Description of catfish
Catfish is the largest inhabitant of fresh water bodies. True, the beluga is not inferior to him in weight. But it belongs to the migratory fish - it enters the rivers only to spawn. Of the permanent river inhabitants, catfish have no equal in weight and size. The meat of this miracle fish is unusual - it is extremely fatty and tender. Various dishes are prepared from it, canned, salted and dried.
The name of catfish in Latin is silurus glanis. Classification of the common catfish:
- Class – Pisces.
- Order – Catfish (Siluriformes).
- Family – Catfish (Siluroidea).
- Genus – Catfish (Siluridae).
- Species – Common catfish (Silurus glanis).
Common or European catfish are found in Russian reservoirs. Belongs to the catfish family.
External signs:
- Color: brown. Brown-green shades predominate. The belly is painted white. The color depends on the living conditions - the color can vary from light yellow to black. Albinos are very rare among catfish.
- There is no adipose fin. The caudal fin is very short. Anal – long.
- The body is covered with mucus. There are no scales.
- The head is wide and flattened. The mouth is huge. Two large mustaches extend from her, and on her chin there are two more pairs of smaller mustaches.
- The tail does not look like a fish, it is very long and flattened on the sides. The length of the tail is more than 1/2 of the body.
- The eyes are wide apart. Set close to the upper lip.
- The lower jaw protrudes forward. The mouth contains many small and sharp teeth, which catfish use to grind rough food.
The dimensions and weight of catfish are in Table 1.
Table 1
| Maximum length | Weight Limit | ||
| historical | modern | historical | modern |
| 5 | 2,5 | more than 300 | 150 |
Such large catfish are rare today; fishermen usually catch fish weighing 10-20 kg.
The largest catfish - heavier than 300 kg - were caught in the 19th century in the Dniester and Oder rivers. The officially registered catfish caught weighed 306 kg. Its length was 3 m, and its approximate age was 80 years.
The common (European) catfish is a sedentary fish. Having chosen a hole for himself, he remains faithful to it all his life - he does not change his place of residence.
Types of catfish
Let's get acquainted with the most famous species of aquarium catfish.
- Speckled Corridor. The average length of a male is 4–6 cm, females - up to 7 cm. They have an olive-brown color with a large number of dark spots, and a yellowish abdomen. There are two rows of bone plates on the sides of the body, and there are hard spines on the dorsal and pectoral fins. The front of the head is decorated with two pairs of antennae.

- Ancistrus. Length - up to 14 cm. Color varies from light gray with a yellow tint to dark gray with light spots. The slightly flattened body is crowned by a wide head. The first rays of the fins are much thicker than the rest and are equipped with spines; there are rows of bone plates on the body. At the base of the head there are hidden spines that open in different directions during danger. The male is distinguished by lush “horns” - soft skin outgrowths on the nose. Females are slightly more massive, the outgrowths are almost smoothed out.

- Tarakatum. The average length is 16–17 cm, the female is larger than the male. The color is cream with large black spots that darken with age. The abdomen of females is light, that of males is creamy-white, and during the breeding season it is bluish. The body is elongated, with a high dorsal crest, a flat abdomen and a thickened base of the tail. The head is wide and flat below, there are three pairs of short antennae.

- Pterygoplicht brocade. Length - up to 20 cm. The color resembles a leopard pattern: brown-black spots with a yellow border are located along the body. With age, the pattern becomes smaller and may disappear completely. The body is flattened and elongated, covered with scales in the form of bone plates. High dorsal fin, lush pectoral and ventral fins.

- Synodontis. The average length is 6–9.5 cm, the male is smaller. The color is gray-beige with black-brown spots, the belly is slightly darker. The body is stocky, slightly flattened laterally. The caudal fin consists of two blades, the dorsal fin is in the form of a triangle. The fish is big-eyed and has six antennae near its mouth.

- White-spotted agamixis. Size - up to 12 cm, the female is more massive and duller. Color: brown-black with pale yellow spots. The body is large, elongated, with bone plates and spines. The head is massive, flattened, and has three pairs of mottled whiskers. The dorsal fin is triangular, with a tooth on the front ray, the ventral fins are small and rounded. The female is distinguished by a large shapeless abdomen.

- Callicht. Size - up to 15 cm. Color - from olive green to dark gray with large dark spots, males are distinguished by an orange anterior ray in the pectoral fin. The body is elongated, slightly flattened on the sides, on which there are two rows of bone plates; the back is not completely covered with them. The head is wide and flattened on top with three pairs of antennae at the mouth.

- Brochis or green catfish. The average length is 8–9 cm, the male is smaller and has a less rounded abdomen. The fish have greenish sides, a brownish back and a bright yellow belly. The head is large, the body is high, which smoothly descends towards the tail. On the flat sides there are two rows of hard plates and a two-blade tail.

- Catfish anchor. Size - up to 3.5 cm, the female is longer and more massive. Color - from reddish brown to dark brown with dark spots and stripes. The upper body profile is curved, the pectoral fins are proportionally long, and the skin has tubercles.

Did you know? The river catfish is distinguished by its extraordinary cunning and manages to hunt while staying in one place. To lure prey, it imitates worms by smoothly moving its antennae. When the prey is nearby, the catfish quickly draws in water along with its future lunch.
Habitat
Catfish live in rivers and lakes throughout the European part of Russia. There are none except in the Arctic Ocean basin. This freshwater giant is thermophilic, therefore it is found more often in reservoirs belonging to the basins of warm seas - the Aral, Black, Caspian and Azov. It is rare in Baltic waters, and if it is found, it is small in size.
Amur catfish live in Siberian rivers, which differ from the European species in appearance - color and size. The Amur catfish is not as large as the European catfish.
Most catfish are found in rivers of southern latitudes - in the Volga, Kuban, on the Don, in the Dnieper, on the Ural River. This fish easily tolerates slightly brackish water, so it can be found in river mouths and in slightly salted sea areas.
Appearance and habits of catfish
The common catfish, also known as the European catfish or simply catfish (Silurus glanis), is the largest freshwater fish in our reservoirs. Under natural conditions, it grows up to 3 m and reaches 180 kg of weight. In past centuries, when the animals were larger and their numbers were much higher, the captures of five meter-long specimens weighing 300 - 400 kg were recorded.
The common catfish is a representative of predatory fish of the catfish family. He leads a sedentary, isolated way of existence and does not leave his habitable place throughout his life, which under favorable conditions can last about 50 years. Even in search of food, which is mostly obtained in the dark, the catfish does not swim far from its site.
Only forced circumstances, such as a depleted food supply, shallowing of a reservoir or turbidity of the water in it, which catfish cannot tolerate and die, force them to leave their beds - deep-sea holes and snags. Sexually mature individuals temporarily leave their native penates during floods, migrating to the upper reaches of the river in search of suitable places for spawning, after which they return.
In small rivers and lakes, where the spring melting of ice is limited to a small flood, from which the water is not as cloudy as in a flood, and does not force the catfish to move, they spawn in the same reservoir and very often in their home.
Catfish, like all fish of the catfish family, are a territorial species that does not tolerate proximity to their relatives. Only in the cold season, infringing on their proud character, do they gather in groups and sleep in wintering pits. Young catfish are more sociable and prefer to stay together until they grow up and feel strong.
If you don't look closely, you might think that this fish does not have an abdominal region, especially when it is hungry. In many ways, this optical illusion is facilitated by the shape of the catfish’s body, most of which is laterally compressed, and the long anal fin, which goes directly into the tail. The wide forehead of the predator is separated by disproportionately small eyes, set so high that it seems that if it weren’t for it, they could merge together. A pair of long whitish mustaches adorns the upper lip. Four more small yellowish outgrowths are located on the giant’s chin.
The whiskers are not only an organ of touch, with the help of which the catfish orients itself and searches for food in an unlit environment, but also serves as bait for it in the hunt for small fish. Hiding in ambush or buried in the silt, the river giant puts its whiskers on display, imitating a living worm with them, and thus lures fish. When the object of the hunt, who has his eye on the fleshy decoy, is nearby, our hero, with a sharp forward movement, grabs it with his huge mouth, and the strong jaws that close after this, densely studded with small and sharp bristle teeth, will not leave the victim a single chance of salvation.
The color of catfish depends on the age of the fish, the time of year and the composition of the water. The coloring of young catfish is brighter and more contrasting, although in general it is rather gloomy in this species of fish. A black back, dark green sides camouflaged with light olive spots, and a gray or dirty yellow belly are considered the typical coloring of adults. In lake catfish, darker tones predominate; in river catfish, the coloring is much lighter.
Where live?
Catfish wisely stay in the depths. Their large size and caution make them stick to the bottom. They are uncomfortable in shallow water. They are afraid of the light. Catfish is a predator that hunts at night. For rest, he chooses the darkest and deepest places in reservoirs.
Catfish live in pits where sunken logs, trees, and snags accumulate. If the river is shallow, the giants hide in beaver holes. They look for any recesses where they can hide. While it is light outside, the catfish lies down in its shelter - resting and digesting what it has eaten. As soon as it gets dark, the barbel goes hunting - someone will fall into its huge mouth.
The largest catfish caught by people

There is an opinion that this fish eats the bodies of drowned people, and can also pull under the water a person who has sailed far from the shore. She won't be able to swallow him, but she can easily drown him.
A large catfish, more than three meters long, was caught in eastern China. Its huge mouth reached 90 cm, and human remains were found in the giant’s stomach. In Russia at the moment there is no documented evidence of cases of cannibalism of these fish.
Interesting fact! On average, a catfish lives 40 years, and the maximum life expectancy recorded to date is more than 80 years.
In 2011, the largest catfish in Europe was caught in Italy. Its length was 2.5 meters and its weight was 114 kg. Roberto Godi, a lucky fisherman, with the help of several other people, caught the fish for 50 minutes.
After the fish was weighed and photographed, Roberto released the trophy back into the river. His catch was awarded the title of the largest of those that were caught in the reservoirs of Europe.
The previous “record” was recorded a little earlier in Spain. A catfish was caught in the Ebro River that weighed 111 kg.
On May 1, 2009, the world's largest documented catfish was caught in the Mekong River in Thailand. With a length of 2.7 meters, its weight was 293 kg. This world record was recorded in the presence of Thai authorities and the head of the World Wildlife Fund, Zeb Hogan.
According to unconfirmed facts, large catfish were caught in different countries and at different times:
| Fishing place | Length | Weight |
| Ukraine, Dnieper river | 4 m | 288 kg |
| Ukraine, Dniester river | 4.3 m | 320 kg |
| Poland, Oder River | 4.6 m | 400 kg |
Types of catfish
There are about 30 families in the catfish order. But only ordinary and ictalur catfish have a characteristic “catfish” appearance. In addition to the common (European) catfish, several more interesting representatives of the catfish family (Siluridae) can be found in the reservoirs of Russia and the world.
Som Soldatova
Soldatov's catfish (Silurus soldatovi) is a large fish without scales. Features of the species and facts from its life:
- Length – up to 3 m, weight – 80 kg or more.
- It is similar in size and color to the European catfish. The back and sides are gray-brown, with streaks. The belly is light.
- It feeds on fish, but can also swallow waterfowl.
- Usually hunts at night.
- In autumn it goes to depth, where it mainly rests.
- Doesn't eat in winter.
- Ripens in the 4th year of life. Lives 30 years or more.
Soldatov's catfish is a rare fish listed in the Red Book of the Russian Federation. The number of this catfish is constantly declining. Its fishing is prohibited by law.
Habitat: Amur River basin, Ussuri River and Lake Khanka. Spawns in June-July, entering coastal thickets. The fish lays eggs on plants, among which the fish builds a kind of nest.

Amur catfish
The Amur catfish (Parasilurus asotus) is not afraid of brackish water. It is also called Far Eastern.
External signs:
- It reaches 1 m in length and weighs 6-8 kg.
- The head is large, wide, flattened.
- The body becomes thinner towards the tail. There is a small fin on the tail.
- Body color is dark green. The belly is light.
- The anal fin is large, almost reaching the caudal fin.
- The lower jaw protrudes forward. There are two pairs of whiskers on the muzzle.
Features of behavior and habitat:
- Loves warm waters.
- Prefers standing or slowly flowing water.
- In the summer, it goes into channels, floods and the coastal zone.
- In autumn it goes deeper.
- Doesn't build a nest.
- Hunts from ambush in the evenings and at night. The basis of nutrition is small fish, shellfish, frogs, and crayfish.

Puberty occurs in the fourth year of life. Spawning time is the end of May – the first half of July. Males do not guard eggs laid on aquatic plants.
Fishermen annually catch about 10 tons of Amur catfish. The fish is an object of sport and recreational fishing.
Habitat: waters of Japan, China and Korea. In 1933, 22 breeder fish were released into the waters of Primorye. The catfish got into Baikal and spread throughout Primorye. Refers to valuable commercial fish. The meat is tasty, medium fat, with few bones.
Channel catfish
Channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus) is a fish of the Ictalurus family. Representative of catfishes of North America. Industrial production facility.
External signs:
- Body length – up to 132 cm. Usually – no more than 57 cm.
- Maximum weight – 4.5-9 kg. In the entire history of the fishery, the largest channel catfish was a specimen weighing 26 kg.
- The body is painted in a dark color - bluish-olive, gray, black. The belly is light. There are spots on the sides.

Omnivore - eats fish, shellfish, insects, small mammals. Found in the USA, southern Canada, and northern Mexico. Since 1972, channel catfish have been bred in Russia - in the Kuban. From the ponds it penetrated into the rivers of the Don and Kuban systems. They are bred in the Moscow region, in the Urals.
African catfish
A heat-loving fish that lives in the Jordan River and reservoirs of South and Southeast Asia. It looks like an ordinary catfish. It has an elongated body, slightly flattened laterally. The second name is sharmut. Capable of breathing atmospheric air. In addition to gills, the African catfish has an organ riddled with blood vessels - this is a prototype of the lung, which allows the fish to survive in the air for 15-45 hours.

Natural enemies of catfish

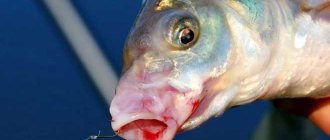
Photo: Catfish fish
The only enemy of adult catfish is humans. Not a single river fish can compare with them in size, much less attack them, so they live in the open spaces of the water quite freely and suffer only from human activity. At the same time, adult catfish bite less readily, but still the main cause of their mortality is fishing.
Underwater hunting for catfish is much less common, in which hunters go down with scuba gear - this way you can catch even the largest of them. But many adult catfish still manage to successfully live to old age. It is more difficult for young fish to do this, mainly because they bite much more readily and are caught more often.
But even young catfish are not threatened by anyone except humans. Other predatory fish can be a threat to them only while they are still very young; they also often eat eggs or fry. It can be pike, burbot, asp, and almost any other river fish. But juvenile catfish are usually protected by an adult male.
Interesting fact: The electric catfish is one of the most interesting catfishes. It lives in Africa and is capable of generating strong electric currents - up to 350 volts, thanks to organs located under the skin that cover most of its body. Using electricity, this catfish stuns its victims and protects itself from enemies.
Lifestyle of the common catfish
Catfish are homebodies. They rarely go on long journeys. Giants have not left their homes for decades. They sit in their holes, coming out only to hunt. Due to its terrifying appearance and size, the catfish is not capable of long-term pursuit, so it catches fish by attacking suddenly - from an ambush.
Spring Summer
With the onset of spring, when the flood begins, the catfish leaves the hatching hole. It rises upstream, enters floodplains and floodplain lakes, where it lays eggs.
About a month passes from the moment of awakening from hibernation until spawning. All this time, the catfish eats a lot - it makes up for the hungry winter times by eating fish and other living creatures that come across. All summer the catfish actively hunts - preparing for winter.
Hunting strategy:
- Quickly break into a school swimming past, or pounce on a single fish that has approached at a distance sufficient for a throw.
- The powerful flexible tail is used to stun several fish at once - if a school is attacked.
- Large catfish are slow and rarely manage to catch fish. The giants have to be content with amphibians and mollusks.
- Large catfish prey on young animals. They lie with their mouth half-open, and when the flock approaches, they suck in water along with the prey.
Other behavioral features of catfish:
- It cannot be said that the catfish is completely nocturnal. He often “wanders” at dawn. And sometimes during the day it appears on the surface of the water, showing its dark slippery sides.
- Catfish can be seen - and not only during spawning - basking in the sun. They float to the surface and lie belly up. There is a sign that the appearance of catfish during the day is a harbinger of inclement weather.
- If there are prolonged rains and floods, and the water becomes cloudy, the catfish is forced to leave its hole - it looks for a quiet backwater and goes to places where there is no turbidity.
- Catfish hunt every night. Specimens weighing 16 and 32 kg emerge from their shelters at sunset. First, the catfish walks in circles around its nesting area, then swims upstream - looking for prey. It happens that a hungry fish, in search of food, swims very far from its hole. But regardless of the distance, the catfish always returns home in the morning.
Autumn winter
Catfish love warmth - almost all species of the catfish family come from tropical zones. Therefore, they stop their active lifestyle early. Already in September, the catfish goes to its wintering place. From October-November - depending on climatic conditions and water temperature, the catfish, having fattened up over the summer, stops hunting.
He settles down for the winter in pits. Moreover, it does this before other fish. The giant buries its flat head into the mud. A fallen predator becomes completely harmless to the fish and other living creatures that make up the barbel’s daily diet.

Catfish spawning
When spawning occurs, catfish fishing temporarily stops. Violation of the law threatens with a considerable fine and confiscation of gear. The ban is valid for 20 days. At the same time, fishing from the shore, even with one tackle, is strictly prohibited. The female catfish carefully selects a secluded place where she then lays eggs. Algae and flooded trees serve as a kind of incubator. Individuals choose areas with standing water or calm currents. To spawn, catfish swim into reed thickets, water meadows, and underwater plants.
The female lays eggs in the dark or at dawn. There are not many eggs; their number is determined by the size of the female. Parents are on duty at the masonry for seven days, protecting it from the inhabitants of the reservoir. The time comes and the fry are born. Adult catfish abandon teenagers and return to their favorite places. Weakened parents rest and gain strength. After a while they begin to hunt.
Sexual maturity and spawning period
As soon as spring begins, the catfish sets off on a journey in search of a secluded place to spawn. The spawning begins during spring floods. With the early onset of spring, spawning begins in May. The temperature favorable for spawning is 14-16°C.
Sexual maturity in catfish occurs in the third year of life. Fish can reproduce when they reach a weight of about 3 kg and a length of 60 cm. Fish of the same age category gather in groups. Females look for a male to mate with that matches their age and size.
Small males run the risk of being swallowed by females even during mating games - the number of applicants is reduced.
During spawning, catching catfish is prohibited by law. The fine is tens of minimum wages and confiscation of fishing equipment. The ban is set for 20 days. The ban is categorical - you can’t fish even from the shore, even with one tackle.
Catfish carefully select a place where they can spawn. The female deposits it on aquatic plants growing in the coastal zone. Ideal conditions for spawning are a weak current, or even better, its complete absence.
To lay eggs in shallow water bodies, catfish go:
- into the reeds;
- to flooded meadows;
- in a thicket of grass and algae.
In deep reservoirs, catfish look for pools or flooded ravines.
When the female chooses a male to her liking, the couple goes to a secluded place to spawn. The catfish, using powerful fins, prepares a hole for the nest, using tree roots and straw for this purpose. Spawning occurs at night, before the morning hours. The eggs are large and there are few of them. The number of eggs depends on the size of the female.
After fertilization, the eggs are covered with mucus, which holds them together and allows them to stick to the surface of plants or snags. The parents watch the nest for about a week, driving away dangerous and curious inhabitants of the reservoir. When the fry are born, the parents swim away to their favorite holes. After spawning, the couple rests at great depths, not even rising to get food. And only after 1-2 weeks they go to pick up the survivors.
Reproduction
Catfish become sexually mature at the age of 4-5 years. At this age, the weight of the catfish reaches 3 kg, with a length of 60 cm. Spawning of catfish begins when the water temperature reaches 16-18 ° C. Depending on the region, this can occur from early May to early July.

For spawning, catfish choose a place in the coastal zone among aquatic vegetation, with a weak current or its complete absence. In those places where there are a lot of catfish, they chase each other and entangle themselves like snakes, all this is accompanied by splashes and rolling blows heard from a great distance.
Each female catfish is followed by 3-4 males, from which she chooses one. The female chooses a male that matches her in age and size. Then the resulting pair drives away the remaining males and builds a primitive nest in the form of a hole in the ground and remnants of vegetation. Spawning occurs at night or early in the morning. The female lays eggs in the nest and the male remains to guard it. Catfish eggs are large, the diameter of each egg is 2-3 mm, the total number of eggs ranges from 11 to 480 thousand eggs and depends on the size of the female. For every kilogram of the female’s mass there are 30 thousand eggs.
You may be interested in: Shimano Stella FI Reel

The female catfish leaves immediately after spawning, and the male remains to monitor the nest and drive away other inhabitants of the reservoir from it. Juvenile catfish emerge from the eggs on about 10 days. They are 6-8 mm long, at first they stay in the nest and feed from the yolk sac. After 7-10 days, they begin to swim and look for food, but do not move far from the nest. The male stays close to them all this time and protects them from enemies. Four weeks after hatching from eggs, young catfish disperse from the nest, keeping in groups of several individuals.
Having fulfilled his parental duty, the male, following the female, returns back to his favorite hole.
What does catfish eat?
The catfish's diet depends on its age. Catfish fry eat:
- planktonic crustaceans;
- leeches;
- mosquito larvae;
- tadpoles;
- small water beetles.
Grown-up catfish quickly display predatory habits. Having reached 4 cm in length, young predators begin hunting for fry of other fish. Catfish, growing up, begin to feed mainly on fish. Supplements to his diet include:
- frogs;
- crayfish;
- shellfish
The catfish becomes a full-fledged predator by the age of three. Having reached sexual maturity, it continues to grow. The diet of an adult catfish contains a variety of protein foods:
- fish;
- crustaceans;
- shellfish;
- birds;
- rodents;
- frogs;
- small mammals;
- large insects.
If the prey is large, the catfish cannot eat it right away. Then he waits for the dead creature to begin to rot and decompose. For this reason, catfish are often called scavengers.
The catfish will not perish from hunger - if there are few fish and other large bait in the reservoir, it devours any organic matter. If there is no ordinary food, the giant can eat ordinary bread.
Methods of catching and baiting catfish
The most effective and targeted way of catching catfish is considered to be fishing with a quox using a regular donkey, adapted for an onboard fishing rod and equipped with a fishing reel.
It is not known exactly for what reasons, but it is the sounds of the quok that lure the predator out of cover and attract it to the boat. Rising to the surface of the reservoir - to the source of the sound, the fish meets on its way the bait prepared for it, which is lowered 2-3 meters above the bottom. To do this, the bait is first placed on the ground, releasing the line to the aisle, then raised, winding the required footage onto the reel.
Of course, you can catch catfish with the same gear without quoting, that is, while it is feeding, but finding its feeding places and the paths leading to them is much more difficult than stumbling upon a fish sleeping in a shelter and attracting it with a quok.
In other cases, the capture of catfish is random. A float rod and spinning rod catch only small catfish weighing 2.5-6 kg, which are not afraid to go out in search of food on grassy shallows and riffles, especially in the spring, when the feeling of hunger overcomes fear in juveniles who have been hungry over the winter.
Despite the fact that the popular bait for catfish is live bait and frogs, large earthworms - crawlers, placed several on a hook, bring good results. Live crayfish and leeches, familiar to our hero, have also proven themselves well in this capacity. passengers parasitizing on his body. Slightly spoiled beef pulp, mussel meat - a bivalve mollusk and chicken giblets also serve as good bait for catching catfish.
Fishing for catfish
The best time for fishing for catfish is summer. Catching this fish is every angler's dream. Many ways of hunting giants have been invented. Catfish is the most coveted trophy in fishing.

What you need to know when preparing for fishing:
- The rod and reel should be ten times more powerful than pike fishing gear.
- The braided cord must have a diameter of at least 0.3-0.5 mm.
- It is almost impossible to pull the giant ashore, so a boat is needed.
- The catfish, having “taken a ride” with the fisherman in the boat, weakens over time. Inexperienced fishermen need to remember that a fight with a catfish is life-threatening.
When fishing, the rod must be tied to a stake driven into the ground or to strong branches. Even fish weighing 4 kg bite very sharply, the rod instantly takes off from its place.
Silicone baits
Catfish, like any predator, bites on any attractive bait, but the best results are shown when equipped with jig baits (silicone baits).
Catfish bite on any silicone bait:
- twisters;
- vibrotails;
- rippers.
The sinker is selected in proportion to the depth of the hole. If the depth is large, take a sinker weighing 30-40 g. The optimal size of the bait is 15-20 cm. If the catfish swallows the bait, a strong hook is needed. The fisherman needs to be prepared for strong resistance.
Spoon
Catfish respond especially well to large, oscillating spoon baits. The spinners have a wide surface, which does not allow slow retrieving in currents. It is recommended to use spinners when fishing in holes - where there is quiet and stagnant water.
Examples of suitable spinners:
- Storling 25 g. Classic version. For catfish, take a palm-sized spoon. An oscillating spoon with a noticeable concavity near the tee.
- Atom 20 g. Similar to the Storling, but has a tapered end near the winding ring.
- Kuusamo Rasanen 20 g. The spoon is decorated with a red ball. Moves smoothly in water.
Kwok
Kwok is a device that, when its cup-shaped part hits the water, makes a sound that is tempting for catfish. Hearing the beating of the quok on the surface of the water, the hungry catfish rises from the depths. Kwok material is wood or composite material.
Donka
Bottom tackle is the most common fishing rod for catching catfish. Fish are always more willing to eat natural bait. Another plus is that the angler can install an unlimited number of rods. Typically, the tackle is made up of a large hook and a sinker weighing 100 g. The bait is put on the hook.
Best bait for catfish
The catfish readily attacks any living creature. For a giant to be interested in bait, it must be of animal origin and be quite large. The bait must stay well on the hook, otherwise it may fly off when it hits the water. You can secure the bait on the hook with regular thread. Suitable baits:
- Crawls. These are large worms - they remain alive for a long time and move on the hook, attracting the attention of the fish. Thread 2-3 worms onto the hook at once. Crawls are uninteresting to small specimens; large predators will react to it. Crawlers are found after rains, in the dark. They appear in parks, on personal plots, crawling out of the ground onto its surface.
- Medvedka. Large insect, garden pest. To lure the mole cricket, they bury a bottle of beer in the garden - there should be a little bit of it. The neck is covered with gauze. This is one of the best baits.
- Frog. Favorite catfish delicacy. Frogs remain alive for a long time and move, which attracts predators.
- Live bait. Fish are the basis of the catfish diet. You need a fish that is familiar to the catfish, so they take it from the same reservoir in which they are going to fish. Gobies, bleaks and roaches are suitable.
- Leeches. They, like crawlies, are strung in a bunch. Place 3-4 pieces. The suction cups of leeches are cut off so that they do not stick to the hook or bottom.
- Perlovitsa. You can find this bivalve mollusk in any body of water.
- Chicken liver. It is dried in the sun before stringing.
- Locust. Several insects are left on the hook.
It is impossible to guess which bait the catfish will like more - live or dead. Som is a gourmet. We need to find an approach to it. To achieve a goal, you have to try many options.
Proper complementary feeding
Most fishermen, devoting a lot of time to preparing bait, do not engage in bait at all. But in vain. Catfish readily respond to tasty food. Experienced fishermen claim that good bait allows you to significantly increase the number of bites.
The mustachioed giant, unlike other predatory fish, eats, in addition to fish, all kinds of protein living creatures. To attract catfish you can use:
- Offal. Ground skin - pork or beef - will do. Catfish will also not refuse to taste intestines, lard, meat, chicken stomachs, and other offal. To ensure that meat or offal for bait attracts catfish, it is recommended to dry or fry them.
- Bird feathers. This is a cheap bait that needs to be fried a little over the fire.
- Fish fat . It is sold in pharmacies and stores. Add fat to any bait. But you absolutely cannot add vegetable fats - other fish will swim in, and the predator will start hunting for the fish. This will distract the catfish from both bait and bait.
Catfish, having seen that delicious food appears in a certain place, will return to it again and again. But there is no point in leaving bait where catfish do not appear.

Lures do not work:
- on fast rolls;
- aground;
- in coastal areas.
You need to leave a treat:
- at the entrances and exits of pits;
- near flooded snags;
- on a deep-sea reach.
Catching catfish
Catfish is the largest fish among the inhabitants of our freshwater bodies. Catfish is considered one of the most coveted trophies; catching a large catfish is the dream of many anglers. Among them there is even a separate group of fishermen who specialize exclusively in catching catfish, they are called somyatniki.

The best time for catching catfish is a warm summer night, without wind and a clear starry sky. Catching catfish during the day is purely random, with the exception of the spring months, when catfish can be purposefully caught during the day.
You can catch catfish in different ways: with a donk, with a girder, with a quok, with a spinning rod and by trolling.

Donka
Bottom tackle is the oldest and still the most common method of catching catfish. A classic donka consists of a reel, fishing line, lead sinker and hook. For donkey use a strong monofilament line with a diameter of 0.5-0.6 mm, a sinker weighing 80-100 grams, a hook number 12-16 according to domestic numbering. Donks are placed in the evening in a promising place with an interval of 25-30 meters, the fisherman stays next to the donks all night, checking them every hour and a half.

Catfish prefer large baits of animal origin. The best baits for catfish are: crawlers, mole crickets, frogs, live bait, leeches, crayfish, poultry seared in a fire, meat or offal, sliced fish, shellfish, grasshoppers or locusts. The bait must be firmly held on the hook; it must not fly off the hook when it hits the water when casting. As a last resort, you can secure the bait on the hook with regular thread. Catfish are picky about bait, so the angler has to experiment and try different options to please the taste of the catfish.
You may be interested in: Pontoon 21 Cheerful 40SP-MR. Cheer up!
When catching catfish, they often use specially prepared bait, which significantly increases the number of bites. The following are used as bait: meat by-products, ground pork or beef skin, intestines, lard, chicken stomachs, bird feathers and fish oil. It makes no sense to leave bait in places where catfish do not visit. You need to leave bait: at the entrances and exits of holes and pools, near flooded snags, on deep-sea reaches.
Kwok
Catching catfish with kwok is an old and popular way of catching this fish. Kwok is a special device made of wood or modern composite material, which, when hitting the surface of the water with its cup-shaped part, produces a specific sound that attracts catfish.
The process of fishing with a quok is as follows: the angler alone, or better yet together, slowly floats a boat with the current, pulls the bait, which is located 2-3 meters from the bottom and hits the surface of the water with a quok. Hearing the sounds of the quok, the catfish rises from its hole, sees the bait and takes it.

The gear for catching catfish with a quok consists of a strong fishing line that can withstand a breaking load of 100 kg, a 1 meter long leash made of monofilament with a diameter of 0.5-0.8 mm, a large and strong hook and sinker. The line can be spooled on a reel or a short side rod with a powerful reel can be used. A piece of fish, a mole cricket, or a bunch of crawling worms can be used as a bait.
When nodding, you need to make 3-5 blows on the surface of the water, then pause for 10-15 seconds, then make the next series of blows.
Fishermen pass along one promising section of the river several times; if there is no bite, they should either change the bait or swim to the next promising place.

After the bite, the fisherman should not rush to hook; he needs to wait until the catfish properly swallows the bait. When landing a catfish, you should first reel it out and only then pull it to the boat. A catfish caught and brought to the boat is lifted into the boat with a hook.
Spinning
Catfish can be caught using a spinning rod. To catch catfish, you should use a strong and powerful heavy class rod, with a large cast, about 2 meters long. It is better to use a marine multiplier reel, or a spinning reel, but of appropriate power. A strong braided line with a diameter of 0.4-0.5 mm should be wound on the reel. It is convenient to use a boat to catch catfish. A catfish, after dragging a boat with a fisherman for some time, weakens and is easier to pull ashore.

To catch catfish using a spinning rod, I use silicone baits, oscillating spoons and wobblers. Catfish are bottom-dwelling fish, so jig fishing with silicone baits, which can be fished close to the bottom, shows good results. To catch catfish, twisters and vibrotails 15-20 cm long are used. Good results are shown by using baits made of edible silicone, in the shape of a crustacean. The load is selected depending on the depth of the pit where fishing is carried out, often the weight of the load is 30-40 grams. To catch catfish, step jigs are used. Sometimes, if conditions allow it, it is useful to drag the bait along the bottom, lifting mud from the bottom; such wiring attracts the attention of the catfish. After the catfish bites, you need a powerful hook. The fisherman must be prepared for long and persistent resistance.
Catfish can be caught using large, oscillating spoons. Oscillating spoons often have a wide surface, so it is difficult to perform slow retrieving with them in the current. Good results are shown by fishing with spoons in holes where there is no current or it is weak. The best spoons for catching catfish: Storling, Atom, Kuusamo Rasanen.

Some anglers catch catfish using wobblers. To catch catfish, floating or sinking deep-diving wobblers are used. The size of the wobbler should correspond to the size of the intended prey. For fishing, choose wobblers of bright, acidic colors, which are clearly visible at great depths. It is desirable that a wobbler designed for catching catfish has a built-in noise chamber; such wobblers are capable of attracting fish from a great distance.
Zherlitsa for catfish

In many regions of our country, girders are traditionally used to catch catfish. A catfish fishing rod is a wooden flyer with a thick fishing line wound around it. The end of the fishing line is inserted into a split made at one end of the flyer. A sinker weighing 200 grams, a leash 20-25 cm long and a strong large hook are attached to the fishing line. Live bait is placed on the hook. The zherlitsa is installed at night, right on the catfish pit. Zherlitsa is checked early in the morning. Catfish often drag the fishing line into snags; the angler must show great patience when fishing.
Breeding and growing catfish
Catfish are a promising fish species for artificial breeding. Compared to other predators - pike or pike perch, it has important advantages:
- No need for large bodies of water. For feeding, pits or canals filled with water are sufficient. The main thing is to ensure a suitable hydrochemical regime.
- The catfish hibernates during the winter, which makes it easier to keep. There is no need to keep and feed it in wintering ponds.
- Spawning can be carried out in wintering ponds vacated by carp.
- Catfish taken for breeding can be released into water bodies to destroy low-value fish.
- Ponds located near fish processing plants or slaughterhouses can be used for breeding to use waste from these industries.
- Due to their wide range of nutrition, catfish eat not only fish, but also all pond animals.
Catfish are bred in ponds and reservoirs where other fish are bred. Thanks to the predator, fish productivity in artificial reservoirs can be increased to 110 kg/ha. The predator cleans the pond of weed fish, frogs, and tadpoles.
How does a catfish farm work?
An industrial catfish breeding farm has a standard capacity of 50 tons of fish per year. There are also farms with 20 and 100 tons per year. One person can maintain such a farm, working 25 hours a week. Most often, African catfish are bred on such farms.
The production cycle of such farms begins with the release of fry weighing 0.1-5 g. In the farm, you can raise catfish up to 1 kg in just six months. Since fish grow at different rates, the “harvest” is collected weekly, and the caught fish are sorted by weight. Feed consumption on a catfish farm is 1 kg per 1 kg of live weight of fish.
Harvesting manufacturers
For producers they go to natural reservoirs. Harvesting is done in the autumn-winter period. To catch common catfish, straining fishing gear is used. Catching is done a year before spawning in an artificial pond.
Features of harvesting catfish producers:
- Before transporting fish, it must be kept in a cage. The catfish “regurgitates” the food eaten the day before - this spoils the water and worsens transportation conditions.
- The most promising in terms of production are individuals aged 5-9 years. They weigh a little - up to 10 kg. They are convenient to work with.
Spawning in artificial conditions
It is best to use wintering carp ponds with an area of 500-700 square meters. m. Spawning carp ponds are ineffective - in them, catfish eggs, being scattered over the vegetation, are poorly fertilized and sink into the silt, which makes it subsequently difficult to catch larvae and grown young animals.
Catfish eat a lot before spawning. Before breeding, males and females are placed in a wintering pond with nests made from willow roots. Spawning substrate - nests, attached to wire circles with a diameter of 60-70 cm.

What you need to know about preparing for spawning:
- The nests are secured with pegs, 30 cm from the bottom, and 3 m from the shore.
- The optimal depth of the pond is 1 m.
- The optimal water temperature is 20-22°C.
- The catfish are transferred to the pond using a net. It is better to move in the evening.
- There should be an equal number of females and males.
- Before spawning, females need to be given an injection of the pituitary gland of carp fish - 3 mg (in 3-4 ml of saline solution) per 1 kg of weight.
- Spawning will begin one day after being placed in the pond. Spawning duration is 4 hours. The female lays eggs in different nests. It is important that it be quiet during spawning.
Raising young animals
Nests after spawning are completed are taken out of the water. They are placed in special devices - Chalikov apparatuses.
Device performance indicators:
- fertilization rate – 80-90%;
- larval yield – up to 80%;
- incubation duration is 1760-1800 degree-hours.
The larvae are kept in cages where incubation took place. The larvae are transferred to a mixed diet on the 4th day of birth. Rearing is carried out in fry ponds. Replanting rates are 300 thousand fry per 1 hectare of area.
Larval rearing indicators:
- weight gain by fry per month - 2-3 g;
- survival rate – 80%.
Fingerlings gain a mass of 25-30 g. About 70% of individuals survive. Fingerlings are transferred to a wintering pond for the winter. The norm is 2-3 tons per 1 hectare. One-year-old fish are allowed into the feeding carp pond. The norm is 100-200 pieces per 1 hectare.
What species are grown?
In artificial ponds they grow:
- Common catfish . He is fed fresh fish - crucian carp, rudd, as well as granulated salmon feed. The number of catfish weighing 0.1-2 kg should not exceed 50-100 specimens per 1 hectare of pond with artificially grown fish.
- African (clariid) catfish . Tasty and unpretentious fish. Grows quickly. The cost of expensive feed and heating water is about 30% of the cost - this is the only disadvantage when raising African catfish. It needs favorable conditions - warm water, high oxygen content in the water, suitable salt pH level. In a year, if everything is done correctly, you can grow fish up to 2 kg.
- Channel catfish. Not picky, but heat-loving fish. They are successfully grown in the southern regions, where the water temperature remains at 22°C for at least 4 months of the year.
The Amur catfish is recommended as an additional object for warm-water cage culture. Its two-year-olds have a mass of 550-650 g. The fish productivity of the cages is 94 kg per square meter. m.
How does mating happen?
For reproduction, a sexually mature pair of fish is needed, although many breeders advise that there should be several females for one male. The stimulus for the start of spawning is a protein diet. At this time, fish should be given bloodworms, brine shrimp, daphnia, and tubifex live or frozen.
Important! Catfish can eat their eggs, so for spawning and raising offspring it is necessary to provide two separate aquariums.
Let's look at the spawning of these fish using the example of corydoras. Usually the process begins early in the morning. The male stimulates the female with his antennae, tickling her back and sides. After this, it is positioned at right angles to the female’s head and releases milk.
Experts do not fully agree on how exactly fertilization of eggs occurs. Some of them believe that the female passes milk through her intestinal tract and releases it onto the eggs, which are located in the ventral fins. According to others, the milk passes only through the female’s gills and is directed along the body to the eggs.

After fertilization, the female glues the egg to a previously cleaned surface - glass, plant, filter. Once the eggs are laid, mating is repeated until all 200–300 eggs are fertilized. This may take an hour or even longer. Thus, in order to breed these fish, you just need to provide them with appropriate living conditions.
Economic importance and protection status of fish
Catfish is a valuable commercial fish. The meat in it is valued - it is fatty, tasty, tender. And in the old days, catfish swim bladders and skin were also used. Glue was made from bubbles, and “glass” was made from leather for windows. At the beginning of the last century, the production of catfish from one reservoir amounted to thousands of tons. Today the catches are an order of magnitude lower.
Uncontrolled fishing and poaching have led to a widespread decline in the catfish population. Today, in many reservoirs where catfish were found in abundance, they have become rare. In many regions, catfish are listed in the Red Book and are under state protection.

Methods for raising catfish in captivity
Thanks to its unpretentiousness, catfish has become quite widespread as a fish that can easily be raised in captivity, simply by creating suitable living conditions. There are four ways to raise catfish in captivity.
1) Cage method. Catfish spawning takes place in specially equipped cages. After the fry hatch from the eggs, they are separated from the adults.

2) Pond method. The fish are placed in the limited space of the pond and grown almost in natural conditions. In this case, all young animals are caught and raised in hatcheries or spawning nursery areas.
3) Pool method. With its help, catfish can be successfully grown even at home. At the same time, the sizes and types of pools do not play a special role and can vary significantly.
4) Feeding method. The only way in which catfish is grown together with other species of fish. At the same time, it is used not so much for obtaining meat in the future, but as a main assistant for reducing an excessively large population of fish in water bodies. If this procedure is not required, the catfish must be selected in such a way that its dimensions do not exceed the size of other fish and it would not be able to hunt them. However, it must be taken into account that in such conditions, after the spawning of the catfish comes to an end and the fry emerge from the eggs, they are in serious danger of being eaten, if not by the catfish themselves, then by other fish living in the reservoir.
Interesting facts about catfish
Catfish is also known for its unusual habits and characteristics. Below are interesting facts that will surprise the reader:
- The catfish is not only the largest, but also the most cunning. He uses his whiskers as bait - the fish mistakes them for thick worms. Having noticed the prey, the barbel quickly draws in water along with the trusting fish.
- Catfish are unsurpassed greedy and gluttons. They are hungry for any prey. If a catfish sees a nest above the water, it will certainly try to knock it down with its tail. Even if he is not hungry, he will never miss a gaping duck - he will swallow it whole. Young people even attack spoons and animals - calves, dogs.
- Catfish are dangerous. Stories about cannibalism have a basis - these huge fish can attack a person.
- Before spawning, the giants organize wild games. Males try to show themselves in all their glory - they compete in swimming speed and jumping height. Sometimes up to hundreds of fish gather at the games. The noise from mating competitions can be heard for kilometers. The female chooses a worthy chosen one, and the couple disperses all the unnecessary ones.
Catfish is the brightest representative of the freshwater fish fauna. A worthy object for fishing and an interesting species for breeding. Everyone can find their own interest in this miracle fish.
0
0
Copy link
How to catch large catfish?
Experienced somyatniks often make their own quotes, using their own hands.
Where to look?
Large specimens spend time at depths, in pits and barrels. You need to catch the predator during its forays from these places. Fishing will be effective in places where a calm current prevails (places where a steep bank transitions to a sandbank).
We should not forget that catfish do not like bright daylight. You can take advantage of this fact by building a shaded trap. If it is constructed correctly, the fish will become a frequent visitor.
What to catch?
To catch large catfish, it is customary to use three main methods:
- Fishing with bottom tackle. Donka is used in places where catfish emerge from pits, as well as in areas of their mass accumulation. Usually the gear is installed in the evening and checked in the morning. The size of the hook for the donkey should not be less than No. 10, and for pits - No. 35-45. On the shore, the tackle is attached so that it absorbs the jerks of the caught catfish. To do this, use proprietary rubber shock absorbers or a wooden peg. By morning, the catfish caught on bottom tackle loses its strength and can be fished out.
- Fishing with a girder. Having tied the girder to a tree, it is firmly fixed on the shore. Frogs or large live bait are suitable baits. The bait is attached to the hook.
- Spinning fishing. Few people catch a huge predator using a spinning rod. Usually the fish gets caught on this tackle by accidentally touching it. But if a fish refuge has been found, then successful fishing is guaranteed. When fishing with a spinning rod, large spoons are used. The rod must be strong and have a loop on the handle.
Experienced fishermen advise catching the “king of the river” with frogs, mole crickets, locusts, and animal bones.
Fishing tips
- You need to choose heavy-duty tackle, because... the fish has great strength.
- The rod should have good shock absorption and flexibility, but it is recommended to choose a small size (up to 18 m).
- It is better to choose a reel of the “multi” class, marine series, from 4000 to 5000.
- Catfish begin to bite at dusk, and the largest individuals bite late at night.
- The most favorable biting period is indicated by a frame from the moment the fry emerges until September.
- When biting a large specimen, you should not rush to fish. First you need to weaken the fish.
- When catching catfish, it doesn’t hurt to have a hook or a large landing net with you.
Note! To summarize, it remains only to recall that catfish is a large predatory fish. Its size is sometimes intimidating, and not everyone can catch it. When going catfish fishing, you should be well prepared and careful.