Fish dishes are considered one of the most popular. It is believed that raw fish retains most of the beneficial elements.
However, eating such a product is not always safe, since the fish often has worms. It is important to identify the presence of parasites in time to prevent infection.
A tapeworm is a tapeworm that lives and feeds on someone else's body. This is a parasite that can invade:
- fish,
- Animal,
- Human.
The danger comes from worm larvae, which quite easily enter the human intestine. The larvae, entering the body, actively parasitize it, becoming saturated with blood and getting into various areas and tissues.
The tapeworm is distributed almost everywhere from the Far East to America. It is the largest size helminth that can infect humans. The length of the tapeworm sometimes reaches 28 meters.
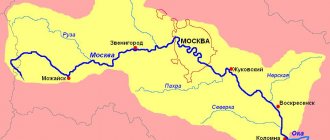
In just one day, the female produces several million eggs. Fish that are infected with a worm always have a swollen belly. When the fish is opened, a long white worm with a flat body is discovered. It compresses the internal organs of the fish, and especially the swim bladder, causing it to rupture.
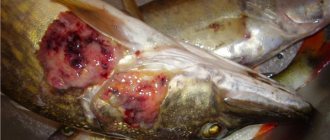
The parasite has another name - fish tapeworm. The worm can reach a length from twenty centimeters to several meters, its width is approximately 15 millimeters. Thanks to the suction cups located on the head, the worm clings to the walls of the belly cavity of the fish, or to the walls of the human intestine. Thus, nutrition occurs with substances necessary for the life of the parasite.
The main sources of infection are:
- Fish,
- Beef,
- Pork.
In most cases, infected pork appears healthy, but in fish, parasites can be seen almost immediately. Unfortunately, such products are not always thrown away; they are often sold along with healthy fish.
It should be noted that most of the parasites live in freshwater bodies. It is difficult to find a body of water in which these organisms do not live. Infection of water bodies with parasites is influenced by:
- Wastewater,
- Activities of birds and animals.
The presence of parasites can be determined by the swollen belly of the fish. Worms often come out when pressed. Poisoned fish usually float on the surface and, if caught, die quickly.
If the catch contains white fish, such as bream or roach, it should be carefully inspected before cutting and cooking. The worm is also often found in the following types of fish:
- Gustera,
- Bream,
- Roach,
- Sinets,
- Pike.
The tapeworm larva grows in the Cyclops crustacean, which is the fish's food. Only after the larva has entered the fish’s body does it become a full-fledged parasite.
Aquarium fish can also become infected with parasites. The worm enters their body with the help of live food.
What it is
Saltpeter is a fish that is infected with the tapeworm parasite. This is a tapeworm that lives in the insides of fish and is quite capable of infecting humans. The main sources of human infection are: beef and pork meat, saltpeter fish.
Affected fish are most often found in natural freshwater bodies of water. Infection occurs through wastewater flowing into the reservoir, excrement of birds and animals. The fish, along with its food, swallows the parasite larvae that are in the water. The peak of the disease occurs in late spring and summer, but in other periods there is a chance to catch infected fish. A photo of saltpeter fish is presented below.
Consumption of saltpeter fish
Freezing fish is a reliable way to get rid of worms (pictured). If the fish weighs less than a kilogram, it can be frozen in a home freezer for about 10 hours. Large fish should be kept in the cold for about a day.
Parasite larvae die when properly salted. Salt should be about 12% of the total weight of the fish. Before use, the product must be kept in salt for about five days.
When frying, great importance is given to the size of the pieces of fish rather than their weight. Small fish should be fried for at least ten minutes. If the weight of the fish is up to 1200 g or the fillet is up to three centimeters thick, it can be fried for about twenty minutes.
Even if the worm is removed from the fish, and the meat is washed and fried, there is always the possibility that there will be tapeworm eggs on a person’s hands, clothes and cutlery, which immediately after entering the human body transform into larvae.

As mentioned above, the most difficult to detect the presence of tapeworms is in pork. In an animal that is infected with parasites, worm eggs are passed along with the feces. The pigs that dig in this mud begin to eat what is on the ground. After a short time, the eggs are swallowed again, which become larvae under the influence of gastric juice. These larvae quickly spread through the bloodstream throughout the pig's body.
Thus, contaminated pork meat can be considered the most dangerous. Undercooked or undercooked pork is considered the most contagious product that can cause significant harm to human health.
The same applies to the situation with cattle. Doctors advise thoroughly cooking and frying meat. While it is possible to prepare dishes with meat most safely at home, eating barbecue outdoors often results in infection with parasites. In any case, you need to have at least basic information about the temperature at which worms die
Doctors do not recommend eating meat with blood. The best solution is to keep the meat on the fire before eating. You should also smoke the fish carefully. If the presence of parasites is suspected, then this product is not suitable for either cold or hot smoking.
Description of the parasite
The tapeworm is a long, white flatworm. It can reach up to 25 cm in length and 20 mm in width. The worm has suckers on its body, which attach it to the abdominal cavity. The tapeworm is capable of fully recovering from even a small piece of its body. It enters the fish’s body in the form of a small larva, and then grows, sticking to the circulatory system. As it develops, it seriously deforms vital organs. The spleen, liver and genitals begin to atrophy. The body becomes intoxicated and metabolism is severely disrupted.
For tapeworm, fish is an intermediate host. Its ultimate target is birds that eat contaminated fish. The worm is a hermaphrodite. In the body of the final host, a bird, it lays larvae, which end up in the reservoir along with excrement. The fish accidentally swallows the larva.
The worm develops in the animal's abdominal cavity, feeding on nutrients. Another bird catches and eats the infected fish. Thus, the tapeworm enters the body of the final host. Afterwards the cycle is repeated over and over again. Infection quickly covers almost all inhabitants of the reservoir. For prevention, all sick fish are caught, and the carrier birds are shot.
What is the danger of tapeworm fish for humans?
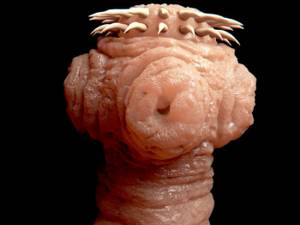
Saltpeter fish can harm a person when the worm has gone through the development cycle and was able to reach sexual maturity in the human body. The broad tapeworm (pictured) causes a parasitic disease in humans called diphyllobothriasis.
A dangerous complication of diphyllobothriasis is intestinal blockage. In many cases, helminthiasis occurs without symptoms and without obvious deterioration in health. To diagnose diseases you can use:
- stool analysis,
- clinical blood test using the enzyme immunoassay method.
Doctors advise taking tablets and drops against parasites for preventive purposes, as well as undergoing simple tests by contacting a therapist.
The meat of fish that is infected with tapeworm looks similar in appearance to healthy meat. However, contaminated meat is less nutritious and significantly inferior in taste.
For the treatment and prevention of parasitic infestations, there is an effective remedy called Bactefort. The medicine consists only of components that comply with environmental standards. All elements are safe and successfully cleanse the human body of parasites. Moreover, the drug has a healing effect.
After eating contaminated meat, the tapeworm larva enters the intestinal tract and stomach, where it attaches to the upper part of the small intestine. You can become infected if you eat fish that contain only plerocercoid larvae.
These types of larvae parasitize fish and reach sexual maturity in the human body. The route of transmission of the parasite is through the consumption of insufficiently fried or cooked food.
It is risky to salt fish and eat it fresh, since the worm larvae are not destroyed without heat treatment. A fish-eating animal can also become the host of parasites. A month after infection, the worm begins to lay eggs. The duration of infection sometimes reaches ten years.
How to recognize infected fish
What does saltpeter fish look like? It develops worse than its uninfected counterparts. He eats poorly, grows slowly, and therefore lags behind in size and looks worse. In the final stages, the fish swims at the surface of the water, sometimes floating upside down.
Why does saltpeter fish float on the surface? This is due to the fact that the tapeworm compresses the swim bladder, making the fish unable to stay deep under water. Infected fish become more vulnerable to the final hosts of the parasite - birds. If while fishing you see a large number of fish that do not sink to the bottom, but swim near the surface, there is a high probability that the entire school is infected with parasites.
Saltpeter bream bites poorly, and it offers virtually no resistance after being caught. An unpleasant odor can be felt in an infected body of water.
The belly of the caught fish appears swollen. In some cases, if you press lightly on it, you can see the head of the tapeworm emerge from under the skin. Opening the belly, you can find a long, light-colored parasite. Infection of fish with larvae can only be recognized using a microscope.

Which fish is dangerous?
The saltpeter worm in fish is most often found in fresh water bodies, but sometimes it is also found in sea fish with white meat. The parasite was found in 47 species of fish. It is most often found in carp species. However, there are fish that are not at risk of infection: peled, pike perch and whitefish. This fish can be consumed without fear.
River fish must be subjected to heat treatment. Even if a worm is not found in the abdomen, larvae invisible to the human eye can infect muscle fibers. You can eat raw fish grown in special fish farms where helminth control is carried out, as well as sea fish with red meat.
Rules for preparing fish products
If you still want to enjoy the catch, then you need to properly heat treat it to minimize the likelihood of infection. The following culinary tricks can help in this undertaking:
- The giblets should be removed from the fish carcass and washed thoroughly;
- It is better to cook clean fillet;
- before cooking, it is recommended to cut the meat into small pieces or process it into minced fish;
- The product needs to be cooked for a long time at high temperature.
Another way to disinfect a product is to freeze it. The pre-cleaned and thoroughly washed carcass is placed in the freezer for at least 10 hours. It is better to use the deep freezing method: the carcass is placed in a freezer for three days at a temperature of -20°C or at -8-10°C for several weeks. Under the influence of such low temperatures, living larvae die.
Whether to eat saltpeter fish or not is everyone’s choice. Do not forget to thoroughly heat treat the purchased product before eating. But it is better to completely avoid eating fish that is infected with tapeworm, and you should not buy dried and salted products from suppliers who are not trustworthy.
infoparazit.ru
Health Hazard
Humans are also susceptible to tapeworm infection. It occurs after ingesting fish meat that has not undergone heat treatment. First, the parasite larvae penetrate the stomach and then the intestines. The helminth attaches itself to the walls of the small intestine, where it can spend about 20 years. The tapeworm carries male and female cells, which means it is capable of reproduction. An adult tapeworm can release a huge number of larvae into the body.
Tapeworm infection can lead to the following complications:
- diphyllobothriasis, which can lead to intestinal blockage;
- necrosis and death of tissue at the site of attachment of the worm;
- anemia;
- allergic reaction;
- problems with the central nervous system;
- oncological diseases.
Is it possible to eat fish with tapeworm?
How dangerous this helminth is for humans is a controversial issue. Many enthusiasts believe that properly cooked fish meat will avoid infection. You can eat a product that is well thermally processed. Unspoken rules:
- fried fish is eaten after processing at a temperature of 55-60°C;
- frozen products - at a temperature of -18-20°C.
Please note that with this processing, a small amount of useful substances is retained in fish meat. But doctors recommend treating the problem more rationally. It’s better not to joke with your health and exclude fish infected with parasites from your diet. As a preventive measure, it is recommended to take anthelmintic drugs, and additionally you can undergo medical tests.
In terms of external signs, the meat of fish infected with a tapeworm does not differ from uninfected products. The key difference is a decrease in taste and nutritional value.
Return to contents
Symptoms of human infection

In the first stages of tapeworm infection, a person may not feel any changes in his body. Tapeworm, unlike other helminths, has less effect on well-being, and therefore its presence in the body can go unnoticed for a long time. Mild symptoms of illness may be mistaken for another disease. Since the worm settles in the intestines, a person may experience problems with the gastrointestinal tract.
The main symptoms of tapeworm infection:
- loose stools or constipation that occurred suddenly and for no reason;
- increased salivation;
- dizziness;
- sudden weight loss;
- intestinal obstruction;
- irritability;
- a feeling that something is moving inside (it is not the parasite itself that is moving, but the muscles contracting under its influence);
- anemia;
- weakness and apathy;
- decreased appetite or, conversely, constant hunger;
- small red wounds appear on the tongue;
- gagging and nausea.
In some countries, tapeworm is specially introduced into the human body so that it helps quickly and effectively lose weight. Afterwards the parasite is removed. You should not do this intentionally, because helminth infection can lead to very serious health consequences.
Symptoms of the disease
The most common helminthiasis caused by tapeworms in fish is diphyllobothriasis. The causative agent is a tapeworm - a wide tapeworm.
The disease develops slowly - the incubation period can last up to 1.5 months. At first, symptoms are completely absent and are mainly associated with disruption of the digestive tract.
- The stool is disrupted: there is an alternation of loose stools with constipation.
- Abdominal pain, bloating, flatulence.
- You may feel dizzy.
- Weakness, fatigue, irritability.
- Appetite may be impaired, and sometimes sudden weight loss occurs.
- Nausea in the morning, maybe vomiting.
- Plaque and cracks can be found on the tongue.
- As a result of a large loss of vitamins by the body (especially group B, C, folic acid), anemia develops.
If at least one warning symptom appears, it is better to consult a specialist. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, treatment should be started immediately. Complications include intestinal obstruction, severe allergic reactions, cancer, dysfunction of internal organs and entire systems.
To confirm the diagnosis, a stool test is performed. During examination, eggs, individual segments, or even adults may be found. You will have to submit it several times. A false negative result can be obtained during the inactive phase of parasite development. The interval should be 3-4 days.
You can take a blood test for antibodies. But a positive result is obtained even if the parasites are in a state incapable of further life activity. This usually happens when eating thermally well-processed infected fish. The body has time to produce the appropriate antibodies.
parazitycheloveka.ru
Order Tapeworms (Pseudophyllidea) Order Tapeworms (Pseudophyllidea) Although tapeworms parasitize representatives of all classes of vertebrates, they are mostly associated with fish. For some species of these worms, fish are the definitive hosts, while others choose them as additional hosts. Crustaceans play the role of intermediate hosts.
The structure of the head end is characteristic of tapeworms. The head of these parasites is equipped with two longitudinal slits or two suction pits. There are usually no hooks on the scolex.
Another structural feature of tapeworms is their open uterus. The opening of the uterus is usually located on the ventral side of the joint. Eggs are released through it as they mature. Each segment, in addition to the opening of the uterus, has two more - the male genital opening and the female, leading to the vagina.
Let's get acquainted with representatives of three families of this order, quite different in their structure and biology.
The Carnation family (Caryophyllaeidae) are small, primitive forms of tapeworms with an undifferentiated body and one set of genital organs, parasites of the intestines of fish.
Caryophyllaeus laticeps is the most common member of the family and is very common in cyprinid fish.
The body length of the cestode is 2-4 mm. The cephalic end is fan-shaped, the bothria are modified into a kind of attachment apparatus. In the anterior half of the body there are numerous testes and vitelline follicles. The ovary and uterus with numerous eggs are located in the last third of the body. The genital openings open at the back of the parasite. In young carnation plants, the testes first develop, and then the organs of the female reproductive system.
The development of this species and other carnation plants occurs with the change of two hosts - the final and intermediate.
Intermediate hosts are oligochaete worms - tubefexes. In their body, a larva, a procercoid, develops from the swallowed egg of the parasite. In the intestines of a fish, when it eats oligochaete worms infected with larvae, an adult carnation develops.
Typically, fish are infected with a large number of cloves - up to several hundred and even thousands of specimens. This parasite is especially dangerous for juveniles.
The Ligulidae family are fairly large parasites with a belt-like, highly muscular body. In the adult stage they live in the intestines of fish-eating birds. Development takes place with the participation of intermediate (crustaceans) and additional (fish) hosts.
A very large plerocercoid larva develops in the body of the fish, almost as large in size as the adult worm. Most of the fish infected with Ligulidae larvae die.
Ligula, or Ligula intestinalis, is one of the most widespread representatives of the family. Its definitive hosts are predominantly gulls, but it is also found in other fish-eating birds.
The adult form of the parasite can reach 1 m in length, although usually the size of the ligula is much smaller, its maximum width is 1.2 cm. The body has only internal divisions, which are not visible externally. Two bothria are placed at the narrowed anterior end of the worm. A groove runs along the entire surface of the worm. Inside the body there is a huge number - from 700 to 2000 - sets of genital organs located metamerically.
The carriers of adult ligulas - seagulls and other birds - scatter a huge number of parasite eggs over water bodies. A larva, a coracidium, emerges from the egg in the water. It is covered with cilia, with the help of which it actively moves.
Coracidium is ingested by copepods, the intermediate hosts of Ligula. In the body of the crustacean, the coracidium turns into a procercoid - an elongated larva lacking cilia.
Together with the crustacean, the procercoid must get into the fish - an additional host. This role for this type of ligula is performed by various types of carp fish. The larvae of other species of ligula parasitize other groups of fish. Ligulas, like all Ligulidae, have a fairly strict specificity in relation to fish - their additional hosts. From the intestine of the fish, the procercoid penetrates into the cavity and grows here into the larva of the next stage of development - into the plerocercoid. The plerocercoid in the body of the fish reaches, as indicated, very large sizes, almost equal to the sexually mature form of the parasite. At the same time, almost all organs are formed in the plerocercoid, in particular the reproductive system reaches a high degree of maturity. It is not without reason that the development of the plerocercoid in the body of a fish requires a relatively long period of time - up to 14 months.
As the plerocercoid ligula grows in the body of the fish, its abdomen swells, the parasite puts pressure on the internal organs of the fish, sometimes causing their atrophy.
A sick fish loses its balance, floats near the surface of the water and becomes easy prey for birds. Sometimes the ligula breaks the fish's body wall and falls into the water.
Ligulosis (as this disease is called) causes great damage to fisheries.
In the intestines of a bird that has swallowed a fish infected with plerocercoid, the development of the parasite to the sexually mature stage occurs very quickly - within 35-60 hours. Ligula begins to intensively secrete eggs and dies after 2-4 days.
The Diphyllobothriidae family unites very large cestodes (some reaching a length of 20 m) with full and clearly articulated body parts, parasitic in the mature stage in humans and predatory mammals, rarely in birds. Their development occurs with the participation of intermediate and additional hosts. The role of an intermediate host is performed by crustaceans, an additional host is most often played by fish, sometimes by amphibians and reptiles, and rarely by mammals.
Broad tapeworm (Diphyllobothrium latum) is one of the common representatives, a diphyllobothriid. The adult worm parasitizes humans and many carnivorous mammals, especially dogs, foxes, arctic foxes, wolves and cats. Widely distributed in the northern regions of the globe. In the Soviet Union, it is found in the basins of the lower reaches of the Lena, Yenisei, Ob, and Pechora rivers, in the rivers of Karelia, on the Kola Peninsula and in some Baltic regions.
A sexually mature tapeworm can reach 15 m in length. Of the helminths that parasitize humans, this is the largest species. The long body of the tapeworm consists of many segments, their number amounts to several thousand. Mature segments are almost square in shape, the largest of them are 1.5 cm wide. The anterior end of the parasite is narrowed, the head bears two bothria. In the center of the mature segments there is a rosette-shaped uterus.
A single set of genital organs is formed in each segment. First, the male reproductive system develops in the young segments, then the organs of the female reproductive system are also formed in them; the mature segments contain only the uterus filled with eggs.
The uterus is located in the center of the segment. It is noticeable to the naked eye and has a characteristic rosette-shaped shape, thanks to which the tapeworm is easily distinguished from other large cestodes that parasitize humans - bovine and pork tapeworms. In these parasites, the uterus has the appearance of a longitudinal rod with lateral branches.
The eggs laid by the tapeworm (the tapeworm's uterus has an opening, while the tapeworm's uterus is closed) are oval in shape, with a cap at one pole. The eggs enter the external environment along with the feces of the owner.
The development of the broad tapeworm proceeds as follows. The egg falls into the water. Here a larva is formed in it - a coracidium, which soon leaves the shell of the egg through the opened lid. Coracidium actively swims in water with the help of cilia. Further development of the parasite takes place in the body of cyclops crustaceans, the intermediate hosts of the tapeworm. The coracidium swallowed by the Cyclops from the intestine of the crustacean penetrates into the cavity and here turns into a procercoid.
Infected cyclops, along with other food, are eaten by fish - additional hosts of the tapeworm. More often than others, this role is performed by pike, ruffe, perch, burbot, salmon, trout, grayling, and whitefish. The procercoids of the parasite, once in the stomach of the fish, penetrate into the cavity of its body, into the muscles and other tissues, turning into the next stage of the larva - a plerocercoid. The larva of this stage is elongated, 0.5 to 1 cm long, milky-white in color, and suction slits are already visible on its head. Extracted from the fish, the living larva constantly contracts and elongates.
Infection of the definitive hosts with tapeworm (humans, carnivorous mammals) occurs if they eat raw or undercooked fish, the body of which contains living plerocercoids. In the intestine of the definitive host, the parasite larvae attach their heads to the wall and begin to grow rapidly. After 5-6 weeks, the tapeworm becomes an adult and begins laying eggs.
The disease caused by the broad tapeworm, diphyllobothriasis in humans, is usually quite severe. Patients experience nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and abnormal intestinal function; Patients often complain of fatigue, weakness, headaches, and irritability. In more severe cases, patients develop severe anemia.
With timely treatment, i.e. removal of the parasite, all these phenomena disappear more or less quickly.
Diphyllobothriasis is most often contracted by fishermen and workers at fish canning factories, who often eat completely raw fish. This disease often occurs in the population of those areas where it is common to eat freshly frozen or lightly spit-roasted fish. The plerocercoids of the tapeworm in such fish often remain alive.
The fight against diphyllobothriasis is carried out primarily by identifying and treating patients and then by protecting freshwater bodies from pollution by sewage, with which the eggs of the parasite get there.
www.rybalka44.ru
Treatment of parasitic infestation

Many patients who think that they are infected with parasites and that something is moving inside them are mistaken. Very often this condition is a consequence of a psychosomatic disorder. Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, you must consult a doctor and not self-medicate.
Usually people go to the hospital when the infection has already reached its worst stage. Intestinal obstruction has begun, and parts of the worm are found in the stool. A special analysis helps to detect the parasite at an early stage.
Since the tapeworm is a hermaphrodite that is capable of fertilizing itself, it begins to actively reproduce inside the human body. In a day, it can lay up to a million larvae, which usually exit the body along with waste products. The parasite regenerates well; to get rid of the worm, you need to completely remove it from the body. Even the smallest particle left in the intestines can cause re-infection.
Only inpatient treatment can help. It lasts approximately 10 days. Special poisons are introduced into the body that should kill the tapeworm. The drug is taken for three days in a row. After a short break, there will be another dose of medication. At the same time, it is worth getting tested for concomitant diseases so as not to aggravate them during treatment for the parasite.
Surgery is prescribed only if intestinal obstruction occurs due to several large worms.
Prevention of disease in humans
It is impossible to completely exclude the purchase or catch of tapeworm fish, since it is quite difficult to identify the parasite by external signs. But in order to prevent human infection, you need to adhere to the following preventive measures:
- Carefully inspect the fish before purchasing, pay attention to the bloating and density of the abdomen. Sometimes when you press on it, the worm can come out.
- Do not buy pre-gutted fish, since it will be impossible to check whether it is infected with tapeworm.
- When purchasing, preference should be given to fish grown in artificial reservoirs. In such conditions, her food is artificial food. In addition, parasite prevention is carried out in specially equipped reservoirs.
- If a tapeworm is detected, depending on the degree of your disgust, the fish should either be thrown away or carefully processed. For this purpose, freezing at a low temperature, well-frying or long-term salting are suitable.
- Infected fish meat, and especially its entrails, should not be fed to domestic animals.
- After processing the fish, thoroughly wash all kitchen utensils that were used.
- It is strictly forbidden to eat river fish raw!
- Do not buy salted fish, as unscrupulous producers do not adhere to salting times. There is a high chance of tapeworm infection.
There are different opinions about whether saltpeter fish is dangerous. Whether you can eat it or whether it’s better to dispose of it depends on whether a person wants to risk their health for the sake of a tasty piece of fish. After all, even a small, inconspicuous larva, once in the intestines, can turn into an adult tapeworm. Be careful. Good health to you!
Is it possible to eat contaminated fish?

So is it possible to eat saltpeter bream? It can be eaten, but to do this you must adhere to the following rules:
- saltpeter bream must be thoroughly cleaned of entrails; it is advisable to eat fillet;
- it is worth cutting the meat into small pieces that are well fried;
- The fish should be fried at a temperature of 55-60 degrees until fully cooked;
- fish can be frozen at a temperature of -18 degrees for 1-3 days;
- fish can be salted, but it must spend at least two weeks in salt.
However, it is worth remembering that even eating well-cooked fish leaves a small risk of infection. Parasite eggs can get on your hands, clothes and kitchen utensils. So it is better to avoid eating obviously sick fish.
Can you get infected from dried or smoked fish?
Many people doubt whether it is possible to eat fish affected by this helminth? Tapeworm in dried fish comes in the form of eggs - a mature individual will not survive in such conditions, but the viability of the eggs is beyond doubt. Smoked meat lovers should also be careful. Sometimes processing is carried out in violation of technology and at an insufficiently high temperature. By eating such products, it is easy to become infected with tapeworm. Fish tapeworm can be found in herring, which is so popular due to its affordable cost.
Remember that you need to buy dried fish only from trusted sellers who have quality documents. Before use, carefully inspect the product.
Return to contents
Smoked and dried fish
Infection through dried fish is possible. An adult tapeworm usually dies when dried, but the eggs can remain viable for a long time. Smoked fish can also be dangerous if the cooking technology is not followed. If the fish has not been subjected to sufficient heat treatment, the risk of infection is very high. Tapeworm can also be found in everyone's favorite herring.
You should only buy fish from trusted sellers. It needs to be thoroughly examined. If you suspect that the fish is infected, you should refuse to purchase.
What is a tapeworm?
What does tapeworm look like in fish? An adult worm is about 20 cm long, approximately 2 cm thick, white in color, and resembles a ribbon (hence the name). The parasite has suckers in the front part of its body.
Most often, the saltpeter worm enters the body when eating white fish. During the day, being in the body of an animal, it can lay millions of eggs. They can only be seen in fish meat under a microscope; they are localized in large quantities in the intestines, liver and fin muscles. Tapeworm in fish is dangerous for humans due to infection, which leads to intestinal obstruction.
The life cycle of a tapeworm looks like this:
- Immature worm eggs are passed through the mammal's feces.
- Most likely they will be swallowed by some freshwater crustacean. This is the first intermediate host; in its body the larva enters the next stage of maturation.
- The crustacean becomes food for the fish. It is the second intermediate host. In the body of the fish, the larva continues its development and enters the stage for its next and final carrier, which can also be a person.
- Entering the body with poorly cooked or raw fish, the worm attaches to the mucous membrane of the small intestine, where it grows to an adult. In the human digestive tract, the incubation period lasts 1-2 months, after which the larvae can be found in feces. Fish tapeworm can live in the human intestine for up to 20 years.
Danger can also await a person when consuming dried fish. Adults cannot live in it, but the larvae continue to exist. Therefore, those who love this product are advised to purchase it only in trusted stores and carefully inspect it before use.
parazite.ru
Is it possible to swim in a contaminated pond?
The period when fish are infected with tapeworm occurs in the summer, when people begin to go out to water bodies to swim. You can only become infected with tapeworm through the meat of diseased fish, so don’t be afraid to swim in the water. Although it is worth remembering that polluted water bodies are dangerous not only from fish helminths. Other parasites may well develop in insufficiently clean water. Therefore, you should be careful when choosing a vacation spot.

Prevention of infection
Sometimes saltpeter fish are difficult to identify. Therefore, to reduce the risk of infection with the parasite, you should adhere to the following preventive measures:
- It is worth giving preference to whole fish rather than cut ones. Often sellers clean and cut low-quality fish that is unfit for consumption.
- The belly of the fish must be checked. It should not be swollen.
- It is worth eating fish that is grown in specialized reservoirs. At fish farms, she is fed with special food, which minimizes the risk of infection with parasites.
- Infected fish must be discarded.
- You should not feed animals saltpeter fish, otherwise they may become infected.
- All kitchen utensils that have come into contact with contaminated fish must be disinfected immediately.
- Only sea fish can be eaten raw. River fish must undergo heat treatment.
- The parasite may die if the fish is frozen first. The product must be kept in the freezer for at least two days at a temperature of -18 degrees.
- If you catch an infected fish while fishing, do not throw it back into the water, otherwise the disease will continue to spread. The fish should be buried in the ground.
Thus, we looked at how to identify saltpeter fish. Tapeworm is a helminth that infects fish and is transmitted to humans. Worm infestation can lead to serious health consequences. Saltpeter fish can be eaten with proper temperature treatment, but it is better not to take risks. Treatment for parasitic infection occurs in a hospital and lasts 10 days. If you do not go to the hospital in time, serious complications are possible, which can result in death.
In what fish can it be found?
Freshwater and saltwater white fish are species in which the tapeworm can live.
Anyone who loves to eat fish needs to have knowledge of the following questions: how can you become infected with a parasite, what does a tapeworm look like in fish, and what is important to remember when preparing food? The tapeworm affects such freshwater fish as bream, roach, pike, bluefish, and herring. Late spring is a period of risk when the likelihood of catching infected fish increases significantly. Fishermen should be especially vigilant.
Infected fish often reveal themselves by behavior: they stay close to the surface and move sluggishly. There is a list of certain signs that tell the fisherman that tapeworm is present in the fish:
- the abdomen is swollen or compacted, pressing can provoke the release of parasites;
- an infected individual floats on the surface of the water surface;
- the fish stops feeding.
When a fisherman catches an infected fish, he should notify the owner of the reservoir and under no circumstances release it back into the water. Sea fish may also contain tapeworm. For example, in fresh pollock. People who buy certified products from a supermarket should not be concerned about contamination. But residents of coastal areas constantly need to be on alert.
Return to contents