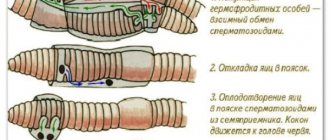
For those who would like to know where to dig up a worm themselves, the information below will be useful. For those who have never held a red worm in their hands, it will be useful to know that this name hides several varieties of this type of bait.
The red worm is one of the best baits for catching freshwater fish, consistently one of the three most effective baits for catching large fish. Most of the city fishermen buy this bait at a fishing store. Residents of private houses in cities and countryside dig for worms in their gardens.
Muckworm
The most popular and widespread type of red worm. One of the best baits for white fish both in winter and in summer. An indispensable bait for catching crucian carp, tench, bream, perch, and ruff. And other peaceful fish have “tender feelings” for this bait, regardless of the reservoir and time of year.

The body of the dung worm is dark, brownish-red in color. The maximum thickness is 8 mm, length is up to 12 cm, but smaller worms (length 5 - 8 cm) are also suitable for fishing. The tail is dark with yellowish rings.
A distinctive feature of this worm is the peculiar pungent smell of manure, which attracts fish.
The name of the worm tells you exactly where to look for this bait - in rotting manure heaps, which can be found near livestock farms or near fields and vegetable gardens. You will need a shovel.
Which worms are best for fishing?
The most popular among fishermen are dung worms; their color is quite bright: reddish-violet or brownish-red in the form of transverse stripes.
But not only with its bright color does such a worm attract fish; when irritated, a bright yellow liquid is released from its dorsal pores, which has a sharp, peculiar odor.
Fish are much more willing to take on a worm that has already cleared itself of its eruptions. To do this, freshly dug worms should be allowed to rest for one or two days.
The cleaned worm becomes less tender and more beautiful, therefore it holds perfectly on the hook and does not stain your hands at all. One of the best and fastest ways to cleanse worms is to put them in hemp oil in the evening, and in the morning they will be ready.
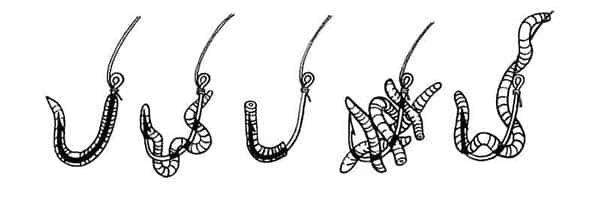
If you are catching small fish, then you can put a whole worm or even a half on the hook. And if you catch a large fish, then it is worth attaching several small worms, but when crawling, they usually attach one.
At the same time, one should remember the remark of L.P. Sabaneev, that a “worm” planted from the head remains unkilled for a long time, its unpierced tail plays merrily and thereby attracts fish....” Let's look at several types of worms that can be stored for a long time and even for the winter.
3 ways to improve your fish bite!

Over 15 years of active fishing, I have found many ways to improve the bite, and here are the most effective:
1. Bite activator . This pheromone additive attracts fish most strongly in cold and warm water. The Fish Hungry bite activator has proven itself to be excellent - Read more…
2. Tackle with increased sensitivity . You should first familiarize yourself with the features of using a particular type.
3. Pheromone baits . They attract the attention of fish, stimulate hunger and cause a schooling reflex, which allows you to collect a lot of fish in one place.
You can get the rest of the secrets of successful fishing for free by reading my other materials on the site.
3 ways to improve your fish bite!
Over 15 years of active fishing, I have found many ways to improve the bite, and here are the most effective:
1. Bite activator . This pheromone additive attracts fish most strongly in cold and warm water. The Fish Hungry bite activator has proven itself to be excellent - Read more…
2. Tackle with increased sensitivity . You should first familiarize yourself with the features of using a particular type.
3. Pheromone baits . They attract the attention of fish, stimulate hunger and cause a schooling reflex, which allows you to collect a lot of fish in one place.
You can get the rest of the secrets of successful fishing for free by reading my other materials on the site.
How to properly prepare worms before fishing? (Video)
Crawling out
The largest of the red worms. One of the best baits for trophy bream, catfish, sterlet, chub and carp. Crawlings grow up to 30 cm long, with a thickness of up to 10 mm. The body has a dark brown tint. In the area of the head, this worm has a dark red thickening with a purple tint. The tail part is lighter than the head part. The end of the tail section is flattened.

This type of worm lives in fields and near fields in rural areas and gardening communities. Sometimes small colonies of this worm are found near manure heaps and compacted leaves. You can find its habitat by the mounds of shiny earth, clearly visible on a flat surface. This worm is collected at night, when they partially emerge from the ground.
You need to collect the worm using a red lantern, moving very carefully, making as little noise as possible. At the slightest danger, this worm hides in its hole. It is almost impossible to get it out of there. There is a subspecies of this worm, which is smaller in size, and the color of the “dwarf” crawl is a little brighter. This crawl is a delicacy for almost any inhabitant of the rivers of the middle zone. It is difficult to store the creeper. In the home environment of a city apartment, long-term storage is impossible.
Underleaf worm
This subspecies of the red worm lives in both cities and rural areas, in places where foliage collected in heaps lies on the ground for a long time. A pile of leaves comes into contact with the soil, lies there for several years, and is watered by rain. A worm appears in the layers between the compacted leaves.

This worm grows 5 cm in length with a diameter of up to 5 mm. The body of this worm is a rich red color. The tail has a brighter color and is decorated with yellow rings. This worm is inactive, but is highly valued by river inhabitants. Perch, ruffe, crucian carp, bream, roach, gudgeon and many other inhabitants of freshwater bodies respond with pleasure to this bait. The odor of this subspecies of the red worm is much weaker than that of the dung worm. But they have an external resemblance.
You may not need a shovel to dig up this worm. It is enough to stir up a pile of foliage with a stick, and then pry up the layers of foliage. Several worms can be found under almost every layer of rotten leaves. They are stored well in the same foliage, which must be placed in a layer in a jar. This type of red worm survives well in a warm and damp place.
Earthworm
This type of worm lives in moist soils in almost any populated area. In some places its concentration is greater, in others there are single specimens. It likes to stay either near water sources (pumps, small standing ponds) or in thick turf of grass, provided that the grass is often moistened. Often such a worm lives near streams that flow in the shade of trees. This worm is also often found under stones.

This worm is pale red in color. It grows up to 8 cm long, with a thickness of up to 6 mm. This worm is happily eaten by roach, chub, crucian carp, gudgeon, bream, and silver bream. Large fish, all other things being equal, bypasses it, possibly due to the poor mobility of this subspecies of the red worm.
It stays at shallow depths, but it is better to mine it with a shovel. When working with turf, a shovel is a must. In places where the vegetation is sparse, but there is a source of water nearby, you can again get it using a strong stick. It is enough to loosen the soil or turn over a stone lying near the water. You can store this worm in a jar by pouring a little soil into it and occasionally moistening the soil with water.
Video “A unique way to extract worms”
This video shows how, with the help of two sticks and a file, worms are extracted, crawling out from the squeak to the surface of the earth.
Likewise, worms are attracted by light blows to planks or other wooden objects lying on the ground.
Do you think that when it rains, the worms come to the surface due to dampness? Absolutely not, scientist D. Gorris proved that they perceive the sounds of rain as the movement of their main enemy - the mole. When it rains, the droplets create vibrations that are similar to the sound a mole makes when it moves.
Some fishermen place a board in the ground and place a metal sheet on the protruding end. Then it is pulled so that it vibrates. Frightened by such noise, the worms climb to the surface, where they are easy to collect.
Such simple methods allow you to get rid of such a difficult task as digging. In addition, it is more fun and less unpleasant than fiddling around in the mud.
You can put the dug up worms in a wooden box with holes for ventilation or in a small canvas bag. The soil in the storage container should be moist. The dug up worms should not be allowed to form a ball, as this will lead to the death of most of them. It is better to take soil for storage from the place where you dug them and there should be more of it.
Waterworm
This subspecies of the red worm lives only on the banks of rivers, in places where small streams oozing from the ground flow into the river. The soil in such places is always soft, slightly rocky. The fertile soil layer in such places is shallow.
These worms are dark red with a purple tint. They do not grow longer than 4 cm with a diameter of up to 3 mm. This worm is well known to fish that collect food that falls into the water directly off the shore. Chub, roach, ide, and perch bite well on the watery worm. This subspecies of worm, like bait, has one big drawback - very thin skin. Any bite means that the bait will have to be changed.
The places where you can find such a worm are described above. You don't need a shovel to find it. A small branch is enough to slightly “knock out” the soil in such a place. It is almost never possible to store it. Fishermen dig such a worm only if they cannot get any other one.
Habitats and fishing methods
Body length varies from 2 cm to several meters (in some species). The height of local representatives reaches about 15 cm. It received its name due to its ability to crawl out of holes to the surface during rain. In fishing, it is used as bait for peaceful species, although predators do not disdain it: perch, pike perch, catfish.
Earthworms can be found on all continents except Antarctica. The favorite habitat is oily soil with a high percentage of moisture. This species is rare in sandy and clayey soils; it is more attracted to black soil.
In dry weather, finding representatives of oligochaetes is problematic. They go deep underground or hide in the roots of vegetation, under the shade of trees, where direct rays of the sun do not reach the ground. In the heat, you can make a generous spill of soil, thereby simulating rain - the crawl will definitely appear on the surface, but in the late afternoon.

If the average air temperature does not exceed 20-25°C, worms can be dug with a shovel. You should start your search in grass vegetation, since its roots retain moisture well.
Everyone decides for themselves where to dig up worms for fishing, but the best way to catch them is to hunt at night with a flashlight. Catching crawlers is done after rain in the dark. This requires a little lighting and sleight of hand.
To learn more:
9 ways to hook maggots
Crawlers are tenacious worms, but the storage area should be prepared before you collect them. The bait is placed in a loose container with leaves and a small amount of soil. It should be kept in a cool place, for example, in the lower compartments of the refrigerator. If these rules are followed, the worm does not lose viability for a month.
Iron worm
A type of red worm that lives in clay soils at a decent depth from the surface. This type of worm is common in the southern regions. It grows up to 10 cm. It got its name because of its peculiar “rusty” color. This worm is loved by carp, carp and bream. Recently, the Californian red worm has appeared on sale. Fishing stores usually sell worms up to 8 cm in size.
It has a bright red color. Close to cities, especially on paid reservoirs, this bait is fully justified. In old reservoirs where trophy carp, bream, tench, and crucian carp live, it is better to take a traditional worm with you.
Where to look for a worm
There is only one immutable rule in choosing bait in natural reservoirs: The fish bite best on the bait that often falls into the water in the spring with meltwater streams, as well as in the summer and autumn with rainwater.
Therefore, the best place to dig for worms is the coastline or areas near the shore. Such areas are clearly visible. Usually a layer of turf is removed there and traces of shovel work are visible. If there is such an area near a reservoir, you can safely put the purchased bait aside, pick up a shovel and get yourself a really popular bait. Usually, “local” bait is more popular with fish.
If such areas are not visible near the reservoir, you should pay attention to buildings located in close proximity to the reservoir. If there is a farm nearby, you should head there for the worm. There you can always find dung, and, therefore, a dung worm.
In hot weather, you need to look for small sources of water - streams, irrigation canals, drained or dry lakes. Near streams, if the soil around such a stream is not sandy, you need to pay attention to small stones, sticks, boards, bricks, under which worms like to “rest”.
Near irrigation or drainage canals in rural or suburban areas, or near dry lakes, you need to pay attention to areas where dried silt borders on vegetation. It is enough to turn over several layers of sod to collect a normal portion of red worm.
During the cold period, it is good to catch worms near heating mains, especially if such a heating main runs underground. The soil above it is usually warmer and you can dig fresh worms there all winter, trying not to appear on sections of the heating main during the period when workers of heating and power networks can notice you. Many avid fishermen living in private homes stockpile worms in their basements and even breed them in sheds and garages not used for their intended purpose.
Breeding worms
The simplest way to breed worms is to create a small (up to 40 cm deep) ditch into which cut grass, tops, potato peelings, and used tea leaves are placed. Such a ditch is dug in with clay (layer 10-15 cm) and covered with foliage (maple, poplar, birch) on top. Periodically, the top layer needs to be removed and compost, fresh portions of potato peelings, used tea leaves, and rotten leaves added to the soil. As an option for garages and basements, instead of a ditch they use large containers, such as 30 - 40 liter plastic buckets, in which water-based emulsion paint is supplied to large construction organizations.

In the fall, soil and worm bait, described above, are poured into buckets. The soil must be periodically watered with water, adding compost and other products that stimulate decay processes. It is best to insulate buckets containing worms a little.
Growing worms in a summer cottage
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=L22QKeVoXAw
How to breed worms for fishing in the country? The simplest way is to dig a small ditch, 30 cm wide. Its depth should be 15-20 cm.
Rotting leaves, grass, hay, and humus are placed in the groove. The top is covered with boards or burlap.
After 7-12 days, earthworms will appear in it. A special dwelling is built for them, which is a wooden box on legs with a removable lid.
Its minimum size is 100 x 100 cm, and its height is 35-40 cm. A mesh with small cells (0.5 cm) is attached to the bottom of the box.
How to breed worms in the country? To do this, the box is placed in a shady place. It can be placed near the compost pit.
About 20-25 cm of compost is poured into the bottom of the box. The worms are moved from the ditch along with a small amount of soil into this new home.
The soil is moistened and covered with burlap. After a week, the box is filled to the top with compost and watered again.
It is necessary to moisten the substrate 1-2 times a week (depending on the rate of drying).