Worms in river fish, pike
It is common today to view river fish as a breeding ground for worms.
Let's look at what helminths can live in it and what to do to avoid becoming infected with them. Almost invisible larvae of parasites that live in river fish can cause quite dangerous diseases. Pike can be infected with the larvae of such worms, which provoke diphyllobothriasis - a disease that affects the intestines and is caused by the broad tapeworm.
Pike plays a major role in the spread of diphyllobothriasis in nature, but other predator fish, such as ruffes and perches, can also be affected. Pike is more susceptible to infection with these worms; it is often eaten in an insufficiently thermally or chemically processed form, so people more often get this helminthiasis from it. The larvae of the broad tapeworm are found in the internal organs, muscle fibers and eggs of pikes.
Symptoms of infestation when eating pike with worms will appear after a long period, from 20 to 60 days. The disease begins to manifest itself gradually. The primary manifestations are attacks of nausea, vomiting, belching, heartburn, loss of appetite, and diarrhea. Further, pale skin, fatigue, weakness, abdominal pain, enlarged liver, and cracked tongue occur. It is also possible to develop a skin rash, convulsions, numbness of the limbs, and unsteadiness of gait.
If you notice such symptoms after eating pike, immediately consult a doctor for timely diagnosis and treatment.
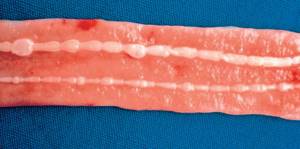
Another type of disease is trienophorosis. These worms parasitize in the intestines of pike (pictured), less often in perch, omul, grayling, and catfish. The liver and sometimes other internal organs are affected. They appear to be white, 2-4 cm long and 2-4 mm wide. Trienophorosis is most common in lake and river fish, but can also affect marine life.
Signs of fishworm infestation
Signs indicating that there are parasites in the human body do not appear immediately. In the process of evolution, worms have learned not to reveal themselves and not to disrupt the life of the host. Therefore, at the larval stages, the symptoms are rather vague, and often a person does not attach importance to the ailment or does not associate it with parasites.
The most common habitat and breeding ground for parasites is the intestines; here, infection with helminths can manifest itself as follows:
- diarrhea and constipation;
- abdominal pain and bloating;
- weight loss;
- intestinal obstruction;
- sleep disturbance, irritability;
- irritable bowel syndrome.
Worms in crucian carp
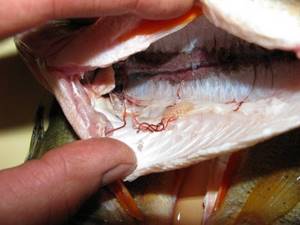
What do worms look like in crucian carp? Example in the photo. These and other river fish may have parasites such as:
- Ligula or Ligula is a large tapeworm up to 70-80 centimeters long and 3-4 cm wide. This type of worm is most common in lake crucian carp. Helminth larvae enter the intestines of crucian carp and other river fish as food. Next, the larva penetrates through the intestinal wall into the blood and from there into the abdominal cavity, where it turns into an adult, reaching large sizes, causing swelling or rupture of the abdomen. Sometimes some of the worms stick out from the belly. Crucian carp affected by Ligulidae are edible only after gutting the bellies and sufficient heat treatment;
- Nematodes that cause phylometroidosis. These are pinkish-red helminths that are located on the head or pectoral fins of crucian carp and other cyprinids, as well as perches. These worms are up to 10 cm in size. They accumulate in the liver, kidneys, and swim bladder. They are not dangerous for humans, but eating fish infected with them, including crucian carp and perch, is undesirable, since the meat becomes watery, loose, and loses its taste and nutritional qualities;
- Flukes that cause postodiplostomosis. This disease can affect crucian carp, carp, silver carp, roach, perch and others. In infected individuals, black dots can be seen on the body, fins, and gills. Each such point is a place in which a capsule with a helminth is located. Being in the body of a crucian carp or perch, these parasites do not produce toxins that are dangerous to humans, so fish affected by post-diplostomosis can be eaten;
- Opisthorchiasis can be contracted by eating raw or undercooked fish. Mainly the carp family. Penetrating into the human body, worms develop and cause symptoms of the disease such as headache, abdominal pain, and fever. The gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas are mainly affected. It is permissible to eat fish infected with the larvae of these worms only if it has undergone sufficient heat treatment (boiled or fried).
How to identify crucian carp with worms? Visually, you can only notice those parasites that accumulate in the area of gills and fins, but individuals located in the body are much more difficult to identify.
Perch has worms
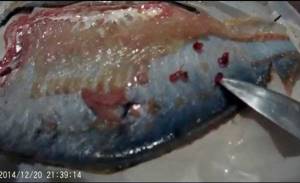
Perches have some helminth infections that were described earlier - post-diplostomiasis, opisthorchiasis, diphyllobothriasis, ligulosis, as well as other diseases.
Methorchiasis affects the human liver and gallbladder. Infection occurs when eating raw or insufficiently heat-treated fish, such as crucian carp, perch, roach, silver carp and others. The larvae of worms in river fish are found in the muscles, gills, and eye membranes.
Gnathostomiasis is a helminthiasis that, upon penetration into the human body, is found in the subcutaneous fatty tissue, lungs, liver and other organs. A person can get sick by eating contaminated raw fish, such as carp, crucian carp, and perch.
In sea bass, helminthiasis such as anisacidosis can be found. The average length of anisakis is 50-60 mm, the body is spindle-shaped, purple-red in color. The larvae of worms in sea bass are found in the abdominal cavity, on the surface or inside the internal organs and in the muscles.
Humans become infected with anisakids by eating sea bass, herring, squid or other seafood contaminated with larvae. In the human body, these parasites infect the gastrointestinal tract. Infection can be prevented by proper cooking of seafood.
Other types of parasites in pike
The cat fluke is far from the only pike parasite. Predatory species of freshwater fish may also contain the following helminths:
- Chinese fluke. This worm also belongs to the group of flukes. It causes the disease clonorchiasis. Signs of invasion are very similar to those of opisthorchiasis. The parasite is localized in the liver. This leads to severe enlargement of the organ, pain on the right side under the ribs and itchy skin.
- Wide tape. This tapeworm can reach sizes of up to 10-12 m. It parasitizes the intestines and causes the disease diphyllobothriasis. Invasion is accompanied by sudden weight loss, dyspeptic symptoms and weakness.
- Anisakid. This is a very dangerous type of parasite. It enters the human body by eating poorly processed fish. Anisakidosis is accompanied by severe gastrointestinal disorders and allergic reactions. To date, no effective treatment for this invasion has been developed.
- Nanophyetus. This flatworm can enter the body not only through food. Its larvae can remain on human hands after cutting fish. Nanophyetus causes inflammation and irritation of the intestines. However, after 1-2 months, self-healing usually occurs, since the life cycle of the helminth is very short, and it is not capable of reproducing in the human body.
Parasites in pike caviar
It is pike that is considered the most dangerous fish living in fresh water and from which you can become infected with helminths. This is explained by the fact that this type of fish is a predator and feeds on most of the inhabitants of reservoirs that are carriers of parasites. Therefore, the probability of infection from pike by parasitic organisms increases to 100%.
It is also important to take into account the fact that the eggs of this predatory fish also contain helminth larvae. That is, if you are concerned about the question - are there parasites in pike caviar, then the answer is affirmative. You can become infected with worms from the eggs of this fish, especially if the product has undergone insufficient heat treatment or is poorly salted.
Routes of infection
Contrary to popular misconception, a person cannot become infected with opisthorchiasis from sick cats and dogs. Also, people cannot become infected by accidentally ingesting water from a pond or river. The only way a person can become infected with cat fluke is by eating infected and poorly processed fish.
Do pike and perch suffer from opisthorchiasis? Fish of the Carp family are more susceptible to this invasion. However, both pike and perch are predators. They eat shellfish and small fish and may well become infected with opisthorchiasis.
Fishermen often ask the question: “Does river pike have opisthorchiasis?” Any freshwater fish that feeds on shellfish can become infected with cat fluke larvae. Invasion does not occur only among inhabitants of sea waters. Both pond and river pike are equally susceptible to this disease.

Parasites living in pike
There are several types of helminths that pike can be infected with.
- Flat flukes (cat fluke), this type of parasite causes the development of opistarchosis, the worm affects the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
- Tapeworms, these parasites cause diphyllobothriasis. Organs that helminths infect: stomach, small intestine and liver.
- Parasites such as liver fluke, Chinese fluke and clonorchisis cause the development of clonorchiasis. The organs that are most affected by worms are: bile ducts, liver, pancreas, duodenum, stomach.
- The flatworm trematode causes metagonimiasis and affects the gastrointestinal tract.
In what bodies of water do they get sick?
In 1923, pike plague broke out in Norway, and a couple of years later in Finland, Switzerland, Sweden, Denmark, Germany and Australia. In 1930, the disease “reached” the lakes near Moscow, gradually penetrating the reservoirs of Belarus, Klyazma and Pskov. After this, an epizootic plague of pikes broke out in Siberia, the Middle Volga, in the Yenisei tributaries and in the Dnieper bed.
The disease occurs episodically in large bodies of water, lakes and reservoirs for several years in a row. The infection spreads to other bodies of water along with the flow of migrating fish or fish transported on ships.
Important. The sources are dead or infected pike, as well as microbial carriers. The infection enters the water through the secretions of living fish and from their decomposing corpses.
Danger of infection for humans
Unfortunately, many of us often underestimate the danger of helminthic infestation. Late diagnosis of an illness caused by infection with parasites can bring a person many health problems with life-threatening complications.
Once inside a person, the parasites take the necessary substances for their life activity and development, which often causes:
- indigestion;
- decreased hemoglobin levels;
- blockage of blood vessels and bile ducts;
- the occurrence of allergic reactions;
- decrease in the body's defenses.
Parasites and diseases of river fish that are dangerous and contagious to humans: which ones and how to destroy them
Today you will find out what parasites live in river fish, what diseases they have, whether they are dangerous to humans and how you can become infected.
Fish is a healthy product that should be in the human diet. Our ancestors said that if you eat it often, you will live a long time.
Any fish is rich in calcium, zinc, magnesium, selenium, iron and phosphorus. And it contains protein that is easily absorbed in the human body.
However, without appropriate treatment, it is a source of dangerous diseases. They, like all living beings, can be carriers of infectious diseases.
Opisthorchiasis
The cat fluke is a small worm. The maximum length does not exceed 18 mm. The harm caused by this parasite to the human body involves not only mechanical, but also toxic effects on internal organs.
If left untreated, helminthic infestation can cause the following consequences:
- cardiac dysfunction;
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequently occurring ailments of the respiratory system (pneumonia, bronchitis);
- risk of developing cancer (liver cancer, pancreas cancer;
- nervous disorders.
Diseases and parasites of river fish dangerous to humans
I will immediately warn the reader that if you carefully look at the appearance of the fish for the nature of diseases and parasites, and also carry out heat treatment (cooking and frying), even if it is not noticeable from the outside, then nothing will happen to you and you will not become infected with anything.
Rubella in freshwater fish
The most dangerous disease for fish is rubella.
Outbreaks occur in spring and early summer. They look bug-eyed and have water bubbles on their scales.
Typically, 90% of fish infected with rubella die. But if you survive, gray scars remain on your body.
A person who eats such fish cannot get rubella, but can be poisoned.
Pox in fish

The most famous disease among fish is smallpox.
In such fish, watery tumors are visible on the body and fins, which will burst over time and scars will be visible on the body. Such fish grow slowly.
Fungi on the body of fish

On the body and fins of some fish you can see something similar to cotton wool - these are fungi.
This fungus prevents fish from breathing and moving. Therefore, their behavior is too active and rubs against stones. The disease occurs when the water temperature is low.
Black dots on river fish

You can see black dots on the body of some fish that look like bubbles in which helminth larvae live.
Such fish should be thrown away or well processed, salted and left overnight in the refrigerator.
Plague in fish
We can also get poisoned by fish if it has the plague.
These fish have reddish scales. It should be thoroughly cleaned of scales and washed under running water.
Tapeworm in fish - is it possible to eat such fish?

Another type of disease in fish, or rather, the fish becomes a repository - a home, as it were, for such tape parasites. In the stomach of river fish, helminths lay eggs and grow into normal adult worms.
Visually, such parasites can be seen and destroyed, but the eggs may not be noticed. Such eggs feel great in frozen, dried, and dried fish. Only after heat treatment during long-term (20 minutes) cooking at least +60 degrees do such worms die.
Diphyllobothriasis
The broad tapeworm is considered the largest tapeworm. This parasite reaches 15 meters in length.
The danger of diphyllobothriasis is as follows:
- serious disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- a severe form of anemia and hypovitaminosis develops;
- development of tissue necrosis;
- intestinal obstruction.
This disease is quite easily diagnosed due to the presence of worm larvae in the feces, which are visible even with the naked eye.
Treatment methods
Treatment of fish parasites can only be prescribed by a specialist in this field, namely a parasitologist or infectious disease specialist. When choosing a treatment regimen, the doctor is guided by the type of parasite, its location, the severity of symptoms, the general condition of the patient and many other factors. All drugs used in treatment are very toxic, so self-administration of these medications is not permissible. The dosage and special diet for the duration of treatment are selected by the doctor.
Treatment of tapeworm should be carried out only in a hospital setting, with the patient taking the medicine in stages, with breaks between them. As a result of treatment, the parasite dies and is eliminated from the body, while the patient may experience intestinal obstruction, and surgical intervention may be required, especially if the parasite is of an impressive size or there are several of them.
Populin or Ecorsol are used to treat opisthorchiasis; treatment of this disease is complex and must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. Clonorchiasis is treated with anti-inflammatory, antispasmodic, choleretic, antihistamine drugs and sorbents.
For metagonimiasis, Cesolom or Biltricid is prescribed; without timely treatment, the disease can affect the heart, spinal cord and brain. Anisakidosis is treated with Albendazole or Mebendazole.
Clonorchiasis
A disease caused by a parasite such as the Chinese fluke can have quite serious complications:
- yellowness of the skin due to liver damage;
- Cirrhosis/liver abscess.
If a child contracts clonorchiasis, in addition to damage to internal organs, significant developmental delays are possible.
In order to avoid the listed diseases, which are quite dangerous to human health and life, you should only eat fish that has undergone high-quality heat treatment.
Is it possible to eat contaminated fish? Is it dangerous for humans?
Plague-infected pike should not be eaten, as if it is cooked poorly, a person can be seriously poisoned. If you cook suspicious fish, you need to use a high cooking temperature.
In order not to expose your body to poisoning, you need to know what sick caught fish looks like. It is also necessary to have an understanding of the behavior of infected fish in water bodies , and if there are any signs of plague, do not use captured fish for cooking.
What is opisthorchiasis and how does it develop?
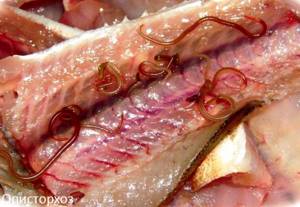
Sometimes thin worms (red worms, rolled into spirals) are found in the meat or caviar of fish when cutting. Based on this, housewives often conclude that the pike is opisthorchiasis and throw it away. But determining the presence of a parasite is not easy.
Opisthorchises (cat flukes) are small trematode worms that form a capsule about 1 mm in size in fish meat. Microscopic examination reveals a worm larva inside the capsule. They reach adult form only in the human or animal body. The size of the fluke by this time can reach 8−19 mm.
Ichthyologists believe that freshwater carp fish (ide, bream, crucian carp, carp, roach, etc.) are most susceptible to infection. Opisthorchis larvae enter their digestive tract from the body of an intermediate host (pond snail).

Eating contaminated fish can also cause harm to humans. The symptoms and treatment of opisthorchiasis have been studied for more than 200 years, the spread of the pathogen in Russia and in the world has been studied. The regions of Siberia and the countries of Southeast Asia are considered the most dangerous.
The disease in humans and animals belongs to the group of invasions that are caused by helminths (helminthiasis). Most often, the parasite affects the human liver and all organs of the hepatobiliary system, but there are cases of damage to the nervous or respiratory systems. The presence of pathogens can cause an acute or chronic disease - opisthorchiasis. Symptoms of the disease in humans appear as:
- pain in the right hypochondrium;
- nausea and bitterness in the mouth;
- heartburn, frequent stomach pain;
- pain in the left side of the lower chest, radiating to the shoulder.
Symptoms resemble those of stomach diseases, pancreatitis or hepatitis; in acute form, they are accompanied by fever, headaches and joint pains that last for 1-3 weeks. Sometimes the manifestations of the infestation are not pronounced, and the person lives with the parasite, excreting its eggs in the feces.
Fish most often affected by worms

Bream
Among marine and freshwater fish there are species that are a source of helminthiasis infection. A person should be extremely careful when eating the following types of product:
- Crucian carp. The most dangerous species is that living in the Far East. Often it is infected with clonorchiasis.
- Ide. Omnivorous fish often carry the Siberian fluke.
- Bream and perch carry ligulosis and diphyllobothriasis.
- Tench. May be a carrier of the parasite that causes opisthorchiasis.
- Pollock can threaten humans with anakiasis.
- Flounder. It is a carrier of many parasites, so it is important to heat-treat the product very well and protect yourself from risks.
What parasites are there in pike?
The presence of thin red worms in pike does not indicate that it is infected with opisthorchiasis. Most often, long (more than 5 cm) worms are a parasitic phylometra nematode, which lives only in the body of the fish, in the area of the head and fins. It is not dangerous to humans.
Eustrongylides is similar to Phylometra and affects all freshwater fish. It can be found in the form of round capsules in milk, caviar, meat of perch, pike and even noble breeds (sturgeon or salmon).
There are other microscopic helminths that parasitize pike and cause the following diseases in humans:
- Nanophyetosis. The larvae live in the skin of fish of all breeds. They affect the gastrointestinal tract of people and domestic animals.
- Anisakidosis. Parasites live in the muscle tissue and gastrointestinal tract of pike and other fish. In humans, it manifests itself in stomach diseases, fever, and severe allergic reactions.
- Clonorchiasis. Caused by the Chinese fluke, it affects various types of fish and is dangerous to humans. Manifestations resemble opisthorchiasis.
If the pike lived in a reservoir where there are carp fish, then it can also be infected with opisthorchiasis. The cat fluke can enter the intestines of the predator along with the infected prey. Despite the claims of fishermen that opisthorchiasis never occurs in pike, you can become infected with it by eating this fish.
Methods for disinfecting infected fish
It is not difficult to destroy adult parasites in the body of a fish. The difficulty is getting rid of the larvae, which are more resistant to negative external influences. During cooking, it is possible to disinfect the product using the following actions:
- cooking;
- ambassador;
- frying;
- smoking;
- freezing

Smoking
When heat treated (cooked) for fifteen to twenty minutes, the larvae die. During frying, it is possible to destroy parasites if everything is done correctly. The fish is not cut into large pieces. This allows the meat to be kept at the required temperature to kill helminths. Hot smoking can kill parasites if the product is processed within two hours.
Read
Features of using herbs against parasites
Salting also allows you to get rid of the infection, but to get results you need to salt the product for two to three weeks. If large fish is salted, the salting time is doubled.
Freezing fish is a simple and effective way to get rid of larvae. They die within twenty-four hours if the temperature is below thirty degrees. Try not to follow fashion and avoid eating dishes that use fish without proper heat treatment.
Is it possible to eat sick pike?
If parasites in pike are found in the gills, crawling inside the abdominal cavity, then this is most likely a safe phylometra. Pike infected with these worms should not be eaten. Its meat becomes saturated with toxins released by the parasite, loses its taste and becomes inedible. The fish can be thoroughly boiled and fed to pets.
Having found round, dense balls about 5 mm in size in the muscle tissue, we can conclude that the pike is infected with Eustronohylides. Inside the capsule you can find worms as thick as sewing thread, about 5 cm long. With a small degree of infection, the meat can be eaten after removing the capsules and thorough cooking.
It is impossible to notice opisthorchid larvae and determine whether there are dangerous worms in the pike. To protect yourself from accidental infection, you need to follow a few simple rules.
Heat treatment
Do pikes have opisthorchiasis and is it possible to become infected with it if the fish has been thoroughly boiled or fried? Such a product may be dangerous if heat treatment was insufficient. Cat fluke larvae die only when exposed to high temperatures for a long time.
To avoid infection, you must follow the following rules for preparing fish:
- The pike should be cut into small pieces before frying. This will ensure uniform heat treatment and help completely get rid of live larvae. You need to fry the fish for at least 20-30 minutes. This time is enough to destroy the metacercariae. While frying pike, the pan must be covered with a lid.
- When cooking fish, boil for at least 30 minutes. During this time, all parasites in the muscles die. Large pike should be cut into slices before boiling.
- It is not recommended to bake a whole pike carcass. It's better to cut it into pieces first. The fish should be kept in a preheated oven for at least 1 hour.
- The safest way to cook pike is stewing. The fish should be kept on low heat until its bones become soft. Only in this case can you be sure of the complete destruction of the larvae.
How to avoid getting infected with parasites?
To the question of whether pike suffers from opisthorchiasis, both fishermen and scientists will give a negative answer. But pikes may still have larvae in their digestive tract that got there when they ate infected cyprinids. If the pike intestinal walls are accidentally damaged, the larvae will penetrate into the meat. In addition to opisthorchiasis, fish can be infected with helminths that pose a danger to humans.
When handling a raw carcass, it is advisable to wear thin rubber gloves. While cleaning and cutting, do not smoke, touch your lips or touch prepared foods (bread, etc.). After finishing working with raw pike, thoroughly wash your hands, knife, and cutting board.

To avoid infection and the development of disease in the human body, you need to properly prepare pike:
- Salting is carried out by generously sprinkling the carcasses with salt. The crystals should also get inside the pike’s abdomen. Large specimens need to be flattened, cutting along the spine. The salting period is at least 5-7 days.
- Drying of pike carcasses can be done after thorough salting. To remove excess salt, the fish is washed and soaked.
- Fish should be frozen at a temperature no higher than -28°C. After freezing for 20 days, it becomes safe; the larvae of most parasites die.
- Fresh fish should be cooked for at least 20 minutes. To ensure that the meat is well cooked, the carcasses are cut into pieces of 150-200 g.
- Fry fresh pike for 20-25 minutes, cutting into pieces no more than 5 cm thick. Frozen fish must first be completely defrosted so that it warms up evenly when frying.
- Baked fish should be cooked or hot smoked for 20-30 minutes, until the meat comes away from the bones.
- Bake pike pies for 40-60 minutes.
To be completely sure that dried or smoked pike is safe, it is best to buy fresh fish and prepare your own snacks. You should not eat raw fish dishes.
How to protect yourself from fish parasites
Fish is a valuable food product that provides the body with useful components.
It fills the body with essential substances and helps improve well-being. Despite this, the product can become a source of danger if certain rules for preparing and consuming the product are not followed. There is no need to give up fish, you just need to follow the conditions for proper use of the product.
Read
About flukes - human parasites
It is impossible to find completely safe fish. It was previously believed that sea fish were less dangerous in terms of helminthiasis, but observations show that almost ninety percent of sea fish are affected by helminth larvae. A product that has passed veterinary control instills some confidence, but only partly. You can expect trouble from fish you catch yourself or buy at spontaneous markets: there is a high probability that the product is contaminated.
To play it safe, make rules that you never break. It is forbidden to place raw fish directly next to other products, especially ready-to-eat ones. There should be a separate cutting board and knife for fish. All areas touched by the raw product must be thoroughly washed with soda solution or dishwashing detergent.
Fresh fish is a perishable product. It can be in the heat for no more than an hour, at room temperature - up to ten hours. In a household refrigerator, the product can be stored at temperatures down to minus eight degrees for two days.
Worms in crucian carp
What do worms look like in crucian carp? Example in the photo. These and other river fish may have parasites such as:
- Ligula or Ligula is a large tapeworm up to 70-80 centimeters long and 3-4 cm wide. This type of worm is most common in lake crucian carp. Helminth larvae enter the intestines of crucian carp and other river fish as food. Next, the larva penetrates through the intestinal wall into the blood and from there into the abdominal cavity, where it turns into an adult, reaching large sizes, causing swelling or rupture of the abdomen. Sometimes some of the worms stick out from the belly. Crucian carp affected by Ligulidae are edible only after gutting the bellies and sufficient heat treatment;
- Nematodes that cause phylometroidosis. These are pinkish-red helminths that are located on the head or pectoral fins of crucian carp and other cyprinids, as well as perches. These worms are up to 10 cm in size. They accumulate in the liver, kidneys, and swim bladder. They are not dangerous for humans, but eating fish infected with them, including crucian carp and perch, is undesirable, since the meat becomes watery, loose, and loses its taste and nutritional qualities;
- Flukes that cause postodiplostomosis. This disease can affect crucian carp, carp, silver carp, roach, perch and others. In infected individuals, black dots can be seen on the body, fins, and gills. Each such point is a place in which a capsule with a helminth is located. Being in the body of a crucian carp or perch, these parasites do not produce toxins that are dangerous to humans, so fish affected by post-diplostomosis can be eaten;
- Opisthorchiasis can be contracted by eating raw or undercooked fish. Mainly the carp family. Penetrating into the human body, worms develop and cause symptoms of the disease such as headache, abdominal pain, and fever. The gastrointestinal tract, liver and pancreas are mainly affected. It is permissible to eat fish infected with the larvae of these worms only if it has undergone sufficient heat treatment (boiled or fried).
How to identify crucian carp with worms? Visually, you can only notice those parasites that accumulate in the area of gills and fins, but individuals located in the body are much more difficult to identify.
How to avoid infestation
The only way to prevent opisthorchiasis in humans is careful processing and proper preparation of pike. If the fish looks sick, it is better not to eat it.
It is also necessary to thoroughly rinse the cutting board and dishes that contained raw fish. Cat fluke larvae can survive on kitchen utensils.
Under no circumstances should you feed raw freshwater fish to your pets. As already mentioned, humans cannot become infected with fluke larvae from other mammals. However, in cats and dogs, opisthorchiasis is very difficult and often ends in the death of the animal. By feeding your pet raw fish, you are putting his health and life in serious danger.
Parasites living in raw fish
All varieties of commercial fish, without exception, must undergo special veterinary and sanitary control before being sent for sale. These rules are accepted and used everywhere, regardless of region. A serious problem in this area is caused by unscrupulous amateur fishermen who fish and sell their catch, which subsequently leads to the fact that the people who made the purchase become infected with parasites. There are certain signs by which infected individuals can be distinguished, but not every person is familiar with them. That is why diseases caused by parasites living in fish are now quite common.
Harmless parasites for the human body
There are a number of parasitic worms that, while causing harm to fish, remain practically harmless to humans. It is important to promptly identify infected individuals and take special measures during cooking. This will help prevent the consumption of larvae and adults found in many types of fish. Experts recommend completely eliminating this food product from the diet if you do not have certain cooking skills.
Helminths
Parasites of this type are most often found in fish. Mostly the carp family is infected: silver bream, bream, rudd. The most dangerous and fairly large parasitic worm is the ligula, which can be seen in the photo. This worm reaches more than 15 cm in length at maturity. Due to its large size, the parasite causes metabolic disorders in the human body, which is fraught with serious consequences.
If you find a ligula inside a fish, you should not rush to throw it away. It is recommended to clean the fish from the entrails, along with which the parasitic worm is removed. After washing the meat, you can safely eat it, since there is no danger to humans in this case. The larvae of the worm do not penetrate the muscle structures of the fish, which eliminates the possibility of infection.
It is important to prepare the product correctly, giving it the heat treatment necessary to kill parasites. Otherwise, in the presence of smaller types of helminths, there is a possibility of human infection with helminthiasis. The disease is the penetration of parasites such as trematodes, cestodes and roundworms into the human body. In the human body, the parasite can be localized in the internal organs or in the subcutaneous tissue.
Schistocephamos
A fish such as crucian carp can contain worms that are slightly smaller in size than ligula - digramma. You can see what the parasite looks like in the photo. Smelt often contains parasites such as schistocephamos, which reach no more than 2 cm in length, as shown in the photo. These parasites are practically harmless to humans, as they are not capable of harming their internal organs. This type of parasite can be found in the intestines of red fish such as trout and salmon.
If such parasites are found, it is recommended to gut the fish entrails and bury them in such a way that animals cannot reach them. Fish can be eaten after thorough washing and cooking.
Cystidicola farionis
In winter and spring, when the greatest activity of smelt is observed, many fishermen wonder whether contaminated fish can be eaten. The parasite is located in the swim bladder and has a peculiar appearance: a thin, thread-like parasite. Cystidicola pharyonis is a thin round worm. It does not harm the human body, but despite this, it is recommended to remove all entrails before cooking smelt.
Trienophorus nodulosus
White balls can often be found in the liver of burbot. When they are damaged, as a rule, a flatworm emerges, which can be seen in the photo. Its length varies between 10-12 cm. Cysts can also be found in other fish. Infected fish can be eaten, the main thing is to completely clean its insides of parasites and cook it, observing certain standards.
Philometra
Fish caught in fresh water bodies may contain thin parasitic worms, which can reach up to 10 cm in length. This parasite is localized in the gill area or under the scales. In the carp family, this worm is most common, localized under the scales in the area where the upper fin is located. In appearance, this parasite resembles veins. Infecting humans is impossible. The intermediate host is crustaceans, without which the parasite cannot be transmitted.
special instructions
Please note that if large helminths are found in the internal organs of the fish, you should not dispose of the entrails by throwing them back into the reservoir. This method of getting rid of parasites risks infecting other fish.
Important! If, when cutting freshly caught fish, you find signs or the parasite itself, do not throw it away, but burn it in order to most likely avoid further development of the “freeloader”.
You should not refuse to eat fish dishes, but it is important to follow a number of recommendations with which you can protect your body from infection:
- do not taste raw fish when cooking;
- boil or fry fish for at least half an hour;
- Before cooking, be sure to cut the meat into small cubes, no more than 1 cm;
- Freeze fish meat first.
Rules and tips for protecting against diseases and parasites of river fish, so as not to become infected
It also happens that it looks healthy in appearance, but any fish can contain larvae. They do not cause any harm to the fish.
The first rule that a person must follow is to cook the fish for at least 25 minutes.
And, probably, everyone noticed that when cleaning fish, flat white worms are found among the entrails.
They can be removed, then the fish can be salted and put in the refrigerator for a day. After which you can eat it.
- Do not forget that fish should be cooked for at least 25 minutes before eating.
- For processing, it is better to use a separate knife and board, which should then be washed well.
- After contact with fish, it is recommended to wash your hands thoroughly.
- You should not feed raw fish to your pets, as they can become sources of infections not only for adults, but also for children.
Parasites living in herring
Russian cuisine does not have dishes with raw fish. But in this case we should not forget about the herring. This type of product is quite popular due to its taste and low cost. Not every manufacturer follows the technology for making herring, so contamination cannot be completely ruled out when consuming this product.
Herring may contain various parasites that are causative agents of the following diseases:
- Ligulosis is caused by a tapeworm that reaches 120 cm in length while living in the human body. The parasite compresses almost all internal organs, which provokes their dysfunction, and also releases waste products that cause intoxication of the body. In this case, symptoms such as fever, dizziness, nausea and diarrhea are observed.
- Opisthorchiasis occurs when a cat fluke enters the human body. The disease is accompanied by damage to the gallbladder and ducts, pancreatic gland and liver tissue. The parasite multiplies quickly, causing symptoms such as a bitter taste in the mouth, headaches, fever, constipation and diarrhea.
- Anisokidosis is a common helminthiasis that is detected in fish and also affects human internal organs. In this case, parasitic individuals live in the intestinal space. Primary symptoms include pain in the abdomen and periodic vomiting. Quite often the disease is mistaken for the acute stage of appendicitis. Anisokidosis is accompanied by the development of characteristic intestinal bleeding, because the parasite cuts into the walls, which is the cause of the development of pathology.
- Diphyllobothriasis – by eating herring you can become infected with the broad tapeworm, which can grow up to 25 meters in length in the human body. Clinically, the disease is manifested by complete or partial loss of appetite, headaches and quite severe dizziness, pain in the peritoneum, enlargement of the spleen and liver.
What diseases provoke
Most parasitic diseases that a person can contract from red fish are caused by the activity of worms or helminths. The main ones are described below.
Diphyllobothriasis
The causative agent is the broad tapeworm. This tapeworm is dangerous to a number of mammals, including humans. The size of a mature individual can reach 15 m and a width of up to 1.5 cm. Only cysts concentrated in muscle tissue or eggs have the ability to invade. They are not difficult to see, as they resemble rounded grains of rice up to 0.6 cm in length.
The main symptoms of diphyllobothriasis:
- digestive disorders - constipation, diarrhea, vomiting, nausea;
- allergic manifestations on the skin;
- weight loss and loss of appetite;
- weakness, decreased performance, increased fatigue;
- dizziness;
- anemia and pathological pallor of the skin of the face.
From the moment of eating red fish until pronounced signs of the disease appear, about three months pass: during this time, the cyst opens, a larva emerges from it and turns into an adult. Only 1 adult worm lives in the human body, whose life expectancy is 13-15 years.
Nanophyetosis
Another disease that is at risk when consuming insufficiently processed red fish is nanophyetosis. The causative agent is salmon flukes, but they are too small to be seen with the naked eye. The body length of adult individuals is only 0.5 mm. The integument of the body is yellowish or grayish in color.
When infected with salmon fluke, the following symptoms occur:
- nausea and frequent vomiting;
- problems with bowel movements (diarrhea or constipation);
- sudden changes in appetite, both increasing and decreasing;
- weight change;
- liver enlargement;
- pain in the right hypochondrium.
Sometimes multiple infections with salmon flukes are possible, which greatly affects the symptoms. The picture may be aggravated by severe intoxication and neurological disorders.
Anisakidosis
When lightly frozen, red fish may contain anisacids, which are human nematodes. The larvae of these parasites are found in all organs of marine life, but most of all they are found in the liver, intestines and gills. Anisakids are also found in red and black caviar.
These helminths have a body shaped like a spindle wrapped in a spiral. The outer covers are painted white or cream. In size, adult individuals grow up to 5 cm. A person is an intermediate host for these worms, but during their stay in the body the stomach can be seriously affected. The larvae also damage the intestinal mucosa.
Anisakides can cause severe symptoms:
- digestive disorders;
- pain in the stomach;
- skin manifestations of allergies;
- dry cough.

Multiple infections lead to severe intoxication with an increase in temperature to 39°C. In severe cases, obstruction of the digestive tract develops, which ultimately leads to peritonitis. If the patient does not receive immediate medical attention, he may die.
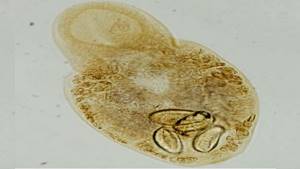
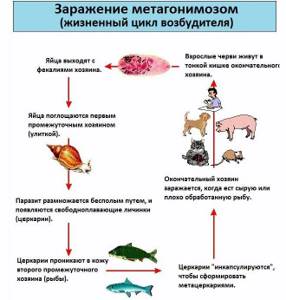
Metagonimiasis
The disease metagonimiasis occurs after the entry into the human body of special trematodes that live in cyprinids and red fish. The parasites are very small - 2.5 mm in length and 0.7 mm in width. They can be found under the scales, in the muscles and in the fat layer.
Symptoms of metagonimiasis are:
- disorders of the digestive system;
- skin manifestations of allergies;
- blood count disorders in the form of eosinophilia and anemia.
Lack of treatment can provoke ulcerative damage to the intestinal walls, internal bleeding and peritonitis.
How to avoid
To prevent infection by parasites, you must follow simple rules:
- It is preferable to eat red fish grown artificially in fish farms. When feeding with artificial feed, the risk of infection is much lower.
- You need to buy red fish and caviar in places where the products undergo preliminary sanitary inspection. There is no need to be embarrassed to ask for a certificate of veterinary inspection, which the seller must have.
- Freshly caught fish should be frozen immediately. Before consumption, freezing is carried out, and the processing time depends on the temperature, which should not be reduced.

Eating raw red fish or caviar is a sure way to parasitic infections. To prevent this from happening, the product should be pre-disinfected:
- freezing for 48 hours at -20°C;
- freezing for 15 hours at -27°C;
- frozen for 4 weeks at -4°C;
- frying at a temperature of 180-200°C in a closed container or in the oven.