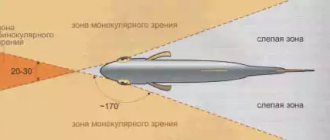
Sturgeon
is a large fish, divided into 19 species. They live in North America, Europe and north-temperate Asia. Some species live in the seas and enter rivers for spawning and wintering. Other species are freshwater. Their main habitat is lakes. They enter rivers only to lay eggs. They lead a bottom-dwelling lifestyle. They have amazing fertility. One clutch can contain several million eggs. In this case, the weight of eggs before spawning can be a quarter of the body weight. For people, caviar is a real delicacy. Therefore, many species are on the verge of extinction. The largest concentration of sturgeon fish is concentrated in the Caspian Sea.
Description
Types of sturgeon
Sturgeon is a genus of fish in the sturgeon family. Freshwater and migratory fish, reaching up to 3 m in length and weighing up to 200 kg (Baltic sturgeon). There are 16-18 species, some of which are listed in the Red Book. The sturgeon is characterized by the following characteristics: longitudinal rows of bony scutes do not merge with each other on the tail; there are splashing holes, the rays of the caudal fin go around the end of the tail. Most of the species are migratory fish, emerging from the seas into rivers in the spring to spawn, some species also in the fall in order to spend the winter here in hibernation. Sturgeon is common in Europe, Asia and the north. America.
Sturgeons stay mainly at the bottom, feed on fish, shellfish, worms, etc. The amount of caviar is very large and amounts to 1/6, 1/5 of body weight; therefore, the number of eggs in large fish can reach several million. Despite such enormous fertility, the number of fish belonging to this genus has already greatly decreased due to merciless and imprudent fishing.
The meat of all types of sturgeon is very tasty, as a result of which they are caught everywhere and eaten fresh, salted or smoked. Among ancient peoples, sturgeon was held in high esteem. Among the rich Romans, this fish was decorated with flowers when served to the table. In Greece, its meat was considered the most noble dish; in China it was reserved for the emperor's table; in England and France, the right to eat sturgeon belonged only to the sovereign and the richest nobles; In Russia, sturgeon meat is also highly valued. However, sturgeon are caught for their caviar and swim bladder rather than their meat. As is known, caviar is prepared from their eggs, and the most beautiful glue is made from the bubble.
Classification of the sturgeon family
The structure of sturgeon fish
Initially, two genera of sturgeon fish were distinguished: sturgeon and skafirinidae. All of them totaled about 25 species of fish, which were found only in temperate latitudes: Asia, Europe and North America. Over time, the population of some of them disappeared.
Sturgeon fish species are very popular in fishing. Today, 17 species of sturgeon representatives are known. The most popular types are:
- Beluga is the most ancient species of freshwater fish. Its life cycle can last 100 years. The largest beluga can reach 5 m in length and weigh 2 tons. The body of the fish is shaped like a torpedo, covered with protective bony plates in 5 rows, dark gray on top and white below. At the bottom of the muzzle there are antennae that provide the fish with a sense of smell, and a sickle-shaped mouth. Females are larger than males. Beluga is a predator that most often feeds on anchovies, gobies, herring, roach and anchovy. Females lay eggs every 2-4 years in the spring.
- The Russian sturgeon is a fish with a spindle-shaped body with a short, blunt snout. The antennae are located at the end of the mouth. Most often, the fish has a grayish-black color on top, grayish-brown sides and a white belly. The Russian sturgeon reaches a maximum length of 3 m and can weigh up to 115 kg. In this case, the life cycle reaches 50 years. In nature, sturgeon can form crosses with sterlet, beluga, thorn and stellate sturgeon. This happens extremely rarely, but similar hybrids can be found. Fish habitat: Azov, Caspian and Black seas.
- Siberian sturgeon. The body of the fish is covered with numerous fulcra and bony plates, and the mouth is retractable. This fish has no teeth. There are 4 antennae in front of the mouth. Habitats of the Siberian sturgeon: the basins of the Yenisei, Ob, Lena and Kolyma. The fish grows to a maximum length of 3 m, reaches a weight of 200 kg and can live up to 60 years. Spawning occurs in mid-summer. The sturgeon feeds on organisms that live on the river bottom: mollusks, amphipods, polychaete worms and chironomid larvae.
- Stellate sturgeon lives in the basins of the Azov, Black and Caspian seas. Stellate sturgeon fish can be winter or spring. The elongated body of the stellate sturgeon is characterized by a long nose, a convex forehead, narrow and smooth antennae and a poorly developed lower lip. The side and top of the fish's body is covered with a dense covering of scutes. The back and sides are bluish-black, and the belly is white. Stellate sturgeon rarely reaches more than 5 m in length and 50 kg in weight.
- Sterlet is one of the smallest fish among sturgeons; it reaches 1.25 m in length and can weigh up to 16 kg. It has an elongated narrow nose, long antennae that reach to the mouth, touching scutes on the sides and a lower lip divided in two. In addition to the usual plates on the body of sturgeon, the sterlet has closely interlocking scutes on its back. Depending on the habitat, the fish can have different colors, but often its back is grayish-brown and its belly is yellowish-white. The fins are universally gray. Sterlet can also be blunt-nosed or sharp-nosed. The fish is found exclusively in northern Siberia.
Features of sturgeon fish
Ancient fish belonging to this family are distributed only in the Northern Hemisphere. They have lived on our planet for 30 million years, so it is not surprising that Sturgeons have retained some archaic and primitive structural features. The basis of their skeleton is not a bony skeleton, but an elastic chord; bony vertebrae are present only at the base of the caudal fin. Even the sturgeon’s skull consists of cartilage, although covered with a shell of bony scutes. Along their entire body there are five longitudinal rows of bone scutes (bugs), one row of which stretches in the middle of the back, two on the sides and two on the sides of the belly. The skin of these fish is bare or covered with irregular small scutes, giving it a rough appearance. Their body is elongated and fusiform, the dorsal fin is moved far back, and the head ends in an elongated snout with a mouth similar to a transverse slit and four antennae. The antennae are located on the underside of the head; they are organs of touch and help fish find food. The sturgeon's mouth is surrounded by a fleshy lip and is capable of protruding significantly when grasping prey.
Appearance
Sturgeon caviar
The body has an elongated and spindle-shaped shape. The dorsal and anal fins are very strongly displaced towards the tail. There are antennae on the muzzle. There are no scales. Instead there are bone stripes. They are called "bugs". Small bone plates are scattered between the bugs throughout the body. The bugs stretch from head to tail. One stripe is on the back. Two are located on the sides. And also two plates stretch along the belly. They are not connected in the tail section. Coloration varies depending on the species and region of habitat. In most cases, the back is dark with a grayish tint. The sides are light brown and the belly is gray or white.
The largest are considered to be Atlantic and white sturgeon. The first lives in the Baltic, North and Mediterranean seas. Previously found in the Black Sea and White Sea, near river mouths. Currently listed in the Red Book, as it is on the verge of destruction. Its length reaches 6 meters, and its weight reaches 400 kg. Such a fish weighing 200 kg produces up to 80 kg of caviar. The second species lives off the west coast of North America from Alaska to California. It is also called the “California beluga” due to its enormous size. The largest representative of this species was caught off the coast of British Columbia (Canada). It reached 6.1 meters in length and weighed 499 kg.
The Siberian sturgeon is a purely Russian fish that lives in rivers over a vast territory from the Ob to Indigirka. Grows up to 2 meters. Normal weight is 65 kg. The maximum recorded weight is 210 kg. The Russian sturgeon is the original inhabitant of the Caspian, Azov and Black Seas. Accordingly, it can be found in the Volga, Kama, Dnieper, Danube and on the Don and Kuban rivers. It differs from other species by its rounded short snout. Maximum length 2.35 meters and weight 115 kg. But given the fact that fish grow slowly, such giants are impossible to find these days. They are all caught at a young age, when representatives of the species weigh 15-20 kg. The Amur sturgeon lives in rivers such as the Amur, Argun, Shilka, and Ussuri. The usual body length is 1.5 meters. Weight is 8-10 kg. Can reach a weight of 60 kg. They say that individual specimens weighing up to 160 kg have been caught. The lake sturgeon is native to North America. He lives in the Great Lakes, St. Lawrence River, Mississippi. Can weigh up to 190 kg with a body length of 3 meters. But for this, the fish needs to live for many years, which is not always possible due to the excessive appetite of people.
What kind of sturgeon can you catch in Quebec?
I first became acquainted with sturgeon in Quebec; I had never caught them before. However, he quickly mastered the local sturgeon fishing for donka and visited several iconic places for sturgeon fishing.
In general, over several years of fishing in Montreal, I have repeatedly caught sturgeon as an additional catch, not only with a donk, but also with a spinning rod, and also engaged in targeted fishing at specific fishing points. So I have formed some personal opinion on sturgeon and methods of catching them.
Let me start with the fact that North America has its own local “aboriginals”, who can be caught in various areas of the North American continent. The white sturgeon, which is the largest freshwater fish in North America, is world famous. It lives in the western part of the continent, in the rivers of the Pacific water basin. In Canada, the most famous main river in the province of British Columbia is the Fraser River, where giant white sturgeon are found.

The blunt-nosed sturgeon (lat. - Acipenser brevirostrum) is found not only in the states, but also in the neighboring province of New Brunswick (Saint John River). Green or Pacific sturgeon (lat. - Acipenser medirostris) is found in the rivers of the Pacific basin both in China and Russia, as well as in the USA and Canada.
Remnants of a once-existing global population include several species of shovelnose bats, named for their flattened snouts. These are modern representatives of the shovel-nosed subfamily (lat. - Scaphirhynchinae), which can also be found in Central Asia in the rivers of the Aral basin: Amu Darya and Syr Darya. And if the situation with the Aral shovelnose is extremely critical (they are listed in the international red book), then in the states these fish live better. You won't find fish like this in Quebec.
The traditional targets for sturgeon fishing in Quebec are two species: lake and Atlantic. Sometimes fishermen from the neighboring province of Ontario come to visit us specifically to catch sturgeon, since sturgeon fishing was recently banned in Ontario. Therefore, it is necessary to know and distinguish between local sturgeon species, especially since lake sturgeon have a size limit.
1. Lake sturgeon
Lake sturgeon (lat. - Acipenser fulvescens) in French - Esturgeon jaune , in English - Lake Sturgeon . The local name in French is also popular - Esturgeon de lac, camus, escargot maillé, charbonnier .

The body has a torpedo-shaped, elongated shape. The color of the back and sides varies from olive brown to gray; belly white; the fins are dark brown or gray. The snout is elongated with 4 antennae. The mouth is located below, vertically, behind the eye line.
Average length from 90 to 140 cm, weight from 5 to 35 kg. Females can live up to 80 years, males up to 55 years. Currently, for sport fishing, the size limit is from 80 to 130 cm.
It prefers the rocky bottom of rivers and lakes with a depth of 5 to 10 m. During the summer heat, it goes to greater depths in search of cool water. Rarely enters brackish water.
Lake sturgeon feed from the bottom using their sensory antennae. It sucks in a large number of small organisms, such as mollusks, larvae of aquatic insects, crayfish, leeches, fish eggs, and some plants. It continues to feed in winter, so it can be caught in winter on girders, but it stops feeding during spawning migration.
Spawning occurs at the end of May - June. Prefers rivers with fast currents and a depth of 0.6 to 5 m, less often in lakes. Males reach sexual maturity at the age of 8 to 20 years, reaching a meter in length. Females reach sexual maturity at 15-32 years, reaching 1.3 meters in length. It should be noted that lake sturgeon do not spawn every year. As the female ages, the interval between spawnings can increase from 4 to 10 years.
The female is usually accompanied by one or two smaller males. She does not build nests. It simply lays from 100 to 900 thousand black eggs with a diameter of 2.7-3.5 mm on stones and gravel. The larvae hatch in 5-8 days.
In North America and in particular in Quebec, its habitat is as follows: in the rivers and lakes of the St. Lawrence River basin, north of Montreal to James Bay.
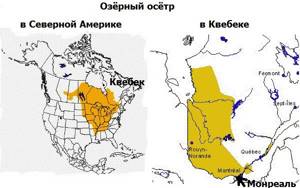
In Quebec, the lake sturgeon is considered a vulnerable species and has a status of "may be designated as vulnerable or threatened." The species is currently considered to be endangered in the St. Lawrence River. Its populations are stable only in a few very localized places and do not recover quickly enough.
The population in Lac Saint-François, west of Montreal, has been decimated by loss of spawning grounds and isolation of individuals due to dam construction and past commercial fishing. The population in the Lake of Two Mountains (lac des Deux Montagnes), destroyed in the early 1950s, continues to recover.
The population in the river corridor between Lac Saint-Louis and Lac Saint-Pierre is characterized by high mortality associated with the commercial exploitation of the reservoir, as well as high natural mortality due to pollution of the reservoirs. There are very few places for spawning and they are of poor quality. That's why there aren't many sturgeon around Montreal.
In general, lake sturgeon fisheries in the North American habitat are experiencing serious problems due to commercial overfishing and habitat degradation. In Quebec, the lake sturgeon population is declining as the sturgeon's late sexual maturity and gregarious behavior make it vulnerable to poaching and overfishing. Natural factors, such as diseases, predators, competition, affect sturgeon much less than humans.
2. Atlantic sturgeon
Atlantic sturgeon (lat. - Acipenser oxyrinchus) in French - Esturgeon noir , in English - Atlantic sturgeon . The local name in French is also popular - Esturgeon atlantique .

The Atlantic sturgeon is the largest fish that frequents Quebec's fresh water. It is the largest freshwater fish on the east coast of North America. On a biological level, it is of great scientific interest due to its origins, which go back at least 200 million years. Adults reach sizes of more than 2 meters, often up to 4 m. According to some estimates, the largest sturgeon weighing 160 kg was about 60 years old.
The Atlantic sturgeon has a stocky, elongated, torpedo-shaped body. It has a long snout and a vertical mouth, like all sturgeons. The sturgeon has a cartilaginous skeleton, no ordinary scales, only several rows of bony plates. The back and sides are blue-black, the belly and head below are white, there is also a white edging on the fins.
The Atlantic sturgeon is an anadromous migratory fish that spends most of its life at sea, i.e. in salt water, and enters fresh water only for spawning. He often visits the St. Lawrence section from Portneuf to the Gulf of St. Lawrence. Reproduction in Atlantic sturgeon occurs every 4-10 years for females and 2-4 years for males.
Sturgeon in fresh water feed on the bottom, mainly crustaceans, insects and mollusks. In the sea it also feeds on shrimp and small fish. During the spawning period, the sturgeon stops feeding, which is why its spawning grounds are not very well studied. At this time, it can only be caught with nets, so it often goes unnoticed. At this time it is caught extremely rarely on donka.
Atlantic sturgeon can often be seen jumping out of the water. There is a version that in this way he is trying to get rid of external parasites, including sea lamprey.
In North America and in particular in Quebec, the habitat of the Atlantic sturgeon is as follows: the first population east of Trois-Rivières along the St. Lawrence River to and around Anticosti Island (Île d'Anticosti); the second south from Gaspésie along the Atlantic coast of North America to and including Florida.
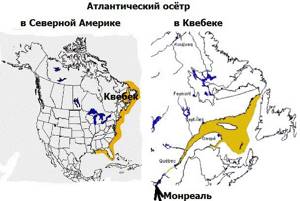
Like lake sturgeon, Atlantic sturgeon is prized for the flavor of its meat. Since the late 1960s, there has been a decline in commercial fisheries production. Mainly due to the influence of man who disturbed its habitat: the construction of hydroelectric dams on the Manicouagan and Outardes rivers near Baie-Comeau, the creation of a sea canal, the construction of a pier in Portneuf (45 km east Quebec City), the creation of artificial islands and the use of pesticides for Expo 67 (Montreal).
After the almost complete cessation of commercial fishing between 1967 and 1975, the Atlantic sturgeon population experienced a recovery. The spawning grounds are still not well studied, but individuals marked with transmitters are currently being monitored. Dredging, changes in bottom topography and various pollution are factors that lead to the degradation of sturgeon habitats.
Therefore, like the lake sturgeon, the Atlantic sturgeon is also classified as a vulnerable species. In Quebec, it has a status of "may be designated as vulnerable or threatened." However, there are no size limits for catching it, especially since the chance of catching it during sport fishing with a donk is very small - it goes higher upstream than Lake Saint-Pierre (lac Saint-Pierre) extremely rarely.
Atlantic sturgeon is caught commercially in the St. Lawrence River, mainly in the area between Montmagny and Saint-Jean-Port-Joli. Water temperature is the main limiting factor for its fishing. During the summer heat, sturgeon quickly die in nets, and the quality of its meat deteriorates. Therefore, in the middle of summer there is a “dead” season for catching it.
How to distinguish Quebec sturgeons
Given the above about the habitat and feeding habits of lake and Atlantic sturgeon, the chance of catching an Atlantic sturgeon around Montreal is extremely low. From the stories of local fishermen, I realized that many simply do not really know what kind of fish they catch...
In fact, the same lake sturgeon may have its own separate populations, which will differ from each other in appearance and color. In addition, young lake sturgeon have some spots on their sides, due to which they can be classified as a different species. Lake specimens have a blunter snout, while river specimens have a more elongated snout. So, around Montreal, one species is almost always caught - lake sturgeon , in French - esturgeon jaune , in English - lake sturgeon .
However, it is very easy to distinguish lake sturgeon from Atlantic sturgeon. Firstly, the lake sturgeon does not have bony plates between the dorsal and caudal fins; secondly, between the anal fin and the tail there are 2 bone plates.
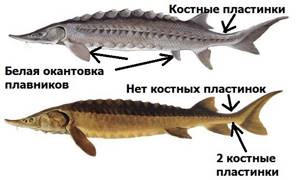
Thirdly, the fins of the Atlantic sturgeon are edged with a white stripe. The sterlet is widely known in Russia - it also has a characteristic edging on its fins and tail.
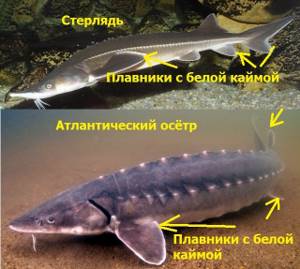
If there is no white edging on the fins, then we can say with great confidence that you have caught a lake sturgeon. This is the easiest way to distinguish sturgeon; the presence or presence of bone plates near the tail can only confirm this.
Traditional sturgeon fishing with donka in Montreal
In Montreal and its surrounding areas, sturgeon are traditionally fished in a targeted manner at some locations. In other places it is caught occasionally. And although at the beginning of the season it can also attack jig baits, sturgeon is mainly caught on a donk, using a traditional sturgeon fishing rig .
I know of the following fishing spots around Montreal: Lachine lighthouse, Ile de Visitacion park, Beauharnois power plant, Sainte-Catherine dam and Longueuil harbor headland (Marie-Victorent park). It is quite possible to catch sturgeon there at different times.
As bait you can use: worms, liver, meat, insects. Previously, you could use shrimp and pieces of fish, but the most popular is the use of a large bunch of earthworms.
Sturgeon meat is traditionally used for smoking and is considered very tasty and delicacy. Caviar is practically never found, since the season opens after the end of spawning. In addition, the meat can be used for kebabs, cutlets and dumplings.
Reproduction and lifespan
Sturgeon fry
Sexual maturity in sturgeon usually occurs in the 2nd and even 3rd decade. Fish go to rivers to spawn. This period varies among different species from March to November. The maximum is usually recorded in July. Those species that move late winter in rivers. Eggs are deposited on rocky or gravel bottoms. The depth varies from 4 to 20 meters. A prerequisite is flow. That is, eggs are deposited in running water.
The incubation period lasts about a week. Mature fry are carried away from the spawning grounds by the current. The young generation quickly adapts to the aquatic environment and feeds first on plankton, and then moves on to larger living creatures. Sturgeon do not spawn every year. As for life expectancy, it is very long. The same white sturgeon can live more than 100 years. Other types are in no way inferior. So we can say with confidence that this family belongs to the long-livers.
Sturgeons feed mainly on mollusks, roundworms (nematodes), and fish. Of the latter, gobies, anchovy, and sprat are very popular. They hunt at the bottom. The depth range varies from 2 to 100 meters. Young individuals prefer not to go deeper than 5 meters.
Spawning
Not all female sturgeon spawn every year. Only sterlet breeds annually. Representatives of sturgeon spawn in the spring-summer season in the fresh waters of fast-flowing rivers. It has an adhesive structure, so it attaches perfectly to flagstone or pebbles.
Larvae emerging from eggs have a yolk sac, which determines the endogenous feeding period. The fry can independently consume external food by the time the endogenous bladder completely resolves. Then the exogenous period of active nutrition begins. After this, the fry may linger in the river waters, but often the larvae slide into the sea in the summer of the same year. This is how sturgeon reproduce.
Feeding the fry
The first food for sturgeon fry is zooplankton, such as daphnia. Afterwards they begin to eat representatives of crustaceans. The exception is the predatory beluga fry, which do not have a yolk sac and begin to eat independently while still in the river.
Further development of sturgeon to sexual maturity occurs in sea waters. Migratory representatives of sturgeon are divided into spring and winter species. For the former, it is common to enter rivers in the spring. They spawn almost immediately. Winter fish enter the river in the fall, spend the winter, and spawn the following spring.
Sturgeon spawning
Species of sturgeon that live near the shores of seas and oceans spawn in rivers. They enter the river waters, swimming against the current. At the same time, they can cover long distances. Then they return to the sunny water again.
Semi-anadromous species do not move up rivers; they breed in estuaries. Freshwater sturgeons lead a sedentary lifestyle. Sturgeon spawning occurs in the same places where they feed.
The breeding season of sturgeons occurs in spring-summer, but they can begin to migrate to the spawning ground at different periods of the year. For this reason, sturgeon are divided into seasonal races. This is winter and spring. The former begin to migrate in the fall, before the eggs have matured, and the latter in the spring, before laying eggs.
Puberty occurs between 5 and 21 years of age. Female sturgeon spawn once every 3 years, males more often. Peak spawning is July.
Fresh water and a strong current are considered a necessary factor for breeding offspring. Sturgeon do not breed in salty, stagnant water. The water temperature should be no higher than 22 degrees. Females spawn in crevices, between stones. At one time, she is capable of laying up to several million eggs.
Before going to spawn, the sturgeon stops eating and subsists on internal reserves for a long time. During migration, the male sturgeon's milk ripens, and the female sturgeon's caviar. In the deep places of the river, she begins to lay eggs, and he waters them with milk. Afterwards they go back to sea.
Habitats
Sturgeon fishing
Sturgeon can be found in almost every major Russian or Siberian river. In European Russia, in the northern rivers, despite the particular abundance in the Yenisei and Ob, Russian sturgeon. anyway, he is a very rare guest and swims in by accident. Once, near Ust-Tsylma, like a huge curiosity, an Ob sturgeon was caught. This Siberian sturgeon has some differences from sturgeon from the Black Sea or Caspian basins, and Siberian fish can reach a weight of up to 210 kg. The beluga can reach the same gigantic size.
The Volga is considered the most numerous sturgeon; this river rises quite high, and already in the Urals and in the reservoirs of the Black Sea basin, sturgeon is already found in much smaller quantities. Sturgeon are sometimes found in the Volga River up to the city of Rzhev, but after Yaroslavl small sturgeon become quite common, this proves that the fish comes to these areas to spawn.
The sturgeon belongs to the family of migratory fish, like pink salmon, and in the open sea it is a very rare occurrence and tries to stick to river mouths and freshwater parts of the sea; and in the Caspian Lake - its northern part. But, despite this, the bulk of sturgeon live in the Caspian Sea itself. From here, from April, sturgeon begin to swim into rivers to spawn. He most often walks in small schools and tries to stay in the fastest and deepest places in the reservoirs; It swims slower than the sturgeon, but faster than the thorn. From the Dnieper in May the return journey begins, but in the Volga and the Urals the sturgeon remains much longer, and along the Yenisei (along Krivoshapkin) it turns down only by August 25th.
The course of the sturgeon, like all migratory fish, depends on a fair wind: in the opposite wind direction, the fish will crowd near the shallows in front of the mouths and wait for the long-tailed fish to return to the river at the same time as the waves.
The number of sturgeon increases significantly from mid-May. But the fish entering the river at this time no longer spawn here, but remain on the Yatovs for the whole winter and will spawn only a year later. In the Volga, from the city of Rybinsk to the city of Samara, sturgeon spawn almost at the same time as sterlet or a little later - in early May. In the lower reaches of the Volga, near Sarepta and Tsaritsyno, and in the Kura River, sturgeon spawn at the end of June or July (mostly).
Sturgeon spawning is very short and lasts only 3-4 days. Maturation and spawning is a fairly quick process; all eggs ripen simultaneously in each individual fish, and they are all spawned together.
Small sturgeon live for a long time where they hatch from the eggs, and then migrate to the sea, where they remain until they reach puberty - up to five years, or even more. It is not known for certain how long sturgeon live in the river. Most likely, they swim away as soon as they turn one year old, but sometimes two-year-olds are also found in rivers. It is noteworthy that these osterata, as experienced fishermen say, stay in the same flock with sterlet. this suggests that the bulk of young fish go to sea, most likely in the same autumn or during high water, before reaching one year of age.
Young sturgeons at first feed on small crustaceans, and as they mature they begin to eat shells. Shells are the main food of adult sturgeons, which only when they reach a significant size of about 1.5 meters begin to eat other fish.
Unfortunately, despite the extreme fertility of sturgeon, the number of this fish species is significantly decreasing from year to year. Today in the upper Volga, for example, sturgeon is very rare. The main destroyer of sturgeon is man, since predatory fish or birds are dangerous to him only at first. Most often, sturgeon becomes prey for catfish. One of the sturgeon's enemies is the small parasitic crustacean Dibcelestium sturionis. It is found on almost all representatives of sturgeon fish.
Sturgeon breeding
More and more sturgeon are being bred at home. If you follow all the rules of the technological process, you can end up with fish that will not be inferior in quality to those caught in the natural environment.
It is grown on a plot of more than 30 square meters. It should be located away from roads and heated in winter. There are about 7 swimming pools installed on the premises. First, the fry are placed in a small pool with a diameter of a couple of meters. Its depth is no more than a meter. Because fish grow at different rates, they are regularly sorted into different tanks.

Swimming pools must be kept clean. Therefore, they are cleaned of silt every day and 10% of the water is changed. Be sure to ensure that in winter the water temperature is at least 18 degrees, and in summer 20-24.
Sturgeon breeding farms must have:
- swimming pools;
- autonomous source of electricity;
- compressor;
- filters for water purification;
- pumps.
Water must flow constantly. If it is dirty, the fish will begin to get sick and die. To save money, water from wells and boreholes is often used.
The fish are fed with nutritious, high-calorie food. In this case, they give preference to waterproof feed. They swell in water and settle to the bottom. Fry are fed about 6 times a day, adults 4 times a day. To prevent the fish from refusing to eat, food is given at regular intervals.
It has been observed that sturgeons in captivity grow faster than their wild relatives. By the age of 4, their height is one meter, their torso girth is 35 cm. It is at this age that they stop actively growing.
Number
Distribution of sturgeons
This family belongs to the most valuable commercial fish. The most important population is the Caspian. In the middle of the last century, up to 18 thousand tons of Russian sturgeon were caught annually. And at the beginning of the 20th century, the catch reached 40 thousand tons. The decline began after the construction of hydroelectric power stations that blocked the rivers. They cut off the fish's path to spawning grounds. In 1980, the number of sturgeon in the Caspian Sea was estimated at 60 million individuals. Over the next 15 years, it decreased by 3 times and amounted to 20 million individuals. Today, the number of unique fish continues to decrease. This is happening due to renewed sea fishing and poaching.
Cooking methods
There are many culinary recipes on how to cook delicious sturgeon at home. Fish can be baked, smoked, stewed, boiled and fried both in a frying pan and on the grill.
How to bake the whole thing in the oven?
To bake a whole sturgeon in the oven, the fish must first be cleaned and gutted (we described above how to cut up a whole carcass for baking). After this, you can start cooking.
How to bake a sturgeon carcass in the oven:
- Pour lemon juice over the fish (40 milliliters will be needed).
- Chop 10 grams of garlic and mix with salt (10 grams). Rub the sturgeon with the garlic-salt mixture.
- Grease a baking sheet with vegetable oil and place the carcass belly down.
- Place in an oven preheated to 200 degrees for 40 minutes.
Fish can be served with salad, vegetables or herbs. You can also top the baked sturgeon with mayonnaise.

How and how much to cook sturgeon?
To cook sturgeon, the fish must be cleaned, gutted and placed in already boiling water. When the liquid boils again, turn the heat to low. You can add salt, bay leaf, and peppercorns to the broth at your discretion. The fish is cooked under a closed lid.
During the cooking process, foam will appear on the surface of the broth, which needs to be removed. In this case, the fish must be completely in the broth, otherwise the meat will cook unevenly and will be dry. You can also add a little vegetable oil to the liquid. Due to this, the broth will become more flavorful and the fish juicier.
Cooking time for a whole carcass is approximately 40 minutes. If the sturgeon is prepared in pieces, the cooking process lasts about 25 minutes.

When using household devices, the sturgeon cooking time will be different:
- multicooker: 40 minutes on the “Stew” mode;
- steamer: half an hour;
- pressure cooker: 35-40 minutes.
The larger the fish, the longer it takes to cook. There is no need to be afraid that you can overcook the sturgeon. With prolonged cooking, the taste of the fish only improves.
How to fry in a frying pan?
To fry sturgeon in a frying pan, cleaned and gutted fish must be cut into portions. Then add salt and pepper to taste, leaving for a quarter of an hour.
After the specified time, the fish pieces should be rolled in flour and placed in a frying pan with hot vegetable oil. Sturgeon should be fried on both sides until golden brown.
Fried fish is served to the table along with fresh vegetables and herbs.
How to cook in a slow cooker?
To prepare sturgeon in a slow cooker, you will need to fry onions, carrots, fish fillets and pickled champignons in butter. Each ingredient is fried separately from the others.
The juice that remains from the mushrooms must be mixed with 1.5 tbsp. l. flour. The resulting mixture is simmered over low heat until it thickens. Then add 400 grams of sour cream and salt to taste.
Place all ingredients in a multicooker bowl in layers and pour sour cream sauce on top. The fish is cooked on the “Stew” program for 30 minutes. 10 minutes before the end of cooking, sprinkle the dish with grated cheese.
Alternative ingredients for stewing sturgeon in a slow cooker can be seen in the video.
How to smoke?
The process of smoking sturgeon, either hot or cold, should begin with salting the product. To do this, mix salt and ground pepper in a bowl. The resulting mixture is thoroughly rubbed onto the carcass or pieces of fish and placed in the refrigerator compartment for 24 hours.
After the specified time, you can proceed to smoking. However, some chefs advise pouring a small amount of white wine over the fish and letting it sit in the refrigerator for another 24 hours.
When the sturgeon is salted, the excess salt must be wiped off with a paper napkin. After this, the product is dried (the fish must be wrapped in gauze to protect it from insects) and then sent for smoking.

Hot way
To prepare hot smoked sturgeon you need:
- Light the fire and pour wood chips into the smokehouse.
- As soon as white smoke appears, place a grate on the smokehouse, place fish carcasses on top of it and cover with foil.
- Smoke the product for 2 hours at a temperature of 85 degrees.
Be sure to wrap the finished smoked sturgeon in cling film and put it in the refrigerator compartment for storage. The shelf life of the product is 2 weeks.

Cold way
To smoke fish using the cold method, you can salt the product as described above, or prepare a different composition. To do this, you will need to mix 120 grams of salt with a tablespoon of granulated sugar, a pinch of ground coriander, two bay leaves, a teaspoon of dried dill and the same amount of basil, as well as peppercorns at your discretion. Place the dry mixture in a liter of boiling water and boil for 5 minutes. Place the carcass in the prepared brine, put pressure on top and put it in the refrigerator for a couple of days. The amount of ingredients is indicated for 1 kilogram of fish.
When the fish is salted, the product must be washed and hung to dry for 10 hours.
How to cold smoke sturgeon:
- Light the fire and pour wood chips into the smoke generator compartment.
- When white smoke appears, place a grill with fish in the smokehouse.
- Connect the generator to the container. The sturgeon is smoked under a closed lid for 2 days. Temperature: 30 degrees.
- After this, the fish must be hung out to air for 12 hours.
Shelf life of the product is 3 months. In this case, the fish should be wrapped either in paper or film and stored in the refrigerator.

How to cook on the grill?
Before frying fish steaks on the grill, the product needs to be marinated (a method for making a marinade for sturgeon was described above). After marinating, you can proceed directly to frying the meat.
How to make sturgeon kebab:
- Thread the marinated pieces of fish onto skewers, alternating with vegetables (tomatoes and onions).
- Place the skewers on the heated grill.
- The shashlik cooks in 25 minutes. The fish should be covered with a golden crust.
Sturgeon kebab is prepared quite quickly. Therefore, it is necessary to turn the steaks frequently so that the pieces of fish do not burn, but cook evenly.

How to pickle?
To salt sturgeon, the fish must be cleaned, gutted and cut into fillets, which must then be divided into portioned pieces.
Mix 50 grams of salt and 15 grams of granulated sugar. Rub the prepared mixture onto the fish pieces. Also, the workpieces must be lubricated with dry spices intended for fish.
Place 3 bay leaves, 5 grams of black pepper and the same amount of coriander into the container in which the sturgeon will be salted. Next, lay out the pieces of fish. Cover the container with a lid and place pressure on top.
The fish stands at room temperature for 6 hours. Then the container should be placed in the refrigerator for a couple of days. After 48 hours, the salted sturgeon can be served.
Fishing methods
Sturgeon are caught exclusively with powerful spinning and feeder rods, using bunches of worms, shellfish and fish as bait. Poaching methods of fishing (samolov) are very popular.
Commercially, sturgeon is highly valued for the taste of its meat and richness in caviar. Almost all parts of the fish are edible; glue is made from the air bubble. The richest country in the world for sturgeon is Russia.
Despite the fact that consumerism towards this type of fish has brought it to the brink of extinction, the sturgeon fishery is still huge. The main catching areas are the Black, Azov, Caspian Seas and their basins in Russia.
Sturgeon dishes
Sturgeon meat is valued because it has no bones, has a dense structure and excellent taste. How to cook sturgeon? Often the fish is baked whole, first stuffed with tomatoes. Sturgeon dishes go well with lemon juice. It is widely used in the preparation of fish soup or simply dumped.
Fish is used in dishes with virtually no waste. Meat and cartilage are used. Fish is boiled, steamed, baked, smoked and fried. It makes delicious shish kebab and aspic. Pieces of fillet are added to salads for taste.

Fish is extremely rarely salted. Its meat quickly absorbs salt and then becomes dehydrated. This is reflected in the taste of the fish. It is usually salted before smoking or drying. Only live fish or today's catch is suitable for salting. It is cut up and then mixed with salt and sugar. The resulting fillets are placed in a glass container and pressure is placed on top. To make the fish tasty, the resulting juice is regularly drained.
Regardless of the type of sturgeon, in restaurants their meat is called sturgeon.
Properties of sturgeon
Useful
Sturgeon meat contains easily digestible protein and fats. The protein of sturgeon meat is complete, contains all amino acids and is absorbed by the human body by 98%. The content of fish oil in meat ranges from 10 to 15% and is a highly nutritious product. Sturgeon is an excellent source of potassium. phosphorus. it also contains calcium. magnesium. sodium. chlorine. iron. chromium. fluorine. molybdenum. nickel. Sturgeon is rich in vitamin B1. AT 2. S. RR.
Sturgeon contains a large amount of healthy fatty acids that help reduce blood cholesterol. That is why their regular use significantly reduces the risk of developing myocardial infarction. Sea fish contains large amounts of iodine. necessary for normal functioning of the thyroid gland.
In almost all types of fish, especially sturgeon and herring. It also contains fluoride in large quantities, which promotes bone growth. This is why, by the way, children used to be given fish oil to drink to prevent rickets. Record holder for sodium content.
Dangerous
It is not recommended to consume sturgeon in large quantities if you have diabetes or obesity, and you should completely avoid it in case of individual intolerance.
It is also worth noting that the causative agents of botulism live in the intestines of sturgeons. easily getting into the body or eggs of fish if you do not cut it alive. This is possible in specialized factories that operate on modern equipment. That’s why you shouldn’t buy caviar secondhand, because poachers cannot comply with all the conditions for its production. Caviar poisoning is quite common.
Sturgeon nutrition
The sturgeon's diet depends on its age. Thus, fish fry prefer zooplankton, worms and crustaceans. Young animals prefer insect larvae and snails. Adult sturgeon mainly feed on protein foods. They consume especially a lot of food before breeding. They eat everything they can find on the bottom, small fish and algae if there is not enough protein food. During spawning, the sturgeon feeds on vegetation.
The exception is the paddlefish. It feeds on phyto- and zooplankton. The paddlefish obtains food by filtering water through its gills.
Interesting Facts
- Sturgeon fish is one of the oldest and most sought after fish on earth. Archaeological finds dating back to 3 thousand years BC. e. showed that sturgeon caviar was already successfully used in canned form by sailors in those days. In the army of Alexander the Great, sturgeon caviar was used as food for soldiers.
- In the middle of the 20th century, an Atlantic sturgeon weighing 213 kg was caught in the Neva, from which 80 kg of caviar was obtained.
- In the last century, one observant French woman noticed that the hands of women working in sturgeon caviar processing plants, despite their hard work, remain beautiful and smooth. Then the miraculous properties of black caviar were urgently studied and a line of cosmetics was launched, which enjoyed incredible success. Currently, the production of such cosmetics has been suspended due to its unprofitability.
How to prepare sturgeon?
Any fish needs to be prepared before cooking. To do this, the product is cut, gutted and cut into fillets. The skin of the sturgeon is very hard and studded with scutes made of bone tissue (called bugs). Fish have no vertebrae or bones (cartilage is used instead). A distinctive feature of the sturgeon is that it has a notochord called a viziga (a light vein that is located in the cartilaginous spine). It is this vein that must be removed, since four hours after the death of the fish, the vizig begins to absorb toxic substances.
How to cut and clean?
If the fish is frozen, it should sit at room temperature until it thaws. If you are cleaning a live sturgeon, then after catching it you must put it in the freezer for 60 minutes. During this time, the fish can be “euthanized.” After this, the main blood vessels should be opened and the sturgeon bled by making cuts on the gills. If this is not done, the blood will clot and soon begin to decompose. Because of this, the taste of the product may deteriorate.
Step-by-step instructions on how to cut sturgeon:
- Rinse the carcass thoroughly under water.
- Using a knife, remove the “bugs” from the back and sides.
- To clean the belly and other parts of the sturgeon’s body from scales, you need to move from the tail towards the head. However, near the abdominal area, you need to work with a knife extremely carefully so as not to damage the skin.
To bake a whole sturgeon, you need to properly cut the fish. For these purposes, the carcass should not be doused with boiling water, otherwise the skin may peel off. The product must be cleaned and gutted with care. There is no need to cut off the head. The main thing is to get rid of the gills along with the viper. The “bugs” should be cut off one by one so as not to spoil the appearance of the fish.

How to gut and remove a viziga?
To properly gut a sturgeon, you must adhere to certain rules, namely:
- Lay the carcass on its back and make a longitudinal cut on the belly from the head to the tail.
- Remove the entrails, being careful not to touch the gallbladder. Otherwise, the fish meat will have a bitter taste. If the bladder ruptures, the area where the bile has entered must be sprinkled with salt and carefully scraped with a knife.
- Remove blood clots from the vertebral cartilage. Rinse the carcass thoroughly from the inside.
- Make a couple of cuts on the vertebral cartilage from the inside of the carcass near the tail and head.
- Pull out the vizig. This must be done extremely carefully, trying not to tear it. What is contained in this white vein is poisonous. If the vizier breaks, the fish must be thoroughly washed under water.
In order not to spoil the fish carcass, the vizig can be removed in a completely different way. To do this you will need to cut the tail a little. The white vein will be located inside the vertebral cartilage. You need to pry the vizig with something sharp (either a needle or a knife) and pull it out with smooth movements.
How to remove gills?
The gills are removed after the head with the main fins is cut off. A sharp knife is suitable for this; you just need to cut off the gills.
How to remove mucus from sturgeon?
To remove mucus from sturgeon, you will need to thoroughly rub the carcass with sea salt. After this, the fish needs to be washed.
How to wash sturgeon from mucus? The fish needs to be poured with boiling water. Thanks to this, the mucus will quickly disappear from the surface of the carcass, and the skin will quickly peel off from the meat.

How to marinate?
To marinate sturgeon, you must first cut the fish and remove the entrails. After this, the carcass should be doused with boiling water to make it easier to remove the skin. Remove the backbone and rinse the carcass again. Divide the sturgeon into steaks and place in a pan for marinating.
How to marinate sturgeon for barbecue:
- In a deep bowl, mix vegetable oil (a couple of tablespoons), dry white wine (a glass), the juice of one lemon, ground white pepper and salt (to taste) and chopped onion.
- Place the fish pieces in a bowl with the marinade and refrigerate for a couple of hours.
After the specified time, the marinated sturgeon can be sent to the grill.

Comparison
Representatives of the sturgeon order have significant differences that distinguish them from other bony fish. This is primarily a cartilaginous skeleton, the basis of which is the notochord, which does not have vertebrae. Insufficient buoyancy is compensated by a large rostrum (prenostril section of the skull) and an increase in the load-bearing plane with the help of pectoral fins. Their swim bladder is reduced (smaller), and their mouth is located in the lower part of the head, which is due to their predominantly pelagic (marine) lifestyle. There are differences from other bony fish in the structure of the intestines and heart.
As for gastronomic differences, it is not for nothing that sturgeon has long been nicknamed the “king fish”. The name speaks for itself: it has no equal in taste. In addition, sturgeon and its closest relatives are good in any form - boiled, fried, baked or salted. Sturgeon caviar is a recognized and expensive delicacy, the production of which is brought under state control. And in Iran, for example, poachers still have their fingers cut off for illegally catching sturgeon.
Commercial value of sturgeon
Sturgeon fish belong to the first group according to the culinary and trade classification. The food industry uses them fresh, frozen and smoked. Royal fish is highly valued for its nutritious meat with a delicate taste and exquisite caviar. Fish fillet has a characteristic taste reminiscent of pork. Various original dishes are prepared from sturgeon. It is suitable for smoking, stuffing, pickling. It produces aromatic kebabs, excellent aspics with herbs, canned fish, and excellent salads from boiled fillets.
The indisputable advantage of sturgeon is its non-waste nature. It has only about 14% inedible parts. In addition to the fillet, the head with the vertebral vein (elm) is eaten. The skeleton contains useful substances.
Homemade menu for young sturgeon
Young animals need food with a high protein content - it contains a sufficient amount of essential and non-essential amino acids. Sturgeon breeders use fishmeal or other aquatic organisms and animals as the main source of protein. However, during the cooking process, protein loses its nutritional value, so during the first year of life it is recommended to add multivitamin premixes and fish oil to the basic diet.
The daily menu for young animals consists of:
Crude protein content (based on dry matter) in juvenile sturgeon
- dry skim milk
- fish meal,
- hydrolyzate,
- trembling,
- vitazara,
- fish oil,
- multivitaminized premixes.
During feeding, young offspring must be kept in the right conditions. Broods up to 1 year of age are kept in 10-liter aquariums at a water temperature of 15–17 degrees. One aquarium can contain up to 500 young individuals. Practice has shown that with proper maintenance, a 68% brood survival rate can be achieved.
Types of sturgeon and their classification
Species of sturgeon include:
- beluga,
- Kaluga,
- sturgeon
- sterlet,
- stellate sturgeon,
- Shoveler
Beluga
Beluga is the largest migratory fish from the Sturgeon family. Its weight sometimes reaches a ton, and its length is 4 m. The thick and round body is ash-gray or greenish in color, the belly is white. The fish looks like a pig. The predator's mouth is the entire head, a thick, fleshy lip is surrounded by antennae that perform the function of smell. The yellowish nose is upturned and slightly translucent.
Beluga is an omnivore, eating small fish. From the sea - sprat and anchovy, from the river - roach, bream, carp and others. The age of the king fish reaches 40 years. It spawns in April - May, laying up to 8 million eggs at a depth of about 15 m. After spawning, the beluga goes to the sea. Lives in the Black Sea, the waters of the Caspian and Azov seas. In winter it hibernates.
Kaluga
Kaluga is a fish from the beluga genus and belongs to freshwater. It has enormous weight, large body size, and lives in the river basins of the Far East.
Lopanos
Shovelnose, a freshwater fish, is found in the tributaries of the Amur.
Stellate sturgeon
Stellate sturgeon is found in the Black, Caspian and Azov seas. The body is elongated, blue-black on the sides, the lower lips are poorly developed, and the nose is long. The size of the stellate sturgeon is up to 6 m, and its weight is up to 60 kg.
Sterlet
Sterlet differs from other sturgeons in size and appearance. Its length on average is 40-60 cm, weight - about 2 kg, but larger individuals are also found, weighing 6-7 kg. The sterlet has a spindle-shaped body of a gray, yellowish tint, without scales, with a long narrow nose. Mouth with bipartite lower lip, elongated. There are protective bone shields (50-70 pieces) on the sides and along the back.
The fish lives in cold, fast-flowing rivers of Western Siberia, and in lakes with clean water. Leads a gregarious lifestyle. In winter, they hibernate in groups to a depth of 15-20 m. Sterlet spawns in the spring, in May, and lays about 150 thousand eggs in the upper reaches of fast-flowing rivers. It feeds on invertebrates, larvae, eggs of other fish, and eats mosquitoes and midges. Young animals eat benthos. Unlike other sturgeons, the sterlet leads a sedentary lifestyle and does not go to sea to spawn.