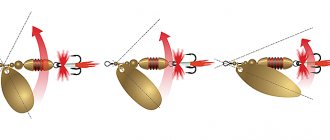
Description and numbering of rotating spinners.
Spinners are one of the most common types of spinning lures, which have been used almost since the first days of the invention of spinning fishing. They are used for catching almost any predatory fish and are very effective for fishing for pike and perch .
This bait in its traditional design is a wire rod around which a metal petal rotates under the influence of water resistance.
It is this rotation, which forms the basis of its operating principle, that gave rise to the name of the spinner – “spinner”. There is a core (weight) under the petal, and a triple hook is usually used as a hook.
It is noteworthy that the spinner does not in any way resemble the live fish that it imitates - not in its appearance, not in its play in the water. And at the same time, such bait is very effective, and in some cases even irreplaceable. The secret is in the powerful hydroacoustic wave it creates.
- Do you want to go fishing, but don’t know where to start, what gear to choose, where and how to fish?
The e-book “Fishing for Beginners” will answer all your questions and will be the best assistant in mastering this activity. More details
A predatory fish notices it with a lateral line located on both sides of its body and capable of picking up sound at frequencies inaccessible to our hearing aid. Moreover, he pays attention to the spinner from afar, since in a dense water environment sound waves are weakly attenuated, which is why they are transmitted over long distances.
Observing the behavior of predatory fish, scientists discovered that the pike, blind in both eyes, is capable of providing itself with food for many years thanks to the lateral line, which serves as a natural radar endowed to it by nature.
The number of the turntable conventionally indicates its size and weight, determined by numbers from 00 to 6 in the following order: No. 00; №0; No. 1; No. 2; etc. up to No. 6. As the numerical value of the number increases, the geometric dimensions of the bait increase. In most cases, the number and weight of the spinner are indicated on its packaging, but many well-known manufacturers of fishing accessories duplicate them on the petal of the spinner.
Classification of spinning lures
According to the nature of the game, all spinning lures are divided into two groups. They are rotating and oscillating . The first group includes fishing lures, the game of which consists of rotational movements around a certain point in its attachment. Oscillating spoons or spinners produce, respectively, oscillatory movements. Despite their different characters, such as rolling, swaying, etc. All this is defined by one term - “oscillating spoon”.
According to their outlines, these artificial baits are symmetrical and asymmetrical.
According to their sizes, they are small (from 20 to 30 mm), medium (from 50 to 70 mm) and large (from 90 to 110 mm).
There is also a division according to the degree of mobility of the spinner . Here the weight of the bait no longer plays a role. It all depends on the thickness. In this case, spinners are also light (0.6 - 1.0 mm), medium (1.2 - 1.8 mm) and heavy (2.5 - 3.5 mm).
Names have also been invented for very small and very large baits. In the first case, these are “fly spoons”, which are used for fly fishing. Lures of the second type, without further ado, were called “especially heavy.” These include all spinners whose length exceeds 110 mm. It is not recommended to use them when fishing with a spinning rod. They are more suitable when fishing on the track.
All spinners were invented to imitate:
• calmly swimming small fish. Most models of rotating and oscillating spinners belong to this type;
• sick fish. It is well parodied by asymmetrical oscillating spoons;
• a fish running from being chased. This is a spinner with increased drag, the game of which resembles yawing around;
• insects. A small rotating spoon bait works well with this type of imitation;
• There are also fancy spinners. They are always brightly colored. There is no question of imitation of anything.
Each type of listed spinners is built according to a specific plan. They are used depending on certain conditions, the fishing season and the type of fish caught. For example, a spinner that imitates a calmly swimming fish is recommended to be used when fishing for pike and pike perch in grassy or snags, as well as among stones or in clear water. A chub standing on a stream under a dam or simply in a rapid stream reacts well to a “sick fish.” The asp really likes “a fish fleeing from a predator.” He also loves “insects”. Fantasy models are used to catch any fish swimming in the upper layers of water. These baits are especially effective when fishing on a sunny day in clear water.
Spinner baits are made from sheet metal, the best of which is copper and alloys based on it (tompak, cupronickel, etc.). Recently, bimetallic metals have been successfully used - iron coated with a thin layer of copper, or less often - tin or zinc. Stainless steel is considered a less suitable material. Occasionally, its soft varieties are used, which do not require additional processing. Aluminum and alloys based on it, due to their lightness, are not used at all.
A significant part of the spinner models were designed according to the spoon principle. As the transverse convexity decreases, it turns into a curved plate. Moreover, transitional models will completely retain their original basis. They differ only in equipment, appearance, surface finish and thickness of the metal used. It is enough to give the spoon an edge, slightly change its shape, otherwise trim the edges, install other equipment, and you can get a new model range of artificial baits that differ significantly in their game and purpose. True, you should know that every change can lead to the appearance of a spinner with radically different properties, which are not always used in fishing.
Happy fishing!
Design features of turntables.
Structurally, the spinner is a fairly simple bait that does not use any complex and cutting-edge technologies. As was already mentioned at the very beginning of the article, everything is very simple - a metal rod is passed through the through hole of the core, and a petal is attached to it using a clamp, rotating around it during movement.
The metal rod is twisted into loops at both ends, to which: on one side the main fishing line is tied, and on the other a hook - a tee - is held.. Between the clamp and the core there is a metal ball and a cone - reflector, which act as a bearing and reduce friction at the points of contact, while the petal is rotating.
There are also turntables that do not use a clamp in their design. In them, the petal is placed directly on the rod through a through hole arranged in it.
Clampless spinners are quite narrowly targeted due to the fact that they have a fixed angle of rotation, but for certain cases related to fishing conditions and techniques, this feature can be considered ideal.
Thanks to its design, such a bait is capable of “starting up” literally from the first seconds of the dive; it does not fall like a stone to the bottom, but calmly descends in a spiral, thanks to the slowly rotating petal that performs the function of a parachute, but provided that the fishing line is free from tension, and the line-layer bracket after The casting point remains open until the bait is submerged.
As a rule, in overgrown places, such as “toad grasses” (swamps), it is very difficult to carry out a full-fledged long-term retrieve, but using a clampless spinner , you can precisely throw it out the window (a place clear of vegetation) and already count on a bite at the first moment of a dive or short-term retrieve .
Another type of rotating spinners are the so-called tandems, which use two petals at once, and the petals have different sizes and rotation frequencies. Also used as tandems is a combined installation of a spinner with a soft bait or fly. Combined spinners - tandems combine the qualities of several baits and are very effectively used for catching large fish, showing themselves most clearly when hunting pike. The most common ways to classify turntables are by the shape of the movable petal and the nature of the load. Let's consider each type separately and in more detail.
Classification of winter spinners according to planning characteristics
Before you begin to consider the various options for wiring spinners, you need to bring all the variety of baits to some kind of structure. Agree, the wiring of a heavy “nail” and the lightest “perch” made of thin tin cannot be identical, although from the outside everything will look like an alternation of strokes, which, in principle, is the basis of any wiring. Since it is impossible to give unambiguous recommendations regarding the placement of even a specific spinner in different environmental conditions, we will focus on general principles, dividing all existing spinners into two types.
The first type includes “carnation” spinners and other lures with similar planning characteristics. Since there are also novice fishermen among our readers, we note that this type of spinner is characterized by the fact that the spinner is always in a vertical or almost vertical position at the moment of immersion. The movement of the spinner away from the center of the hole is caused either by an uneven flow of water around the spinner, or by a slight tilt of the spinner relative to the axis of fall.
The second type includes gliding spoons, which at the moment of immersion occupy a horizontal position, and in this form, with greater or lesser fluctuations, sink to the bottom. Structurally, such spoons are more or less wide and curved plates. Gliding spoons are characterized by a wider and more sweeping action than “clove” type spoons.
Classification of spinners by petal shape.
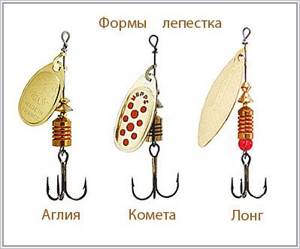
According to the shape of the petal, all turntables are divided into three classes proposed by the famous French company Mepps:
- Aglia;
- Comet;
- Long.
Each type of spinner differs not only in the shape of the petal, but also in another extremely important parameter - the angle of rotation (does not apply to clampless spinners).
"Aglia" pinwheels have a fairly large and convex petal, almost regular round shape, and the angle of rotation is 60 degrees. Such an impressive angle contributes to an equally serious drag of the bait, making it advisable to use surface fishing with it with a dive of 50 - 80 centimeters, as well as using a spoon in still water.
Which is very appropriate when fishing in reservoirs with a lot of bottom algae, snags and other obstacles in the way of the bait. The Aglia spinner is irreplaceable when fishing in the current; due to its impressive tenacity, it allows itself to be carried quite slowly along the watercourse.
Turntables of this type have a high rotation speed, start up with a slight delay necessary for swinging the petal, and work well both on slow and fast retrieves. Most predatory fish are caught well with them, and some species simply adore the high rotation speeds of the spinner, which emit powerful vibrations when retrieved quickly.
Trout spinners are produced with exactly this petal shape and have proven themselves very well when fishing in the upper layers of reservoirs preferred by the salmon family. High-frequency vibrations attract perch very well, which is also not indifferent to spinners with the “Aglia” petal shape.
Turntables of the “Comet” type are equipped with an oval-shaped petal, and its rotation angle is 40-50 degrees. This is an ideal option for fishing in the water column. Many experts consider them to be the most versatile, allowing you to use different types and speeds of retrieve and fish at different depths, both in currents and in still water. Almost any predatory fish can be caught with the Comet; this type of petal can be considered the “golden mean” between its narrow and round shape.
Long spinners have a long and narrow petal, similar to a willow leaf, rotating at an angle of 30 degrees during wiring. This angle and shape of the petal ensures minimal drag and low petal rotation speed. The spinner starts up very quickly and works well with a slow retrieve even at the petal stop limit.
“Longs” are well suited for fast water, held in the current, and also used for bottom fishing. Spoons for pike perch, which prefer to hunt closer to the bottom, have a typical petal shape; pike also do not ignore the low-frequency vibrations of the Longs’ petals.
Basic parameters of spinners
This is your first time picking up a spinner. What to expect from her? How to apply it correctly? What is it made for? What kind of fishing is it best for? It is quite difficult to answer all these questions at once. Spinner baits are very versatile. Their diversity is great, and no two fishing days are the same. Therefore, to give strict recommendations, to put it mildly, is incorrect. We will try to analyze the main parameters of rotating spinners, taking into account which, with at least minimal experience, it is quite easy to navigate the choice of one or another bait.
Petal rotation angle
This parameter is key, since the behavior of the bait in the water depends on it. A spinner with a small angle of rotation of the blade (30 or less) produces weaker noise, has less drag and, therefore, low “buoyancy”. It works great both in calm water and in currents, when moving both at an angle to it and against the stream. Such spoons most often imitate small, narrow-bodied fry. Quite often they are used in the bottom layer of water and can be equipped with an additional head weight or an external weight. An example is the Aglia Long model from the French company Mepps.
Basic parameters of spinners
A spinner with a medium blade rotation angle (about 45°) is universal. Such baits are equally good for all types of wiring. They work both in calm water and in currents, and in this case its advantages over other types of “spinners” are especially obvious. The fact is that such a spoon “holds” the stream, and when fishing against the current, it “rests” quite strongly and rises slightly with the flow. In strong currents, it can be used to fish for drift and even “expose” it on the stream. When moving along the current, the spoon does not stick, the petal works stably. Both fry and insects can imitate bait. The most obvious example of this type of spinner is the Comet model from Merrs.
Spoons with a large rotation angle (60° or more) are the noisiest and most stubborn in the water. High drag allows the bait to pass at a depth of only a few centimeters. In a stream, such a spoon goes high, quickly drifts, and when cast against the current it resists very strongly. But at the same time, it works better than others for demolition and at one point. Even the smallest baits of this type are capable of attracting a predator from a great distance due to the intense sound. These spoons imitate both fry and insects. An example is the Aglia model from Mepps. How can you determine the angle of rotation of the bait at first glance? The answer is simple. The narrower the petal and the more elongated its shape, the smaller the angle of rotation will be. The petals, close in shape to an oval with a size ratio of 1:2 along the axes, rotate at an angle of about 45°. Rounder petals have a rotation angle close to 60°.
Lure weight
The next important parameter of the spinner is its weight. The lighter the spoon, the higher it goes and the closer it flies. The weight of the spoon must be considered in combination with its main characteristic, that is, the angle of rotation of the blade, as well as its geometric dimensions. The more compact the bait is at the same weight, the further it flies, the deeper it goes, and the less it rises in the stream. At the same time, baits with a narrow angle of rotation of the petal go even deeper and fly the farthest, while those with a wide angle do the opposite. Based on this, it is necessary to choose bait for specific fishing conditions. For example, if you are fishing on a river with a strong current, the object of fishing is grayling, which prefers small spoons, and today it is standing at the bottom, then you will need a compact bait with a narrow blade and a weighted core. For example, the Toni-Z or Agat model from the Swedish company Myran. For fishing in a shallow overgrown bay when hunting for perch or pike, the classic Aglia with a wide blade rotation angle and high “buoyancy” will be optimal. And for reconnaissance in force on a river replete with a wide variety of conditions - streams, creeks, bays, a universal version such as Comet from Merrs, or Colonel from the German company Balzer, is best suited.
Petal rotation frequency
An important characteristic of the spinner is the rotation speed of the blade. The intensity of the noise emitted by the spinner and its frequency spectrum depend on it, as well as on the angle of rotation. The blades with a high rotation frequency have proven to be very attractive for perch, chub and grayling when fishing in shallow depths and strong currents. Slowly rotating petals suit the taste of pike, pike perch, catfish, and ide when fishing at significant depths and in calm water. But there is no strict pattern here; sometimes everything happens exactly the opposite. The rotation speed of the petal depends on its mass (thickness, type of metal and size), as well as configuration. Narrow thin petals rotate fastest. The slowest ones are the wide and thick ones.
Spoon color
Any fisherman is well aware that fish distinguish colors and react differently to them. That is why the color spectrum of baits produced in the world is very wide. If you look into the angler's holy of holies - a box of lures, you won't see any colors. Here you can find silvery baits that look like fish fry, and bright fancy baits bursting with orange or lemon color, and speckled black ones, and mother-of-pearl ones - your eyes will run wild. How to choose the color of the bait and why is there such a variety of colors? It is simply impossible to answer this question unequivocally. There is a saying - there are no comrades according to taste. It’s the same when fishing - today the predator prefers a silver one, tomorrow a copper one, and next time a red one, a color unlike anything else. Nevertheless, I will try to give some advice.
All colors can be divided into imitating and provoking. The first ones are designed to imitate natural food sources as accurately as possible: fry, larvae, insects. The latter affect the visual perception of the predator, provoking it with its brightness to attack, although objects of this color do not exist in nature.
How to choose the color of the bait and not make a mistake? The old rule - in clear weather to fish with dark lures, and in cloudy weather with light ones - does not always apply. Once on the shore of a body of water, pay attention to the transparency of the water. If the water is clear, start fishing with simulating colors, choosing as the object of imitation the most characteristic, in your opinion, predator prey in a given body of water. For example, if the reservoir is replete with verkhovna or roach, silver colors work great. In ponds and lakes with dark but clear peat water, yellow and copper spoons that imitate crucian carp or tench have proven themselves well. At the same time, in clear sunny weather, beware of bright polished sparkling spoons, and during rain or fog, even mirror chrome can work.
In summer, when hunting for insectivorous fish (chub, ide, grayling, trout), imitations of beetles and mayfly larvae (Comet Black Fury or Bug from Mepps) give excellent results.
If experiments with imitating colors do not give results, try switching to provocative ones. Sometimes they unexpectedly bring amazing results. So, more than once I caught pike in peat reservoirs with bright lemon or orange-carrot-colored spoons, while there were no bites at all with ordinary metallic colors.
Early in the morning, when hunting for pike perch on rocky ridges and sandbanks, poisonous green baits helped me out more than once. I don’t know what the pike perch liked so much about the green baits, but it attacked them greedily.

The holographic colors are especially worth highlighting. Shimmering with all colors, they work both as imitators (the shine of natural scales) and as provocative. “Holographs” can be used in a variety of conditions - in clear and muddy water, in sunny weather and in rain. Many spinners consider the repeatedly tested and proven holographic baits to be especially catchy.
When fishing at great depths, it is necessary to take into account that when the bait is immersed to a depth of more than 5 m, the colors change. So, red becomes brown-green, yellow - brown, silver - dark gray. And at depths greater than 10 m, only blue and green colors are distinguishable. These are the colors that Finnish fishermen most often use when trolling in deep lakes.
The color of the bait sometimes becomes a decisive factor in the fight for the catch. This is precisely what explains the widest variety of color solutions in the production of modern baits. By boldly experimenting with the color of the bait, taking into account the characteristics of the chosen reservoir and the objects of your hunt, you will certainly achieve success.
As you have already noticed, all parameters of spinners are interconnected. Only their combination determines the behavior of the bait in the water and its catchability. But learning to navigate this issue is not difficult: everything comes with experience.

Share
Classification of rotating spoons according to loading method.

front-loaded rotating spoons - the load is placed in front of the blade. The location of the load in the design of the spinner quite seriously affects its behavior in working condition and requires a special approach and different wiring methods.
Front-loaded (jig) spinners have a fixed or removable weight. They are often called unloaded spinners, because the removable design of the weight allows you to use the spinner without it. Front-loading spinners are very well suited for fishing in deep water, and such a spinner begins to play already when immersed and is used with a wide range of retrieves, including stepped ones. Such turntables fly a fairly decent distance and work perfectly at different depths, in the middle and lower horizons, which is also their advantage.
Back-loaded spinners are considered the most common and popular; they can be recommended for beginning spinning anglers to master this type of bait. Of course, they are inferior in casting range to front-loaded spinners, but they fly very well and can be equally actively used both from the shore and when fishing from a boat.
With the right choice of type and size of such a spinner and a well-chosen method of guiding it, you can catch any predatory fish. There are also unloaded spinners, which do not have a core at all, but this is too light and a specific bait - “for everyone.” To use light baits, you need an Ultra rod - a light class with a test of 1 - 7g and a fast action , the handling of which requires certain skills. You can throw light baits far with a more powerful rod using a special device - a bombard , but this is another topic that requires a separate article.
Color of the spinner.

When choosing the color of the turntable, it is necessary to take into account not only the features of the reservoir, which we have already discussed, but also certain circumstances, such as lighting and water temperature. Both factors are directly related to the time of day and weather conditions.
Visibility and water temperature greatly influence the behavior and activity of both predatory and peaceful fish. In accordance with this, when choosing a spinner, you need to focus not only on its size and petal shape, but also on the color of the spinner. The angler's primary task is to draw the fish's attention to the bait and provoke an attack on it. To do this, you need to choose the right color of the spinner and the method of its wiring.
In clean, clear water it is better to use dark, not too “blinding” baits, and in muddy water – vice versa. But even in the muddiest reservoir, I do not recommend fishing with a spinner polished to a mirror shine - it can scare away a predator with its unnatural shine. The spoon should flicker in the water column, and its reflections should resemble the reflection of light from fish scales. In very bright sunlight, a highly sparkling spoon can be lightly smoked over a fire, giving it a slight “tinting” effect.
In general, the choice of the color of the spinners is a little less critical than other types of baits, since the decisive factor for successful fishing in this case is not the appearance, but the hydroacoustics. If you should pay attention to the color of the bait, it’s the color of its core, since, ultimately, the attention of the object of fishing is focused on it. Often, spinners use edges or colored cambric, with a masking hook called a tee.
The color of the core and edge is of particular importance when fishing for certain species of fish that show an interest in certain colors. According to my observations, perch is partial to red, pike perch loves gray and brown tones, and pike prefers white and acidic colors.
Yuri Morgun, Moscow

1. The thickness of the fishing line primarily affects the performance of the spinner! And that means, one might say, the fish are biting. Therefore, it is very important to take this point into account. And depending on the size, type and weight of the spinner, you should select a fishing line of the appropriate diameter. Basically, when winter trolling, I use a fishing line with a diameter of 0.1 to 0.16 mm. I consider the color of the line, especially in winter, to be a significant factor. I try to use options of transparent material or blue, light blue shades. They are less noticeable in winter's cold and usually clear water.
2. The main criterion is depth. Up to 2–3 m I use a vertical beam, and deeper I use a balancer. Another important factor is the size of the expected production. If I'm targeting a small coastal bass, I use a spoon. If I’m counting on larger trophies (primarily perch, pike), then I fish with a balance beam. But for pike perch, in addition to the balancer, the “correct” verticals of the appropriate weight are very suitable.
3. Recently, I have been actively and quite effectively using twisters coupled with jig heads equipped with a blade (see article by V. Matveychikov in No. 12/2008).
Advantages and disadvantages of rotators.
The main advantage of rotating spoons is their simple design, which provides good catchability and makes it easy to repair. A wide range of spinners makes it easier to choose them and the opportunity to purchase high-quality spinners at relatively inexpensive prices. Moreover, if you have plumbing skills, you can make rotating spoons yourself.
It is also worth noting that spinners are in high demand among beginner spinners, since the technique of using them does not require special skills and can provide a good catch. Most experienced spinning anglers prefer this particular bait, because it often catches real, trophy specimens.
There are practically no disadvantages to this type of spinners; the only and easily removable one can be considered the twisting of the fishing line, which occurs due to the rotation of the rod of the bait in the place with its petal and entails the removal of “beards”. To eliminate this kind of trouble, it is enough to slightly bend the tip of the axial rod in front of the petal, thereby preventing its rotation. Also, in some cases, it helps to use braided fishing line, which is less susceptible to twisting, or to use a swivel at the junction with it.
The characteristic features of rotators can in some cases be considered disadvantages, and in some circumstances - advantages.
One of these features is the fact that for the spinner to work properly, nothing should interfere with the rotation of its petal and the movement of the bait itself. This is despite the fact that the turntable itself must be in a mobile state all the time, which is often hampered by its open hooks - tees that cling to everything that appears in their way. Such conditions are not always feasible, for example: when trolling in places with dense bottom vegetation or in reservoirs with a not entirely clean bottom.
The next detail that should be taken into account when using spinners is the need to use sensitive and well- balanced tackle , allowing you to control the condition of the blade. The vibration from the rotating blade is transmitted along the line to the tip of the tip, to the rod itself and to the reel.
By the tip of the whip and the vibrations transmitted to the rod, you can judge the behavior of the spinner and determine even minor fish bites. You can also clearly feel the vibrations of the bait while winding the fishing line onto the reel. -free reel in combination with a fishing rod , you can easily control not only the spinner, but also any spinning lures, if necessary, adding or decreasing the rate of rotation of the reel handle.
You can train and experiment in clear water, observing the lure, measuring and evaluating the behavior of the tackle in different situations, analyzing and remembering how the bait responds to certain manipulations of the rod and rotation of the reel. By regularly practicing watching the lure, over time you will be able to easily judge the position and condition of the bait during fishing and easily control it.
The horizontal arrangement of the hook-tee in the working state of the spoon promotes its engagement, but thereby impedes the passage of the bait and does not allow its use in reservoirs even with sparse vegetation.
General tips on how to catch and retrieve a spoon.
It would seem that there are no secrets in spinning fishing - cast away and wind the line onto the reel. Thinking like this is a big mistake. The correctly chosen speed and nature of the bait's movement affects the fishing result almost more than a precisely selected spinner. Of course, it is simply impossible to give any definite advice on which fishing line to catch this or that fish, there are too many other factors. But in general, you should adhere to several general principles that will help you return home with a good catch:
- The more active the bite, the faster the retrieve and vice versa.
- In cold water the bait should certainly move slowly, in warm water it should move faster, but not necessarily.
- When near-bottom fishing, we maintain a low retrieve speed, almost at the level of the petal stopping. Wiring when fishing in the upper layer of water can be very different and is chosen, first of all, depending on the mood of the fish itself. The ability to catch the mood of a predator comes with time.
- Sometimes, when retrieving, a sharp pause (8-10 seconds) is very effective when the bait is in the upper layer of the reservoir, ensuring the free fall of the spoon to the very bottom. After which you need to lift the spoon from the bottom with a sharp jerk and begin a uniform retrieve. Very often, after a jerk that lifts the bait from the bottom, a pike attack immediately follows. This is explained by the fact that while the bait is falling, it attracts the attention of a predator, who does not dare to attack it, trying to see it. The jerk of the bait, simulating an attempt to hide, serves as a signal for a lightning attack, preempting the flight of the victim.
- The next very effective technique is alternating fast and slow retrieving, using two to three fast turns of the reel handle, followed by two or three slow ones, which in many cases brings good results.
Where it is not possible to fish with rotating lures due to frequent snags, spinners come to the aid of silicone baits - non-snagging baits on offset hooks.
I will be very glad if my articles help you in mastering spinners and spinning rods in general. Happy fishing! Please share your opinions and comments in the comments.
How to choose a lure for pike

When choosing a lure for pike, it is worth remembering that bright baits, which are used in sunny weather, will scare away the predator. In cases where the water in a reservoir is clean but dark, it is advisable to use gold and copper baits. When fishing at a significant depth, the shade of the spinner will fade, and at a depth of 5-10 m, the pike can distinguish only two shades (blue and green).
If an angler has a bad bite, you can use spinners painted in unnatural colors or baits that have a combined color.
Important!
The most catchy are spinners, the color scheme of which is similar to the shade of real fish living in this reservoir.
Spinner size
Depending on what kind of fish the fisherman wants to catch, the size of the spoon should be selected. For small fish, a small bait is enough. If you plan to become the owner of a good catch, it is recommended to select spinners whose length reaches 3-12 cm. It is better not to use longer options.
Spinner weight
The weight of the spoon depends on what kind of tackle you plan to use to catch a predator. For soft tackle, you should choose a light spoon. It is important to take into account that too light baits are carried away by strong currents, so it is advisable to use them when fishing in quiet bodies of water.