Fishing on the Kuban River
The Kuban River delta includes:
- Her sleeves.
- Some bodies of water with running water.
- Some bodies of water have standing water.
What kind of fish are there?

There is a sufficient amount of various fish in the river. For example:
- Pike.
- Som.
- Carp.
- Mullet.
- Perch.
- Chub.
- Asp.
- Zander.
- Carp.
- Rudd.
- Bream.
- Silver carp.
- Crucian carp.
- Roach, etc.
THERE IS FISH IN Kuban!!! Sudak in Krasnodar
Fishing in the flat part of the Kuban River
The river is home to most of the carp fish (carp, bream, carp, roach). Among them there are specimens of impressive size - an important factor influencing the attractiveness of places for fishermen and vacationers.
Crucian carp are hunted in bays, which in summer are overgrown with dense coastal vegetation, which makes the process of catching decent specimens difficult without a boat. The latter is convenient for trouble-free fishing of promising places.
The flat Kuban has a low flow rate. It is visited by many spinning anglers who are not left without prey, where pike and perch are present. There are many places suitable for lovers of float gear. Fishermen, using fly rods and match rods, catch bream and bream. Carp lovers prefer to use donks, which are equipped with makushatniks. Many people prefer feeder gear.
Large bream in the lower Kuban is caught in early spring. It also bites in the summer, but the catches are smaller and are represented more by bream. In summer, individuals sometimes respond to plant baits, although they do not refuse animals. The latter become more catchable during cold spells in autumn and early spring.
The arrival of autumn rains encourages fishermen to go to Kuban for tugun, which has tasty and tender meat. If you're lucky, you can come home with a loot worth 10 kg. Although more often the catches include 7…9 kg individuals.
Pike, which bite well in the summer, become more active in the fall and are caught in large quantities, without giving preference to any special baits. Of the latter, silicone ones are the most popular among fishermen.
In winter, fishing begins after the ice freezes. Initially, it appears in areas of bays, straits, and off the coast, gradually moving towards the middle of the channel. In the arsenal of fishermen: girders (there are pike perch, but more often pike are caught); jig tackle, on the jigs of which, to improve catchability, bloodworms, maggots, and worms are attached (perch, roach, and less bream are caught en masse); float gear, used more for catching bream and roach.
Features of Kuban fishing
Fishing in the upper reaches of the river

The Kuban River flows into the Sea of Azov and a large delta has formed in this place, which creates all the conditions for the life of various species of fish. The upper reaches of the river are distinguished by clear and ideal clean water.
The river has a fairly fast current in some places, which creates ideal conditions for the life of Caucasian chubs and barbels. To catch a chub, you need to have reliable tackle, since carp are characterized by great resistance when fishing. A spinning rod can cope with this task, but to catch a barbel, you will have to arm yourself with a donkey. If you use a regular float rod, then with a certain skill you can catch any fish.
Flat areas

In such areas where the current is not significant, the main representatives of the cyprinid family, such as carp, carp, bream and roach, live. Moreover, some of them grow to impressive sizes. This factor is the main one that influences the attractiveness of these places. In bays where there is practically no current, you can count on catching quite large crucian carp. Unfortunately, these places are characterized by the presence of coastal vegetation, which greatly complicates the fishing process.
The fishing process can be simplified and made more effective if you use a watercraft. Using a boat you can easily fish the most problematic areas. To catch carp, many fishermen use a makushatnik, as well as well-known feeder gear for catching carp.
The lower section of the Kuban current

These places are interesting because there is practically no current here, which attracts not only fishermen, but also ordinary vacationers. Here, spinners hunt for pike and perch, and ordinary fishermen catch bream and trout. It is better to count on catching large bream in the early spring, but fishing for pike, perch and sorog continues into the summer. But this does not mean at all that bream stops biting in the summer. No, he continues to be caught, but more breams are caught. As a rule, in the summer, fish prefer baits of plant origin, but they do not refuse animal baits.
With the arrival of autumn, when cloudy and rainy weather sets in, many fishermen actively catch tugun, which is distinguished by its tender and tasty meat. During this period, individuals weighing up to 10 kilograms are found here.
As for pike fishing, during this period it attacks any bait, including artificial ones. The most catchy baits may be artificial baits made from edible rubber.
Fishing on the KUBAN River. Fishing with a donk and a float rod. Fishing angeln la pesca câu cá fishing
The best paid fishing bases in the region
All paid fishing bases in the Krasnodar Territory are equipped with an entrance and walkways. If anglers come to fish for several days, they can stay in hotel rooms or separate houses.
Sports and fishing complex "Plastuny"
This paid recreation center is located approximately 19 km from Krasnodar. This complex has two large artificial reservoirs (about 40 hectares in area), into which a large number of different fish were released. You can also fish at the mouth of the Kuban River, where you can catch large crucian carp, carp, catfish, grass carp and carp. The weight of individual caught specimens reaches 4-4.5 kg.
Read: Coho salmon fishing in Kamchatka
The complex is equipped with places for fishing, there are gazebos and barbecues, and boats and catamarans are available for those who wish. And not so long ago, a house was built on the territory of this complex for those wishing to spend the night.
Recreation center "Pariyev Stavov"
This base is located more than 60 km from Krasnodar. On its territory there is a large pond - its area is 22 hectares, with paid fishing. But even just a vacation will have to be paid for.
Near the pond there are canopies that protect from sun rays and rain, and there are bridges from which it is convenient to fish. Also on the territory of the base there are cottages with rooms, a bathhouse and a swimming pool.
Fishermen do not leave here without a catch - carp, crucian carp, silver carp or grass carp.
Pond near the village Spiky
This artificial reservoir was stocked with fish several years ago; crucian carp and carp can be caught in it. The fishing fee is not too expensive: 600 rubles per male fisherman.
Golden carp
You can get to this base from Krasnodar in about 30 minutes by your own transport. People fish here from the shore or from the bridge, and those interested can rent a boat. If the bait is chosen correctly, then even a novice fisherman will not leave here without a catch. For those who come to fish for a few days, a house with rooms will be offered, there is free parking, as well as a recreation area with gazebos and a place for barbecue.
Pond in the village School
Read: Black Sea coast of the Caucasus
This artificial reservoir is medium in size (about 5 hectares), it was stocked with fish about 7 years ago. The place is equipped with a large canopy and barbecues. The cost of fishing is 200 rubles per fisherman.
This money will pay off quickly, because in this reservoir you can catch carp, carp, pike perch, silver carp, grass carp, varieties of bream and crucian carp.
Super base
This fishing base is located near the village of Novomyshastovskaya. On the territory there is a hotel for those wishing to relax for several days, parking, and equipped fishing areas. You can catch pike, catfish, and crucian carp in this place.
Base-hotel "Fisherman's Luck"
This fishing base is located approximately 50 km from Krasnodar and is located near a forest next to the 2nd Kochety River. On the territory of the base there is a hotel with double rooms, there is a kitchen with a stove, refrigerators and utensils.
Almost all types of river fish are caught here; the catch rate per day is up to 5 kg; you will have to pay extra for excess fish caught separately.
Temryuchanka
This fishing base got its name from the settlement next to which it is located - Temryuk. Those wishing to fish for several days will be accommodated in trailers or cottages, boats are provided, and there are bridges for fishing with spinning rods. Access to the base is paid. Carp, pike, rudd, crucian carp, pike perch, asp, bream and catfish are caught here.
Shapovalovsky Ponds
This fishing spot has four artificial reservoirs, each of which is equipped for fishing from the shore. All of them are well stocked with catfish, carp, grass carp and other river fish. For fishing for 12 hours you will have to pay 350 rubles.
Read: Fishing on Lake Zizice
Bream fishing

Some fishermen prefer to catch bream, which in these places is quite large in size, especially in flat areas. To catch this fish, it is better to have a watercraft, and use a bottom fishing rod as a fishing tool, selecting the weight of the sinker depending on the strength of the current. The fact is that in different areas there are currents of different magnitudes, although in flat areas it has a minimum speed.
Bream can be found in areas:
- where are the steep banks;
- where the bottom is strewn with shells, which are included in the diet of bream;
- where there is significant depth.
Bream is equally active at any time of the year. At the same time, one should take into account the fact that bream is a rather shy fish and to successfully catch it you need:
- Pre-feed the place to collect as many fish as possible at the fishing point.
- For feeding over long distances, it is better to use special feeders.
- In cases of decreased biting activity, you should switch to other flavors.
Properly selected equipment plays an important role in catching bream and this factor must always be taken into account.
Fishing for sabrefish

Chekhon also moves around the reservoir in schools, choosing areas with fast currents. Chekhon prefers to be at a considerable depth, so it makes no sense to look for it in bays or floodplains. It rises to the surface of the water only on hot days. With the onset of cold weather, it goes to a depth of about 15 meters.
Mass migrations of saberfish are observed in the spring. During this period you should look for it:
- within the pits;
- in small areas;
- in areas with complex bottom topography.
At the height of summer, saberfish are interested in the following areas of the reservoir:
- boundaries of fast and slow flows;
- places of entrances and exits from pits.
Worms, maggots, and caddis flies will be used as bait. Good results can be obtained if you put a fly, wasp, gadfly or some kind of artificial bait in the form of a wobbler, twister or vibrotail on the hook. The fact is that sabrefish are considered a predatory fish. Large sabrefish are caught on 4-centimeter fry.
During the fishing process, you should regularly throw bait at the fishing point, which can keep the saberfish at the biting point for a long period. A bottom fishing rod with a feeder is perfect for catching sabrefish. At the same time, you need to take into account that the saberfish does not take bait from the bottom. To successfully catch sabrefish, you need the bait to be raised above the bottom level. It is better to add various baking powders to the bait, as well as elements of hook bait, in the form of maggots, worms, etc.
1. The old bed of the Kuban River. "Old woman". Fishing with a float rod. Fishing. Fishing angeln la pesca
Fishing place “Zamanukha” Krasnodar city
Krasnodar residents like to gather on the old bed of the Kuban River to catch roach, perch, pike, crucian carp, and shuplets. The place is free, anyone can come here. But because of this, you can’t expect any amenities here. The reservoir is partially overgrown with grass; people fish in the existing clearings.
The fishing place “Zamanukha” is located on Kubanonaberezhnaya Street in Krasnodar, to the right of the bridge.

Fishing for catfish

Catfish is a fish that is found in the Kuban River, and in sufficient quantities. The dream of every fisherman is to catch this river monster, although this is not so easy if it concerns large catfish. Here you can catch catfish both from a boat and from the shore. The main thing is to find a promising place with significant depth.
Catfish are a nocturnal predator and are best caught after dark. If you use a boat and a quok, you can count on catching this predator in the daytime. The fact is that the sounds of the quok attract the predator and it rises from the bottom, heading to the place where these sounds are coming from.
When going for catfish, it is better to take an assistant with you, especially if fishing is done from a boat. It is difficult for one person, when biting a large individual, to cope with this river giant. He is capable of turning the boat over or breaking the gear, especially since someone else needs to steer the boat.
In Kuban, a fisherman caught a huge catfish and sold it for 25 thousand rubles
Fishing for chub and podust

The chub represents the carp family, and these representatives are distinguished by significant strength and resist fishing to the last strength. As a rule, the most active chub bite is observed in mid-August - early September. During this period, it can be caught with spinners and wobblers. Warm sunny days, without significant gusts of wind, are considered the most productive for fishing.
It is advisable that complete silence be maintained during the fishing process. To catch it, it is better to take a strong and reliable fishing rod.
Catching undermouth begins with finding the place where it prefers to feed. Podust likes to be:
- in the area of rapids;
- in areas with complex bottom topography;
- in areas of sand and clay gullies.
Podust shows the greatest activity at the end of May and at the beginning of June. For baiting the hook, a worm, maggot, or algae balls are suitable. This fish can be caught both with a regular float rod and with a donk.
Three species of Kuban chub. Part 1. Alexey Shanin. Anglers Chronicle.
Pike fishing in the Krasnodar region
There are many estuaries in the Krasnodar region, which are located in its western part, a flat area near the Sea of Azov. The Azov estuaries, or, as they are also called, floodplains, occupy a large area. They represent an extensive system of shallow lakes overgrown with aquatic vegetation. Almost all estuaries are interconnected by many channels and passages, some of which have access to the sea. Most of the tunnels were formed due to human intervention. Estuaries located near the Sea of Azov are connected to it by channels; some of these estuaries can only be reached through the sea. Most estuaries contain fresh water, but there are also estuaries whose water is brackish. Basically, the floodplains have an insignificant depth, which on average is 1 m. But there are estuaries, the depth of which varies between 2-3 m. The coastal zone is a multi-kilometer wall of reeds with small bays, which separates the estuaries from each other, the solid ground is mostly absent. Most of the territory of the Azov floodplains is impenetrable thickets of reeds and cattails. Therefore, shore fishing in estuaries is impossible. Due to the shallow depth and warm southern climate, the water in the estuaries warms up faster, which favors the rapid growth of underwater plants. In the warm season, vegetation rises to the surface of the water, and some estuaries become like a continuous carpet of grass with small lakes scattered across it. It is impossible to find two identical estuaries; they differ not only in shape, but also in the types of fish living there, water composition, vegetation, bottom topography and soil composition (shell rock, silt, sand).
Lifestyle of pike in the estuary
In the estuary, pike lead a mostly sedentary lifestyle; they occupy convenient places near reeds or in thickets in open water. Pike spend almost all their time in their favorite stopping places, with the exception of the spawning period. Before spawning, pike begin to gather in groups and move along the estuary to the spawning grounds. Spawning grounds are sparse thickets of reeds (reedyak) with shallow depth. In estuaries, pike spawning begins around the end of February and continues until mid-March. But every year the spawning period of pike changes, it depends on natural conditions and water temperature. For example, last year in 2007 the winter was warm, and the estuaries were covered with ice for a short period only in January, and the rest of the time there was open water in the estuaries. The air temperature in January and February ranged from 0 to 10 °C, so pike spawning was in full swing already in the second half of February. And in the first half of March, the spawned pike began to show activity in relation to the bait.
After spawning, the pike stays for some time near the spawning grounds in clean water near the reeds, actively feeds and recuperates. In the period from April to May, as the water warms up, the pike begins to move along the estuary behind schools of small fish. At this time, the pike stays in areas of the estuary with cloudy water, since the water in other areas is crystal clear and the bright sun shines. In June-July, pike occupy their camp sites, where they remain until the next pre-spawning migration.
Behavior, weather, tides
The behavior and activity of pike is influenced by many natural factors: the direction and strength of the wind, the water level and its transparency.
In my opinion, pike are most active on windy days. As for the direction of the wind, in the warm season the fish are active in almost any direction, with the exception of the east. Thus, the most favorable wind directions for catching pike in the warm season are any western directions. In the cold season, the wind from the south is more favorable. Strong winds (7-12 m/s) force the pike to leave their shelters (shallow water in reed thickets). On such days, the pike stands near the reeds. As for generally windless weather, in complete calm the pike is more cautious and even timid. In such fishing conditions, it is necessary to very quietly approach the expected pike site and behave as quietly as possible in the boat. Pike hears and feels extraneous noises and water vibrations very well. Even waves that move away from an anchored boat due to careless actions can spook a pike standing near the boat at shallow depths. What can we say about knocks, loud steps and objects falling to the bottom of the boat. The quieter you are in the boat, the greater your chances of catching a trophy pike!
The water temperature in estuaries with shallow depths rises to 28-30 °C in summer, and pike move to deeper places, to springs, and go under carpets of vegetation. During such a hot season, a surge in pike activity is observed at dawn and lasts until a maximum of 9 a.m. Lowering the air temperature even by a few degrees helps to increase the activity of pike. During the cold season, particularly in winter, a sharp drop in air and water temperatures puts the pike into a kind of stupor. She becomes very passive and lethargic. And when the water temperature rises, the pike becomes more active. During winter pike fishing, on sunny days, the water warms up by 1-2 °C during the midday hours and towards evening - this is where an increase in fish activity is observed.
The water level in estuaries depends on the direction of the wind and its strength, the amount of precipitation, as well as the number and size of rivers flowing into the estuaries. An easterly wind blows water out of the estuary. On the contrary, the westerly wind blows it from the sea, and the transparency and salinity of the water changes. As the salinity of the water increases, the pike becomes less active. Also, schools of Azov herring (puzanka) and rams enter the estuary with salt water. After the water has settled, groups of pike begin to destroy schools of fish that have entered the estuary. Pike pursue their victims for a long time, moving around the estuary.
Search for pike
Each of the Azov estuaries is different from the others. They differ not only in shape, but also in fishing conditions: the presence of aquatic vegetation and its diversity, the nature of the bottom (mud or shell rock), the salinity and transparency of the water and, of course, the depth (a difference of even 20-30 cm has a significant impact on the quantity and plant density). There are two main, fundamentally different places to search for pike in the estuary: near the reeds and at a distance from it, in clear water among the grass.
Typically, pike are always caught in any of these listed places, but the difference is primarily in the size of the fish living there. If in reed thickets the weight of a caught pike generally does not exceed 2.5 kg, then in clear water its weight is much greater. There are days when for some reason the pike is capricious or is not caught at all in clear water among the grass, and near the reeds a feast of fattening pike can unfold. Often such accumulations of pike near reeds or even in the depths of thickets occur in winter. Such a concentration of pike in certain places can be caused by a sharp drop in water temperature, pre-spawning migration, a change in wind direction, and a difference in atmospheric pressure. In the warm season, pike are found in the estuary near the reeds in small windows among the grass and in clear water. Since algae rise to the surface of the water in summer, the estuary becomes like a carpet of holes. The role of the carpet is played by plants, and the holes are areas of open water with less grass or no grass at all. Such areas of the estuary are also called “progales”.
There are various gaps that differ in shape, size and depth. The larger the gap, the greater the chances of catching a trophy pike in it. It is worth paying more attention to areas with cloudy water through which the bottom cannot be seen. Often in such places a lot of pike accumulate, the sizes of which can be very diverse - from 1 to 7-8 kg. In the cold season, when the water temperature drops, the vegetation sinks closer to the bottom and visual search for gaps is difficult. In unfamiliar estuaries it is easier to look for gaps using the free drift method of a boat. In order to detect a gap, it is necessary to closely inspect the surface of the water while drifting. When you notice a gap, quietly get closer to it and anchor 3-5 m from the border of the grass and the dump. Right on the drop from the grass to the depths, many pikes like to ambush small fish that accumulate in the clearing during cold times. If you anchor right on the border of the seaweed and the drop-off into the clearing, you can scare away the pike standing there. From the surface of the water, the hole looks like a dark or light spot (depending on the color of the bottom) against the background of brown aquatic vegetation. In strong winds, the wave height above the gap is much greater than in areas with aquatic vegetation. Polarized glasses greatly help in finding the missing spot during the drift.
Tackle
For estuary fishing, I use a 9-foot single-handed 8-grade rod, floating torpedo line, and buoyant and neutral buoyancy leaders. The leader is mainly used with a diameter of 0.40 mm. This thickness of the leash is quite enough to fish out violent pikes. While fishing, the pike often dives under the carpet of grass and, after swimming a few meters, stops. In the vast majority of cases, fish that have gone into the grass disappear. In order to hold and not let a pike rush into the grass, you need to have a sufficiently strong leader material. Various leader materials can be used, such as Kevlar, braided steel wire. I prefer leashes made of hard wire material American Fishing Wire (Tooth Proof), the breaking load of which is 17 kg. The insignificant weight of a leash made of hard material does not at all affect the streamer’s play in the water. After catching a pike, the bent leash can be easily straightened by hand.
Front sights
As for streamers, pike is a very voracious and curious predator that shows interest in any streamer swimming in its visibility zone. More spectacular and exciting pike fishing occurs with surface baits. Floating imitations of frogs and mice (Gliser Foam, Deer Hair Frog), made in a non-snacking version, work flawlessly. In late autumn, after the first light frosts, the best bait for catching pike on the grass and in the reeds is an imitation frog. The Deer Hair Popper “lifts” a pike standing in the grass well. For pike fishing, poppers made of various floating materials are mainly used: polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam, deer fur.
As for streamers, almost any streamer attracts active, both medium-sized and trophy pike. But when the activity of the pike decreases, it begins to be capricious in its choice of prey. Often the pike simply chases the streamer and bites the tip of its tail. In the cold season, there comes a period of fishing when only the choice of a suitable fly and the method of presenting it gives the desired result. Real “work” fishing begins in winter. At this time of year, pike are sluggish and often picky. Inactive pike respond well to streamers Magic Tail Minnow, H2O Pike Streamer, Pike Zonker, made in both sinking and floating versions.
Fishing technique
So, you went fishing in one of the estuaries of the Azov flood plains. As I already mentioned, there are two main places to search for pike in the estuary: near the reeds and at a distance from it. Which of these fundamentally different places to start fishing from depends on the angler. It is not easy to predict where the more active fish will be. Therefore, when fishing in unfamiliar estuaries, you should start from places located at a distance from the reeds.
After you have anchored the boat at a suitable opening in the grass, use your first casts to fish the drop off the grass to depth. After which you can begin fishing the central part of the gap and the opposite dump. It is not advisable to start fishing from the far edges of the gap, since noisy fishing for caught pikes can alert the predators standing near the boat. You should fish the gap in a fan-shaped direction, gradually increasing the casting distance. After the place has been fished, we weigh anchor and continue rafting downwind in search of the next place. The most catchable and favorite places should be recorded on a GPS navigator, marked with a buoy or a stuck reed, to facilitate the search for re-fishing. A catchable hole with a large number of pike can “work” throughout the day. If during fishing there is a lull in the pike bite, then you need to pause and let the place rest for a while. The larger the gap, the more pike can concentrate in it. As a rule, the first to be caught are the most active and often not very large pikes. Large “mothers” mainly choose their mooring sites in the middle of a clearing on a clear bottom and often stand in groups of several. After catching a large pike, do not rush to leave it. Smaller pikes are more agile; they are the first to grab the bait, so after a lull it is worth carefully combing the water area of the gap. Almost throughout the year, pike aggressively attacks all kinds of surface streamers and poppers; even in winter, the toothy pike is not averse to biting the bait moving near the surface. But in winter it is more advisable to use large streamers and fish the lower layers of water.
A lot of pike are standing right on the grass carpet in small spots of clear water. In such places, fishing is possible only with surface floating streamers and poppers made in a non-snacking version. When fishing in such places, after hooking the pike, it is necessary to force the landing and not allow it to dive into the grass, otherwise the fish will be lost.
If the pike does not show itself in open water, you should move closer to the reed thickets. Some estuaries have small bays in the reed zone, which are inhabited by pikes. More attention should be paid to sparse thickets of reeds (reedyak). It is advisable to anchor the boat in such a way that when casting as far as possible, the bait splashes down on the border of the reeds and open water. When the pike begins to feed, it settles in the reeds right on the border with open water or in a zone 1-2 m from it. If a strong wind blows while visiting a reservoir, it is worth checking the windy side of the estuary. A wave rising from the wind forces the pike into the very depths of the reed thickets or into clear water. If there is insufficient water level in the reeds, the pike will come out and stay close to the reeds. The fly must be brought to one point several times and as loudly as possible in order to lure and provoke a grip on the pike. After splashdown, we do not start wiring immediately, we pause for a few seconds, and then with sharp but short jerks we begin to select the cord. After the border between the rare reeds and open water has been fished, moving closer to the reeds, we begin to cast the streamer directly into the thickets of the reeds. We carry out wiring at medium and slow speed with both short and long pulls. For fishing directly in the reeds, it is better to use poppers and floating streamers with glass or metal noise capsules. After hooking, you need to “pull” the pike out of the reeds and complete the landing in clear water. If this is not done, after hooking the pike will rush into the reeds along a zigzag path. In the best case, the pike will get away or get stuck tightly, and you will have to climb into the reeds and free it, in the process scaring away all the toothy ones standing in that water area.
Gliser Foam
Hook: No. 4/0, Cannelle 1327 Installation thread: Kevlar Thread Tail: several silicone threads Body: Streamer Brush Back: “foam”
Gliser Foam
Hook: No. 2/0, Gamakatsu F314NS Thread: Kevlar Thread Tail: H2O Steve Farrar's Blend fibers in assorted colors, stacked on top of each other, flanked by a rooster scalp feather Body: Streamer Brush Back: Flashabou fibers layered with Streamer Hair fibers Eyes: Molded Eyes
Deer Hair Frog
Hook: No. 2/0, Gamakatsu F314NS Mounting thread: Kevlar Thread Legs: several silicone threads Body: sheared deer fur
Deer Hair Popper
Hook: No. 4/0, Cannelle 1327 Mounting thread: Kevlar Thread Body: sheared deer fur Brush: rooster feather Legs: several silicone threads Tail: Flashabou fibers, several rooster feathers
Pike Zonker
Hook: No. 2/0, Gamakatsu F314NS Mounting thread: Kevlar Thread Body: Ice Chenille Brush: rooster feather Legs: several silicone threads Tail: rabbit skin strip
Articulated Flash Pike
Hook: No. 3/0, Cannelle 1327 Thread: 140, UTC Thread Body: Big Fly Brush Tail: Streamer Hair, Flashabou and Krystal Flash on top
Magic Tail Minnow
This streamer has proven itself well when catching capricious and inactive pike. He is also good at “picking up” a pike that has attacked or gone out for another bait several times before. In this model, a noise capsule is installed on the shank of the hook to additionally attract the attention of pike standing in the thickets of grass. This streamer can also be made in a floating version if, instead of a capsule, a piece of “foam” is attached to the fore-end. In this design, the streamer can be successfully used for catching pike in the summer on the grass and in the reeds.
1. Attach the mounting thread to the shank of the hook and secure a piece of monofilament fishing line.
2. Attach a noise capsule or a piece of foam to the fore-end. Then apply Head Cement to the area where the fishing line and capsule are secured.
3. Secure the Ultrasuede Magic Tail.
4. Tie several segments of Flashabou Lazer on top of the ponytail.
5. Attach the Streamer Brush to the shank of the hook and form the body of the fly by wrapping the material around the shank.
6. Secure a piece of fishing line with a diameter of 0.45 mm, adjust the length of the bump stop, and cut off the excess fishing line.
7. Secure the eyes with epoxy glue.
Fishing gear on the Kuban River

The main fishing gear on the Kuban River are:
- Spinning.
- Float rod.
- Leash.
- Feeder.
When going fishing, you should take care of spare equipment, since hooks are quite common here. Once the tackle is hooked, it is sometimes quite difficult to unhook it, so you have to break it off. In this regard, the presence of spare leashes with hooks is mandatory.
Popular fishing spots in Kuban
Fishing on the river near Temryuk
The place is among the best where you can successfully fish in Kuban. Not far from the city there are many floodplains and estuaries, which are connected by channels and artificial canals.
All promising places are located between the Sea of Azov and the road leading to Temryuk. Anglers go fishing more often:
- to the canal in Golubitskaya;
- to the site located in front of the Maly Akhtanizovsky Estuary;
- to the Peresyp region;
- on the Bolshoi Akhtanizovsky Estuary.
They fish on canals from the shore, in estuaries - from a boat. In these places you can catch carp, crucian carp, tench, carp, rudd, roach, bream, perch, and pike. Different tackles are used: float, bottom, spinning, fly fishing. They are caught using worms, maggots, flies, dough, semolina, and corn.
Fishing near Krasnodar
The most visited fishing spots in the city:
- backwater located in the 30th Anniversary of Victory Park;
- embankment (Rozhdestvensky Park) on YMR.
Areas with good access to water. They are especially popular among fishermen on vacation with families who do not like privacy and prefer to have various amenities nearby (for example, barbecue, which can be ordered nearby in a cafe).
In the indicated places there are pike perch, mullet, pike, carp, gobies, carp, perch, roach, silver carp, ide, and chub. You can catch them with a donkey, rings, spinning rod, feeder, or float. They take bait with them (worm, maggot), it can be found on the shore. The best is considered to be the green worm, which is harvested at the latter stage.
Fishing in Kropotkin on the Kuban River
The city is on the high right bank of the river. The distance from Krasnodar to the northeast is 145 km. The Kuban near the settlement is winding, with many places where you can fish. The best areas are considered to be within the village of Dmitrievskoye (45 km from Kropotkin), beyond the village of Novoukrainskaya (25 km). They are the most fishy in terms of the number of underwater inhabitants and their species composition.
Fishing within the city of Kropotkin is no different from the process in other flat areas of the river. Float rods, spinning rods, and donks are used. If you're lucky, your catches may include catfish weighing up to 5 kg.
Fishing on the Kuban River in the Taman region
Anglers consider the region a fishing paradise, as it offers a wide range of freshwater species to catch. Kuban in the region is represented by a floodplain, which abounds in estuaries with sea and fresh water, numerous eriks, and canals.
They fish for carp, catfish, ram, crucian carp, pike perch, bream, and silver carp from the shore; they use boats that allow them to get to the most catchy places. The coolest time is autumn, when there are many large, sometimes trophy, specimens available. It is at this time that fishermen from many Russian cities come to the region.
Starotitarovsky estuary
The reservoir belongs to the Azov-Kuban estuaries of the Taman Peninsula, located near the village of Starotitarovskaya. It is 10 km long and 2 km wide. People hunt here for pike perch, catfish, pike with spinning rods, fishing rods, rudd, perch, crucian carp with float rods, and bream, tench, and carp with donkeys.
Fishing on the estuary is possible from a boat or shore. The bite is finicky, often absent altogether. This situation makes the place not very popular. Although those anglers who know the reservoir catch large fish in it.
Kuban River: how to get there
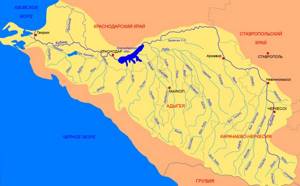
The Kuban River flows into the Sea of Azov, and it flows through the territory of the Krasnodar Territory. Its beginning is located in the Karachay-Cherkess region. It also flows through the territory of Stavropol. Its length is about 900 kilometers. On this route you can find a huge number of fishing spots.
In addition to fishing, these places are distinguished by the presence of picturesque places that predispose to active recreation. Therefore, here you can meet not only fishermen, but also ordinary tourists who spend a lot of time in tents near the reservoir. And getting to these places is very easy, just visit the Krasnodar region.
Igor 02/16/2018










