Sima is a fish of the salmon family.
Sima is a migratory fish. For most of its life it lives off the coast of the Far Eastern seas, and for spawning it returns to the rivers of Primorye, Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, Japan, to the places where it once appeared.
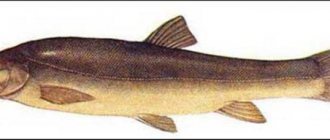
Sima - the fish whose photo is presented above - reaches a length of 63 cm, and its weight is about 6 kg. It has a silver color, which is diluted with black spots on the back and sides. The fish spawns at 3-4 years of age. During this period, the sima turns a bright crimson color. After spawning, the migratory fish dies, and the juveniles in the second year of life end up in the sea, where they live until adulthood.
What kind of fish is this
This is a predatory fish of the salmon family, common in the North Pacific Ocean. It is similar to coho salmon and chinook salmon. Sima leads a gregarious lifestyle, which has an elongated, slightly laterally flattened body, which is covered with small scales.
The Sim's body is dark gray in color. The abdomen is white. During the pre-spawning period, the fish gather in large schools and the body color of the masu fish changes. It takes on a cherry hue.
There are two forms of this fish:
- An anadromous Sim who lives in the sea and enters rivers to spawn. A distinctive feature of this fish is its pale color, on which yellow and black spots are clearly visible.
- A residential Sim who, for unknown reasons, only lives in rivers. It has another name - variegated fish, associated with the variegated coloring of the body of this fish. The main color background is light olive, on which vertical spots are visible.
The head of this fish is large. Eyes of medium size. The mouth is big.
Flocks of salmon go to spawn in rivers flowing into the Pacific Ocean. This fish does not grow to large sizes. The maximum length of this fish is 80 cm. On average, the weight of the masu fish ranges from 10 kg.
Nutritional value and calorie content
Sima is a type of red fish, and in terms of its beneficial properties it can be compared with both salmon and trout. It contains unsaturated fatty acids Omega-3 and Omega-6, which prevent the development of atherosclerosis; amino acids that protect against cancer and diabetes; Selenium is a vitamin that delays old age and gives longevity.

Sima - a fish, the recipes for which are presented below - should be in the diet of every person. It has a low calorie content (208 kcal per 100 grams), is high in protein (20 g) and fat (13 g), and contains no carbohydrates at all. This is an excellent nutrition option for athletes and all people who are on a diet or simply watching their health.
Sima: how to cook in the oven and in a frying pan
Juicy sima is obtained by baking in the oven (in foil). Additionally, you can use any vegetables, but it is preferable to take tomatoes and zucchini. The vegetable juice will saturate the sima meat, and its taste will become even more delicate.
Cut the fish into steaks, 2.5 cm thick, sprinkle with lemon juice and place in the refrigerator to marinate for at least an hour. At this time, cut the zucchini and tomatoes into thin rings and distribute equally on each sheet of foil. Place steaks on top. Salt, pepper, wrap and place in an oven preheated to 200 degrees for 30 minutes.

A whole sima is baked in a similar way. Fish weighing 1-1.5 kg should spend only 1 hour in the oven.
Many people find fried sima dry. Therefore, before sending the fish to the frying pan, it needs to be marinated. To do this, for 1 kg of sima cut into portions you will need: 250 ml of milk (boiled water), salt, pepper, dried dill, 2-3 drops of apple cider vinegar (you can use wine), 2-3 cloves of garlic (squeezed through a press). Prepare a marinade from the ingredients, pour it over the fish and leave at room temperature for a couple of hours.
After the specified time, remove the Sim from the marinade. Without removing any dill or garlic from the piece, roll the fish in flour and place in a hot frying pan with oil. Fry until golden brown on both sides. Sima (fish) turns out very juicy, but after marinade with milk its taste is more delicate. Cook in a frying pan without a lid.
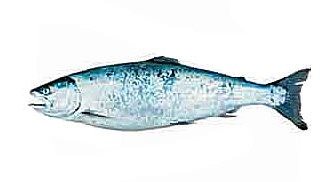
Sima (also called masu, Oncorhynchus masu) belongs to the salmon family and is the oldest species of Pacific salmon. It is closely related to the rainbow trout; moreover, young salmon have orange stripes on the sides, not as bright as those of the trout, but still quite noticeable.
Another underwater inhabitant with which the sima can be compared is pink salmon. However, the mama has fewer gill rays, and its mating plumage is striking in the richness of its palette.
Features and Characteristics
On average, the length of an adult is 63 centimeters and the weight is 6 kilograms. Externally, the salmon can be compared to coho salmon or small chinook salmon, but the dark spots on its body are much larger and more numerous. They completely cover the back and sides, with the same scattering on the caudal and dorsal fin.
The sima is especially beautiful during the mating season - she dresses in a very bright and expressive outfit: her olive-colored body is covered with scarlet stripes. Fish entering the river have light crimson stripes, while spawning fish have darker stripes.

Masu is a fish that is conventionally divided into two forms:
- checkpoint
The fry slide into the sea. But after 3 or 4 years they return to the river to spawn, and then they are already large fish, reaching a length of about 0.5 meters or more. Migratory individuals swim in Kamchatka, Sakhalin and coastal rivers, as well as in rivers near the islands of Hondo and Hokkaido.
- residential
For some reason, the fry do not slide into the sea, but become permanent inhabitants of their river. They are distinguished by their constant variegated color and short length of about 20 centimeters. As a rule, the majority of the catch consists of dwarf males. Individuals of the residential form choose mountain rivers of Taiwan, Japan, and Sakhalin.
Where does he live?
Sims love warmth, so they can be seen along the Asian shores of the Pacific Ocean. Fish leading a sedentary lifestyle are found in the mountain rivers of Taiwan and Japan - here they occupy the ecological niche of trout. Anadromous species swim in the rivers of Korea, Japan, Sakhalin and Southern Kamchatka.
Sims live in all coastal waters. They are the southernmost and warmest-water representatives of Pacific salmon, which are distributed mostly in the Sea of Japan.
When the fish becomes sexually mature, its back becomes darker, and the side stripes acquire a beautiful crimson hue - they unite into a wide longitudinal line on the abdomen, which becomes lighter. It is not surprising that “shima” is translated from the Japanese and English as “cherry salmon.”
The Kamchatka salmon is small in size - about 1 - 2 kilograms, while the Primorsky salmon is much larger: its length is 71 centimeters and its weight reaches 9 kilograms.
What does it eat?
Sima is a predator. However, compared to other Pacific salmon, anadromous salmon can also feed in freshwater bodies. As for the seas, the basis of its diet consists of crustaceans and juvenile fish.
The “Kamchatka menu” of young fish consists of insect larvae and salmon eggs. If we are talking about the Sea of Okhotsk, then here the masu eats small fish like gerbil and capelin.
Features of spawning
Sims are considered sexually mature when they reach the age of 3–4 years. They go to spawn in early or mid-summer. Migratory individuals die immediately after spawning. Residential fish (most often dwarf males) go to spawn next year. Newborn fish up to 1 year of age live in fresh water bodies. In the second, and sometimes even in the third, year of life they begin to roll into the sea. Marine life, taking into account the age of the juveniles, lasts for 2 - 3 years. The "juveniles" living in rivers are also called wheatears or pied wheatears.
Suitable places for spawning are the upper reaches of rivers and key channels.
In the river, juveniles prefer fast currents and avoid calm waters. These same sections of rivers are favored by passing Sims as they travel upriver.
Significance for fishing
Masu is a valuable commercial fish and the subject of active breeding in many fish factories in Primorye. Its production is carried out in the seas (bays and bays), when the fish goes to spawn and approaches the coasts. As for the rivers, there is no industrial fishing here. Recreational fishermen are only allowed to catch salmon swimming to spawn if they have a permit. Otherwise, such fishing is equivalent to poaching. It is also poaching to catch resident masa without having the appropriate license. The fine is the same as for catching large migratory fish.
Free fishing is allowed outside the river area, unless, of course, nets are used.
To catch “pied fish,” a spoon is used, and suitable bait is boiled red caviar and caddis, which are always abundant in mountain rivers. In the sea, salmon are caught using lures, usually by trolling.
The most suitable areas for catching masu are areas where the depth is about 1.5 meters and the current is 0.5 m/sec.
How to salt Simu fish in 12 hours
Red fish (including sima) retains its full beneficial properties only when salted. All other methods of processing it are less preferable.
In order for the sima fish, the photo of which is presented above, to cook faster, its fillet is cut no more than 1 cm thick. For salting, salt and sugar are used in a 1:1 ratio. The exact amount of spices depends on the weight of the fish.

Salt the Sim must be in a glass container with an airtight lid. It is not recommended to use plastic, otherwise the fish may have a specific taste. Pour a little dry mixture of salt and sugar onto the bottom of the container, place chopped plates (pieces) of sima on top, another pinch of the mixture on top, then a layer of fish and then in the same order. Cover with a lid and place in the refrigerator for 12 hours.
Ear from Sima
The first dish that fishermen prepare from the sima catch is fish soup. It is believed that it is from this representative of the salmon family that it turns out the most delicious.
The ingredients for the soup include the following products (per 2 liters of water): potatoes - 700 g, onions and carrots, garlic, lemon, dill, salt, pepper, cherry salmon. Recipes for preparing fish soup from other types of fish are not entirely suitable in this case, due to the particularly delicate taste of the meat. If you add it to the pan even a few minutes too early, the fish will fall apart.

Remove the bones from the sima and cut into pieces. Place a pot of water on the fire, and while it is boiling, peel and cut the potatoes into cubes, onions and carrots into strips. Place all vegetables in boiling water and cook over low heat until the potatoes are ready. Then put the fish, dill and salt to taste into the pan. Cook over low heat for 5 minutes. Remove from heat and add garlic to the soup. Serve with lemon wedges.
Fishes of Sakhalin
Cherry Sima.
We have already talked about this wonderful fish in our section. But almost two years have passed since then. And today, when the next season of licensed masu salmon fishing has opened, the editors, at the request of new readers of “Better than Bondage,” decided to repeat that publication, making it more detailed.
Our expert is Vitaly NIKITIN, head of the laboratory of freshwater and coastal fishes of SakhNIRO, candidate of biological sciences:
– Sima is one of the six representatives of the Pacific salmon, which begins to enter the rivers earlier than all of them, even during the spring flood. This is an anadromous species, noticeably different in appearance from its relatives by the strongly concave edge of the anal fin (this is how it can be distinguished, for example, from pink salmon of the same size).
There are other differences too. The sima has fewer gill rays. In adult fish, transverse dark stripes and large round spots of almost black color are located on the body; in the sea this color has a weak intensity. The richness of the colors of the beautiful wedding attire is striking. When reaching sexual maturity, the back of this salmon darkens, the stripes on the sides of the body become bright red with a crimson tint, and on the belly they merge into a common longitudinal stripe, which is lighter in color. It is no coincidence that shima means “cherry salmon” when translated from English and Japanese.
– What is its habitat?
– Sima is characteristic only of the Asian Pacific coast. It spawns in rivers from the northern coast of Kamchatka to Japan. It is found everywhere on Sakhalin, but in varying quantities.
– At what age does this species spawn?
– The life cycle of the masu salmon, like that of other Pacific salmon, is divided into freshwater and marine periods. Its juveniles spend several years, most often up to two years, in rivers, then slide into the sea (downstream juveniles are called “smolts”). The duration of the sea period is usually one year. Sometimes, depending on the age of the juveniles, it lasts two to three years. In the sea, this fish feeds on crustaceans and fry of other fish (greenling, saury, anchovy, sand lance, smelt, etc.). Winters in the Tsushima Current zone and off southwestern Sakhalin. In summer it is found in the Sea of Okhotsk and in the northwestern part of the Sea of Japan. Then, at the age of three to five years, she returns to the reservoir where she was born in order to die after spawning.
The salmon enters the rivers of southern Sakhalin en masse in two or three waves from mid-May; the spawning run in different areas continues until mid-June - early July. During the specified period of time, licensed fishing for this strong, beautiful, delicious fish opens, which thousands of amateur fishermen are eagerly awaiting, preparing for it as if it were a holiday.
– How does the spawning itself proceed?
– After entering the rivers, the masu still continues to feed, and fishermen know that at this time they are well caught with spoons. Spawning on Sakhalin takes place from the second half of July until September. The day before, like other species of salmon, the masu salmon begins to develop its nuptial coloration, which we have already roughly described. Males develop a small hump, jaws enlarge and curve, and teeth grow. The tips of the dorsal, anal and lower edge of the caudal fins become white. There are oval spots on the back and fins.
The fish lays eggs in the upper reaches of rivers, in small tributaries with weak currents and pebble-mud soil, in which nests are made with a depth of 10 to 45 cm. The fertility of females is 1170 - 4950 eggs. The incubation period lasts 50-70 days. However, the larvae emerge from the soil only in March-April of the following year. By the end of July, the fry reach a size of 40 mm. At this time, their sides and abdomen become silver, the back becomes olive with a blue tint, and large black oval spots stand out on the sides, between which there are small spots with blurred edges. Juveniles 50-60 mm long move to the reaches and rifts of the core part of the river, where they feed on larvae, aquatic and aerial insects, salmon eggs and fry.
– Are these the same juveniles that many fishermen consider to be a separate species of fish, calling them “pied”, “wheatear”, “sculpin”?
– This also includes already sexually mature dwarf male masu salmon, which sometimes reach a weight of 170 g and a length of 19 cm; in the watercourse they are dark brown or black in color, depending on the color of the water in the river. I would like to emphasize once again that they are all sima, this is a scientific fact that you cannot argue with. In addition, no dwarf females were found in the rivers of Sakhalin, so there is no reason to talk about the existence of a residential form of masu salmon and, moreover, that the so-called “sculpin” is an independent species. Its unrestrained harvesting of the Sim population causes significant harm. And therefore, if a “false wheatear” is caught, it must be carefully removed from the hook and released into the water. If the young salmon continue to bite, it is necessary to change the place of fishing or stop it altogether. Then it will be rewarded a hundredfold.
– Are dwarf males a natural anomaly?
- Against! Nature “invented” them as a safety mechanism for procreation. The fact is that real, marine male masu salmon, the first to enter the rivers, often do not reach the spawning grounds located in the very upper reaches in the required numbers, and then dwarf males participate in the fertilization of eggs.
The dwarf forms of males are not typical for only masu salmon; this phenomenon is also typical for sockeye salmon, chinook salmon and salmon - European salmon.
– Does Sima have commercial significance?
– Unfortunately, specialized studies of its reserves are not carried out in any region of the Far East. However, as expert estimates show, they are small. Therefore, masu salmon is primarily an object of recreational and sport fishing. This year, our region has been allocated 50 tons of cherry salmon for these purposes, of which 10 tons - in southwestern Sakhalin, 30 tons - in eastern Sakhalin, 10 tons - in Iturup.
There is no commercial fishing for this fish; small quantities are caught as bycatch along with pink salmon.
– What trophy specimens of “cherry salmon” can Sakhalin fishermen count on?
– Individuals of this species reach a length of 62 cm and a weight of 3.7 kg. The largest specimens are found in the northeast of Sakhalin. In the south of our island there are smaller Sims, but sometimes you also come across “giants” weighing 2 kg. Those who want larger trophies will have to go to Primorye, where, if you're lucky, you can catch a masu fish up to 71 cm long and weighing up to 9 kg.
G. YURGIN. Newspaper “Fisherman of Sakhalin” No. 19 May 19, 2011