Red fish is a nutritious food that is considered an excellent addition to the basic human diet. Recently, the general trend is a minimalist approach to the methods of preparing fish dishes. This really makes sense, since from the point of view of nutritional value and benefits for the body, meat that has not been thermally processed for a long time, has not been salted with a large amount of salt or has not been exposed to smoke in a smokehouse for a long time, retains more vitamins and amino acids. But before you completely surrender yourself to fashionable culinary trends, you should ask yourself a question: are there parasites in red fish and are they dangerous for humans?
Helminths in fish: what they are and why they are dangerous to humans
Fish is an essential food product in the human diet, but it is not always possible to purchase a high-quality product that will meet all requirements and sanitary standards. Recent studies show that any fish, both sea and river, can be wormed, and parasites pose a huge danger and threat to human life.
Very often, tapeworms - cystodes, roundworms - nematodes and flatworms - trematodes are found in fish. Some of them are absolutely safe, that is, they do not parasitize the human body, but some species pose a huge threat.
Safe parasites
It is worth noting that not all worms pose a danger to human health. Moreover, a large amount of fish comes to us already frozen, and the worms die at a temperature of -15-20 degrees in a few days (usually about a week). Moreover, with proper heat treatment, helminths also die, so the risk of infection is minimized. The following types of worms that are safe for humans include:
- all flatworms are diplostoma;
- round – saw-meters;
- some types of tapeworms.
Diplastorms and pilometers parasitize only fish; moreover, these worms parasitize the lens of the eyes and scales, therefore, with proper processing of the carcass, the adult larvae are removed before cooking. Cestodes are tapeworms, and not all of them are dangerous to humans. There are two known species that parasitize fish - the common Ligulidae and Schistocephalus solidus are small in size and parasitize only small fish.
Prevention of infection
To prevent human infection with helminths, it is necessary to exclude the possibility of consuming dishes made from raw or almost raw fish (freshwater and sea) and some seafood, in particular squid. Since it is not always possible to avoid consuming fish containing parasites, the most important thing is to adhere to simple processing rules - thermal processing using temperatures above 60 ° C or long-term pre-freezing. Salting, pickling, and cold smoking are not reliable methods of prevention, but in most cases, if carried out correctly, they can also kill helminth larvae that are dangerous to humans.
What do worms look like in fish?
Worms or helminths are worms, so it is not difficult to visually identify them; they differ from each other in structure, shape and body size. It is worth noting that it is small worms and their larvae that are most dangerous to humans.
You can find worms with the naked eye, but they may not pose a particular danger to humans. A much more serious danger to humans is the larvae; they can only be seen in laboratory conditions using special equipment. Worms can also be found in salted fish, but it is not a fact that they will be alive. There can also be worms in frozen fish, but usually they die at a temperature of -20 degrees.
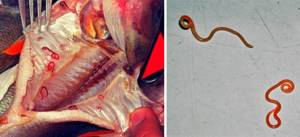
There are several varieties of worms that differ from each other and may look different in fish:
- The Amur fluke is a parasite of river fish, usually reaches no more than 1.5 cm in length, has a flat shape, and causes the disease opisthorchiasis in humans.
- Echinococcus is a tapeworm up to 0.5 cm long, does not cause disease, and can parasitize humans exclusively in an intermediate form.
- The broad tapeworm is a dangerous parasite for humans; it can reach a size of up to 12 m; most often, one or two individuals live with a person, no more.
- Trematodes - cause the disease metagonimiasis in humans, small worms measuring 2-2.5 cm.
- Nanophyetosis is a small parasite, its length is no more than 0.5 mm.
Sometimes the presence of worms in fish can be determined even without cutting the carcass, but by its appearance. Fish infected with parasites have cloudy eyes and their bodies are lined with small spines. Adults can be found when cutting fish. You can become infected with worms from fish in any form - from fresh, lightly salted and frozen, so be careful about the choice and processing rules.
Types of worms that INFECT humans
While a wide range of helminthic parasites are present in marine and freshwater fish, only a few species are capable of infecting humans. There are a moderate number of nematodes, flukes and cestodes that have ever been found in humans, but only a few of them cause serious disease. However, most cases of helminth infection are associated with socio-cultural and behavioral factors that increase the risk of infection in the population (primarily the habit of people eating raw fish).
Nematodes (roundworms)
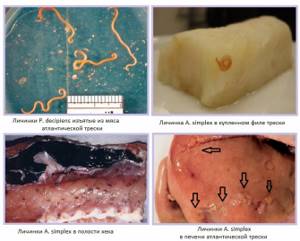
They look like thin worms 1.5-2 cm long twisted into a spiral. The most dangerous of human helminthiases, caused by nematodes entering the body from marine fish, is anisakiasis or anisakidosis. Most often, this disease is caused by the larvae of helminths of the species Anisakis simplex and Pseudoterranova decipiens. Less commonly, the cause is Contracaecum osculatum . Infection of humans by sexually mature helminths has not been recorded.
Adult A. simplex worms, during their normal life cycle, are parasites of marine mammals, such as whales, dolphins, and porpoises, which act as their definitive hosts. And sea lions are the definitive hosts for P. decipiens. When infected, a person acts as an accidental and unnatural host, since the parasites cannot survive inside him for long.
The eggs produced by female worms are excreted from the body of the definitive hosts along with feces into sea waters. The larvae that hatch from the eggs are ingested by marine invertebrates (for example, crustaceans of the family Euphausidae) and develop into third-stage larvae. When crustaceans are eaten by fish or squid (intermediate hosts), the larvae are released and pass through the gastrointestinal tract, and then invade the mesentery, viscera, or muscles. If infected fish or squid are eaten by marine mammals, the larvae are released in the intestines and develop into adults.
People acquire Anisakis simplex larvae by eating raw, undercooked, lightly salted, pickled or smoked herring, cod, mackerel, salmon or squid, and Pseudoterranova decipiens larvae are transmitted from cod, halibut, and flounder.
The most common cases of the disease are recorded in North and South America, Asia (China, Korea, Japan), Western Europe (France, Finland, Great Britain, Sweden).
Cestodes (tapeworms)
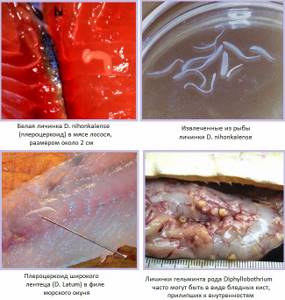
They are in the form of white larvae 1-2 cm long, or pale small cysts. In the human body, these parasites grow several meters in length. Cestodes that can be transmitted to humans from marine and freshwater fish are limited, for the most part, to helminths of the genus Diphyllobothrium.
Infection with cestodes occurs, as a rule, only in countries where fish is eaten raw, pickled or undercooked (for example, Alaska, USA, Canada, Scandinavia, Japan, Chile, Peru, Russia).
Worldwide, at least 13 species of Diphyllobothrium parasites have been recorded to infect humans, with D. latum , D. dendriticum and D. nihonkaiense being the most prevalent.
Diphyllobothrium latum is one of the longest human worms, sometimes reaching 10 m or more in length. It can live in the human intestine for more than two decades.
Immature eggs are released in the feces of the definitive host and must be released into the aquatic environment. Under appropriate conditions, the eggs mature (in approximately 18 to 20 days) and release oncospheres (first-stage larvae) that develop into coracidia (swimming larvae that attract potential first intermediate hosts). After being ingested by a freshwater crustacean, the coracidia develop into procercoid larvae.
After the crustaceans are consumed by a second intermediate host, usually a minnow or other small freshwater or marine fish, the procercoids are released and migrate into the meat of the fish, where they develop into plerocercoids. These larvae are already an infective stage for humans. Since people rarely eat undercooked minnows or similar freshwater fish, they do not represent an important source of infection. However, these small secondary intermediate hosts can be eaten by larger predator species such as trout, perch and pike. In this case, the plerocercoid migrates to the muscles of larger fish and people can become infected by eating it raw or poorly cooked. After ingestion of infected fish, plerocercoids develop into immature adults and then into mature tapeworms, which are localized in the small intestine of the human body.
Trematodes
Although 33 species of digenetic flukes (flukes) have been listed as being transmitted to humans through the consumption of fish, crustaceans or molluscs, only a few of them pose an actual zoonotic threat.
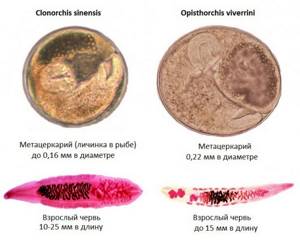
It is impossible to see such larvae in fish meat with the naked eye.
Parasites of freshwater fish that are dangerous to humans are Clonorchis sinensis and Opisthorchis spp . Fish belonging to the Carp family are the main intermediate hosts of these helminths. Clonorchis sinensis is an endemic species in the People's Republic of China, the Republic of Korea, Japan, and Vietnam. Infection (clonorchiasis) is acquired by eating raw, poorly cooked, or improperly preserved freshwater fish. Infection with Opisthorchis viverrini is most often recorded in southeast Asia, in particular in Thailand and Laos, and is called opisthorchiasis.
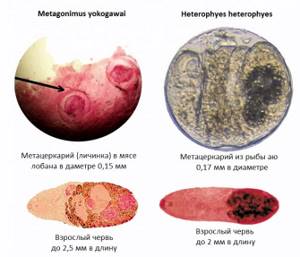
It is impossible to see such larvae in fish meat with the naked eye.
In addition, representatives of the Heterophyidae family are considered dangerous to humans. This group includes small flukes that ultimately live their life cycle in the intestines of birds and mammals. The infective stage (metacercariae) can be found in a wide variety of freshwater and marine fish. The most common pathogens are helminths of the species Heterophyes heterophyes and Metagonimus yokogawai . These parasites, ingested through raw, pickled or improperly cooked fish, often cause heterophyosis and metagnosis in people in the Middle East and Asia, especially the Philippines, Indonesia, Thailand, the People's Republic of China, Japan and the Republic of Korea. The accumulation of large amounts of these helminths in the small intestine can cause inflammation and necrosis.
What do flatworms look like in fish?
Parasites in marine fish are usually found in the stomach, liver, spleen, and muscles. Most often, the worms curl and take the form of a spiral or ring of white or yellow color. The helminth Nanophyetus is pear-shaped, about 0.5 cm long. Also, crustaceans can parasitize marine fish. They make special moves in the muscles that can be seen with the naked eye. At the same time, they create a small transparent capsule around themselves. Any fish affected by worms has a characteristic appearance - small swelling and irregularities.

Lagula-type worms are often found in river fish. Carp fish are most often infected. Also in river fish you can find helminths Dactylogyrus vastator, which lay larvae on the scales and gills. If a fish is affected by trematodes, the lens of the eye becomes dull and may fall out completely. The wide tapeworm is found exclusively in freshwater fish; it can be seen when cutting, as the worm reaches truly enormous sizes - from 10 m.
Is it possible to return an item?
Claims regarding the acceptance of defective purchases are accepted only within the expiration date. Please note the following return cases:
- After the expiration date, you can no longer exchange what you purchased..
- If the product is expired , then it should not be in the store. If this does occur, then responsibility for this rests with the store administration.
- A purchased item in normal presentation cannot be exchanged . If the buyer still wants to return the purchase, then this must be done at the checkout.

Here are some tips on how you can get defective goods back:
- replace them with the same one , but with a normal shelf life;
- replace the damaged product with a similar one;
- return the goods, having received the previously deposited funds for them.
It is important to know! If they refuse to return the money to the buyer, but the receipt has been preserved, then they should contact Rospotrebnadzor.
What diseases do worms carry in fish?
Many fish helminths can cause serious illness in humans, so it is important to know about them and be able to take timely measures. For example, worms in red fish can cause a dangerous disease called nanophyetosis, which is characterized by severe diarrhea and nausea. In complex forms of the disease, anemia appears. This group of worms is characterized by resistance to temperature treatments, so you should pay attention to these varieties of fish.
Diphyllobothriasis
The disease is caused by the broad tapeworm, which lives in freshwater fish. Larvae from fish enter the intestines and from them adults grow up to 15 m. Such a worm can live quietly in the body for several years; there have been cases of parasitism for 15 years. The main symptoms are weakness and nausea on an empty stomach, frequent dizziness, vomiting, unstable stools, and possible skin rashes.
Anisakidosis
The larvae of this worm infect all types of marine fish. Worms provoke the occurrence of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, causing nausea and vomiting. The incubation period ranges from several hours to a week.
Opisthorchiasis
The causative agent of this disease is the Siberian fluke. The size of the worm does not exceed 12 mm; it parasitizes not only fish, but also mammals. Symptoms of the disease appear within a few days after the lesion - the temperature rises, the person feels general weakness, nausea, and vomiting may occur. If infection with opisthorchiasis does not occur for the first time, then the symptoms will not be so obvious, this is the main danger. Self-medication and getting rid of worms using traditional methods are strictly contraindicated!
Clonorchiasis
The causative agent of this disease is the Chinese fluke. It can parasitize fish from the Amur River, as well as water bodies of China, Korea and Vietnam. The main symptoms are fever, vomiting and nausea, weakness and poor health.
Metagonimiasis
These worms are transmitted through freshwater fish - rudd, silver carp, gudgeon, catfish, carp. The worms are up to 2 mm in size and parasitize in the intestines. The disease begins to manifest itself after one to two weeks of infection. A person experiences nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and stomach pain.











