Every bottom fishing enthusiast has his favorite places for this exciting activity. They have already been well studied and fished, and here, as a rule, the fisherman clearly knows the nature of the surface and the structure of the bottom, catch points and unfavorable areas where they should not cast due to the presence of hooks.
Upon arrival at an unfamiliar body of water, many inexperienced fishermen immediately begin installing fishing gear and try to start their favorite exciting activity as quickly as possible. But if you hurry, you will make the fish laugh.
Choosing a fishing spot
First of all, you need to evaluate external signs, such as remains of traces of fishing by previous visitors:
- traces of the use of bait and lures;
- trampled grass;
- fire pits;
- remnants of bait and food packaging.
One should only regret this behavior of fellow hobbyists, but it occurs quite often.
Having chosen a place based on external features, you should find out the nature of the bottom and depth at the intended fishing site.
How to find out the nature of the bottom
For this purpose, a specially shaped marker weight is used. Its weight can vary, from 30 to 100 grams or more. The choice depends on the strength of the current in the reservoir; the stronger it is, the heavier the marker should be.
The marker sinker can be equipped with a metal rod, which allows for free wiring in silty areas overgrown with aquatic vegetation.
Otherwise, it will be carried away by the force of the current, and the result will not correspond to the place being tested. The general rule is that the marker weight should be close in weight to the weight of the main gear.
The first cast of the marker sinker is carried out to a maximum distance, which is determined depending on the size of the reservoir.
After the marker tackle falls into the water, you need to count the time from the splash of the sinker to the weakening of the line, indicating that it has reached the bottom of the reservoir. The counting interval should be approximately a second; the counting number quite accurately corresponds to the depth of the reservoir at the measurement location.
Sinkers for carp fishing
The bottom topography can be determined by slowly fishing the control gear by the nature of the movement of the load. In this case, the rod is held approximately at a right angle to the casting direction:
- If the load moves jerkily, as if sticking to the bottom, and significant force is required to break it, it means that the bottom in this place is muddy.
- Smooth movement of the marker without jerking means that in this place the bottom is clay or sandy.
- If the load moves with a knocking sound, which is felt even by the hands holding it, it means that there is a colony of shell rock in this place.
- When moving a marker load through thickets of vegetation, its behavior can be defined as a uniformly loaded movement. The shape of the marker weight allows it to not get caught on it when moving in the grass.
The most promising places for catching bottom fish are the boundaries between the muddy and clay-sandy bottom cover. To more accurately determine its location, you need to perform several control casts and install a limiter on the reel.
Measuring the depth in a promising fishing location can be determined with sufficient accuracy by the time of deepening the control load by keeping a count. And to get more accurate data, you can use a marker float.
Basic method (jigging)
The jig method of scanning the bottom is the main one. Amateur feeders must know a simple technique for studying a reservoir if they dream of becoming professionals in a difficult task.
There are plenty of advantages to this simple method:
- study in detail the depths in the designated area;
- actually thoroughly determine the relief;
- find out the structure of the soil;
- with a high probability of choosing a promising fishing spot.
Scanning with a jinning line is not difficult; you will need: a set of sinkers, a fishing rod, and the fisherman’s attentiveness to determine the moment the equipment touches the bottom.
Holding the end of the rod as low as possible, we pull the load along the bottom with the rod
It is advisable to divide the bottom exploration tactics into stages:
- The feeder throws the equipment to a given point and from the moment the marker touches the water - the marker reaches the bottom - remembers the time period.
- After the load lands, the fisherman jerks his rod upward. The concept is that the load should rise from the terrain after each movement of the fishing rod. Experienced anglers must time the drop of the sinker with each jerk, repeating the amplitude and strength of the exercise.
An increase in the time of lowering the load means the presence of a hole. If the interval is shortened, the deepening of the reservoir decreases.
Bottom dragging method
Another method regarding the question of how to measure depth while fishing is dragging along the bottom. The tactics of use are based on determining the structure of the relief and are used at the final stage of studying the visually outlined zone of the intended catch of fish, when suitable places, differences, and thresholds are identified. The prospects for the chosen method are a high percentage of finding sandy, hard surfaces, algae, silt, shell shells, and pebbles.
Read more
How to catch catfish on a feeder?
Dragging tactics involve the use of a heavy marker, when the rod slowly drags the load without the possibility of surfacing when reeling in. Scanning steps:
- The fisherman throws a marker to a given point and waits for it to sink to the bottom.
- Further, the pulling of the load proceeds slowly.
- They pull the rig along the ground to the shoreline.
- The marker moves smoothly on a flat bottom and begins to catch on the edges.
- Using this method, a general picture of the topography of a reservoir is created.
To use drawing, it is necessary to cast a weighty sinker in the shape of a pear or ball.
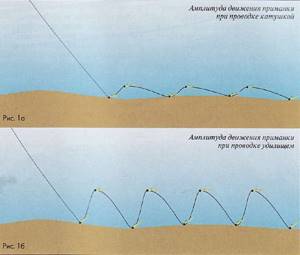
On the pull we determine the structure of the bottom, on the jerk we keep score
Sequential cast method
Several common methods of scanning reservoirs have been outlined above. Each has pros and cons, which affect the definition of terrain to varying degrees. Many beginners use the sequential casting method to find out the characteristics of the bottom. They throw the equipment into different fishing zones, time the time of falling, lowering to the ground - counting out loud: one, two, three, four. Then the casting range is reduced by a certain amount by turning the reel, and the actions are repeated.
The indicated tactics of how to check the bottom before fishing have many disadvantages:
- the structure is not determined, the relief is approximate;
- before each subsequent cast you need to step back or adjust the distance using the reel;
- a large number of throws is a waste of time.
The question of how to use a depth gauge is relevant along with other methods of determining the properties of the bottom, but only as an initial method. The device is attached to the surface of the part, then the depth of the hole or groove is assessed. If necessary, additional rods are attached for extension. The depth dimension is transferred to digital format. Don’t forget about cleanliness, so after use the depth gauge should be wiped with machine oil.
Depth measuring gear
Fans of float fishing measure the bottom with overloaded tackle, monitoring the position of the float in relation to the surface of the water.
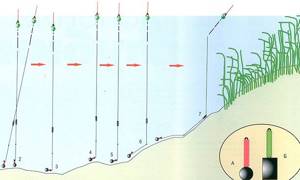
Accurate determination of the topography of the bottom of the reservoir at the fishing site can be done with fly gear with an overloaded float by step-by-step wiring.
Experienced fishing enthusiasts use specially made marker gear to determine the bottom topography. They can have a different structure with a blind or sliding float.
In the first case, the depth is determined by the position of the float in relation to the loads located at certain distances from float to float.
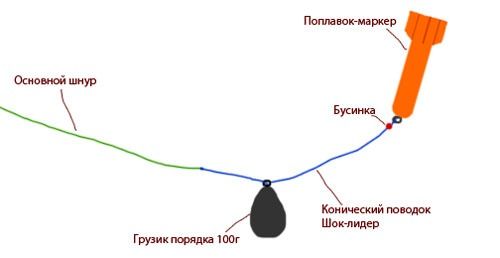
Marker tackle with a sliding float allows you to reliably identify promising places for fishing from the bottom.
More accurately, the depth at the intended fishing location can be determined using a sliding marker float. You can buy equipment for this at any specialized store or make it yourself.
Marker float
It should be taken into account that a normal marker float costs around 500–700 rubles. This float floats up quickly, which is very convenient when monitoring the bottom.

It is very important that the carrying capacity of the float does not exceed the weight of the marker sinker. The best option would be if this difference is 25–30%. For example, if the float “pulls out” 20 g, then the load must be 30 g, otherwise the float will lift it from the bottom.
Detailed method for measuring depth
In this case, intermittent movement of the test equipment along the bottom is provided. The amount of each advance can be controlled by the number of turns of the coil. The smaller the step, the more detailed image of the relief can be obtained. Let's say that the reel removes 10 centimeters of line in one revolution of the spool. Consequently, when moving with 5 turns, the marker load will approach the shore by 50 centimeters.
Before starting test casts, you need to prepare a marker rod for measurements. To do this, at a certain distance from the handle or reel mount, a certain distance (40-50 centimeters) is measured and a mark is applied to the form with a marker.
The marker weight for the feeder is moved during the tests until the line is fully tensioned. After this, the line is released step by step from the reel until a float appears on the surface of the reservoir. By counting the number of times the line is dropped and knowing the distance to the marker, it is easy to determine the height of the float, which will be equal to the depth of the reservoir at the measurement site. But the main thing in this case is not the determination of the true depth, but the nature of the change in the bottom topography, in order to know where the feeding table, perspective slopes, upper and lower edges, and natural depressions are located.
To accurately hit them when casting, the line on the reel is clipped. If the relief and cleanliness of the coast allows, the line of the marker and working fishing rods is stretched on it and clipped at the same distance from the reels.
Advice! On an overgrown bank, you can use pegs driven 2-3 meters from one another. The fishing line from the marker and working gear is wound parallel to them and clipped at the same distance from the end.

Similar measurements are carried out several times at different angles relative to the coastline.
In this way, a true picture of the fishing area is obtained, since feeder fishing uses from 2 to 4 rods at the same time.
Cool places
When the necessary research has been carried out to determine the relief and composition of the bottom, you can begin fishing using the data obtained. In our recommendations, we will look at the example of bream fishing, since its habits are most characteristic of other species of this family.
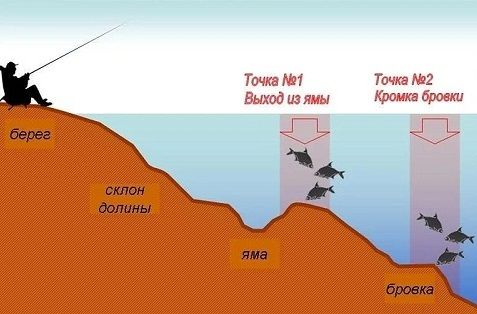
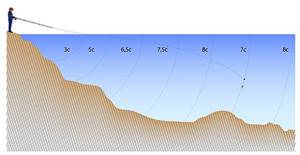
Approximate diagram of the reservoir and the most promising fishing spots.
For a marker rod, a heavy action feeder blank of the maximum available length is used, at least 4 meters. Usually it is not used for fishing, but only for surveying the area.
The current in the river carries with it a lot of nutritious objects for feeding. They naturally settle in the depressions of the bottom, where fish find them.
The natural deepening of the bottom ends at the edge, where turbulences of water are formed and numerous whirlpools are formed and a reverse current can even occur. All this actively erodes bottom sediments containing large amounts of biologically saturated plankton, which is a nutritional mass for fish.
Most fish of this species have a body shape close to an oval, which suggests feeding with the body tilted forward, so searching for food objects on slopes is most natural for them.
Having received an idea of the bottom topography in the place chosen for fishing, the angler is already able to suggest casting points to promising places. Now you can start hunting.
Associated fishing factors
But measuring the depth and establishing the bottom topography is not enough. You also need:
- Choose the right gear depending on the strength of the current. Obviously, light assemblies with little weight can simply be carried away from the chosen place with tangled leads. And the demolition of gear begins from the moment it enters the water during casting.
- In moderate and strong crosswinds, the same consequences are likely to a large extent, and the leashes can become very tangled.
- The correct selection of bait is of great importance. Its composition depends on the time of year; if in the spring animal components are required, then towards the end of summer and autumn it is better to use plant compositions. And, of course, all kinds of fragrances are effective.
- Baits and baits are also used according to this principle. Bloodworms, maggots, and small dung worms in a bunch are effective at any time.
- When fishing on a muddy bottom, there is a danger that the bait will sink into it. To avoid this, you can use foam balls, which are placed on the leash a few centimeters from the hook. When fishing, they lift the bait, making it accessible to the fish.
It becomes obvious that the success of fishing depends on many factors that directly affect the behavior of the fish. One of them is weather conditions. The activity of the fish is affected by atmospheric pressure, or rather its stability during the several days preceding release. If the weather forecast expects a pressure drop, fishing can most likely be cancelled. One sign of a change in pressure may be a dramatic change in wind direction.
Determination of the composition and structure of the bottom
Naturally, while measuring the depth, experienced fishermen simultaneously determine the composition and structure of the bottom. The result of fishing directly depends on this. It is very important to find an anomalous point in a given area where food will linger or there will be shelter from predators. This certainly attracts peaceful fish there, and there is a chance of a trophy specimen biting.
The drawing method is used to study the soil. The load is pulled through at a minimum reeling speed, fixing the nature and structure of the bottom at the tip of the feeder. The sensitive quivertype conveys any change in composition, as evidenced by its behavior:
- The soft structure of the bottom or bottom algae are transmitted by light continuous tension.
- The clean sandy bottom provides minimal resistance; the tip, making a slight tremor, bends almost under the weight of the load.
- If the sinker lands on a spot strewn with shell rock, the tip begins to constantly tremble and “cowardly”.
- When the load moves downward, the resistance weakens, and when it rises, it increases.
- If a sharp edge or local bump is encountered along the path of the sinker, then a sudden increase in load occurs, which quickly goes away when more force is applied.
Having determined the optimal point for casting, you need to mark landmarks on the opposite bank and clip in place. Experienced feeders can easily send the feeder to a given point, so they quickly create a feeding spot on the bottom and “put the fish on the feed.”
fishelovka.com











