The success of jig fishing depends not only on a properly selected spinning rod, but also on equipment, namely such an element as a jig head.
This small metal weight can change the course of even the most elusive fishing! Do you have any doubts? We will prove it. In this article, we will present the most complete theoretical basis with specific examples and tips on what a jig head is, what types they are classified into, we will indicate the important parameters of this element of jig equipment that should be taken into account when choosing a fishing spot, and we will show an interesting video. All you have to do is reinforce your theoretical knowledge with practice!
Content
- 1. What is a jig head
- 2. Types of jig heads
- 2.1 By weight
- 2.2 By material
- 2.2 In relation to the hook
- 3.1 Jig heads with hook and resistance property
- 3.2 Jig heads - non-hooking
- 3.3 Streamlined jig heads
- 3.4 Noise jig heads
What is a jig head
Jig head or the English equivalent of this concept jig-head is one of the types of sinkers used for jig baits when spinning jig fishing.
A sinker is an element of equipment whose purpose is to increase the weight of the fishing line and hook and deliver the bait to a given depth.
Read the most detailed information about monofilament fishing line, its characteristics, installation methods, storage and care here
Thus, a jig head is a sinker that has a certain shape, to which a hook is attached (or not attached). The name “head” appeared due to the fact that the sinker is fixed in the head part of the bait and connected to it into a single structure.
Area of use : all types of fishing with jig baits. The type of fishing rod used is a spinning rod.
Video: catching pike with a spinning jig
Jig fishing is extremely interesting and varied. The angler has the opportunity to experiment in choosing fishing line and equipment, which makes it one of the most favorite types of fishing among anglers.
Views: 677
Similar articles:
- Jig-rig: installation, wiring methods, advantages and disadvantages Just 3-4 years ago, when jig-rig was just gaining popularity, many…
- Catching pike with a jig in the fall How to catch pike with a jig in the fall and where to look for a toothy...
- Catching pike with silicone. The best silicone lures for pike Silicone lures for pike are baits that are consistently popular...
- Fishing for pike with a jig in winter from ice Ice fishing for pike with a jig in winter (the progenitor of which is all…
Types of jig heads
2.1 By weight
According to this parameter, this equipment element is divided into the following types:
- for fishing with nanojig style – weight up to 3 g;
- for microjig fishing – weight from 3 to 7 g;
- light – from 7 to 21 g;
- medium - from 21 to 42 g;
- heavy - 42 grams or more.
This parameter is important when fishing at depth and in reservoirs of different current speeds. Also, the weight of the cargo is determined based on the characteristics of the spinning rod and the size of the future prey.
Examples of using weights under various fishing conditions:
- Standing water and a depth of 2 m - the weight of the head is taken to be 2 or 3 g. The stronger the water flow and depth, the weight of the load must be increased accordingly.
- Depth 6 m with current at a speed of 3 m/s – weight 30 – 45 g.
- Depth 4 m and current up to 2 m/s - weight from 12 to 15 g.
- Large pool and depth from 4 to 6 m - weight from 10 to 14 g.
- Depth from 6 to 10 m – weight from 14 to 20 g.
- Depths greater than 10 m require the use of weights ranging from 18 to 30 g.
Weight is an important parameter that affects the diving speed, depth and casting distance. It is believed that when choosing a weight, one should be guided by the time (speed) of deepening the load, which on average should be from 2 to 5 s. In this case, it is worth taking into account the natural factors of the reservoir and terrain, which can reduce or increase this time. You always need to experiment.
Useful video on how to select weight depending on the depth of the reservoir (author of the “Fishing PRO” channel)
Advice: for beginner spinning anglers, the optimal weight is considered to be sinkers from 1.5 to 3.5 g. This weight should be tested at short distances, feeling the behavior of the sinker in the water. Then choose a sinker with a suitable weight.
2.2 By material
Jig heads made of lead metal have gained popularity in fishing due to their affordable price, availability of the metal itself and ease of processing, which allows any interested angler to easily make such an element of equipment at home. The downside is that over time the cargo begins to oxidize and become covered with a white coating.
One of the ways to eliminate this drawback is offered by the DEEVER channel - fishing with DEEVER
Tungsten - are made not from pure tungsten, but from an alloy that includes this metal.
Advantages of tungsten:
- metal has an advantage in weight category in relation to lead;
- tungsten heads are much more compact than lead ones (if you take each element in the same weight), this affects the casting distance;
- more durable ones, for example, retain their shape when hit by stones;
- good sound animation, which appears when you tap on stones, which attracts fish in troubled water
The disadvantage is the high price.
Sinkers made of brass are used in fishing, but this is not a practical alloy, which, due to its soft qualities of the material, quickly becomes unusable.
2.3 In relation to the hook
Jig heads equipped with a “bait holder” hook are distinguished by the fact that they have a hook in the form of a ring in the upper part of the head structure and a latch that serves as a stopper and has a variety of shapes. The stopper's job is to prevent the bait from falling off the hook. A jig head with a specific shape lock is selected according to the weight, length of the bait and fishing conditions. For example, when microjigging, heads with a spherical-shaped lock are predominantly used or dispensed with without it.
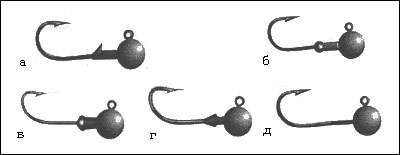
a — a retainer in the form of a “spike” or “needle”; b - “ball”; c - “mushroom” (umbrella); g - “arrows”; d - without lock.
The characteristics of the hook should also be taken into account. So, when catching a large predator, it is better to use hooks made of wire of a larger diameter, and hooks made of thin material are better used in snags, since they can easily unbend when unhooked.
Important! The size of the hook for a jig sinker depends on the specific bait, its size, shape, etc. So, with large baits, large hooks are used and vice versa. You should also take into account the fishing location (a clean reservoir or with vegetation and stones), and the activity (behavior) of the predator. Large hooks allow you to successfully complete most bites, but also affect the number of hooks and vice versa.
Hooks for jig heads can have the following numbering:
- from No. 10 to No. 1, where the 10th number is the smallest hook;
- from No. 1/0 to No. 5/0, where No. 1 is the smallest hook in size.
Important! Different manufacturers number their products differently.
Jig heads with no hook or separate ones. This type of sinker is equipped with two eyes, a hook with an attachment is attached to one (for example, through a ring or directly to the eye), and to the other - a fishing line.
Jig heads with ears are popularly called a Cheburashka sinker. This type of sinker has found its application in microjig fishing and more.
There are other forms of double eye sinkers, such as

When does a pelagic jig work?
There are several conditions and situations where pelagics can be successful.
First - catching pelagic fish
Horse mackerel is a classic pelagic fish that stays in the water column, never sinking to the bottom of the reservoir.
Our, more famous and understandable perch, is also generally a pelagic fish, which often moves in a vertical direction in a reservoir, and therefore there is no point in catching it only with a bottom step. The same applies to chub, ide and, to a lesser extent, pike and pike perch.
Secondly, the fishing location does not allow the use of bottom fishing
The water area or the nature of the bottom do not allow the use of a classic step. These may be significant differences in depth, muddy or cluttered bottom. In such cases, it is better to place the bait at some distance from the bottom.
Non-trivial fishing conditions - the presence of a thermocline, poor lighting at the bottom
As you know, fish stay in the most comfortable zone of a reservoir, most often this is actually the area near the bottom. There the water is more oxygenated and cooler.
However, sometimes the thermocline interferes (area two in the figure). Without going into too much physical detail, this is the area that separates the warm/cold water regions. And, if under normal conditions it is the area of cold water at the bottom that is more saturated with oxygen, then in the presence of a thermocline (most often observed in standing deep reservoirs (less often on rivers with a slow flow) in the summer heat and/or in simply warm weather) cold water near the bottom gradually loses oxygen.
And the fish gradually begins to move to the thermocline region - to its lower or upper boundary, depending on its sensitivity to oxygen starvation. And this is the area of application of pelagic jig, and not the classic bottom jig.
Such areas are well served by a high-quality echo sounder, but not everyone has one. Therefore, “ordinary” fishermen should look for such zones experimentally. Based on weather conditions, fish activity and experience.
The following species of predatory/semi-predatory fish are sensitive to the thermocline: pike perch and sabrefish. Pike and perch are less sensitive.
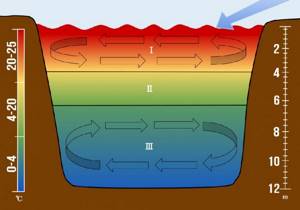
Thermocline (zone 2), warm water rich in oxygen (1), cold water depleted in oxygen (3)
Often it is the pelagic jig that becomes the key to passive pike, perch, pike perch, which wander confusedly around the reservoir, either in search of prey, or in search of cooler water...
This situation was often observed in practice in June-August on small and medium-sized rivers in pike pits. At the bottom, the predator completely refused to take the bait, while when the bait fell or rose in the final stage of the retrieve, active furious attacks followed - the pike itself dictated the timeliness of using the pelagic jig.
The depth does not allow fishing along the bottom
Frequent occurrence in quarries, large rivers, seas, artificial deep lakes. For example, it is not always possible to fish qualitatively along the bottom at a depth of more than 10-15 meters with ordinary tackle, and not everyone has powerful tackle designed for such reservoirs. In such cases, pelagic fishing in the water column will come to the rescue.
It’s not for nothing that the fishermen “road workers” came up with a multi-story path, in which the baits are placed on top of each other at a distance of 1-1.5 meters vertically. Initially - pike perch tackle, but it is successfully used for catching other predatory fish. The same option can be used on a spinning rod by tying, for example, an additional twister on a lead leash above the main bait by a meter and a half. But the aesthetics are lost, and therefore the pelagic jig goes into battle.
Types of hooks
- Jig heads with one hook. Scope of application: microjig. The equipment comes in combination with an eared weight, a pellet on a fishing line when fishing using a leash or without a leash. A special feature of single baits is that they can have from one to several notches on the fore-end, which affects the quality of the bait’s attachment.
- Jig heads with doubles. This type of sinker is used when equipped with eared weights. Typically, doubles are taken with a long fore-end for ease of mounting the bait.
- Jig head with offset machine. An offset hook is one that has a certain shape on the bend of the fore-end. Such hooks are good for creating rigs with “non-snag” baits. They are used when fishing in snags and grass. Offset hooks can also be used in conjunction with an eared weight.

Read everything you didn’t know about the retractable leash here
Tips for choosing a jig sinker
- For fish, a bait that lowers slowly during the pause phase of the retrieve is more attractive, so the weight of the head weight should be as small as possible.
- The less the load weighs, the fewer snags there will be!!!
- The jig head should allow the bait to sink to the bottom so that the fisherman can feel it with the tackle.
- Remember that not only the sinker has a certain weight, but also the bait itself with the hook, as well as accessories that can be used in the case of installation using an eared sinker or a “bullet”.
What are balanced and unbalanced jig heads?
Any jig sinker is equipped with a ring. For balanced heads, such a ring is located in the central part of the load, which allows you to hang on the thread in a horizontal position. When retrieving, at the moment of reeling, the fishing line bends slightly forward, and when stopping, it immediately rushes down. This is convenient for stepped wiring style.
Unbalanced - when reeling in, they swim horizontally, and at the moment of a pause they slowly sink. It is better to use such weights when fishing in shallows with long casting and a uniform fishing style.
useful links
https://spinninglive.com.ua/elementyi-spinningovyih-osnastok/svinets-protiv-volframa-v-lovle-dzhigom.html - an article about a comparison of two metals: lead and tungsten. Which is better?
https://ulovmesto.ru/dzhig-golovki/ - detailed article about the types and shapes of jig heads;
https://viktor-andreev.ru/spinning-dzhig-golovki-gruz-golovki-vidy-1105.html - Viktor Andreev about jig heads;
https://ru.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jig head - an encyclopedic article about jig heads.









