What is a fly line and what is it used for?
The structure of the fly fishing line itself is fibers intertwined or glued together in a special way. In addition, this fly fishing line is equipped with a special braid, this parameter can ensure longer-term use of this fly fishing line in a pond.
The use of this cord is carried out when conducting fishing processes of a jig or twitching nature. In addition, the use of a fly cord leads to a more accurate process of casting bait; the use of a fly cord makes the equipment more sensitive.
Various types of cords are used - soft or hard. When using types of fly line with a soft character, the fishing process is more enjoyable, although it will require more concentration from the angler himself. If we talk about rigid types of fly fishing cords, they are significantly inferior in terms of casting range, although with these cords the angler practically does not encounter the processes of tangling the equipment, even in the case of rare tangling, the untangling process is not very labor-intensive.
What is it and what is it used for?
The cord behind the structure is woven or glued fibers into a braid . For additional protection, braid can be used, which increases the service life when fly fishing in salt water.
- Most often used for jigging and twitching fishing.
- Braided fishing line wins in terms of casting accuracy. The fisherman feels the bite.
- The cord may be soft or hard.
- Soft, pleasant to work with, but require attention.
- Hard ones lose in range, but almost never get tangled, and if a beard has formed, it’s easy to untangle.
Fly Line Classes
There is a special system for classifying fly fishing lines. In order to properly use a fishing rod with a fly line, it is necessary that the main elements of this rod are fully combined with each other.
It is with the correct selection of elements that long-distance casting processes will be carried out with great ease, and over long distances. The process of classifying fly lines is carried out using the AFTMA system. It is this class system that allows you to assemble this equipment in such a way that all the elements are combined with each other.
There are classes in the system from zero to fifteen. Zero classes mean super light equipment models. The fifteenth class is super heavy among fly fishing equipment. The basis for this system was the initial thirty feet (nine meters and a tail) of fly fishing braid.
Based on the weight parameters of a given section of fly line, the relationship to a particular class in the system is determined. For example, your fishing rod is marked sixth class, and this will mean that you should select fly fishing lines of the same class for this fishing rod.
Depending on what kind of bait will be used, the parameters of the class of equipment chosen will also depend. It would be much more correct to initially purchase the fly fishing line itself, and based on its parameters, you should select the rod itself.
Characteristics of fly fishing lines
The properties of fly fishing lines depend on the following characteristics:
- — parameters of the material used;
- - differ in the types of their weaving;
- - according to the parameters of weaving the fibers themselves in the cord;
- - what kind of impregnation was used for this cord;
- - on the density parameters of the cord used;
- — parameters of the surface of the cord itself;
- — wear resistance characteristics;
- - diameter.
The American classification system is less clear to most anglers, but the Japanese system raises many questions. It is always worth asking the sellers about the basic characteristics of the cord you are purchasing, so that no problems arise later. Although, if you buy for your region, the store already sells appropriate cords tailored to the terrain and weather conditions of that region.
Fly fishing gear
One of the most crucial moments is the choice of fly fishing gear. It consists of the following main elements:
- blank (rod)
- coil
- cord
- underbrush and bait
With this set of fishing accessories you can begin to get acquainted with fly fishing.
Additional details you will need later:
- floats and connectors
- carabiners and leashes
It is important to assemble such a fishing rod so that it is comfortable and obedient in the hands of a novice fisherman.
Rod
Fly fishing rods or blanks are usually divided into classes. As the class increases, the strength of the blank increases, and the rod is able to withstand greater loads.
It is best to take your first steps in fly fishing with a 6-7 class fishing rod. Its strength is enough for both 200 gram grayling and 4 kilogram lenok.
Rods usually consist of 2 or 4 legs:
Two-piece models are more reliable because they have fewer connections, which reduces the number of breakdowns.
Four-piece fishing rods have the advantage of being longer. The form can be made from different materials:
- bamboo
- fiberglass
- carbon fiber
You can successfully fish with a rod made of any material, as long as it is not too flexible.
Particular attention must be paid to the handle. If the material used is leather or rubber, then it is better to refuse such a fishing rod. Only a cork handle is worthy of consideration for fly fishing.
[rs]
Coil
Fly fishing reels are divided into three types:
- automatic
- cartoon
- ordinary
For a beginner fly fisherman, an ordinary model with an adjustable brake is suitable. The brake can be quiet or equipped with a ratchet. It is important that when the brake is in the tightened position, the cord does not come loose from the drum when tugging strongly on it. The weight of the reel should not exceed the weight of the fishing rod.
drum should accommodate 30-60 m of 0.4 mm diameter extension line under the fly line. The optimal volume of fishing line will be such that the cord does not rub against the edges of the reel when wound.
[rs]
Fly line
Along with the rod, fly line is the most expensive part of the tackle. This is explained both by its special parameters and rapid wear even with careful use.
During active fishing, you have to change the line twice during the season. The store may offer a sinking or floating option. With a floating model, it will be easier for a beginner to cast the equipment.
As for the class of the cord, it must correspond to the class of the fishing rod. Therefore, the optimal solution would be to purchase grade 6-7. Of all the colors, it is best to give preference to a white cord, which is most visible in the water.
After training on the shore or after fishing in dirty water, you should clean the cord with a special product, which is sometimes included in the box.
Leader or leash
A fishing line with a reducing diameter is used as a leader in fly fishing gear. For a beginner, the best option would be a taper of 0.5 mm to 0.2 mm. The thick end of the leash is tied to the cord, and the fly is mounted on the thin end of the fishing line.
The diameter of the undergrowth should be thinned as follows:
- 0.5 mm length 125 cm
- 0.45, 0.4, 0.35, 0.3 and 0.25 mm, 15 cm long
- 0.2 mm length 60 cm
The total length of the leash will be 2.6 m. If the length of the rod is less than this figure, then it is necessary to shorten the section with a thickness of 0.5 mm. In strong winds it is more convenient to use short undergrowth. Therefore, you should prepare several leashes of different lengths in advance.
It is imperative to check the condition of the fishing line on the leash after a series of casts for any knots. They reduce the strength of the fishing line, so such undergrowth must be replaced immediately.
Fly line shape
Fly fishing cords are available in a variety of shapes and sizes. It should be noted the most common groups of fly fishing lines by shape:
- - cords having a cylindrical shape;
- - torpedo-shaped cords;
- — there are also cords that have a double cone shape.
Cylindrical models of fly fishing cords are characterized by the same thickness parameters along the entire length of the cord itself. This form of fly fishing line is marked in the form of the letter L; these types of fly fishing line are characterized by low price parameters. It should be noted that these types of cords are not universal, and therefore are not suitable for all fishing conditions.

Torpedo-shaped cords are weighted models; they are designated using the letters WF; these cords are weighted on the front part. In these cords, the main section itself is thin and light, which gives a lot of advantages when making long-distance casts.
Double cone cords are characterized by the fact that they have a flat central section and also have a process of tapering the cord towards its end. These cords are designated by the letters DT. The use of these cords is most justified when making ring casts; this cord provides a softer delivery of bait to the fishing site.
These are the main groups of fly fishing lines, but on their basis a great many different varieties have been created, but they should only be used if you have some experience.
Characteristics
Properties are determined by the following parameters:
- Material;
- Weaving type;
- Joining fibers in jute;
- Using impregnation;
- Density;
- Surface;
- Wear resistance;
- Diameter _ If the American markings and their translation into SI are clear, then with Japanese cords problems arise for beginners. The thread weight number (dtex) is indicated on the spool . For example, cord index 1 corresponds to 245 dtex. 245 dtex –2.45 g per 100 m . And the conversion of the diameter in the ratio 1:0.3, that is, the number 0.2 is indicated, means the diameter is 0.06 mm;
- Test;
- Color;
- Strength, that is, elongation (sometimes they simply write that it is close to zero, in truth, 2–7% ).
- What waters will the fishing be in (salt or fresh, tropics or northern latitudes). There is no need to worry too much when purchasing. We sell cords that correspond to the conditions of the region, but if you plan to fish outside, then it is advisable to take a closer look.
Classification of fly fishing lines by weight
There is a single standard for classifying braided fly fishing lines and that is AFTMA.
Following this standard, the weight in grains of the first 9 meters (30 feet) is indicated on the spool (Gran is a system of weight measurement in the USA and Great Britain). The classes of line and rod must be the same.
| Cord class | Weight of first 30 feet in grains* | Weight in grams |
| 1 | 60 | 3,89 |
| 2 | 80 | 5,18 |
| 3 | 100 | 6,48 |
| 4 | 120 | 7,78 |
| 5 | 140 | 9,07 |
| 6 | 160 | 10,37 |
| 7 | 185 | 11,99 |
| 8 | 210 | 13,61 |
| 9 | 240 | 15,55 |
| 10 | 280 | 18,14 |
| 11 | 330 | 21,38 |
| 12 | 380 | 24,62 |
| 13 | 450 | 29,16 |
| 14 | 500 | 32,40 |
| 15 | 550 | 35,6 |
This standard includes:
- Color;
- Calculation for water type and climate;
- Casting distance (close or far);
- Classifies by buoyancy.
Question: Why do fly lines taper in length?
Very often fly fishermen ask why this happens and they are also often answered incorrectly. In fact, everything is very simple:
- The casting distance depends on the taper of the braided line.
- It makes it easier to control the accuracy of the bait falling into the water.
Cords based on purpose
- Universal - do not have their own designation.
- Presentation (DT, TT or WF) - fished with small flies of different types.
- Fished with nymphs with an indicator or loaded (nymph or indicator) - withstands a large load.
- Use a streamer (WF with a shortened head).
- Pike, bass (strong WF with shortened head). Used for long-distance casting of heavy and large baits.
Forms
There are several types of braided fishing line:
- Cylindrical (Level – L) – floats on the surface of the water.
- taper cord (DT) - goes with a cone at the ends and has a thickening in the middle. To extend the life of the line, fishermen turn it over. Mainly used for circular casting with a soft and silent landing of the bait on the water.
- Torpedo cord (Weight forward - WF). The leading edge thickens. Convenient for beginners in fly fishing on long casts, also popular with professionals. To make this cord heavier, lead or tungsten powder is added under the braid. WF has additional classes:
- WF Nymph - casts against the current using heavy nymphs.
- WF Bass Bug - used for fast retrieve of very large and heavy pike, barracuda, marlin flies.
- WF Steelhead and Salmon Taper - these lines are used only for ring casting.
- WF Spey Salmon - catch salmon.
- SH (shooting head) - a sinking line is used for long casts.
- ST (shooting taper) - a sinking line for circular casting of flies.
- A cord with a triangular profile at the front (triangle taper - TT) - the movement of such tackle is easy to adjust in any wiring. The cast is accurate, with the ability to adjust during the flight. Due to its similarity to a torpedo-shaped line, it is best used for long-distance fly casting, but ring casting (with a whip) can also be done without difficulty.
Density
Braided fishing line can be of several types of density, and therefore have different buoyancy.
- Floatihg Line - floating cord (F).
- Hover - located at the surface, only under the film of water (H).
- Intermediate - with neutral buoyancy (I). Such a cord is classified as sinking, but has zero buoyancy. Which is why it goes down the slowest.
- Floatihg/Sinking - the line has a sinking end and combined buoyancy (F/S).
- Sinking Line 1 (Sink 1) - slowly sinking line (S1).
Some tips for choosing cord density for different purposes:
- The sinking one is chosen based on the speed of immersion, because the depth of fishing depends on this.
- The sinking cord can be numbered S2 and S3.
- If you need a fast sinking one, then buy S4.
- S5 is already a super fast-sinking line.
- Well, S6 is an instantly sinking braid.
- Double markings are possible on the spool, for example, S5/S6, meaning the head body with a depth coefficient of S5, and the end with a coefficient of S6. This line is used in deep water and when fishing deep holes with strong currents.
When marking the cord, it is determined by the following indices:
- the first two letters indicate the design of the cord,
- the number shows the class,
- the last letter is the buoyancy of the cord.
Here are some examples:
- DT6F – double-cone cord (DT), class 6, floating (F);
- WF7FS – torpedo-shaped (WF), class 7, floating with a sinking end (FS).
- Fly Line, L, 9F, 30 Iards - fly line (Fly Line), with a cylindrical braid (L), floating class 9 (9F), 30 yards (30 Iards) long, which in the metric system means 27 meters.
Care and storage of fly fishing line
You need to know that fly lines need care, especially after use. In most cases, on the label that is located on the reel itself, there is an inscription notifying the angler about the means for carrying out the cleaning process of this cord.
Wiping should be done using a foam or felt napkin, which must be moistened with a special solution or ordinary soapy water. Under no circumstances should you use any kind of oils or fats or various chemicals for the cleaning process.
In addition, it is not recommended to carry out throwing training processes on grass. Also, do not throw fly lines in places where they may be exposed to sunlight. There is no need to place these cords in hot places.
How to make a fly fishing line with your own hands?
For the process of making your own fly fishing line, you should take pieces of fishing line number 35, the pieces should be the following lengths: 20, 20, 19, 18, 16 meters. It should be laid in such a way that there are three ends on one end, and three on the other side, with the short ends attached to the long ones.

It should be attached to a peg, and then the process of weaving a regular braid is carried out. You should get four pieces of these braids. Then they should be woven together.
The resulting cord must be secured on a nail or hook and soaked in water. A weight is attached to the second end and waited for it to dry completely. After complete drying, you need to impregnate the cord with a special mixture consisting of paraffin and wax, with the addition of technical Vaseline.
Tips for beginner fishermen
- Beginners should initially decide on the fishing parameters and fishing conditions themselves, and select the cord itself for them.
- A floating line warrant in the fourth class area will be most suitable for beginners.
- To avoid snags, use thicker cords.
- If you are fishing for perch, a sliding type line is suitable.
- It is better for a beginner to consult with the seller when purchasing a cord.
- It is necessary to carry out proper care of the fly fishing line, which will ensure a longer service life.
Should I buy or make my own leader for fly fishing?
Many beginning fly fishermen often wonder what is better, buying ready-made leader or making it yourself from pieces of fishing line of various diameters. Practice shows that experienced fly fishermen use both purchased leader and make it with their own hands when the need arises.
The main problem with purchased undergrowth is the limited configurations that manufacturers can offer. At the same time, when fishing, conditions can sometimes arise under which only a self-made undergrowth with the correct length and configuration will allow you to implement the desired fly feed.
Another significant drawback of store-bought fly leaders is that they are not available in most fishing stores. You can buy undergrowth only in large cities, and only if the models you need are in stock. What to do if you forgot the underbrush at home or they simply ran out? It is precisely for such situations that the skill of making your own undergrowth from pieces of fishing line will come in handy; fortunately, you can buy it in absolutely any fishing store.

How to make fly fishing leader from fishing line
To make undergrowth with your own hands from pieces of fishing line, you can use the most ordinary and inexpensive fishing line. It is only desirable that it be fresh enough.
More expensive fishing line is better used for the thinnest part of the fly fishing tackle, that is, in the leader, and inexpensive options are suitable for homemade leader.
A simple formula for homemade undergrowth
If you don’t want to waste time studying a huge number of formulas developed for creating homemade undergrowth, then you can use a simple, but working and fairly universal scheme:
• 0.50 mm – 0.5 m (part of the undergrowth) • 0.40 mm – 0.5 m (part of the undergrowth) • 0.30 mm – 0.5 m (part of the undergrowth) • 0.20 mm – 0.5 m (part of the undergrowth) • 0.16 mm – 0.6 m (lead)
As can be seen from the example, all pieces of fishing line are the same length, and each subsequent part of the undergrowth is reduced by 1 tenth of a millimeter. In this case, the last part (0.16 mm) is already a leash. That is, the undergrowth itself is 2 meters long plus a 60 cm leash. In total we have 2.6 m - the classic length of the monofilament part (leader + leader), which should usually be equal to the length of the fly rod.
The leader example given is best suited for #5 and #6 grade tackle and can be easily adapted for smaller and larger grades.
For class #4, start the thick part of the leader with 0.40 mm or 0.45 mm and end with a diameter of 0.16 mm, to which you attach a thinner leader. For classes #7 and #8, on the contrary, increase the thickness by 1 tenth - the thick part is 0.55-0.60 mm, and the thin part is 0.20-0.25 mm. Next is the leash.
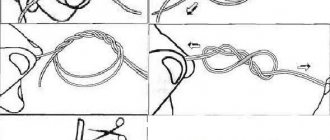
Knots for creating undergrowth with your own hands
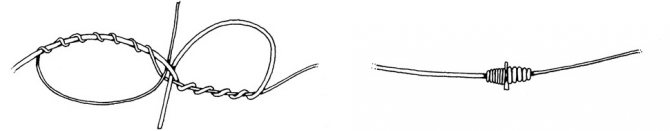
To tie pieces of fishing line together, a Blood Knot fly knot is usually used (Blood Knot → more about the main knots in fly fishing). It is not so easy to knit and you will have to practice for some time before you can form it quickly and without errors. However, this unit is one of the most compact and reliable in terms of connecting pieces of fishing line made of the same material - monofilament + monofilament or fluorocarbon + fluorocarbon.
After tying and carefully tightening the knot, you can further strengthen the knot by coating it with a thin (.) layer of super glue or covering it with UV glue as in the photo. In the second case, the knot will be completely covered with glue and will be shaped like a spindle, which will completely eliminate the clinging of various debris on the knots of homemade undergrowth during fly fishing.

Recommendations
1. When you prepare parts of the undergrowth, immediately cut off pieces of fishing line with a sufficient margin in length. Longer free ends when tying pieces of fishing line will greatly simplify the process of forming a knot, and will allow you not to waste the part that will have to participate in the undergrowth. For comfortable binding of parts of the undergrowth, a margin of 10 cm is usually enough for each side plus 50 cm of the undergrowth. That is, the total length of the cut pieces should be 70 cm.
2. If you are not completely sure of the quality of the knot you have formed, then do not cut the free ends close to the knot - leave the ends 2-5 mm long. They do not scare away the fish, as it may seem, but at the same time they will reduce the likelihood of the knot coming undone when hooking or retrieving.
3. For fishing in the wind or when working with heavy and saily flies, always make shorter leaders. When using small flies and when catching very wary fish in clear water conditions, increase the thin part of the leader while reducing the thick part.
4. If you are just starting to master fly fishing, then don’t be lazy and immediately tie 10-15 reserve fly lines that you use most often. In case of tangling or breakage, this will allow you to quickly change the leader and continue fishing.

Summarizing all of the above, we can highlight the following advantages of homemade fly fishing leaders:
Advantages
– Significant savings. The cost of one homemade undergrowth does not exceed 20 rubles. The cost of high-quality purchased undergrowth, as a rule, starts from 160 rubles. a piece.
– To make a leader for fly fishing with your own hands, you only need to find fishing line of different diameters, which can be easily bought at any fishing store. Purchased undergrowth can only be found in specialized stores located in large cities.
– Homemade undergrowth can be made of any length (within the permissible limits of the gear used) and configurations, which will allow you to create the most suitable undergrowth even in the most difficult situation.
Flaws