerks of different strengths and amplitudes and pauses of different durations
Based on the type of jerks, there are two types of twitching:
Hard twitching is a wiring consisting of sharp jerks and pauses. This kind of twitching is also called angry or harsh twitching. Shows itself well when catching active fish. Hard twitching is used when fishing an unfamiliar body of water in order to detect fish and provoke it to attack.

Soft twitching is wiring consisting of soft jerks or pulls. Used to catch predatory fish in a passive state. Soft twitching can force even well-fed, sluggish, sleepy and apathetic fish to attack.
The most commonly used are six types of twitching wiring:
- Rigid monotonous twitching wiring
- Hard rhythmic twitching wiring
- Tough chaotic twitching wiring
- Soft twitching wiring
- Stop and go wiring
- Jerking
Hard monotonous twitching

Hard monotonous twitching shows good results when catching perch, especially when it is active and hits fry in pots.
- After casting the wobbler, the angler removes excess line slack
- The tip of the spinning rod is inclined towards the water, the fishing line lies on the surface of the water
- A continuous series of jerks to the side is made, with pauses of 1 second, to the shore or side of the boat. It is a jerk that is done, not a stretch. The amplitude of the jerk is about 40 cm.
- By rotating the reel handle, the angler removes the slack in the fishing line.
For hard monotonous twitching, you should use a wobbler that does not have its own game. Perfectly suitable for this type of wiring of minnow wobblers, various degrees of depth. When fishing with deep-sea wobblers, the pause can be increased to 3 seconds. When twitching monotonously, you should increase the sharpness of the jerk when casting long distances, when using soft fishing line and when fishing with large wobblers.
You may be interested in: Asp
Hard rhythmic twitching

Hard rhythmic twitching is the main fishing technique for pike. Unlike monotonous twitching, wobbler jerks are performed in cycles, several jerks at a time, followed by a pause, followed by a cycle of several jerks. The fisherman selects the number of jerks, their strength and the duration of the pause.
- After casting the wobbler, the angler makes two soft jerks with the tip of the spinning rod; the amplitude of the jerk should be no more than 30 cm.
- By winding the fishing line with a reel, the angler gets rid of sagging fishing line.
- Pause 2 seconds.
- Repeat wiring.
An angler can diversify the fishing by changing the number of jerks, their amplitude, and making pauses of different durations.
For example:
- 2 short jerks, 1 long
- 2 short jerks, 2 long ones
- 3 sharp jerks, 2 smooth ones
- alternate short and long pauses
Hard chaotic twitching
Hard chaotic twitching is good for catching pike, especially when it refuses to respond to other types of fishing.
Hard chaotic twitching is similar to the previous method, but differs in that the cycle of jerks and pauses is different each time, different from previous jerks.
Soft twitching

Soft twitching is used when hard twitching does not work. Soft twitching is somewhat similar to stop-and-go wiring.
- After casting, the angler selects excess line slack
- Positions the spinning rod at an angle of 45 degrees to the water
- Covers the reel shackle
- Performs slow, uniform retrieving by twisting the reel handle, while slightly shaking the tip of the spinning rod, the swing amplitude is from 20 to 40 cm
Soft twitching can be used when fishing not only with minnow wobblers, but also with shad, crank or fat wobblers. When fishing in a strong current, you should slow down the retrieve so that the current does not disrupt the action of the wobbler.
Stop and go wiring

Stop and go wiring can be considered a type of twitching, since the bait moves unevenly with such wiring.
- The wobbler is thrown to the place of interest to the fisherman
- Make 3-4 turns of the reel handle, then pause for 1 to 3-4 seconds, depending on the activity of the predator
- During the pause, you can lightly play with the wobbler, twitching it with the tip of the spinning rod
- Then the cycle repeats
Stop and go fishing is especially effective when fishing at shallow depths and low predator activity. Composite wobblers show good results.
Jerking

Jerking is a twitching retrieve performed not with a minnow wobbler, but with a special bladeless wobbler called a jerkbait or simply a jerk.
Stop and Go Wiring
This type of twitching is used for pike hunting and consists in the fact that it is used when the pike is “in a bad mood,” that is, inactive. When other types of twitching, with the help of which anglers catch such a predator as pike, are not suitable and do not bring a positive result, then a special method of guiding a wobbler is used, which is called Stop and Go. Such twitching is carried out through a series of slow postings, alternating with fast postings. Such wiring can be done either by jerking the spinning rod or using a reel.
Stop and Go posting is carried out as follows:
- three or four slow turns of the coil;
- pause about 3 seconds;
- light jerk of the spinning rod.
The last stage - a light jerk of the spinning rod should be so light that the wobbler does not work in the usual sense of the word, but barely rolls from side to side.
Then the cycle repeats.
Pike fishing by twitching

Pike is the number one target when twitching. The best places for catching pike by twitching are reservoirs overgrown with underwater vegetation with standing water or weak currents.
Having cast a wobbler, you should not rush to start retrieving; often the pike, attracted by the splash, attacks the bait as soon as it touches the water. After casting, wait 5-7 seconds and only then start retrieving the wobbler.
When fishing for pike by twitching, you should make long jerks with a small amplitude. When catching active pike, there is no need to pause between jerks; when catching passive pike, long jerks should be alternated with stopping the bait for a few seconds. In hot weather and when pike activity is low, the duration of pauses can be increased to 10 seconds. The more active the pike, the shorter the pauses between jerks should be.
When fishing for pike in a heavily overgrown reservoir, you should keep the tip of the spinning rod high enough from the water level so that when jerking, the wobbler does not go deep and does not cling to underwater vegetation.

When fishing for pike in the spring, the best places for fishing will be in shallow waters, where the sun warms up the water faster and the pike stays in such places before or after spawning. For fishing in such places, a minnow wobbler 7-10 cm long, with a depth of 20-30 cm, suspended or weakly floating, is well suited. The main fishing technique for fishing in such conditions is uniform, not too aggressive jerks.
To catch pike in the summer, either surface baits (poppers, walkers) or floating shallow-water minnows with large blades can be used, which prevent wobblers from catching on grass and water lilies. The best wiring is small twitches with a smooth winding of the line.
Autumn is the best time to catch pike by twitching. At this time of year, pikes attack both surface wobblers and deep-sea ones with a depth of 2-2.5 meters. In the fall, aggressive twitching with sharp jerks of wide amplitude works well. Pauses play an important role; it is during pauses that pike most often take the bait.
Fishing for perch by twitching

Catching perch by twitching is a catchy and exciting way of fishing. Twitching can be especially effective during perch feeding. When fishing for perch, you should use retrieval at a slow pace with sharp jerks with the tip of the spinning rod. It is desirable that the wobbler moves forward with sharp deviations to the right and left. The movement of the spinning rod during a jerk can be both up and down and from side to side. If the perch is in an inactive state, then when fishing by twitching you need to take pauses between jerks, during which the perch takes the bait.
Twitching for beginners when fishing for perch and pike
To catch perch and pike, beginners usually use small minnow class suspenders with a large blade area. The intensity of the jerks should depend on the activity of the predator, and the less active it is, the harsher, more intense and sharper they should be.

When choosing wiring, a novice twitcher should not delve into the intricacies of chaotic twitching; it will be enough to comprehend monotonous and rhythmic twitching. The last two methods are very similar to each other, because the second is just a cycle of repetitions of the first.
When monotonous twitching, after casting the bait, you need to quickly reel in the free line, lower the tip of the rod to the water and make the first sharp shock jerk (not pulling), and then take a short pause. Then the jerks are repeated simultaneously with reeling in the main line. The tip of the rod during jerking should move in one line with the same amplitude.
This type of wiring, among other things, ensures timely hooking of fish, which significantly reduces the likelihood of it disappearing.