Description of the Verkhovka
This small fish, which is called the redhead, oatmeal, and in some places chikoy, belongs to the ray-finned fish from the carp family. Verkhovka has some similarities with a small bleak , with which it is often confused. But the difference between the verkhovka and the bleak lies in the slab body and larger head. Bleak is a somewhat flat fish.
The crown is distinguished by a short lateral line, attributable to 2-12 scales, compared with the head with large eyes, an upper mouth and, of course, small size. This fish never grows more than 9 cm, and most often its length is about six centimeters.
The color of the top has a light green tint, the back is slightly darker, and the sides have a silvery tint. In the water, flocks of crowned moths sparkle like sparkles. In the sun, the scales of these fish become dazzling silver. The fins are transparent, matching the color of the water. On the sides you can see something like a bluish stripe. Depending on the color of the water and other conditions in a particular reservoir, the color of the top can change, be a little lighter and darker. The life of this small fish is also short - no more than four years.
Verkhovka as live bait
Like bleak, verkhovka is a delicate fish with easily falling scales that can be removed even with your fingers. This makes it a very weak live bait, but still there is no alternative to this fish in catching perch and other predators with it. But you can only grab it by the lip. However, perches often willingly take the dead top if some movements of the bait are made in the form of simple retrieving or jerking.
How to catch perch with live bait
It is worth noting that fishing for striped fish with live bait can be organized throughout the year, both in open water and during the freeze-up period. The most favorable months are May, July and August . In spring, the fish actively feed after the spawning period, which corresponds to the May time period of zhora. From mid-summer, the predator begins to actively feed on fry due to its wide distribution and easy accessibility, which fishermen need to take full advantage of. During the rest of the year, the bite of the striped robber is cyclical and is associated with weather conditions.
Important! Non-stormy, calm weather is characterized by stable bite. In winter, bursts of activity occur during thaws and sunny days.
Perches feed exclusively during daylight hours. The most favorable fishing times are morning and evening hours.
Important! If the fish is passive, it is better to use small live bait, since perch does not particularly like to chase active prey. When the predator is highly active, the size of live bait is increased, resulting in larger specimens being caught.
Let's consider the most popular fishing methods, delving into the structure of the gear structure and installation design.
Catching perch with live bait and a float rod
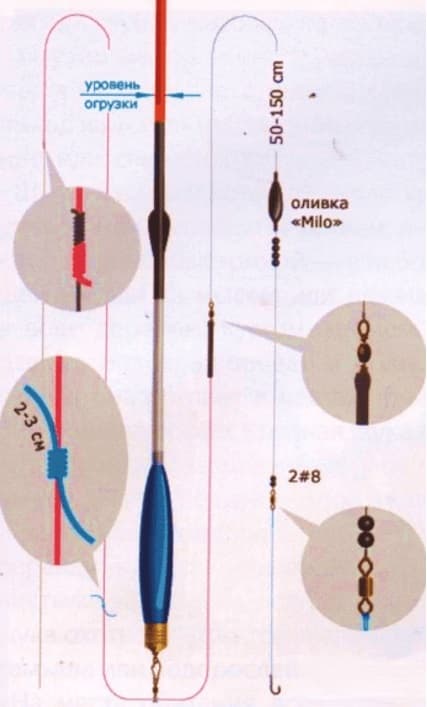
Tackle for catching perch with live bait using float rigs is selected based on average rod tests, range 20–40 grams and length ranging from 4 to 6 meters in telescopic version. It is advisable to have a light carbon fiber fishing rod, since fishing is quite dynamic and you will have to re-cast the tackle quite often, and to control and realize the bite, constantly hold the rod in your hands.
A reel is not used to reduce the weight of the tackle; the fishing line is tied directly to the tip of the rod. The fishing line used is monofilament. The fish's lips are quite weak and during sharp hookings the monofilament compensates for the overload. The loads are used stationary, assembled from lead pellets. Floats are used in the form of a spindle, with a short antenna and a low keel. The signaling devices are attached to the fishing line and are deaf. As a rule, floats above 10 grams are not used in perch live bait fishing.
The result of the bite is the predator’s self-hatching, which is expressed in a sharp movement of the float towards the nearby shelter. Fishing is careful, without forcing. Otherwise, the hook will tear the fish's mouth and the catch will be lost.
Catching perch with bottom tackle
For the most part, trophy perch are caught using hooks, delivering live bait into the holes and furrows of the underwater relief. Spinning rods with a median action and a soft quiver tip no longer than three meters are suitable as tackle. There will always be enough dough from 15 to 30 grams. A lightweight spinning reel with a friction clutch and a spool capacity of up to 100 meters of monofilament with a diameter of 0.2 mm is the most suitable option. The weight used is sliding, in the shape of an olive. Sliding doubles help to securely fix the bait, regardless of the distance and force of casting. The tank installed on a stand on the shore is equipped with an audible alarm.
Donks in the classic style are used with the addition of elastic bands. This type of gear is placed in clean areas of water areas adjacent to holes and riffles in order to plan for a school of perch to move to warmer shallow waters. Catching perch with live bait in the fall and closer to winter with bottom gear is the most productive and successful, since the fish migrate less and try to get to the points where they will winter.
Catching perch with mugs and girders
Catching perch with live bait in the summer using circles is carried out in the windows of water thickets and at the junction of water backwaters with the walls of coastal vegetation. Shore baits are placed near dead wood and among snags, placing live bait in the water floor. They use a thin rig made of 0.18-0.20 mm monofilament and a single hook, loaded with an inconspicuous sliding olive. In winter, from the ice they use bets similar in design to pike options. The only difference is a thinner monofilament line and the absence of a leash. They try to place the fry a little higher than at half-water, not allowing him to play widely, which is achieved by limiting the length of the leash to 15, maximum 20 centimeters.
Verkhovka habitats
Verkhovka lives in the upper layers of rivers with weak currents, oxbow lakes, lakes, in dug pits and reservoirs, adhering to not very silted places with hard clay-sandy soil. This is a typically schooling fish that feeds all day and in the dark. At night in good weather under the moon you can always see circles on calm water - this is the melting of the tops and bleak. During prolonged bad weather, as well as in spring and autumn, the verkhovka goes deeper. But for the most part, the upper layers of water are its home. This is a very shy fish. Often, from hitting the water with an oar, from knocking and even screaming, flocks of crowned beetles jump out of the water - splashing in all directions. The same picture happens during a driven hunt of perches, which also in a flock drive a flock of perches aground and begin a feast. Then the water boils from the frightened top leaders fleeing. Such boiling “cauldrons” attract seagulls, and they serve as a guide for anglers with spinning rods who come to these places and catch perch with small rotating and oscillating spoons.
I advise you to read: Catching boiler perch
What kind of fish is bleak?
Content
The official terminology calls the fish bleak, popularly – verkhoplavka, sebel and verkhovodka. Small fish are found in the upper layers of the reservoir, less common in the middle layers of water. She tends to float passively on the surface of the reservoir, waiting for small insects, mosquitoes, flies, and their larvae.
On the surface of the water, other types of riding fish are also well caught, which to the untrained eye resemble bleak: tops, bystryanki and buntings. The surest way to determine the type of prey is to count the number of scales on the side surface of the fish: for bleak - 52-55 pieces, for bystryanok - 44-50 pieces, for verkhovka - 12-14.
Bleak has a short life cycle, the maximum duration is 6 years. Trophy individuals reach a weight of 100 g and 25 cm in length, usually growing to 50-60 g in 5 years.

Small fish live in the upper horizons of the reservoir
Appearance of the sticker:
- an oblong body with a straight ridge and a bulge on the abdomen;
- large dark-colored fin with cutouts;
- the body is thin, the sides are practically absent, creating a flat surface;
- many small steel-colored scales with a sheen;
- silver-blue back with an olive tint;
- large lower jaw;
- belly light in color;
- fins are gray or dull yellow.
Habitats and lifestyle
In February-March, it emerges from its wintering grounds and begins to swim in the upper part of the water, preparing for spawning. In April or May they begin to spawn. Spring fishing for topwater is more effective at a depth of 50-75 cm.
It has a schooling reflex, so it tends to form large schools that swim around the pond, looking for food. It is an indicator of the presence of predators in the area, because upon detecting natural enemies (pike perch, chub, pike, perch), the flock is divided into small groups, including 20-30 pieces. Small flocks are more maneuverable, it is easier for them to slip past the predator. To survive in an unequal battle, it is endowed with good speed abilities; not every predator is able to catch up with bleak.
In the morning and evening, the bleak goes out hunting; the basis of its diet is small insects. Catching tactics - collecting fallen insects, catching them on the fly, knocking them down with splashes. To catch perch, it is better to use cloudy days with rain, when, due to wet wings, insects are not able to fly high, becoming prey for bleak.

Emerges from wintering grounds in February-March
Fishing in winter becomes more difficult; when cold weather sets in, the fish slide into the deeper layers of water, not showing activity in relation to food. It begins to be caught well in the spring from the ice when there is a sharp warming and warm water enters the holes.
Bleak has its own preferences regarding habitats:
- avoids overgrown rivers and ponds with standing water;
- does not like strong currents;
- loves calm rivers flowing in flat places and having gentle banks;
- prefers winding places in the river;
- swims in rivers with high concentrations of oxygen.
Read more
What is Salapin porridge for fishing and how to prepare it?
Spawning
Mature individuals go to spawn at the end of April, the process continues until the beginning of June. The spawning period directly depends on the water temperature; the optimal temperature is 15-17°C. It reaches sexual maturity at the age of 2-3 years, although the length during this period is only 5-7 cm. Bleak has a tendency to spawn in shallow water, dividing it into many portions of 3-4 eggs. In warm weather it spawns with pauses of 2-3 days, and in cold regions spawning lasts for 30-40 days.
For the survival of the species, it is endowed with good fertility; the number of eggs depends on the weight of the female. There are 300-400 pieces per 1 g of mass, that is, a female weighing 10 g is capable of laying 3-4 thousand eggs. The clutch size is 3000-5000 eggs; they are attached to hard surfaces, snags or plants. Incubation lasts 3-7 days, the duration is affected by water temperature.
The hatched fry gathers in schools and begins to actively feed on plankton; in just one year, the fry gains 6-8 g of weight.

The spawning period of bleak directly depends on the water temperature
What does bleak eat?
Zooplankton is the basis of the bleak food supply. Fish find various larvae, worms, eggs, and small crustaceans. They especially love the following insects:
- midges, flies;
- mosquitoes;
- small butterflies and insects: bugs, woodlice;
- phorids, stem beetles.
The perch constantly floats on the surface, waiting for the butterflies to fall. As a supplementary food, the fish eats the seeds of various plants and consumes small algae to a small extent. The fisherman’s usual bait also leads to active sebela fishing: a worm, dough, bread crumb. A good catch is observed for maggots.
Verkhovna spawning
Verkhovkas become capable of reproduction quite early - by the age of two years of their short life, when they reach a size of four centimeters. Spawning occurs in several stages, starting from May-June and often in July. The optimal water temperature for spawning verkhovka is 15-25 degrees. The eggs are deposited at a depth of about one and a half meters. Females stick it to the bottom of aquatic plants: water lilies, pondweed, arrowhead, even to objects floating in the water. The eggs mature for about a week and the larvae hatch ready for independent life, that is, capable of moving in the water and feeding.
Fishing Features
Season
Catching bleak in the spring before spawning is distinguished by its peculiar feeding. Like all other fish, our heroine is gaining strength after a winter lack of food, preparing for the most important event in her life.

During spawning, both the smallest fish and the first-spawned individuals can bite.
Fishing for large bleak in summer is carried out throughout the daylight hours, but it is better to position yourself so that your shadow does not fall on the water and does not frighten the already timid fish.
The second zhor is called pre-winter, although it occurs quite early, in late August - early September. It’s the so-called “Indian” summer at this time. With the onset of autumn cold weather and bad weather, the bleak descends into wintering pits and remains in them until spring.
During long thaws of 3-5 days, the fish wake up and bite even in the dead of winter. Winter bleak fishing during such periods can be especially successful.
Once, in the gulf of Sura with a flowing spring on February 23, we excitedly caught 3-4 kilograms of this fish in half a day! In total, there were eight of us in a spot measuring approximately 10 by 20 meters; it turns out that the total catch was more than 25 kilograms of bleak!
What does the verkhovka eat?
At first, the fry greedily feed on zooplankton, which includes rotifers and cladocerans. Next, the verkhovka begins to feed on various larvae, eats beetles, insects, and will not refuse fish eggs, being a very harmful fish in cultural reservoirs. During the daytime it feeds on mayflies, flies and other flying insects, and by night it goes to the depths, where it continues to feed, only now on zooplankton. Despite its small size, it is a very voracious fish.

Mounting a fishing rod on a bleak
Installing the equipment for a bleak is practically no different from the equipment for a float fishing rod. A fishing line is tied to the rod or reel. A float and weight are attached to it. Afterwards, a leash and a hook are tied to the main line using fishing knots.

for standing water

for long casting
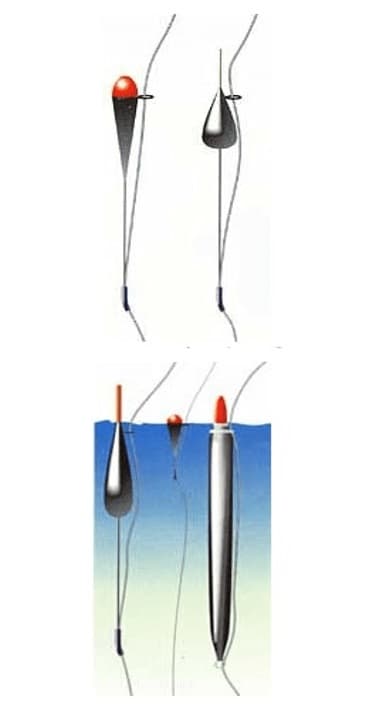
loading float equipment according to books
Equipment with fine settings is not as important for a simple amateur fisherman as for a sports fisherman. It is in sport fishing that gear adjustment comes to the fore. After all, prizes in the competition are at stake. More information about the installation of bleaching gear can be seen in the video from the TROPHY TV Channel.
Spreading
The verkhovka lives in most reservoirs of Russia, Europe, southern and northern latitudes, without affecting the northern rivers and reservoirs of the Middle and Far East. Although the verkhovka is distributed in many countries and regions, and in large quantities, this fish, due to its insignificant size, is not in demand as a food product, although its meat is fatty and tender. They say that canned food, sprats, and cutlets are made from verkhovka. True, cleaning and gutting such a fish is hard labor.
I advise you to read: How to cook verkhovka
Winter fishing

Winter fishing for bleak is possible during the thaw period, as mentioned above, or on the last ice. First, the horizon where the fish may be located is scouted. To do this, use a tackle with a garland of leashes located every 40-50 centimeters on the main line.
At the first bites, the desired horizon is fed using a dump feeder and fishing begins with a nodding rod with a miniature jig made of lead or tin. Heavy tungsten bleak usually spits out.
Winter bait for bleak - ground crackers with crushed bloodworms. It's also a good idea to add some bran or coconut flakes.











