There are times when any fish can be caught well in the same body of water. It happens - only white or only predatory. And sometimes you sit or throw a spinning rod for half a day, but there’s no use. How and what is this connected with? Is it possible that all the fish in a pond suddenly conspire and begin to “go on strike”? It is clear that this is nonsense. But still, what determines such drastic changes in the behavior of fish?
Factors influencing biting
In fact, there are not very many of them. Basically, the effectiveness of fishing depends on:
- water temperature - if it is too low, the fish stands still so as not to lose the calories necessary to maintain body temperature; at high levels, it becomes “boiled”, barely mobile, and is forced to go to depths, where it does not always feel comfortable;
- solar activity, or the amount of cloudiness during daylight hours, since in shallow and relatively transparent reservoirs, instead of feeding, fish are forced to hide from the sun’s rays in snags and other shelters;
- the frequency of precipitation, on which the maintenance of normal water levels in the reservoir depends;
- atmospheric pressure (BP), fluctuations in which are the most common culprit for the lack of bite.
How to track barometric pressure
You can track atmospheric pressure in different ways, the simplest and most popular is various applications for a mobile phone, preferably with GPS reference.
Weather forecast with pressure for several days, Screenshot of Yandex.Weather
For a more accurate on-site forecast, it is better to use a simple barometer. They are available in the form of separate devices, built into watches or navigators and show pressure values at a specific point and in real time.

A barometer in a watch measures barometric pressure directly in the fishing areas and at a specific moment in time.
You can track pressure using natural signals:
- clear, sunny and calm skies means high pressure;
- cloudy skies are low pressure;
- the appearance or strengthening of wind means that the pressure begins to drop into the low pressure zone.
Share link:
Optimal pressure for fishing

The best atmospheric pressure for fishing is the pressure that is most common in your area. There are no average indicators, since each region, settlement or body of water is located at a different altitude above sea level. The lower the reservoir is located, the greater the atmospheric pressure will be and vice versa. If we take, for example, the Moscow region, whose average altitude above sea level is 160 meters, the average blood pressure for it will be within 745 mm Hg. Art. At the same time, normal pressure for the Caucasus region (for example, the area of Pyatigorsk), located at an altitude of 500 meters above sea level, will be 720 mm Hg. Art. etc.
How to find out the optimal indicator for your region?
In our age of the Internet, finding out the optimal indicator for your zone is as easy as shelling pears. Just go to any weather website and calculate the average values. Those who are too lazy to bother with such calculations can find a site about their city on Wikipedia, where its location above sea level is indicated, and based on these data, track the average blood pressure using the following table.
How does (BP) change depending on altitude?
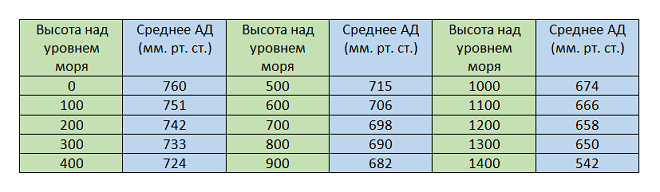
Any fisherman should have a barometer at home, which can be used to track all fluctuations in blood pressure . Those who do not have such a “gadget” in their arsenal can track pressure using readings on weather websites, where pressure is also indicated. If within the next 2–3 days it does not deviate from the norm by more than 3–5 mm Hg. Art., conditions for fishing are quite favorable. Such minor deviations have almost no effect on the behavior of the fish.
Normal atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is usually measured in the following quantities:
- mmHg;
- inches of mercury;
- pascals.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, atmospheric pressure is usually measured in mm of mercury; in other countries, higher number systems may be used.
Accepted average value of normal atmospheric pressure
760 mmHg 29-30 inHg 101.3 kPa
At this pressure, the weather is always good with little or no wind, the sun may be shining, the sky may be clear.
We recommend: How to make a spoon from birch bark
Pressure below 760 mmHg is considered low pressure and is an indicator of bad weather and a harbinger of storms and rain.
If the pressure exceeds 760 mmHg, this means that the pressure is high. And this will lead to the appearance of anticyclones and climate change in the near future.
How do pressure changes affect fish?
But the above does not mean at all that if the pressure is slightly lower or higher than normal, then future fishing is “covered with a copper basin.” Although fish are sensitive to pressure fluctuations, they quickly get used to it if it remains at these levels for a long time.

Barometer
For example, if normal atmospheric pressure for fishing (average blood pressure in the area) is 740 mm Hg. Art., then due to a long cyclone it can drop to, say, 730. Minor fluctuations, which can occur even during the day, are experienced relatively easily by the fish. But from a decrease of 10 points, the fish begin to, as they say, “go crazy.” The atmosphere puts less pressure on the water, causing its density to change. All the location settings that the fish had before are lost in water with changed density, which is why the fish is in such prostration that it has no time to feed. It automatically goes deeper into those layers where the pressure is still at an acceptable level.
The same thing happens with the arrival of an anticyclone. Due to excess pressure, the entire fish floats to the surface until its body fully adapts to the new conditions.

It usually takes the fish 2 to 3 days to completely adapt to new conditions, after which everything returns to normal. But, nevertheless, uncharacteristic, different from the average, atmospheric pressure for fishing has a detrimental effect on the quality of the bite. It is the anticyclone that is especially dangerous . High pressure is usually accompanied by clear skies and no precipitation. If it lasts for a very long time, the level of the reservoir begins to fall, the water warms up too much and becomes poor in oxygen, which is why in many reservoirs, especially shallow and poor in vegetation (that have recently been cleared of algae), some specimens of white fish (crucian carp, carp) may simply start to get sick and die. There, the fish simply have nowhere to hide from the scorching heat and lack of oxygen.
White fish tolerate low pressure more easily, but bite less readily. She waits for stabilization sadly, clumsily and without appetite. For predators, gloomy weather is an excellent time for hunting.
Influence of atmospheric pressure depending on the season

Spring bite
The most wonderful time for fishing is early spring, when the water temperature begins to rise, hungry predators, and most of the ichthyofauna are actively biting on any bait.
The bite may drop due to gusty winds, a sharp drop in temperature and strong pressure surges.
From mid-April, the fish become more picky and willingly bite in light winds and stable weather throughout the day. She is also reluctant to take bait in cloudy waters, which is associated with melting snow.
Summer bite
In summer, when the water rises to more than 25 degrees, the fish becomes apathetic, and its behavior is highly dependent on atmospheric pressure. Cloudy but windless days are considered optimal weather for fishing.
The predator takes bait well on days with short thunderstorms. It is best to go fishing either at dawn or at night, when the temperature is slightly lower than during the day.
Autumn bite
In the fall, as soon as the temperature drops, the fish begin to actively take the bait. For fishing in the autumn season, it is better to choose warm days with light winds.
Pike bite more actively in September on cloudy days, until the first cold, then the bite drops. But carp breeds have low activity in the fall.
Winter bite
In winter, most fish are very susceptible to pressure fluctuations. If it has changed up and down several times in a short period of time, you should not expect a good bite, even if it stabilizes. It needs to stay at the same level for 2-5 days, then there will be a bite.
Whether there will be a bite or not depends very much on the combination of ambient temperature and pressure. So, if in winter the barometer rises by 25-30 mm, and the thermometer drops by 7-12 degrees, you can’t expect a bite.
Also in winter there will be no bite if it drops by 9-11 mm and at the same time the temperature changes. The bite will resume only when these parameters stabilize.
The bite will be good if high pressure is combined with low air temperature, and low pressure will be on days of thaw and mild frosts.
To decide which pressure is best for fishing, you must first decide what you want to catch and then, depending on the season, choose the optimal days for fishing.
Fishing at high pressure

Three days have already passed, the sun is hot outside, we can go. The fish have adapted to high pressure, but you won't catch many of them in the sun. The bite is best in the morning (especially near the shore on a float), so by 4 am we should already be there. It is white fish that manage to raise the most on such days. Predators do not like high pressure, since all prey on warm days becomes more mobile and “hangs out” mainly in the upper waters, into which pike and other toothy guys rarely try to climb, and if they do, it’s more by inertia, in the heat of the chase. At high rates, predators are sluggish and sullen.
But crucian carp, carp, bream, white bream, grass carp, chub and other “herbivores” from their company bite excellently. At least at first. It is better to fish at pressure 3–7 days after it is established. Prolonged high pressure has a detrimental effect on the bite, but not because of the pressure itself, because of the scorching heat that it brings with it and, as a consequence, because of the lack of oxygen, which is a consequence of rising water temperatures.
During periods of prolonged high atmospheric pressure, bottom gear is best suited for fishing. At depth, far from the shore, there are still plenty of moving specimens. The same is advised for those who want to catch bigger fish. These will have to be caught on a feeder. It can be effective even at lunchtime.
Atmospheric pressure and its effect on biting

Natural factors and especially atmospheric pressure greatly influence the behavior of fish. In addition, such facts as air temperature, time of year, water temperature, moon phase, wind direction and intensity, water level and its transparency are of no small importance. 3Despite the abundance of external factors, you should focus on atmospheric pressure as one of the most important indicators.
Atmospheric pressure has a serious impact on human life, and even more so on the behavior of animals and fish. Atmospheric pressure depends on weather conditions, and the well-being of all living beings depends on the level of atmospheric pressure.
Why does pressure affect fish?
Barometer and fishing
Atmospheric pressure only partially influences fish behavior directly. But the indirect influence is exerted by the consequences of changes in atmospheric pressure. As a result of pressure changes, the density of water and the level of oxygen in it changes. But this already seriously affects the behavior of the fish.
The water in a reservoir has its own hydrostatic pressure, which differs from atmospheric pressure, but there is a certain connection between them. If there is a big difference between them, then the fish loses orientation, its appetite decreases and lethargy appears. In such conditions, the fish may refuse any bait.
What atmospheric pressure activates the bite?

The best bite can be observed in conditions where atmospheric pressure has stable parameters for several days, or even weeks.
Increased atmospheric pressure also has a positive effect on biting, but only if it is stable.
The worst conditions for fishing are pressure drops and low pressure. Although not all fish species react equally to such changes. Increased pressure has a positive effect on small fish, which move to the upper layers of water in search of food. When pressure is low, predators become more active. Small fish become lethargic, so predators spend less effort and energy in search of food. With low pressure, you should not count on biting small fish, but you can catch large fish.
Effect of pressure on fish air bladders
Inside each fish you can find an air bubble, inside of which there is oxygen, nitrogen and some carbon dioxide. The bubble is provided by a mixture of gases as a result of the work of a small gland called the red body. But since there is little blood in the fish, the process of gas entering the bladder is not very active.
The air bubble provides neutral buoyancy for the fish at any depth, so it can easily move along any horizon. As a result of pressure changes, the fish has to additionally adjust the gas concentration in the air bubble, which takes a lot of the fish’s energy. In such conditions, the fish simply lies on the bottom, without making any adjustments and waiting for the atmospheric pressure to stabilize.
The fish's air bladder is directly connected to the lateral line, which helps it navigate through the water. If the pressure is not stable, the movements of the fish are also unstable: it is simply lost in space and has no time for food, because it is busy with its own problems.
Fishing at low pressure

If you are wondering which pressure is better for fishing - high or low, the answer will definitely be high. But only if you are going to hunt white fish. If you are following predators, it is better to fish at pressure below normal. At such a time, the entire white fish brethren are sluggish and clumsy - just a paradise for pikes, perches and other predatory underwater “beasts”. Well, when paired with small fish, predators also take lures very well, and their pickiness for some special varieties drops significantly.
How does the bite depend on the weather when fishing for carp and other fish of the carp family?
Home > Fishing techniques > How does the bite depend on the weather when fishing for carp and other fish of the carp family

Carp is very sensitive to weather changes. It immediately comes to mind that it is impossible to predict the behavior of carp. In fact, if you carefully break everything down, you can draw certain conclusions based on all the factors.
One of the important factors affecting the fatty activity of carp is the amount of oxygen in the water. And its quantity is related to atmospheric pressure. The content of dissolved oxygen in the surface layers of water increases if atmospheric pressure increases.
While fishing, many people have noticed how on a clear, sunny day (when the pressure is high), schools of crucian carp in the pond rise to the very surface and stand almost motionless for a long time.
Carp is no exception. This behavior is also typical for carp in those reservoirs where oxygen is in short supply. Well, firstly, these are oxbow lakes, and secondly, they are low-flow lakes, rivers in which the current is very weak. In hot weather, the air is usually well heated, the pressure is high, and, as we were taught in the physics course, when the air temperature rises, the oxygen content in it decreases. This is also true for water. That is, when a lack of oxygen begins, the carp moves to the surface layers of water or to the shallows, densely overgrown with reeds, reeds, etc. The oxygen released by these plants during the day creates a very favorable zone of the reservoir.
Several times I tried to wade through the jungle of reeds and reeds, to see large carp at a depth of 30-40 cm. But as soon as you make one careless movement, they disappear with lightning speed, leaving behind a small whirlpool. Small carp weighing 250-300 g are less careful, so here you can already count on success. In such cases, you need to use a short 3-meter rod, a fishing line of about 0.2 mm. The reel is better to be inertialess, and the hook is number 5 or six. But if you are baiting maggots, then the tackle must, of course, have a sinker. The best option is to hang the smallest pellet at a height of 40-50 cm from the hook. At such depths (about half a meter), the use of even light floats camouflaged to match the color of the surrounding environment is unacceptable.
On a clear, sunny day, a short green “goose” in the shallows scares away fish. The tactics for fishing without a float are as follows: sitting in the reeds or reeds, I attach the bait and quietly approach the water. You should try not to stick the fishing rod too far out of the reeds and cast it along the reed thickets. The mass of the attached pellet is enough to cast it 8-10 m.
With this kind of fishing, a light shot falls to the bottom, and bait, for example, maggots, sinks quite slowly. If the amount of oxygen is sufficient and the carp is feeding, the bite will follow immediately. You will immediately feel it, as the line will be pulled to depth.
This method can even catch rudd, which drags the bait, on the contrary, into the coastal grass.
If we are fishing on a crust of bread, we can cast the tackle without a sinker. First you need to quickly lower the bread attachment into the water and pull it out. As a result, the weight of the bread crust increases and it is enough to throw it 8-10 m.
But when the pressure is low and the weather is cloudy, the carp behaves completely differently. The amount of oxygen in water decreases primarily near the surface of the water. And in order to compensate for atmospheric pressure and in the swim bladder, the carp is forced to go to depth.
On rivers these are usually holes near the fairway, and in lakes these are the deepest holes. Again, fish nutrition depends on the persistence of the low pressure period. If the pressure is low for more than 3-4 days, then the carp gets used to such weather conditions and begins to feed again, so you should look for it at depth.
The behavior described above is true not only for carp, but for almost the entire cyprinidae family - bream, crucian carp, roach, ide, etc.
Many aquatic organisms are a real barometer, predicting a rapid change in pressure and the associated movements of fish.
Haven't you noticed? - like invertebrate mollusks, bivalves and mussels, when pressure decreases and usually worsening weather, they crawl into deeper parts of the reservoir. And, conversely, with an increase in atmospheric pressure, pearl barley tends to run aground, and pearl barley can sometimes float on the surface, clinging to some aquatic plant.
Wind also has a significant impact on the behavior of carp. In the countless channels of the Volga delta, the mouth of the Don, the Syr Darya, where with the wind from the sea the water quickly rises and at the beginning the lowest banks are flooded, the favorite places of both medium and large carp.
In my practice there was the following case. I was fishing in one of the Volga rivers. Although the banks were densely overgrown with reeds, I managed to find an area where I could cast a feeder and fish with a float rod. The channel was about forty meters wide. A fairly strong current constantly carried the float away. The bite was bad - there were small roach the size of a palm. In the end, I got tired of constantly casting the fishing rod, and I set the depth to 70-80 cm, about 2 m from the shore and 1 m from the feeder. The bait was 5-6 maggots. Now it was possible to calmly admire the surrounding nature... The wind swayed the reed panicles in the blue sky, on the opposite bank dry grass rustled and invisible birds squeaked, and flocks of fry scurried almost at their feet in the sun-warmed shallow water.
Only then did I notice that the water was rising. Gradually I had to retreat further and further. Fortunately, there was a small hillock nearby, on which I settled down, spreading an armful of dry reeds...
At about eleven o'clock, when the sun was almost at its zenith and the heat was rising, the float, jumping a couple of times, energetically moved into the depths. I hooked and carefully brought half a kilo of carp into the landing net. Then another and another. An hour later, there were already seven fish of approximately the same weight flopping around in the cage.
The thought flashed through my mind that it would be nice to change the hook and use a larger one. But then the float’s antenna was slightly sunk, so cleverly that it was barely noticeable.
I hooked and immediately realized that a serious fight was brewing! First of all, the carp pulled into the middle of the channel, so all I had to do was adjust the reel brake.
I wasn’t worried about the leash—the 0.16 mm “braid” wouldn’t let me down, but the main line with a diameter of 0.25 mm was a cause for concern. And most importantly, hook No. 6 was clearly too small.
Meanwhile, the fish moved up against the current and took about 50 m of fishing line. Finally I managed to stop her. Then the carp changed tactics and quickly moved to the opposite bank, trying to escape into the reeds. But he stood tightly, evenly, like a wall. In the middle of the channel, the carp apparently rested its “snout” on the ground. Meter by meter I brought him to the shore and then, finally, I saw him: as fat as a pig, he was 6-7 kg. Here he rested again... The rod was arcing, the line was at its limit, but he couldn’t budge. Finally, the carp made his last attempt in the fight for life - he instantly turned around and walked along the reeds downstream. Then I realized that I had lost “close” contact with him. Rybina managed to entangle the forest in the grass...
A couple of minutes later I was already pulling out the tattered line. Of course, there was no leash with a hook.
After some time, I managed to catch a couple more small carp, but by evening the water began to subside, and there was not a single bite in the coastal zone.
There is a semi-anadromous carp, which enters river mouths only during spawning. It gains weight in the sea, in highly desalinated areas. It behaves somewhat differently in low winds from the sea. Such a carp often comes out to shallow areas of the sea overgrown with sedge adjacent to the mouth of rivers. Locals call this zone “kut”. In a warm wind, such a carp often bites in the vast “windows” of coastal vegetation literally at a depth of half a meter.
On the relatively small rivers of central Russia the picture is approximately the same. I had to catch carp in many places. For example, Belaya Kalitva. This is a small river, in the floodplain overgrown with impenetrable thickets of reeds and reeds. Carp is often found here. It lives mainly in holes or thickets inaccessible from the shore.
According to my observations, with a stable southern wind, when the water rises by 30-50 cm, the largest specimens most willingly stay in the coastal zone, of course, in areas of the river rarely visited by fishermen. The current in Belaya Kalitva is very weak, the bottom is muddy-sandy, and silted in the reeds.
I witnessed such a case. At the edge of the reeds at a depth of half a meter, early in the morning large rudd and carp up to 400 g were biting well.
The water level was 20 centimeters above normal. Usually I drive a pole with notches at the fishing site, on which I determine the water level and, accordingly, the fishing strategy.
Carried away by the excitement of the bite, very close by I suddenly heard such a splash... as if a person had fallen into the water. But what kind of people are there? Unless there's a herd of cows a kilometer away.
Leaving the fishing rod and hiding behind the reeds, I began to observe. We didn't have to wait long. About twenty minutes later the handsome carp jumped out of the water and plopped sideways onto the water like a pancake. Compared to the carp I caught, he looked like a giant. The depth at which he “walked” was a little more than 40 cm.
When there is a “miner”, a wind that drives water into the lower reaches of large and small rivers, the carp moves away from the shore and looks for the deepest areas, usually these are holes in the fairway.
But as often happens without exceptions, but in general, by the direction of the wind, and therefore by the water level in the rivers, you can easily judge where to fish today in the coastal zone or, conversely, in the depths.
Quiet, hot days are the weather in which the carp is passive. First of all, these are oxbow lakes that have lost connection with the new channel, stagnant or weakly flowing lakes in the absence of abundant springs.
As I already said, as the water temperature rises, the oxygen content in the reservoir drops. Calm weather makes the situation even worse. Excitement, on the contrary, stirs the water, slowly enriching it with oxygen. But if low atmospheric pressure persists for quite a long time, this aggravates the situation. It’s a paradox, but even in summer, death is possible. I encountered a similar situation in the summer in the Kursk region near the Seim River.
The weather was stifling and windless. The temperature rose to 34-35 °C during the day, and decreased very slightly at night. It seemed like a thunderstorm was about to break out.
Day after day passed, but nothing changed. In such weather, elderly and weather-dependent people feel unwell, as there is a clear lack of oxygen in the air. Pisces are no exception.
Walking with a fishing rod early in the morning, I came to a small, shallow quarry. Its entire surface was covered with “green stuff,” which is what fishermen call blooming microscopic algae. And then I noticed that in many places (near the shore, at the bottom) there were dead carp, roach, and bee-eaters.
Later, I asked a local resident if anyone had released poison into the quarry, but received a negative answer - it was a typical fact of summer death.
It’s good that in the steppe regions of southern Russia such weather conditions very rarely develop. It is better to let a weak wind blow, which, due to the open area, enriches such bodies of water with oxygen.
As a result, in persistent hot weather, any wind always improves the bite. During such periods, the time of day does not significantly affect the diet of the carp. I give the following example. I arrived at a small lake connected by a channel with the Northern Donets late, somewhere around noon.
Many fishermen have already gone home with insignificant catches - with one or two, maximum four small carp. There was a fairly simple explanation for this: the weather was hot, windless throughout the entire July week, and there was plenty of natural food in the lake. Moreover, many fishermen dumped bait into the water almost in buckets, caring little about its quality. I also had a feeding place in a secluded corner among the reeds.
The surface of the lake was smooth as a table, only occasionally small roaches left circles somewhere in the middle.
Meanwhile, the weather began to change - a north wind blew, cirrus clouds appeared. It was decided to change the strategy - to look for fish not in the baited area, but to head to the southern “bald” shore, where no one had ever fished, the reason for which was the bare, sandy-clay bottom. Not a bush, not a blade of grass. Having thrown a piece of cake as bait, put a bunch of maggots on the hook and made myself comfortable, I began to watch the float. The depth was about 1 m, the water was muddy.
About 15 minutes later the first roach was caught. Then the second one. A decent wave shook the float from side to side, but could not nail it to the shore - it was held in place by a solid five-gram weight.
Finally, the long-awaited sharp bite! I hook a decent carp, then a second, a third...
On the way home, I met a fisherman I knew. He saw my catch - 10 thick golden beauties from 700 g to 1 kg. Questions rained down: “How?”, “Where?” To tell the truth, then I hid the essence of the matter from him, let him guess for himself.
In calm, warm weather, good signs of biting are the south, southwest and west winds. Although, this is true not only for carp, but also for all carp. But with a cold north wind (if there was no heat before) the bite is the worst.
Water temperature is another important factor influencing the feeding intensity of carp. The range of 21-27 °C is optimal. But with sharp fluctuations, for example, with a sharp temperature of up to 16-17 ° C, the carp feeds very poorly. At such times, he goes to the deepest places. Here you can seduce him only with a very tasty bait.
In the autumn, when the temperature gradually decreases, the carp moves little, it bites even at a water temperature of 6-8°C. Here, both the quality of the bait and its quantity, and of course the bait, play a decisive role.
Carp can also be harvested in winter, but we will talk about this later. Many people believe that in the spring, just before spawning, the carp bites very poorly or does not bite at all, since the water is still cold. But, based on my experience, I can say that this is one of the best biting periods, albeit short-lived.
In spring, its zhor appears at a water temperature of 10 ° C, and sometimes at 8-9 ° C. The whole question here is where to look for carp.
Once I was fishing in April. The ice had already melted, and although the sun was hot, the water was still cold. At first I tried fishing at depths of 6-8 m. To no avail. Then it was decided to move to a shallow bay, densely overgrown with last year’s reeds.
What a striking picture was revealed to me - life here was literally in full swing. The fish, hungry during the winter, rushed to the sun-warmed shallows. You didn't even need bait!
Roaches and carp were greedily taken for worms, maggots, and shit. When making long casts, you just had to be careful, because the depth under the boat was a little more than 1 m.
The reasons for the concentration of fish in shallow waters are very simple - the water here is cleared of turbidity faster, warms up easily, all this has an optimal effect on the development of organisms and plants in the water. Therefore, in such places in the spring the best carp feeding grounds are located.
In addition to all of the above, rain and its character affect the carp’s bite. If it has been drizzling for a long time and it has become noticeably colder, the carp’s bite is usually very weak or absent altogether. But in warm rainy weather with periodic clearings, when the sun peeks out from behind the clouds every now and then, carp can fish very well at shallow depths of about 1-1.5 m during the day. People called such rains “mushroom rains.”
Atmospheric pressure is slightly increased during such periods. The carp runs aground. It bites well even after a warm downpour, provided that it has not become noticeably colder.
This is very noticeable in rivers with steep banks that are easily washed away. After rain, the water is quite cloudy, but this is not a hindrance for the carp.
Once I was fishing on the Volga. In the afternoon a terrible thunderstorm broke out with heavy rain. It was difficult to stand on the slippery bank: muddy streams of water mixed with pieces of clay flowed into the river
Having withstood the onslaught of the elements, I decided to continue fishing, but to use dung worms rather than maggots as bait. Why worms? I reasoned something like this: the rain washed out the banks, which means a lot of animal and plant food got into the river. The carp should approach the shore. But how will he find the bait in muddy water?
First of all, due to the sense of smell and sensitive cells of the lateral line, which perceive the slightest hydroacoustic vibrations. But who creates them more? A maggot that quickly dies in water, or a worm? The answer is clear.
My guess was confirmed, and in the end I ended up with a catch. In general, the existing opinion that fish do not take well in muddy water due to clogging of the gills is quite controversial. In the estuaries of Azov, when the wind blows from the sea, the water is very muddy, the color of coffee, but the fish (catfish, carp) are great.
I have seen this in practice, and local residents confirm this.
I know of one river where sand is washed nearby and dumped into the water every single day. Nevertheless, the carp takes it, and not bad. And in the surf zone of many lakes with loose soils, the water becomes very cloudy, but the fish come here and actively feed.
Apparently, fish have certain physiological characteristics that allow them to adapt and survive in such conditions.
The nuances of blood pressure changes
It should be taken into account that, even if the optimal atmospheric pressure for fishing, averaged for the area, has been established outside, there is no need to rush. After the blood pressure has been kept at unusually low or high positions for some time, the fish must adapt to it.

But the worst fishing happens when the pressure fluctuates constantly and significantly. For example, today it can rise by 10 points, the sunny weather will last for a couple of days, and the day after tomorrow clouds will appear overnight and it will drizzle for a couple of days. Then again it will be partly cloudy or sunny, then cloudy again. At such moments the fish is in complete prostration. She does not have time to adapt to one conditions before they are replaced by others, and absolutely opposite ones. It is clear that at such a time, regardless of the sun on the street or the rain, she has no time for appetite.
So, despite the fact that the best atmospheric pressure for fishing is the average for the area, you can fish even at a stable low or high level. The best pressure is one that stays at the same level for several days and does not fluctuate twice a day. It is at this pressure that the fish are most active and inclined to take the bait.
Other factors
The ideal pressure for fishing is a myth. Experienced fishermen know that they need to consider weather conditions for winter fishing in general:
- Temperature dynamics;
- Direction of the wind;
- Wind speed;
- Illumination;
- Dynamics of pressure changes.
There is simply no best pressure for biting fish. It must be taken into account only in conjunction with other factors - temperature, wind, cloudiness. Clear frosty weather is usually characterized by high pressure. The appearance of wind and a decrease in barometer readings indicate that clouds are likely to appear. Minor fluctuations can be ignored. But a long-term constant decrease indicates that the anticyclone will soon be replaced by a cyclone, and vice versa.
The best weather for winter fishing is constant. This is clear frosty weather (high pressure), or cloudy, cloudy, warm with low pressure. In one case, the fish will actively move, in the second, it will calmly feed in place. It bites poorly with sudden changes and constant changes, and even then not always. Before the sudden change there are short bursts of strong biting. But this does not mean that there is no bite due to pressure, which is simply an indicator and meter of ongoing phenomena.

The most important wealth of an angler is personal experience!
Of course, valuable advice from scientific ichthyologists or carp fishing experts is very necessary for us, but the most valuable information will be the one that is based on purely personal experience. Correctly recognizing the slightest changes in the behavior of carp, knowing its habits and taste preferences in a specific body of water is only possible when you already have your own “baggage” of knowledge.
Well analyzed and sorted out in the mind “on the shelves”.
You can read a lot of articles on different sites about trouble-free carp fishing, but (.) this will not be a panacea, that is, “golden” advice for any situation.
Since each region of the country has its own specific nuances that affect the behavior of fish (pressure, wind, weather conditions, terrain and even phases of the moon). And even between lakes located nearby, there can also be differences.
Therefore, your own understanding of all these processes, based on analysis and many years of observation, is what will give an excellent result.
Next, we bring to your attention the main points (basics), based on which you can learn to make your own forecasts for fishing in the future.
At what pressure do fish bite?
A normal pressure is 760 mm Hg ± 3 mm. Pressure surges in any direction negatively affect the fish’s bite and behavior, since this immediately changes the density of the water and the amount of oxygen dissolved in it.
Observations show that a gradual decrease in pressure has a positive effect on fish biting. This is especially noticeable in the activity of pike. There is an assumption that this is due to the fact that the fish senses an upcoming change in the weather and instinct pushes it to actively feed.
With a gradual increase in pressure, a deterioration in the bite of predatory fish is noticed, while peaceful ones continue to feed as usual. But there can always be exceptions, because pressure is not the only factor.
Pressure surges
Any sudden and significant change in pressure has a strong physiological effect on the condition of the fish, up to its disorientation in the water column, which forces it to refuse to feed.
The fish tries to compensate for the pressure by sliding into the depths or moving to shallow areas, or hanging in the upper water horizons.
Different layers of water have different illumination and temperature. By changing the depth in an attempt to compensate for the pressure, the fish finds itself in unusual conditions.
High and low blood pressure
When atmospheric pressure increases, the density of water increases, and the fish rises from the depth; when the pressure decreases, on the contrary, the fish goes to deeper parts of the reservoir, if possible. This is how the fish adapts to the changed pressure and at this time the fish bite weakens or stops altogether.
After adaptation, if the pressure remains stable, the fish resumes activity and the fish bite is restored. The larger the fish, the more sensitive it is to changes in pressure.
Fish bite better when the pressure does not change for a long time. Any sharp net affects the fish bite in a bad way. If the pressure has increased or decreased significantly and does not change for a long time, the fish adapts to it and begins to feed normally - the fish’s active biting resumes.
For a fish to stop feeding completely, something more serious must happen than a change in atmospheric pressure. Therefore, you can go fishing without paying attention to it.
Useful post? Like and subscribe to our channel!
Source
Increased and decreased
Before we talk about how changes in pressure affect the fishing process, let’s briefly look at what atmospheric pressure is, as well as which value is normal, and which is high or low.
Atmospheric pressure is the force with which air (aka the atmosphere) presses on the surface of the earth and the objects on it. Air has its own mass, and therefore has a similar effect. The strong influence from the outside is balanced by the force of pressure inside living organisms.
The normal value with which air affects the surface of the earth is 760 mm Hg.
This is equivalent to the fact that the air creates a force of 1.033 kg per 1 cm square of the earth's surface. Any fluctuations in the pressure of air masses mean a change in the force of the air, which is felt by every living organism on the planet.
Naturally, fish are no exception, and therefore it is logical that they change their behavior under low or high pressure. The fisherman, in turn, needs to know the behavior of a particular fish when the pressure changes, otherwise he risks being left without a catch where there was an intense bite yesterday.
What you need to know about blood pressure
Every lover of sitting on the shore with a fishing rod should be aware that pressure for catching fish is a very significant indicator. Many fishermen are surprised why a few days ago the catch was simply excellent, but today the fish are not biting at all. Ichthyologists claim that sudden changes in the behavior of river inhabitants may just be associated with changes in this value.
- If the atmospheric pressure is high, the weather will soon begin to return to normal, and the amount of precipitation will decrease several times. In winter, with high temperatures, the air temperature usually drops slightly, and in spring and summer, on the contrary, it becomes warmer.
- At low pressure in the atmosphere, the probability of precipitation increases several times. Due to the fact that the air becomes more humid in the summer, the air temperature drops by several degrees, but becomes warmer in the winter.
Fish biting for the most part depends not on the atmospheric value itself, but also on whether the fish has had time to get used to such changes.
While river inhabitants adapt to new conditions, fishing will be ineffective, since the fish’s interest in food is minimal.
Wind and season
This is one of the most difficult weather factors. The fact is that the carp’s bite in the wind can change dramatically. This is explained by this. It depends on what kind of wind is blowing:
- direction of current in a closed body of water;
- wave height and frequency;
- food and oxygen content in a specific area of a pond or lake;
- water temperature;
- responsiveness of the gear;
- casting accuracy and much more. etc.
Agree, not taking this weather factor into account is a big mistake. Moreover, the carp bite in the wind can change dramatically.
For example, south or west winds most often bring warming. Naturally, this has a beneficial effect on the bark in spring or autumn.
On the contrary, the wind from the north and northeast is accompanied by cold air, which turns out to be a lifesaver in the summer in extreme heat. However, during spring or autumn fishing, it will make the carp forget about food.
Wind strength is also important in carp fishing. Often, during complete calm on a hot summer day, carp practically do not bite. However, as soon as a light breeze blows, the fish’s appetite immediately awakens. Why? There are several reasons why the carp bite improves in the wind:
- Due to waves and ripples, the water is saturated with oxygen.
- The smell from the bait and the flavorings used by the fisherman spreads faster throughout the entire water area of the reservoir.
- Insects or plant seeds enter the reservoir, which contributes to more active feeding of the fish.
True, the carp bite in the wind can decrease sharply. This is most often observed during sharp and strong gusts, which create a lot of noise that frightens the fish.
For example, this is the splash of high waves, the loud rustling of reeds or coastal bushes, or the sounds of the surf hitting the shore. As a result, most carp go to deep holes, dumps and pools, where they wait for more favorable weather.
Large individuals can still feed in such weather. However, they swim alone.
And the unnatural movement of the bait due to strong wind is unlikely to tempt the fish.
Conclusion: a good weather factor for carp fishing will be a slight wind of up to 8 m/s. However, with a gusty storm wind, the speed of which is more than 15 m/s, the fish are predominantly inactive.
It is also important to remember that the carp bite is often much better on the windward shore. This is explained by the fact that food particles are brought here from all over the reservoir by currents and waves.
Naturally, the carp immediately moves there. In addition, in areas near the windward coast, the oxygen content increases, which improves the metabolic processes of fish.
Including digestion. This means that the carp also actively feeds in the windward part of the reservoir.
Therefore, every angler should remember this.
The only exception is fishing in the fall, when the leaves fall. Once in the water, they begin to decompose and rot, absorbing oxygen and emitting an unpleasant odor.
Of course, the fish tries to avoid places where leaves accumulate, and this, as a rule, turns out to be the windward part of a pond or lake. Therefore, in the fall it is recommended to catch carp in areas on the leeward side of the reservoir.
There is less debris and warmer water - all these are favorable conditions for fish activity.
As you can see, the carp bite in the wind can change in one direction or another. There are many nuances, but every carp fisher should know and take them into account.
Fishing at low and high pressure
Among all weather conditions, it is atm. pressure has the greatest influence on the favorable or negative outcome of fishing. Moreover, pike, perch, catfish, carp and roach react completely differently to lower and higher barometer values.
According to the observations of fishermen, when the pressure drops, predatory fish begin to hunt more actively and it does not matter whether there is wind or not, sunny or cloudy weather, regardless of the time of day and phase of the moon.
Especially if it has dropped, after the weather had been stable with high atmospheric pressure for several days, the predators begin to really eat.
There is a hypothesis that they are trying to get enough before the weather changes, fearing that it will become much more difficult to do so later.
Signs of pressure changes
First of all, when going fishing, a fisherman can always find out the value of atmospheric pressure using a home barometer
. This will allow him to decide what gear to take and what fish to start hunting for.
However, you always need to be on guard, since during the day the weather, and therefore the air pressure, can change. For example, if there is fog in the early morning, then the weather is likely to improve and the atmospheric pressure to increase. If the weather worsens, gusts of wind are a clear sign that air pressure will decrease.
Factors influencing fishing:
- ambient temperature;
- wind direction and strength;
- degree of illumination.
There is a relationship between air pressure and its temperature.
In winter, at low pressure, the air is characterized by a higher temperature than at high pressure. However, the temperature itself does not affect the bite, since conditions at depth are completely different. On the contrary, high pressure is characterized by frosty but calm weather. Typically these conditions are clear and there is virtually no significant wind movement.











