Out of the water nelma smells like cucumbers. This smell of freshness correlates with the coolness and cleanliness of the water bodies that the fish choose to live in. The representative of the salmon family does not tolerate polluted or warm waters. By the way, there are several genera in the family. Nelma is a whitefish. Among them, the fish is the largest, growing up to 1.5 meters and gaining a mass of 50 kilos.
Nelma fish
Description
The long body of nelma looks like a “torpedo” or “spindle”; it is slightly flattened from the sides.
Eight small fins are located on the body:
- dorsal;
- anal;
- fatty - it has no rays and is a fold of skin;
- tail;
- abdominal;
- lateral.
The caudal fin is noticeably forked, equal-lobed and, together with the dorsal fin, has a darker color than the rest.
You can distinguish nelma from other salmon by its small triangular head, which is disproportionate to its body. The mouth is large with many small sharp teeth, they are even on the tongue. The lower jaw is strongly elongated and protrudes forward; it is longer than the upper jaw. A characteristic feature of the fish is also its dorsal fin. He is sharp and tall. There are about 100 scales in the lateral line (from 80 to 120 pieces).
The back is gray with a greenish, bluish or brownish tint. The belly is white, the rest of the body is covered with large silvery scales. There are no dark spots on the body, whereas other whitefish representatives have them.
There are two species of white fish, all of them “emerged” from the Arctic:
- The true whitefish is a resident of the Caspian Sea, where it later came from the Arctic Ocean basin. She prefers warm and calm waters.
- True nelma is an inhabitant of cold waters.
The white fish differs from the nelma in its smaller size, faster growth and sexual maturation. The appearance of both populations is the same. The lifespan of fish does not exceed 22 years.
Spreading
Fish, as mentioned earlier, swim in cold waters. Therefore, it is found in the Arctic and reservoirs connected to the Pacific Ocean. The main habitat is the Siberian and Far Eastern regions.
Looking at the entire world map, it can be found in Canadian and American (Alaska) rivers, that is, in areas with a similar Siberian climate.
Nelma is unevenly distributed. In some places its numbers are large, in others the fish can be counted on one hand. Why? Several factors play a role here:
- climate, which may differ at one latitude;
- nature of rivers - slow-flowing, fast-flowing;
- poaching;
- ecological situation.
Ecology is one of the main factors influencing its distribution in ecosystems. Hydroelectric power plants built in the habitat of nelma raise the temperature of the water and make it cloudy. The fish have to leave these places, the habitat is catastrophically reduced, as well as the spawning grounds. Water pollution is another common cause.
Nelma like wide, clean rivers with medium flows and cold, running water; some are not averse to settling in lakes. This species can be divided conditionally according to habitat into two types - river and lake-river. Representatives of the first group swim most of the time in large rivers of Siberia and near the coastline of the northern seas. The salinity of the water is not higher than 20 ppm. The latter live in lakes and leave them only when going to spawn.
Interestingly, while standing, she keeps her head against the flow. Nelma does not like depth; it tries to stay closer to the surface and does not fall below 2 meters. It prefers a sandy or pebble bottom. Avoids shallow waters and rapids, unlike other salmon. She does not enter such places even during the spawning period.
Nelma is a traveler; she travels very long distances (1500 km) and often swims to the south of Siberia.
Does pike have opisthorchiasis?
The answer to the question of whether pike has opisthorchiasis lies on the surface. Pike, which is a predatory fish species, according to most experts, cannot suffer from helminthiasis. The protective properties of the body of this species do not allow parasites to develop, so the answer to the question of whether pike suffers from opisthorchiasis is negative with 99% accuracy.
In some cases, opisthorchiasis in pike can occur when ingesting contaminated feed fish, but such cases are extremely rare. It is very difficult for a person to become infected with opisthorchiasis from pike, but if you eat the liver of weak, infected fish, the risk of infection increases, because flukes usually infect this organ.
Nutrition
This is a bright representative of the predatory world; it completely ignores plant foods. No wonder its jaws, tongue and vomer are covered with sharp teeth. In the first year of life, fry are forced to eat mixed food due to their small size, but more often plankton and benthos are present in the diet. Then they move on to small fish.
The main food for adults are crustaceans, shrimp, fry and small fish - smelt, vendace, muksun, roach, burbot, perch and carp fry, including their own smaller counterparts, insect larvae. That is why she likes rivers with a small current, where this “good” is enough.
Lake representatives choose places near river mouths, and for the same reason, rivers bring silt with “food” into the lake. Nelma never takes food from the bottom. She prefers to hunt and live in a pack. Schooling fish drown out prey with tail blows and then pick them up.
She goes hunting in the morning and evening, being most active in the morning. During the day he leads a passive lifestyle.
Fish of Siberia Nelma
Nelma (Stenodus leucichthys nelma) is a fish of the salmon family, whitefish genus. Nelma is the largest representative of the whitefish, reaching a length of up to 1.5 m and weighing up to 50 kg. The average weight of nelma ranges from 5 to 10 kg.
Like whitefish, nelma has rather large, silvery scales and small caviar; the belly is white. The body is elongated, fusiform. The sides of the body and belly are white with a silver tint. There is an adipose fin. The mouth is large and terminal. The maxillary bone does not reach the vertical of the posterior edge of the eye. There are many small teeth in the nelma's mouth. Unlike other salmon, the color of nelma is devoid of dark spots. The mating plumage is poorly expressed; only males, very rarely females, develop comb-like and tuberculate outgrowths on the scales and head.
White salmon spawns in the second half of September and October at water temperatures from 3 to 8°, mainly in fast places with sandy and pebbly soil. Fertility 125-420 thousand eggs. The eggs develop between the stones throughout the winter. Nelma grows quite quickly. Over 5 years it grows in length to 80-90 cm and gains a weight of 5-7 kg.
It begins to feed on fry from the first year of life. In the stomachs of 30-day-old fry, scientists found not only various larvae, but also small juveniles of other fish. Adults in the sea feed on smelt, vendace, and juveniles of other whitefish. After spawning, nelma rolls into the sea. Some fish stay in the river for 1 - 3 years, sometimes entering flood lakes in search of food.
Nelma is a semi-anadromous and freshwater fish. Distributed in rivers of the Arctic Ocean basin. It is most numerous in large rivers - the Ob, Irtysh, Yenisei and Lena. Mainly lives in the mouths and deltas of large Siberian rivers beyond the Arctic Circle. Salmon salmon begins to rise to spawning grounds located in the middle and upper reaches of rivers immediately after ice drift; the most intense movement is in June-July.
After about two months in August and September, it reaches the south of Siberia and enters numerous rivers and streams. But nelma does not choose all rivers for spawning and does not enter all rivers. Having entered the river, nelma stays closer to the bottom and walks along the bed itself. As it moves further, it often rises to the upper layers of water. The nelma avoids shallow places and riffles.
Rising along the river to the spawning grounds, nelma continues to feed, destroying a large number of small fish along the way. When nelma feeds in the morning and evening dawns, it is found in the middle and upper layers of water. Its feeding is similar to that of an asp; nelma hunts for small fish very energetically - it breaks into a school of small fish and crushes it with its tail, and then collects the confused fish.
Only salmon can truly frighten a fisherman with its splash on the river; no other fish in Siberia (perhaps with the exception of taimen) makes such loud and amplitude splashes. Moreover, these splashes sometimes occur 5-10 meters from the shore near bushes or snags, where the fry are kept, or in wide, quiet bays next to a strong current.
All salmon species of commercial importance are under special protection of the state, therefore fishing for nelma is prohibited in all southern and central regions of Siberia. The exception is the northern outskirts of Siberia, where nelma is harvested industrially by fishing cooperatives and then sold throughout the country. But very often, amateur fishermen catch nelma as bycatch while catching other fish. It is quite difficult to catch salmon in the south of Siberia with sports gear - its concentration is not as high as, say, in its permanent habitat, for example, in the Ob delta. In those places, fishing for nelma is allowed and you can successfully catch it there with a spinning rod.
When catching nelma, it is necessary to take into account that it is shy and cautious. Her defensive actions are very energetic and strong. Nelma is a rheophile, that is, it always stands in the water with its head against the current. To live, she needs only clean and running water. When taken out of the water, nelma is fragrant with the smell of fresh cucumbers. White salmon dies without water in just a few minutes and bleeds heavily through the gills.
Nelma are caught on spinners and large narrow-bodied spoons, usually silver in color, matching the color of the fry of smelt or vendace, which the nelma are accustomed to feeding on. Basically, nelma is caught, like ide, in the upper and middle water horizons at a depth of up to 2 meters from the surface, or even near the surface. This is a typical feeding level for nelma.
Evening fishing is often worse than morning fishing. Catching nelma at night is unlikely. Sometimes it is caught during the day, but on quiet and cloudy days. Nelma resists very energetically. But, having made several sharp throws, he is completely exhausted, lies down on his side and allows himself to be calmly picked up by the landing net.
The number of nelma is declining everywhere due to massive fishing by poachers and deteriorating reproductive conditions. Work on artificial reproduction and release of juveniles into natural reservoirs is at the experimental stage and is being carried out in small volumes.
Nelma meat has the highest taste qualities. Perhaps, nelma is one of the most delicious fish in Russia and you can prepare literally any dish from it and all of them will turn out to be one of the best. The most interesting dishes: fish pie made from nelma, shish kebab (tastes similar to chicken shish kebab) and, of course, lightly salted nelma or nelma stroganina.
Seasonal behavior
With the beginning of rivers breaking up from ice, schools of sexually mature individuals begin to move from the Arctic Circle to spawning grounds. All summer they move upstream, gaining weight. Intense movement of fish in the rivers is observed in mid-July.
By September they reach the southeast of Siberia, where they stop to spawn in numerous rivers, keeping to the bottom. Nelma, living in inland lakes, spends their entire lives in them, and spawns in tributaries.
After spawning, it fattens up until the next summer and gradually slides down to the sea. Some individuals can remain in the channel for up to 3 years. The young live in spawning rivers for 2-3 years, and then descend into a large body of water.
Briefly about opisthorchiasis
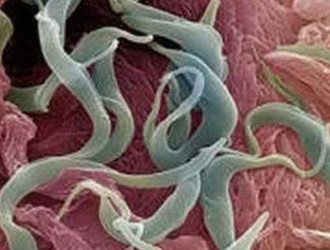
Opisthorchiasis is a disease in which the ducts of the liver, gallbladder and pancreas are damaged. The disease is widespread in Russia, Kazakhstan, Ukraine, as well as the countries of Southeast Asia.
Rare cases have been recorded in Europe and North America. Given the patterns, the disease is common near fresh water bodies.
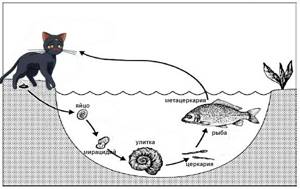
It has now been established that people and animals who eat fish as food can become infected. This occurs when eating fish infected with parasitic flatworms from the genus Opisthorchis.
The parasites were first discovered in 1891 by Professor K.N. Vinogradov, during an autopsy of a human corpse. In the liver he saw a worm that had attached itself to the liver.
Harm to humans
The presence of this type of parasite in the human body causes many problems. They are capable of drawing the mucous membrane into the cavity, pinching it, causing a violation of the integrity of the tissue and blood circulation. The disease can manifest itself in the form of jaundice and other symptoms, for example, fever, nausea, etc. As a preventative measure, you can be diagnosed for opisthorchiasis.
The presence of a large number of both the parasites themselves and their eggs can lead to a slowdown or cessation of fluid flow due to disruption of the flow of bile and pancreatic secretion.
Spawning
Sexual maturation of nelma occurs late, and is not related to its size or weight. This is a very slow growing fish. Males mature at 5-10 years, females at 8-14, and their life expectancy is only 20-22 years. In addition, the female does not mark eggs every year, but once every 2-3 years, since the journey from the habitat to the spawning ground takes on average six months.
So uncontrolled fishing has a negative impact on the population, and today the small number of nelma causes concern among experts.
Having gone up the river and found a place with a sandy-stone bottom, the female begins to spawn non-sticky, small, light-colored eggs. The water temperature at this point cools down to 6-8 °C. At one time, the female lays 120-400 thousand eggs. They develop within 250 days between large stones. Larvae usually appear in April.
Unlike other salmon representatives, nelma does not die after spawning. Females and males cannot be distinguished by structure, that is, they lack sexual dimorphism. Their color does not change throughout the year; males do not wear “nuptial plumage.”
How to properly process fish before eating
It is worth noting that the larvae of parasites are quite resistant to both low and high temperatures, maintaining their viability for a long time. To make it clearer, we give the following examples:
| Temperature | Lifespan of a parasite |
| 26-32 below zero | 2-3 days |
| 8-12 below zero | 17-20 days |
| 100 degrees above zero | about 15 minutes |

As you can see, if you want to protect yourself from parasites entering the body by freezing, you will have to spend much more time waiting than choosing the path of high heat treatment.
If you want to make smoked fish, it is better to choose the hot smoking method, since cold smoking requires additional freezing and salting.
To get rid of parasites, fish is cut into small pieces and fried in a frying pan at a temperature of 100-120 degrees for at least 20 minutes .
In order not to spread parasites around the house, it is recommended to use separate cutting boards and knives for fish.
This way you will be sure that the worms will not get onto other objects, creating an additional threat of infection.
It is also not recommended to give raw fish to your pets. Of course, they will swallow it with great pleasure, however, in the future it is through them that parasites will be able to enter your body.
Salting
Correct salting in this case will look like this:
- The proportion of salt to fish is 1 to 5 .
- Before salting the fish, keep it in the cold 2-3 26-32 degrees Celsius.
- Salt must be applied in several layers.
- During the second week of salting, the fish is disinfected.
The period depends on the size of the fish. It is believed that fish sizes up to 25 cm require a period of 21 days . If the fish is larger, then it must be salted for 40 days .
The value of fish and its use
Nelma is a valuable commercial species and has high quality meat. 100 g of fish contains 160 kcal. Its main components include only proteins and fats with polyunsaturated fatty acids. The latter are very beneficial for the body - they normalize lipid metabolism, remove “bad” cholesterol, and, therefore, help prevent cardiovascular diseases and prevent the formation of cholesterol plaques.
It also contains fat-soluble vitamin D, which is necessary for the absorption of calcium; with a lack of vitamin, there is a risk of developing rickets. The indigenous peoples of the Far North, who lack ultraviolet radiation, replenish the vitamin D deficiency in their bodies by eating salmon.
Among minerals, it is rich in chlorine, sulfur and fluorine. Also present are zinc, molybdenum, nickel, chromium, and vitamins - nicotinic acid or vitamin PP.
In cooking, it must be subjected to careful heat treatment. Eating Japanese cuisine, in which fresh fish is often one of the ingredients, is unsafe for health. This is all due to the fact that nelma is infected with a helminth - a broad tapeworm that can settle in the human intestines and nanophyetoses - roundworms that prefer to settle in the small intestine. The latter cause prolonged diarrhea with a large loss of fluid and nutrients. The larvae of roundworms can provoke the development of intestinal ulcers.

Nelma is delicious fried, boiled, baked, or smoked. Fish broth and cream go well.
Fishing methods
Nelma is highly valued for its taste. Balyks and smoked products made from its tender, fatty meat are very popular. It is also valued in canned form.
Such a demand for salmon provoked its mass destruction and subsequent bans on industrial fishing, which had previously been developed.
Amateur fishermen catch nelma with a spinning rod, using silver-colored spinners and spinners as bait, reminiscent of vendace and smelt.
Amateur fishing for nelma is prohibited. The exception is when it is caught as bycatch while catching a completely different fish.
At the end of the video: catching nelma with a spinning rod.
Make it more visible in user feeds or get a PROMO position so that your article is read by thousands of people.
- Standard promo
- 3,000 promo impressions 49 KR
- 5,000 promo impressions 65 KR
- 30,000 promo impressions 299 KR
- Highlight 49 KP
- Golden promo
- 1 hour of promo screenings 5 RR
- 2 hours of promo screenings 10 RR
- 3 hours of promo screenings 15 RR
- 4 hours of promo screenings 20 ZR
Statistics on promotional positions are reflected in payments.
Share your article with friends via social networks.
Get continental rubles by inviting your friends to Kont.
Wealth of Yakutia: fish:
It is impossible to tell a story about Yakutia without fish. Yakutia is much richer in fish than even in diamonds. Chir, whitefish, muksun, nelma, vendace. In Yakutia, there are approximately three and a half lakes for every resident, not counting rivers and rivulets (!). It is clear that in some places no human foot has ever set foot, but these figures give an idea of the fish.

We visited the Stroganina festival - an annual holiday where everything is at once: a fair, songs, competitions, crafts, and buffets:
Of all the dishes in the world, there is nowhere to enjoy stroganina in Moscow - there is no such fish, there are no sanitary standards.
After all, raw fish must be frozen for some time at temperatures ranging from -30, -40, -50 - so that the parasites are guaranteed to be killed (which, I thought, were not present at all in Yakut fish, but I don’t want to check).
About 1,400 Yakutians fell ill with diphylobothriasis (infection with the broad tapeworm), Galina NIKOLAEVA, chief specialist and expert of the epidemiological surveillance department of the Rospotrebnadzor Office for Yakutia, told NVpress. – I would like to note that if we take the average Russian indicators for diphylbothriasis, then the indicators of Yakutia are very high and are growing every year.
Every year, the largest number of cases of infection are registered in Zhigansky, Bulunsky, Kobyaisky, Namsky, Olekminsky, Suntarsky, Khangalasssky districts and Yakutsk. Also, in the last three years, Mirny district has joined these statistics. But in the Neryungri district people get sick the least often.
Mostly pike, tugun, perch, and burbot are infested with parasites. Commercial species include omul, vendace, and less commonly, whitefish and muksun.
But if you are a fan of lightly salted fish, when the percentage of salt and exposure required for disinfection are not achieved, then the risk of getting diphylbothriasis is very high. The anamnesis of the sick shows that most often people become infected by eating lightly salted tugunki - they caught it, immediately salted it and ate it.
— The sanitary and technical condition of the sewage system plays an important epidemiological role. A person infected with diphyllobothriasis excretes about 2 million tapeworm eggs in one portion of feces. Thus, along with the discharge of household wastewater, eggs end up in the external environment,” explains Margarita KORNILOVA, head of the department of sanitary supervision, licensing and registration. – Unfortunately, the realities of life are such that sewage water in treatment plants is not fully disinfected. In Yakutsk last year, part of the ultraviolet lamps failed and there is not enough power to completely destroy the parasites.
Next, the fish, especially the juveniles, feeding on plankton, swallow the infested crustaceans, further maturation of the parasites occurs in them at an intermediate stage, and then the Finnish fish ends up on our table. This is how the parasite cycle occurs in nature.
When pulled out of the water, nelma smells like cucumbers. This smell of freshness correlates with the coolness and cleanliness of the water bodies that the fish choose to live in. The representative of the salmon family does not tolerate polluted or warm waters. By the way, there are several genera in the family. Nelma is a whitefish. Among them, the fish is the largest, growing up to 1.5 meters and gaining a mass of 50 kilos.
Nelma fish
Cultivation and breeding
To increase the population, they are trying to breed nelma artificially. But so far, experts have not achieved much success, since large numbers of fry die in captivity. Today there is not even a technology for growing this type of fish in an artificial environment.
In the 20th century, scientists developed recommendations for growing nelma, but juveniles grew in ponds and lakes with a natural food supply. Later, already in 2009-2010, there were attempts to resume work, but they were of an experimental nature.
Thus, the protection of the spawning grounds and habitats of nelma is of utmost importance for the preservation of its population.
Nelma is a valuable specimen for breeding and fishing; it lives only in clean water bodies, as it does not tolerate pollution. The fish has excellent taste, but the population of nelma has recently decreased significantly.
0
0
Copy link
Gastronomic value of nelma

Nelma is an amazing fish that smells like fresh cucumbers after being caught. This is due to the water in which the fish live. Nelma lives only in clean, clear water. If the water becomes polluted, the fish will leave their usual habitat. The way of life of the nelma and its habitat made its meat absolutely pure. The fish does not have parasites and can be eaten raw. The taste of the meat is very delicate. Nelma has virtually no bones.
The gastronomic value of nelma lies in the fact that this fish contains many micronutrients, vitamins and minerals. The meat is rich in vitamins E and group B. Fish protein is quickly digestible, which is why nelma is an excellent option for dietary nutrition. Meat contains fats and amino acids in the correct proportions, which are necessary for a child's growing body.
Nelma is the oldest fish, which is listed in the Red Book in many regions of Russia. Fishing for this powerful predator is allowed only in the North of Siberia. A large, powerful, strong fish will become a worthy trophy for an angler if he is lucky enough to catch a predator.











