Moonfish (2 m)
The moon fish has an unusual laterally flattened shape. Its weight reaches a ton and its brain is the size of a walnut. The giant feeds on plankton, fry, eggs and larvae of other fish. The moonfish does not have a traditional tail, but instead has a circling frill of a rounded body. There are large fish in the warm waters of the seas. In Asian countries, it is used to make delicacies, but in Europe and Australia it is not recognized due to the huge number of parasites in meat.
The largest sunfish was caught off Indonesia; it weighed 2.2 tons and was about 3 meters long. A huge four-metre sunfish has been spotted off Sydney. They live separately, forming flocks only during the breeding phase. Each female lays up to a million eggs. They serve as food for many predators. The population of exotic fish on the planet is small.
Common sharp-tailed moon
Part of the moon fish family. Habitat: tropical and temperate zones.
It differs from other species in the family by the presence of a rear fin, shaped like a sharp wedge from which the name comes.
Adults reach a length of 3.4 meters and weigh more than two tons.
The fish is huge and clumsy, so it is easy prey for predators. To avoid attack, the common sharp-tailed moon is capable of descending to a depth of more than two hundred meters.

Species of the sunfish family have tasteless, flabby meat. In most countries they are not used for human food, however, in the world, for example, in Taiwan, Japan and Korea, ocean fish is a delicacy. There are many sunfish recipes that are popular at food festivals and holidays.
Giant grouper or guasa (2.5 m)

The giant grouper from the Serranidae family of marine fish can be found on the coasts of Brazil, in the Caribbean Sea. Fishermen call the giants, which grow up to two and a half meters, with the affectionate word “guasa”. The maximum recorded weight of the predatory fish is 363 kilograms. It was exterminated for many years because of its tasty, dense meat.
In recent years, fishing for grouper has been prohibited; the population is gradually recovering. Rock perch lives in coastal reefs and aggressively defends its territory. It is distinguished by its massive carcass and spiny gill covers. Eats turtles and fish.
Health benefits of oily fish
Scientists have proven that regular consumption of fatty fish helps prevent the development of various diseases and pathological conditions, such as:
Dementia (dementia)
A 1997 study published in the journal Annals of Neurology included 5,386 elderly participants from Rotterdam. Researchers found that eating fish reduced the risk of developing dementia ().
Older adults who eat fish or seafood at least once a week are less likely to develop dementia, including Alzheimer's disease. In addition to providing vascular protection, omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil may reduce inflammation in the brain and play a role in brain development and nerve cell regeneration ().
A French study published in 2002 in the British Medical Journal (BMJ) followed 1,774 elderly residents of southern France over seven years. Scientists studied how much meat and seafood they consumed and how this was associated with symptoms of dementia.
The finding was that people who ate fish at least once a week had a significantly lower risk of being diagnosed with dementia over seven years. This study strengthened the Annals of Neurology findings. Thanks to its longer duration, the BMJ study provided stronger evidence of a true protective effect.
Cardiovascular diseases
Consuming 200-400g of oily fish twice a week may also help prevent sudden death due to myocardial infarction by preventing cardiac arrhythmia ().
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), found in fish oil, appears to dramatically reduce inflammation by being converted within the body into resolvins, with beneficial effects on cardiovascular health and arthritis ().
Psephur or Chinese bullnos (3 m)

The river dogfish, a large inhabitant of China's main river Yangtze, is called "paddlefish" by Russian fishermen. The fish from the sturgeon family reaches three meters in length and is distinguished by an elongated nose, reminiscent of a bird’s beak. Chinese individuals often reach a weight of 200 kilograms. Mobile and large fish swim a lot, with their mouths wide open, plankton and small fish enter it. The registered record is 7 meters and 300 kilograms.
The paddlefish is an endangered species; with the increase in industrial emissions, the food supply of the paddlefish is decreasing. A species of two-meter paddlefish is found on the North American continent in the Mississippi River basin.
Sawtooth ray
Family of saw-tailed rays. The main distinguishing feature of the long saw is a protruding growth edged with teeth along the entire length - the rostrum (photo in the public domain).
In outline, the stingray looks like a shark, but the body has a flatter shape, and the gill slits are located at the bottom. There is also a noticeable difference in the location of the pectoral fins, which literally merge with the head.
It lives in coastal areas in waters with warm tropical and temperate climates.
The saw ray feeds on small fish and bottom invertebrates. The size of this species can reach 7 meters.

For a long time, scientists debated the purpose of the rostrum, hypotheses were put forward about its use for digging up prey hiding in the ground at the bottom of a reservoir or detecting it, in the end both versions were confirmed.
Beluga (4.2 m)

The predatory Beluga is the largest representative of the sturgeon. In fiction there are descriptions of 10-meter specimens found in the Volga. The officially registered record is 4 meters 20 centimeters, weighing more than a ton. The large body of the mustachioed fish with a sharp nose feeds alone and feeds on different types of fish and plankton. It lives in inland seas into which freshwater rivers flow (Caspian, Black, Adriatic, Azov). They rise up into river beds to spawn. There the beluga becomes an object of interest for fishermen.
Beluga whales are artificially bred in Turkey, Bulgaria, and on the banks of the Danube in Serbia. Large beluga are crossed with other representatives of sturgeon, resistant species are bred that can spawn near megacities.
Fifth place – Beluga

In 1922, a giant female beluga was caught in the Caspian Sea. Her weight was 1,224 kg, of which 146.5 kg was caviar. Its impressive dimensions, reaching 5.5 m, and weight from 400 to 1,500 kg make this representative of the sturgeon family one of the largest underwater inhabitants. The king fish tolerates both salt and fresh water - its range covers the Caspian, Azov, Black Seas and the rivers flowing into them: the Dnieper, Dniester, Don and Volga.
Huge creatures with a crest of bone scutes on their backs and a sharp nose have inhabited the planet’s waters for 200 million years. Among its neighbors in the hydrosphere, the relict beluga is listed as a long-liver, unlike other sturgeons, it does not die after spawning. Under favorable conditions, the age of the king fish reaches 100 years . However, poachers hunting for valuable caviar, as well as the construction of dams and hydroelectric power stations, prevent her from reaching a respectable old age. These circumstances caused the giant to be included in the Red Book.
Interesting: The strangest animals in the world - list, names, descriptions, photos and videos
Giant freshwater stingray (4.5 m)

The giant freshwater stingray is found in the muddy rivers of most East Asian countries. Australia, New Guinea, Borneo. The largest river stingray was caught two years ago in China, its weight reached half a ton, its body length from nose to tip of tail was 4.5 meters.
On the tail of the fish there are dangerous spines that shoot poisonous needles in moments of danger. With a blow of its tail, the stingray pierces the skin of the bull and the bottom of the boat with a sharp spike (up to 40 cm long). Bathers and fishermen often become victims of stingrays. River stingrays are not specifically fished for, but these predators themselves end up in nets while chasing prey.
Common catfish (5 m)

The common or European catfish lives in deep pools and feeds on fresh meat, fish, and carrion. The largest specimens of fish are capable of dragging swimmers and small animals that come to drink under water. The most gigantic catfish caught was five meters long and weighed half a ton. Fish are found in large rivers, ponds, and lakes on all continents.
The long, soft body of the predator is not covered with scales, the fish’s mouth is huge, and the rows of teeth on the jaws resemble large brushes. The catfish's eyes are small and widely spaced to the sides. Catfish gather in schools only for the wintering period; up to 10 individuals are caught from one pool. For spawning fish, special nests are built. The last large individuals were registered in Italy, on Lake Issyk-Kul, in France.
Blue marlin (5 m)
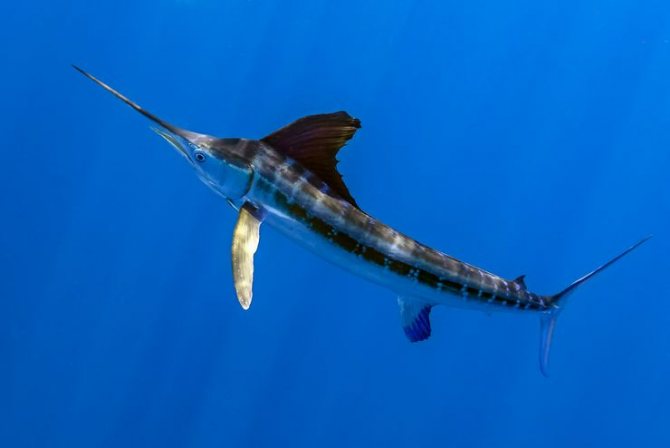

The handsome Atlantic blue marlin is capable of changing color in moments of danger; it turns sky blue. The largest marlin fish reaches 5 meters in length; there are individuals weighing up to half a ton. Marlin is easily recognized by the characteristic bluish tint of its scales and its long, sharp nose, similar to a spear. The predator moves at speeds of up to 100 kilometers per hour, and catching it with a spinning rod is a great success.
With their long noses, large fish are able to pierce a duralumin boat; well-aimed rows of teeth resemble a file. Marlins hunt tuna, flying fish, crash into dense schools, stunning the fish with their powerful tail, swallowing them as they go. This marine predator is from the perch family. Its meat is dense and juicy.
Great white shark (6 m)

The great white shark is the most intelligent predator, capable of moving at speeds of up to 24 kilometers per hour. Large specimens up to eight meters in length have been spotted in the Pacific Ocean. 6-meter giants weighing about two tons were caught. Mostly predators reach 4 or 5 meters in length and 1.2 tons of weight. They feed on large fish, turtles, and birds.
During periods of unsuccessful fishing, they are ready to attack mammals. Swimmers and divers are often attacked. Fishermen's nets are often attacked. The white shark is agile, aggressive, and cunning. Even an iron cage does not always save divers. When sharks appear near the beaches, special ultrasonic repellers are lowered into the water, affecting the electromagnetic receptors of sharks.
Whale shark (10 m)

A whale shark can grow up to 15 meters in length, and the weight of such a predator is about 2.5 tons. Mostly there are individuals up to 10 meters. Giants are inactive, maximum speed is no more than 5 kilometers per hour. Large fish feed on plankton, behave peacefully with swimmers, and allow them to ride on their flat backs.
Whale shark meat is edible; the liver is valued for its high fat content. The shark's skin is spotted, smooth, covered with dermal teeth - hard processes, there are up to 15 thousand of them. The largest shark fish has a flattened muzzle, with a huge, wide-opening mouth. The fish lives in the warm waters of the Pacific, Indian, and Atlantic oceans. Numerous flocks have been spotted off the Philippines and the East Coast of Africa.
The biggest fish in the world

The palm among the largest fish belongs to the whale shark. Despite the fact that the length of the whale shark ranges from 10 to 13 meters, and its weight ranges from 12 to 16 tons , this inhabitant of tropical ocean waters has long remained unnoticed by ichthyologists. Its first official description appeared in 1828. The huge creature has a unique appearance: a torpedo-shaped bluish-gray body is crowned with a large flattened head. The transverse mouth is located in the center of the muzzle.
The shark's mouth is equipped with small teeth arranged in 300–350 rows. However, well-equipped jaws do not pose any danger to either fish or humans. Bloodthirstiness is alien to the slow giants - they only consume plankton and krill. In nutrition, gill slits play an important role in the form of a sieve that strains food. The giant eats a lot and for a long time - feeding takes 6–7 hours.
Interesting: The most predatory animals in the world - list, names, where they live, description, photos and videos
The planet's hydrosphere hides many secrets. In the depths of seas and rivers, giant fish often lurk, larger in size than land mammals. And who knows, maybe a 30-meter gigantic creature still lives in the ocean depths - the prehistoric underwater monster megalodon.
Strap-fish or herring king (11 m)
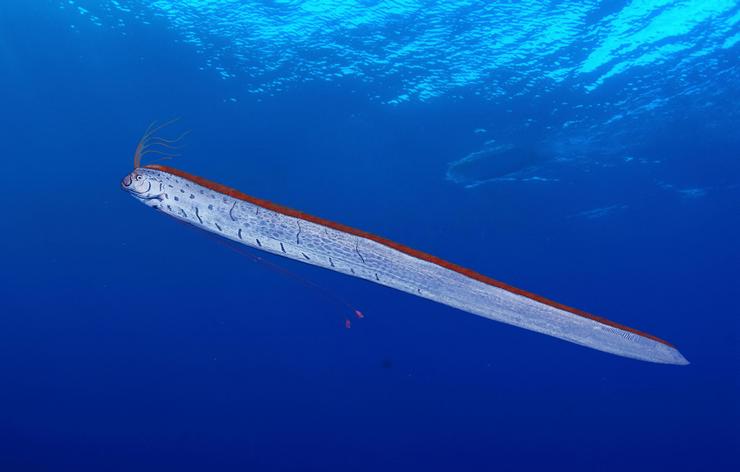

The inedible sea giant belt fish grows longer than 11 meters, with a body thickness of no more than 10 cm and a width of up to 50 centimeters. This fish is often mistaken for a water snake. It lives at a depth of up to one kilometer, swims in an upright position or holds its body at an angle to the horizon. Because of its red, flowing fins that form a crown on its head, and silvery, dense scales, the fish is often called the herring king. It ends up in nets along with herring varieties of commercial fish.
There was a recorded case of the capture of a 17-meter herring king, in the photo he was being held by 20 fishermen. The first descriptions were made in 1771; the largest fish was washed ashore during a storm. The meat of the herring king is inedible and very bitter. Even animals do not eat it, and fishermen call the belt-fish waste.
Animals Nature