At first glance, carp, especially young ones, have a fairly strong resemblance to crucian carp, but they immediately differ from the latter in their four thick and short antennae on yellow, unusually fleshy lips, almost as mobile as those of bream. These antennae sit in pairs on each side and end in roundish, flat heads. In addition, the carp is thicker and longer than the crucian carp, and is not so high in the back (the height of its body is only twice as thick).
The dark gray dorsal fin of the carp is very wide, wider than that of other cyprinids, and occupies almost the entire back half of the back. In addition to its width, it is distinguished by a very strong sawtooth, jagged front ray. It is believed that this hard ray on the fin serves the carp as a weapon of defense against predators and humans. At least, when you have to grab a carp with your hands, sometimes he manages to very painfully slash the angler with a saw in the palm of his hand or between the thumb and forefinger.
All the lower fins of the carp are grayish-violet in color, the tail is red-brown.
Carp's eyes are golden.
Pharyngeal teeth, located in the pharynx, are present in all carp fish and are used for grinding solid food. They are distinguished by their massiveness. Young carp, two to three years old, are much flatter, wider, humpbacked and lighter than adults. Large carps have an almost cylindrical body.
But both in color and in body structure, carp is subject to numerous and strong modifications. On the one hand, there are varieties with a very elongated, almost cylindrical body, on the other hand, there are carps whose body shape is similar to silver crucian carp.
In central Russia, true river carp is quite rare. Pond carp, a form artificially bred by man, predominates here.
Pond carp differs from river carp in having a darker and greenish color of scales, a wider body, and a sharper break from head to back. But the main difference is their extraordinary endurance and fertility. In these qualities, pond carp is significantly superior to real river carp, which rarely reproduces in stagnant ponds.
There are also special varieties of pond carp, the so-called mirror carp, characterized by unusually large and irregularly located scales. As an exception, there are carps almost completely devoid of scales.
The framed Ukrainian carp is also scaleless. This type of fish is easy to clean.
A hybrid of Galician carp with winter-hardy Amur carp - Ropshinsky carp - is adapted to the harsh conditions of the northern and northwestern regions of our country.
The so-called Central Russian or Belarusian carp is characterized by a high growth rate, produces rich offspring, easily tolerates a lack of oxygen in water and is resistant to diseases.
Crosses between carp and crucian carp occupy a kind of middle ground between the two species and appear in very diverse forms. They never reach a significant size, have antennae like carp, but much smaller or at least thinner, and their bodies are much wider than ordinary carp, even pond carp, and in this respect they are similar to the elongated silver carp. In addition, the gill covers of these crosses between carp and crucian carp are not smooth, like those of crucian carp, but grooved.
Geneticists are working to create colored forms of carp. Currently, blue carp have already been obtained, which are not inferior to their ordinary counterparts either in growth rate or in size.
Golden carps are very interesting in color. Red and orange carps have also been bred in Japan, Java and Indonesia. Such colors were found among individuals of river carp and were artificially fixed to mark selection lines during industrial crossing.
Breeders managed to obtain carp of various colors: dark, light, with a pattern on the back or with an ornament on the head. In nature, the range of carp colors is even richer. In tropical waters you can find purple, white, brown and even emerald carp and carp.
Source: otvet.mail.ru
General information
Crucian carp is one of the most common fish in the world. Only in Spain and France is it very rare to find it. In these countries, crucian carp are bred artificially. In Russia it can be caught everywhere, with the exception of Crimea and Transcaucasia. Crucian carp prefer stagnant water and love reservoirs with a muddy bottom, where they look for food or can reliably hide in winter.
They rarely reach a weight of more than 3 kg, and their body length, as a rule, does not exceed 50 cm. The largest individual caught in history weighed 5.5 kg. The standard version of crucian carp is 20 cm in length and weighs about 350 grams. Crucian carp are usually divided into 2 types: gold and silver. The difference between them is not only in the color of the scales, but also in the shape of the body.
The uniqueness of crucian carp is that maleless populations of these fish are often found in reservoirs. Females simply spawn with related species - roach, bream, tench, carp and, naturally, carp. Fertilization as such does not occur, but the growth and development of eggs is stimulated, which then continue the “female” population.
Carp is considered to be a much more valuable trophy in the fishing community. This fish is quite prolific and grows quickly. With good feeding, weight gain is 6-7 grams per day. The food source is small crustaceans, insect larvae, and worms. A real delicacy for him is grain waste, cake or mixed feed.
In addition to scaly carp, there are many varieties of this fish, which are artificially bred in various countries of the world - mirror (Germany), koi (Japan), Ropshinsky (USSR), etc. Usually, already at the 4th year of life, the carp weighs about 2 kg. The standard sizes are: length 50-70 cm, weight 4-6 kg. However, there are also individuals weighing up to 35-40 kg and above.
Most ichthyologists believe that carp originated as a result of the “domestication” of carp. Its homeland is considered to be China, where carp were bred specifically for the imperial family and nobility, who considered this fish a real delicacy. Then the carp spread throughout Asia, and after some time it came to Russia and Europe. Today it is found even in America and Australia.
Why are carp and crucian carp often confused?
Often, even experienced fishermen, having caught a small carp weighing up to 1 kg, carelessly send it to the fish tank, mistaking it for an ordinary crucian carp.
There are several reasons for this:
- External similarity (body shape, color, scale size, etc.).
- General habitat (still water, reservoirs with muddy bottoms, snags, edges, depressions, etc.).
- Similar bites (puts the float down or moves it to the side).
- The same baits that these fish readily catch (bloodworms, worms, maggots, dough, corn, etc.).
Of course, it is impossible to confuse crucian carp with large individuals or mirror carp. Therefore, what is described above is more typical for small scaly carp and silver carp, which at first glance have several visual similarities.
Learning to distinguish carp from crucian carp by appearance
Regardless of the gear and type of fishing, it is almost impossible to catch crucian carp in Russia that weighs more than 2 kg. Therefore, if you hook a fish that is clearly larger than a couple of kilograms, then it is 99% carp. If it has small antennae, and the scales are smaller and softer to the touch, then you can cast aside any doubts about your catch.
Only small scaly carp weighing up to 800-900 grams can be easily confused with crucian carp. However, it also has significant differences, “suggesting” that the fisherman is looking at a more noble representative of the cyprinids.
First of all, look at the head. In carp it is more prominent and massive. The lips are fleshy and yellowish, quite mobile. The mouth is much larger than that of crucian carp of the same size. All carp have a small hump on their nose. At the same time, the shape of the head is more angular and elongated than that of crucian carp.
A striking distinctive feature of carp is the mustache that extends from the very corners of the lips. In 80% of individuals they appear already in the first year of life. Despite the fact that the whiskers are curly and short, they are quite easy to notice.
As for the body, even in small carp it is thicker and longer. If an angler takes a carp in his hands, he can, without much effort, slightly bend its body. This technique will not work with crucian carp. Its body is denser due to its high back.
Next, pay attention to the dorsal fin. In carp it is longer and has a protruding front ray, followed by a decent notch. The dorsal fin of crucian carp is smooth and even slightly rounded at the top. The tail and lateral fins can also help distinguish between the two lake “brethren”. In crucian carp they are most often black or dull gray in color, slightly transparent in the light. Carp are characterized by dark purple or even orange fins, as well as a tail with a reddish tint.
Many crucian carp also have slight roughness on the gill arches, which are not at all characteristic of carp. They can be easily felt with your finger. Some experienced fishermen note that crucian carp and carp can be distinguished by eye color. If in the closest relative of the carp they are yellow-golden (sometimes copper) with an enlarged black pupil, then in the crucian carp they are cloudy and slightly convex. The color of the carp's body is more saturated: the back is dark with a greenish tint, the sides and lower part are close to yellow.
Carp differs from crucian carp in the number of pharyngeal teeth. In the “noble” representative of the carp family they are more massive and are located in two rows. He has ten of them in total. Five pieces on each side. Crucian carp have single-row pharyngeal teeth, four on the right and left.
Thus, there are many visual signs by which it will not be difficult to determine which of the two fish described above you caught or simply want to buy in the store.
Comparison
Taking a close look at both fish, you can see how different they really are. What is the difference between carp and crucian carp? Any fisherman will say that first of all, there is a mustache. Carp have them, crucian carp do not.
The entire shape and structure of the head of the crucian carp is simpler, without any interesting features. In carp, the contours of this part of the body are more curved due to a certain hump on the nose. The lips of carp are more “presentable”, fleshy, than those of crucian carp.
The carp's body looks elongated and full. This fish is flexible to the touch and can be easily shaped into an S-shape. The body of crucian carp is tall, compressed and not so flexible. It is covered with tougher, smaller and lighter scales than those of carp.
You can also recognize a fish by its dorsal fin. The carp has a distinctive spike on it on the side closer to the head. Thus, the fin line has a notch. The outline of the fin of crucian carp is even.
What is the difference between carp and crucian carp regarding their size and weight? It lies in the fact that carp grow much larger, and the weight of adult carp can be many times greater than the largest crucian carp.
Sometimes novice fishermen confuse two types of carp fish - carp and crucian carp , often not only in appearance , but also assuming that they have exactly the same habits and lifestyle . However, each species has its own behavioral characteristics , which, accordingly, is reflected in fishing tactics .
Either carp or crucian carp
The fisherman needs to know that in our latitudes a hybrid of silver crucian carp and carp is increasingly found. As a rule, it is called carp carp or crucian carp. It was bred artificially, and the number of individuals is easily controlled due to the fact that males cannot give birth to offspring. The hybrid took the best from its “parents” - rapid growth and weight gain, like carp, and resistance to disease, harsh habitat and oxygen deficiency, which is typical for crucian carp.
Carp carp have virtually no whiskers. Young individuals (up to 400 grams) are most similar to the crucian “relative”, but over time this similarity disappears. Adult hybrid fish already closely resemble carp: body shape, size, fin coloring and even behavior. For example, carp spend the winter without burrowing into silt, but simply hibernate at great depths.
Hybrid forms of crucian carp and crucian carp can live up to 45 years. Only their ability to reproduce is essentially reduced to zero. This does not prevent them from being actively bred on an industrial scale, which is especially typical for Europe and America.
Description of the species, habitat and characteristics
To an inexperienced angler, these representatives of the species may seem very similar. In fact, there are significant differences in the appearance, habits and lifestyle of fish.
Golden carp
Common crucian carp (golden) received its name for the characteristic color of its scales, which have a golden tint. The back of the fish is dark, gray or brownish. The belly is always light, although depending on the situation, it can also have a different shade.
This species lives in overgrown reservoirs of Europe and Siberia, and is almost never found in rivers. He can be called a real swamp inhabitant. He is able to survive in truly extreme conditions. In dry summers, when the reservoir dries out greatly, crucian carp burrow deep into the silt, waiting out the drought there. In the same way, it tolerates severe freezing of small lakes in winter, burrowing to a depth of about half a meter. The crucian carp hibernates in this way until the ice melts. For this reason, there are many shallow water bodies where only crucian carp live.
Other types of fish, even if they get into ponds in different ways, alas, will not be able to survive the winter. Even if the water does not freeze to the very bottom, there simply will not be enough oxygen.
Dense thickets of grass or reeds are the home of this swamp inhabitant. The favorite habitats of crucian carp are the border between the grass and the deep slope. It is often found in “windows” among dense thickets of algae. In the thickets, fish find food, a comfortable temperature and shelter from the sun's rays.
Goldfish
Silver crucian carp has spread even wider on the planet. It is found in most of Europe, Asia, and is especially common in China and Japan. It differs from the golden one by having a silvery color on the belly and sides. Currently introduced to India and some countries in North America. Unlike golden crucian carp, it is often found in rivers, where it prefers places without fast currents. For this difference, some fishermen received the name river crucian carp.
In bodies of water with flow, fish feed on caddis flies, worms, mollusks, crustaceans and insects. This species does not like strong thickets, but if vegetation is present, it often stays near it. The color greatly depends on the type of reservoir, the color of the bottom, the transparency and shade of the water. There are individuals of a dark gray color, and in some reservoirs, on the contrary, almost white.
Recommended reading: Perch fish
This species often does not burrow into the silt, but continues to live throughout the winter. This phenomenon usually occurs in reservoirs with a hard, sandy or clay bottom. This is explained by the fact that a lot of methane is formed in silted lakes during the winter. The gas does not have time to pass through thick ice, remaining in the water, making it difficult for fish to breathe. Having buried themselves in the mud, crucian carp fall into sleep, during which all vital processes are greatly inhibited.
Reservoirs with a hard bottom in winter remain quite comfortable for underwater inhabitants. The depth of the reservoir is perhaps of decisive importance. In shallow waters, a lot of greenery always grows during the summer. Dead algae under the ice consume a significant amount of oxygen, while releasing the same methane.
Fish growth rate
Silver crucian carp grows much faster than its counterpart and is a valuable object in fish farms. Having reached the age of two years, the fish weigh up to 400 grams, especially in the southern regions. With age, the weight of individual fish can exceed 2 kg. The whitebait feeds mainly on zooplankton and phytoplankton. The large one eats animal and plant food, and at times does not disdain carrion.
Silver and golden carp have much in common, but there are also significant differences between them. The mass of common crucian carp reaches two kilograms, according to some sources, more. But for the most part, specimens weighing 0.5 kg are considered a serious trophy among fishermen. Despite its extraordinary vitality, this fish grows slowly. On average, at the age of two years, crucian carp weighs about 100 grams. This is a rather small increase compared to other species of the carp family. After another year or two, he reaches sexual maturity.
It often happens that in small ponds with a poor food supply, only small crucian carp live. Moreover, its size seems to be calibrated. The presence of other fish species in the neighborhood can greatly influence the size and abundance of a species. It is known that rotan is a dangerous enemy of crucian carp, actively eating away the young. They hunt for juvenile crucian carp and perch and pike.
Features of reproduction

Crucian carp spawns in water heated to 14-16 degrees, at a depth of about half a meter. The fish rub against various branches of bushes and stems of aquatic vegetation, to which the eggs adhere in strips. The process can take place several times during the summer, or more precisely, during the time when the water is warm enough. At times, crucian carp can spawn even in August or September. This is especially observed in the southern regions, at a water temperature of 15-20 degrees.
We recommend reading: Catching perch on the first ice with a jig
There is an interesting feature in the reproduction of silver crucian carp: predominantly females participate in the process. Of the emerging fry, females again predominate. In some reservoirs, only females spawn. In this case, the eggs are fertilized by other fish, mainly carp fish. These can be bream, roach, carp, carp, tench and others. The egg of a crucian carp carries a double set of chromosomes and does not need to merge its nucleus with the nucleus of the sperm. For the development of the egg, penetration of any sperm into it is required, which is subsequently resorbed.
As a result of such unusual fertilization, hybrid forms of crucian carp appear from time to time. Unfortunately, hybrids cannot continue the race as an independent species due to infertility. In addition, they are limited in growth and life expectancy.
Waterfowl often become carriers of eggs to neighboring ponds and lakes. Thus, they contribute to the natural stocking of even the smallest and most inaccessible reservoirs with fish.
Indeed, how else can one explain the appearance of crucian carp in forest ponds, the size of which can be several meters. In such “puddles” one of the minnow species often lives next to them.
Features of fishing: what is different in the behavior of carp and crucian carp
In its habits, carp are in many ways not similar to crucian carp. In other words, there are a number of distinctive features in his behavior. Every fisherman who wants to catch the lake’s beauty needs to know them.
Firstly, he seems to take the bait with reluctance. In fact, carp are very careful and will never bite, for example, on a hook with corn lying alone on the bottom. Therefore, be sure to add ingredients to the complementary food that will become the main bait. In our case, this is corn grits or finely chopped corn kernels.
In addition, carp try to stay a little away from the place where the bait ball fell. They will swim around carefully and be extremely selective about their food. While crucian carp, on the contrary, attracted by the unusual smell, rush as close as possible to the aromatic bait and feed on everything they see around.
Secondly, unlike a purely schooling fish, such as crucian carp, carp can move both in small groups (about 10 individuals) and individually. It all depends on the weather. For example, in a strong wind, carps are frightened by the excess noise coming from reeds and coastal trees. Therefore, they go to great depths and try to stay alone. Large individuals also lead a solitary lifestyle. When the water is warm and there is a sufficient food supply, even small carp swim separately.
Thirdly, having felt that it has been hooked, the carp will try to immediately free itself from it. With his first jerk he can tear off even the strongest equipment. Therefore, it is important to absorb this blow when landing fish and tire it a little by holding the rod tip tight and giving the carp a little imaginary freedom. For crucian carp caught on a hook, a sharp jerk is almost uncharacteristic. At most, the fish will resist for the first few seconds.
Fourthly, carp have even better hearing than crucian carp. On some fish farms, this fish is called to feed using a bell. Therefore, the fisherman needs to be as quiet as possible, it is best to dress in camouflage, and also use long casting.
Which is better - carp or carp
It is very difficult to say exactly why carp is better than carp and vice versa. If we talk about taste, then in the fishing community it is pleasant to think that carp meat is in the lead over carp. But it is almost impossible to find significant differences in taste. It all depends on the method of preparation. Carp is better suited for frying, baking, stewing, smoking, but carp is better for boiling and salting.

The former are often used for preparing hot dishes, and the latter for cold dishes. The meat of both representatives will go well with mushrooms, vegetables and fruits. An unusual but good addition to fish dishes would be nuts, grapes, and dried fruits. The combination of ingredients makes the taste of the dishes piquant and original.
They react to:

Carp and carp are not the same fish. There are differences between them. Specimens are distinguished according to various characteristics, the main one of which is habitat. You can catch carp in stagnant bodies of water, and carp in rivers and other flowing waters.
Sources:
https://promysel.com/rybalka/karas/kak-otlichit-karpa-ot-karasya.html https://dlyaribakov.ru/karp-sazan/krp-szn-krs.html https://fermer.blog/ bok/rybovodstvo/ryby/sazan/16381-otlichija-karpa-ot-sazana.html
Tips for successful fishing
- Remember that carp and crucian carp are quite weather-dependent fish. They don't like heat or cold. They feed worse during strong winds and bad weather. Every change in weather conditions and atmospheric pressure is perceived negatively. Therefore, it is best to go fishing if there have been no weather changes for more than a day.
- Pay special attention to bait, which should not be very nutritious in order to feed the fish. Its purpose is to attract the inhabitants of the reservoir with an unusual smell and become a harmonious background for the supplied bait.
- The equipment should be strong, but inconspicuous. Any representative of the carp family is extremely careful. Don't forget about thin leashes and high-quality fishing line.
- Be sure to take several baits with you when fishing for crucian carp or carp. This fish is very fickle. If yesterday she was actively catching on bloodworms and worms, today she can only be caught on corn and vice versa.
Let's sum it up
Despite belonging to the same family, the same habitat, common food supply and taste preferences, carp and crucian carp are significantly different from each other. It's not just about appearance, but also about the biological characteristics and specific habits of each of these fish. Every angler should know about them, because otherwise it will be very difficult to achieve a good result.
The next video will talk about fishing for carp and crucian carp:
Source: promysel.com
In terms of its size and importance for all fishermen, regardless of age and experience, carp ranks first among its relatives. The name carp is not of Russian origin; real river or lake carp or carp are very attractive to many with their unusual beauty; they are covered with large dark golden scales. At first glance, carp, especially young individuals, have a great resemblance to crucian carp, but carp is not high in the ridge like crucian carp and crucian carp does not have such beautiful mustaches on its large lips.
The dorsal fin is quite wide, wider than that of its other relatives, it occupies the entire back of the back. Young individuals of approximately two to three years of age are very flatter, hunchbacked and much lighter, while large ones are almost cylindrical in shape. Carp is a very popular fish and I can even say that it is almost domesticated; it has been subjected to numerous and very strong modifications.
In our large country, they are found with an elongated body, like silver crucian carp, which are more similar to crucian carp, can be found most often in ponds of small lakes, but elongated carp are more often found in rivers in the sea or in large lakes. As for real carp, both pond and river, they sometimes reach enormous sizes and live to a very old age, well, if they are allowed to grow and are not caught.
Both carp and catfish can be considered indigenous inhabitants of the southeastern part of our country, in general, places with high summer temperatures and very low winter temperatures; indirectly, we can say that they need high temperatures for spawning and the development of eggs, and their deep winter sleep. Carp and carp begin spawning very late, sometimes later than catfish, tench and crucian carp. If crucian carp and tench burrow into the silt to overwinter, carp, like catfish, overwinter in pits, but if they burrow, then only in ponds and lakes, but very, very rarely. And the carp comes out of its sleep when the ice begins to break in the southern part in March and in the middle of Russia in April, on ponds and lakes towards the end of April.
The first time after wintering, the common carp is inconspicuous and almost does not swim away from its winter camps, but when the water begins to rise, it rises to the top, albeit for a short distance, and when the water begins to flood the meadows, it goes out to spawn and for food because it is very hungry. Their earliest spawning is noticed in the south of the country around the end of April, but in the middle part spawning occurs in mid-May and most even in early June.
The duration of spawning is always different everywhere; it depends on the age of the fish and on the local habitat conditions of the fish. The process of spawning in fish takes place mainly early in the morning, especially when it’s sunrise, and by about twelve o’clock it stops completely. Carp caviar has a greenish tint and does not differ in size from the caviar of ide bream or other similar fish species. Since the main part of young carp hatch in the summer later than all other river fish, and by the end of September they almost stop feeding and go to the reeds for the winter, they grow very slowly the first year.
Fish grow throughout their short life. In small reservoirs with stagnant water, non-predatory fish grow slowly, the food in it is digested more slowly, it eats less and grows slowly, but in rivers and large reservoirs where there is little food and you have to work hard to get it, the fish grow faster, digestion is fast and constant hunger is frequent. In addition, it is necessary to take into account one more factor of the number in certain reservoirs - this is, of course, a small number of predatory fish; the role of predatory fish in nature is much more important than some non-predatory fish. The reason for the rather rapid growth of carp, despite its rather long winter sleep, is its great gluttony and omnivorousness; carp are real pigs among their brothers. The main food of these fish in spring is young shoots of reeds; they also love the eggs of other fish and even frogs.
Where there are a lot of carp, near the reeds in the morning you can hear their chuckling, the carp does not disdain even carrion and feces, both cow and sheep, the latter is considered a great delicacy for it. Large carp always live in deep holes littered with snags; in lakes and ponds, carp gives greater preference to floating islands and sometimes stays in and among reeds; in small rivers it tries to stay under bridges where it is deep near supports.
Source: podcekay.ru
Differences between crucian carp and carp
There are quite a few differences between carp and crucian carp. The most significant difference can be found in appearance. In addition, it would not hurt for anglers to know what kind of habitat this or that species prefers, as well as what the behavioral characteristics are when fishing for each of them.

By appearance
External differences are clearly manifested in fish in adulthood. The maximum weight of crucian carp very rarely exceeds 3 kg, while it reaches a length of up to half a meter. The average weight is about 400 g and up to 20 cm in body length. Carp is a larger fish. Its body weight can reach up to 6 kg, and its length can be up to 70 cm. There have been cases when fishermen caught giant specimens weighing up to 30 kg. Carp has many varieties, such as scaly (golden), mirror, leathery (naked), Ropshinsky, Parsky, etc. If you catch a fish whose weight exceeds 3 kg, it’s definitely a carp.
Smaller individuals can be distinguished by the following characteristics:
- Torso . Crucian carp has a shorter and flatter shape, which is felt well when you hold the fish in your hands. Look at the dorsal fin: the carp has a clearly visible front sharp ray, under which there is a notch. By the way, fish often use the ray fragment to cut the fishing line when fishing. The lateral fins of the crucian carp are dull gray or black, while those of its relatives are pinkish or purple. There is also a difference in the gills - in crucian carp they have a characteristic roughness, while carp scales are smaller, harder and lighter.
- Head . In carp it has a more convex, massive shape, even when they are still very small. A tubercle is clearly visible on the nose. Its lips are fleshy, yellow, and its mouth is larger than that of a crucian carp, and its mobility is much more active. Carp have small antennae, and most individuals have them from birth - by this feature it is easy to distinguish fish at the fry stage. Crucians, on the contrary, do not have mustaches.
- Teeth . If you manage to open the fish’s mouth and count the number of teeth, you will notice that the crucian carp has eight of them, and they are located in one row - four on the left and on the right. Carp have more powerful teeth, located on two jaws, five on each.

Nowadays, in the depths of rivers and other bodies of water, a special hybrid called carp carp is found. It was bred artificially and as a result acquired the best characteristics of carp and silver crucian carp: resistance to disease and the ability to tolerate a lack of oxygen.
By habitat
The habitats of the fish also differ. Crucian carp is one of the most unpretentious species that can be found in any freshwater body of water. The fish thrives in areas abounding in stagnant waters. Ponds and lakes are their element, especially if the bottom of the reservoir is muddy. The mud is a food source for crucian carp, which here obtains food consisting of organic remains and small worms. In winter, it buries itself in silt and thus maintains its viability until spring.

Carp loves warm water and prefers overgrown reservoirs, as well as deep areas with weak reverse currents and a hard or clay bottom. Rarely visits muddy places. In open rivers and flowing ponds, deep holes and ledges become its refuge. In the summer, when the water is warm enough, fish can be caught in deep overgrown pools, where they dive to a depth of up to 5 m. In autumn, the carp swims even further.

By behavior and catching
During fishing, representatives of each species behave differently. It is believed that catching crucian carp is much easier due to its carelessness . Having discovered the bait, the fish rushes headlong towards it and does not refuse anything that swims around. The process is also simplified by the fact that crucian carp swim in impressive schools and almost never stick together alone. During fishing, crucian carp does not make powerful jerks, but simply flounders for several seconds.
Carp behave more carefully in this regard: they take the bait with caution. To catch it, they often use bait in the form of corn kernels or cereals.
Once hooked, the fish will fight to the last. She makes the first strong jerk, which can damage even the most durable equipment. You need to fish it out slowly to allow it to get as tired as possible. Some individuals prefer solitary swimming, while others gather in schools, the number of which does not exceed 10 individuals.
General description of the carp family
The main feature of the carp family is that their body structure completely lacks a stomach, which is why this type of fish is in constant search of food. Cyprinids are relatively large in size for inhabitants of freshwater rivers. The length of large individuals can vary from thirty centimeters to one meter, and the weight of such fish reaches 20 kilograms. In rare cases, specimens up to one and a half meters long and weighing thirty-five kilograms are found. This species of fish lives up to thirty-five years, but length and weight gain occur in the first half of its life.
The body of carp and carp is covered with scales from head to tail, but there are subspecies that have very few of them and are located only in the upper part of the body. The color of the fish depends entirely on where they live, and can be light golden or brown.
Carp and carp have an excellent sense of smell, which makes it possible to detect minor vibrations of bloodworms or other larvae in the water even at a ten-meter distance. The upper lip has two pairs of thick whiskers, which are taste receptors.
The fish's head is round and blunt in shape. The mouth is large, retractable, with fragile lips (if you make too sharp a hook during fishing, they will remain on the hook). The mouth cavity contains teeth, thanks to which the fish can chew various plants and small larvae or insects.
The fish matures for reproduction at the age of four years, with males entering this period slightly earlier than females. For spawning, carp choose places that are rich in algae. When the temperature rises to twenty degrees, the fish begins to spawn. A few days after spawning, the eggs become fry.
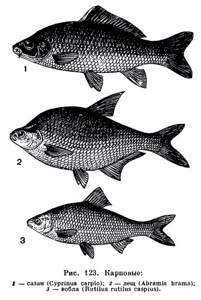
Appearance of carp
Carp is considered the most ancient representative of the carp family. It has an elongated and elongated body, which is covered with large yellow-golden scales. The size of the scales depends on the size of the fish, and the color depends on where the carp lives. The color of the caudal fin is reddish, unlike the rest of the fins, which are grey.
The body of the fish has an elongated shape with a thickening at the head. The body length of the fish can reach a meter in length, and the older the carp, the greater its mass becomes. Depending on the age of the carp, the scale color of the carp also changes, from light to dark.
The dorsal fin, located in the upper part of the body, runs along its entire length. There are also small fins located on the lower part of the body.
Carp is an omnivorous fish and feeds not only on animal food in the form of bloodworms and worms. He also prefers to feed on plant grains that fall into the water after rains or floods. The carp also does not miss the opportunity to eat the eggs of other smaller fish. If the reservoir has an insignificant food supply, then the carp can feed on the fry of small fish. Young carp feed on organic bottom sediments or small plankton.

Types and varieties
Representatives of the large carp family differ in weight, color, and the nature of the teeth on the lower pharyngeal bone ( they are subject to changes depending on the diet of fish that is available in the region of its residence
).
Tribolodon
is the only representative of the genus that can tolerate brackish water; the remaining species live only in continental waters with a wide geographical range.
When talking about carp, interlocutors usually mean several large representatives of the family: grass carp, carp, crucian carp, carp, white and bighead carp. They vary in size, length, weight, and distribution area. Grass carp reaches its maximum length - 150 cm. The fish can gain weight up to 45 kg. The bigheaded silver carp is known for slightly lower indicators. It grows to a maximum of 105 cm, gaining a maximum weight of 50 kg. The smallest fish are considered to be dace and crucian carp. They reach a length of 55-64 cm. The maximum weight of crucian carp is within 3 kg, carp is about 0.50 kg.
Fish has long occupied an honorable place as an important nutritious product in the human diet, and is also a popular decorative species. Among the domesticated varieties, “Goldfish” is common.
Appearance of carp
Carp, unlike carp, has three subspecies, which have their own differences. The common scaly carp has the maximum size of all species:
- Scaly carp have a uniform covering of scales that fit tightly over the entire body. The color of the scales depends on the habitat of the fish and can be light brown or golden. If the bottom of the reservoir has silt, the color will be darker.
- The mirror carp has a significant difference from the usual one; the surface of the body of the fish has practically no scales, and the ones that do exist are located in the upper part of the back. Large mirror carp are smaller in size than ordinary carp and are less commonly found in water bodies. A large specimen of mirror carp may have an enlarged abdominal part, this is due to the fact that there are no scales on the body.
- Naked carp. It is quite difficult to meet this type of carp, as it is considered a rare species. The body of the fish is practically not protected by scales, only in the lower part of the tail or near the gills. This type of carp is considered the least adapted to living conditions.

Scientific classification
Let's start with science. Both fish in question belong to the ray-finned class, the order Cyprinidae. The family is carp, and the genus is carp. However, carp is a species, and carp is a subspecies of the same genus. We can briefly say how carp differs from carp: the first is the result of domestication and cultivation of the second. That's why these fish have so much in common. But despite this similarity, which is manifested in appearance, habitat, and way of existence, these barbels still have their differences.

Habitats of carp and carp
Carp live in bodies of fresh water, but can sometimes be found in places with higher salt levels. Carp are not very picky about the level of oxygen in the water. If we talk about the preferences of fish, then he prefers water with little current or its complete absence.
As for carp, this type of fish prefers water bodies with strong currents and high oxygen levels. For the proper development and growth of fish, the pond must have running water. When a carp lives in a body of standing water, it does not grow to a large size.
According to external data, carp can only be confused with common carp, since both types of fish have a scaly body. If we consider the difference between carp and carp in terms of habitat, then carp loves stagnant water, and the habitat of carp is fast-flowing rivers, which is why it has a more elongated shape.

Differences between carp and crucian carp
The first thing you should pay attention to is the head of the caught fish - in carp it is more massive , larger in comparison with the body than in crucian carp of the same size. Also, the carp has a larger mouth , the lips are fleshy and yellow, and the head itself is more elongated than that of the crucian carp.
The carp has a more elongated, low body , while the crucian carp has a taller body . The shape of the dorsal fin is also different , which in the latter is short and almost even , but in the carp it is longer, the front ray stands out more strongly against the background of the average height of this fin.
On the gill covers of medium and large-sized crucian carp there are roughnesses that are absent in carp. The carp's body is more plastic, flexible - when you pick it up, it is easy to give it an S-shaped bend , whereas its relative has a denser, rigid body .
It should also be taken into account that carp is much more picky about the oxygen content in water, so it practically does not reproduce naturally in small reservoirs with stagnant water , while for crucian carp a low oxygen content in water is not at all a problem in order to reproduce offspring. The latter also has access to same-sex reproduction , during which the eggs are fertilized by other fish species , and only females . This often leads to so-called degeneration , when the average size of the fish becomes smaller . Carp, on the other hand, only require a pair of male and female individuals to reproduce.
Other features of fish
Carp, like carp, become numb in the winter due to low temperatures, and this state cannot be called hibernation; they swim, feed, but the level of activity noticeably decreases. Due to the fact that the fish is omnivorous, it can be fed with any type of complementary food.
Cyprinids prefer to use snags, reeds or holes as shelter. Like the carp, the carp feeds all the time, and everything in a row is used as food. Depending on the temperature of the water in the reservoir, the diet may vary. When the water temperature is less than fifteen degrees, the fish’s diet includes crustaceans, various larvae and bloodworms. When the temperature rises, plant foods appear among the foods consumed.
Looking at the difference between carp and carp in the photo, you can see that the top fish is larger. When fishing for such a specimen, the fisherman has to fight with it for a long time. But when hooking, the carp heads towards the bottom or tries to pull the tackle into snags or reeds, which also creates certain difficulties. Fishing for such fish is a pleasure, and the fight can last about an hour, it all depends on the size of the fish.
Carp and carp are caught using various types of gear. Depending on the habitat, fish can be caught using float, bottom or feeder gear. Many professional athletes prefer to catch this type of fish with a spoon.
In order to determine whether there is carp or carp in a reservoir, it is enough to watch the surface of the water for some time, where you can notice splashes. Carp, like carp, often jumps out of the water, this is the main sign that there is fish in the reservoir. It is worth understanding that the presence of splashes does not guarantee active or passive fish biting. Both species prefer to hide in the shade of trees and are unlikely to be found on the surface of the water, especially in clear weather.
Carp and carp are prey for underwater hunters. Due to the fact that in cold water the fish is inactive, it becomes the main type of prey for submariners with guns.
It seems that it is not difficult to understand the types and characteristics of carp, but often at first glance it is simply impossible to determine what kind of fish you caught, carp or carp. It is known that carp is a domesticated carp, which is why disputes regarding the differences between these fish species will continue for a long time.

Source: winterfisher.ru
What is the difference between carp and crucian carp
What is the difference between carp and carp? A guide for a novice fisherman
Once upon a time, in time immemorial, fishing was a necessity and served people so that they could feed themselves. Today this is a popular hobby that attracts more and more new neophytes.
Sometimes a lot of money and effort are spent on equipment for fishing. But the same amateur fishermen are not always able to distinguish one species or subspecies of fish from another. But after studying its characteristics and habits, you can make sure that the fishing is as effective as possible. For example, what is the difference between carp and carp? The next article will talk about this.












