Finding yourself on an unfamiliar body of water, you have to look for a promising place for fishing, and this is not at all easy. Although it is not easy for novice fishermen, experienced fishermen will be able to quickly identify promising places by the nature of the movement of water in the reservoir. If this is a pond and the movement of water is limited by gusts of wind, then it is somewhat more complicated. In this case, completely different criteria for determining where fish are concentrated come into force.
How to choose a fishing spot on the river
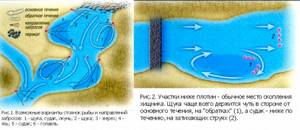
On the river it is much easier to find a catchable place that may differ from the general background or stand out from it. If the river is winding, then it is very easy to determine the nature of the river bottom based on the pattern of the coastline. As a rule, on such rivers, cliffs are clearly visible, near which the river can have optimal depths where most species of fish leading a bottom-dwelling lifestyle can be found. On winding rivers, the nature of the water flow depends on the size of the bends, and the depths can be determined by the color of the water.
Promising places for fishing on the river
They can be bays, oxbows and bends. The outer banks of the bends form cliffs, where there are the deepest places, and the inner banks form shallows. In narrow sections of the river, where there are weak currents, there are deeper places than in wide ones. In areas of rapids, it is easy to determine a deeper place by the color of the water, which in such places has a darker color. Downstream, if you go from the riffle, so-called whirlpools, or deep holes, are formed, where larger fish and predators are certainly located. The current is weaker on the reaches than on the rifts. The depth of the reaches is more constant and can change smoothly from the banks to the core, where the fastest current is present.
On small rivers
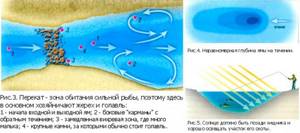
On small rivers, catchable places can be found in pits; on narrow rivers - places where the channel widens, as well as bays; on rivers with a slow flow - narrowing of the channel, places of rapids and channels, and on rivers with a fast flow - spills and bays; on deep rivers - the boundaries of depths and shallows, channels and “furrows” that separate the shallows from the shore, as well as at the border of algae. Fish can be found near blocks of soil that are washed into the water near cliffs.
Places where cattle gathered to drink in the evenings were always considered promising. At this moment, the fish stays closer to the border of the turbidity that the animals raise. Of particular interest are places littered with snags or driftwood. At the very top of the pool, where the current rushes in from the riffle, large specimens of fish, as well as predators, stay. A little further, where the current is not so strong, fish such as ide and chub like to spend time. The middle of the pool and its edges are occupied by other species of fish.
You should not pass by waterways where reverse currents predominate. They are usually located behind various obstacles that change the direction of movement of the bulk of the water. The smaller the distance between the forward and reverse currents, the more interesting the water is for fish.
Holes with thickets of trees and bushes that hang over the water can be
a good place for fishing Shallows that rarely extend into the depths can also be effective.
Choosing a fishing spot

Photo by Anatoly Mailkov
On an unfamiliar body of water, the fisherman immediately faces eternal questions: where, with what gear, bait, and what kind of fish should he catch now? While local fishermen can help him answer the last questions, he must find the answer himself for the first. The question “Where to fish?” remains a problem even on a body of water known to the fisherman, when for some reason the fishing conditions have already changed, and they change almost constantly. The bite of a particular fish is influenced by a large number of factors: the type of reservoir and its underwater topography, aquatic and above-water vegetation, weather, atmospheric pressure, water and air temperature, wind direction and strength, water level, food supply, but the type of reservoir is the main thing .
On small rivers, finding parking areas and feeding areas for various fish is much easier. Here the angler is greatly helped by the outlines of the coastline, the pool, shoals, riffles, and the strength of the current. In rivers of this type, good areas for fishing are considered to be the entrances and exits of holes, places near and after rapids, and the bank edge near aquatic vegetation. In slow-flowing rivers these are areas of narrowing, in fast-flowing rivers these are any bays. Good places for fishing are located near steep banks, along the slopes of the riverbed, at turns with reverse currents, in snags, under branches of bushes and trees hanging over the water. When looking for fish sites, you should be guided by the rule: the more any section of the river differs from the general nature of the water landscape, the more likely you can expect an accumulation of certain fish there.
Aquatic vegetation is also one of the most important factors, especially in closed reservoirs - reservoirs, lakes, ponds, quarries. Aquatic vegetation for fish serves not only as areas for spawning, reliable places of shelter, but even as food for fish of many species. For example, anglers discover the presence of grass carp when they observe how the stems of young reeds or other aquatic plants suddenly begin to disappear under water. This grass carp feeds by tearing off young shoots. The fish does this in the following way: falling on its side, it begins to tug at the stem of the plant until it tears it off.
Having thoroughly studied the habits of fish and the life of plants, the angler will be able to navigate even an unfamiliar body of water, since different plants adhere to different depths. Some aquatic plants in a reservoir can be distributed in the following order: at depths of up to 1 m - sedge, hedgehog, susak; up to 2 m – arrowhead, needleweed, cattail, reed, pondweed; up to 3 m – egg capsule, water lily. At depths of more than 5 m, filamentous algae grow.
The proportion of plant food in the fish diet varies widely, depending on the breed of fish, time of year and other local factors, reaching up to 50%. One of the plants attractive to fish is pondweed, because in places where it accumulates in the water there is an increased oxygen content. Many fish stay in the thickets of uruti. It has delicate leaves, on which you can always find a wide variety of animal food. Some fish, such as roach, dace, podust, chub, ide, bream, are partial to bright green filamentous algae, strands of which are attached to piles, stones and other underwater objects, because the filament serves as a high-calorie and vitamin food. It is believed that fish avoid some plants, for example, hornwort. Fish treat duckweed differently. On hot summer days, some fish like to stand under the leaves of lilies, water lilies, and in water thickets. In addition, any aquatic vegetation serves as a shelter for various mollusks, crustaceans, larvae, leeches, and caterpillars and other living creatures live on the vegetation above the water, that is, food for fish that falls into the water.
In some fish, especially in rivers, daily feeding movements are observed. During the day, these fish try to stay in the riverbed, and in the evenings or nights they go out into the bays, into the shallows, where there is a rich fauna of invertebrates, and they are followed by predators. When the water level rises, the fish leave their usual feeding areas and disperse into the floods, and during the summer drop in level they go to deeper places, often sliding downstream.
You should always start fishing with an external inspection of the reservoir and selecting several suitable areas. After making sure that the bottom in the areas chosen for fishing is clean, without snags and other foreign objects that could catch the hook and break the tackle, you should begin measuring the depths. Typically, anglers do this using a mobile float, moving it higher or lower along the line. If the sinker touches the ground, the float falls into the water. The angler gradually lowers it down until it assumes its usual loaded position. If the selected area suits you, you can scatter the bait and start fishing. This mainly applies to bodies of water with standing water or very weak currents. When there is a current, it is necessary to determine its speed and direction. The easiest way is to throw a stick into the water and watch its movement. A weak current is usually observed in straight sections of the river. The same can be said about the depth, which is relatively uniform in the rapids and reaches.
Scallops and swirls on the surface indicate the presence of large rocks and other similar objects underwater. It is necessary to learn to detect the presence of fish in some areas by external signs: splashes, a chain of bubbles coming from the bottom, the movement of vegetation.
In search of food, fish move in schools, schools, and alone, but there are some factors that it is advisable for every angler to remember. The fish stays: – near bridges, wooden crossings over small rivers, rafts; – in areas of reservoirs with banks overgrown with bushes, trees with branches hanging over the water, and other vegetation, and in these cases the bait must be cast as close as possible to the shore with vegetation; - near the mouths of streams and rivulets flowing into the main body of water, near steep banks: “The bank is steep, but the fish are good.” Fish must be caught not only where it stays, but better where it feeds: - in fast-flowing rivers in areas with a smooth flow; – on fish “paths”, “pebbles” and other non-standard places; - in the morning and evening hours: “Dawn will come and bring a bite.”
True, some fish like to sunbathe, while others at night go aground, into bays, backwaters, where there is a lot of food. In light winds with a slight swell on the surface, the bite improves, as is the case if the wind blows against the current. There is a sign that the wind knocks bream from the bottom, of course, a strong one. The location of the fish is influenced by the oxygen saturation of the water and the light: “In the summer, the fish are under a bush, and in the fall, under a fallen leaf.”
Anatoly Zhuravlev June 4, 2012 at 00:00
How to choose a fishing spot on a lake or reservoir

Fish everywhere, in any body of water, choose characteristic places, which are sometimes hidden under the water column. This is especially true for lakes and reservoirs, but even here, if you look carefully, you can easily find the favorite places of fish. In reservoirs with dense vegetation, fish may be in “clearings” or in windows of clear water. She doesn’t mind stopping at islands that have minor algae thickets. As for reservoirs, fish constantly migrate in them through holes, ravines, along edges and slopes, especially if there is a current in such places.
Determination of bottom relief
If you are very careful, the bottom topography can be determined by the pattern of the river bed and the presence of this or that vegetation. Plants such as hornwort, urutu or villain can grow at depths of more than 4 meters. At depths of up to 3 meters water lilies grow, a little deeper - egg capsules, at depths of up to 2 meters okuga and reeds grow, and a plant such as horsetail has chosen depths of up to 1.5 meters. Coastal plants such as cattail and sedge grow at depths of up to 1 meter. At depths of up to 6 meters, algae called “water moss” grow, invisible to fishermen.
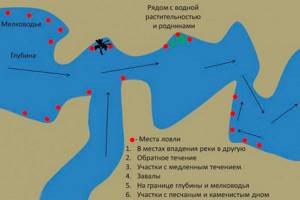
Floating plants such as duckweed and bladderwort can be found on bodies of water and can indicate the direction of prevailing winds.
Features of fishing on the lake
Pike, perch, and sometimes pike perch are often found in the lakes. There are no asp or chub in them. This fish prefers rivers. Features of fishing on lakes depend on their depth. These include the following factors:
- 1. Small lakes have a lot of underwater vegetation, often reaching the surface of the reservoir. Pike walks near it, and large perch lives on the bottom, and you can only catch it in windows that are not filled with algae.
- 2. In deep-sea lakes, large predatory fish choose the deepest places. The small predator hides in reed thickets in the coastal zone.
Lures and fishing techniques are selected taking these features into account. On small lakes there is no point in using bottom gear with heavy baits. Light spinning rods with a flexible, sensitive tip are suitable for them; they work effectively with wobblers that fall to the water line with algae, and rotating spoons. Wherein:
- — the bait should be carried along the surface of the reservoir using the twitching method;
- — if the wobbler clings to algae, it must be replaced with a lighter nozzle;
- — in late autumn, predators must be looked for in holes and caught using jigs and heavy spinners.
Many fishing techniques are suitable for fishing in deep-sea lakes. They are used:
- - wobblers;
- — silicone jig heads;
- - oscillating and rotating spoons;
- - poppers.
The most common method of fishing on such lakes is a uniform retrieve with periodic twitching. If poppers are used, wiring is used above the surface of the water. Silicone jig heads are designed for bottom fishing in areas without dense vegetation. In this case, stepwise wiring is done.
Water level fluctuations
Such conditions significantly affect the life of fish and other organisms. An increase in water level can contribute to the departure of fish from their usual stopping places, which entails a cessation of biting. This, in turn, can lead to an increase in the bite on spills, as it rushes there in search of food.
When the water level drops, the fish may become restless and refuse the bait offered to it. Larger fish slide downstream, leaving their usual places and shallow rivers.
If the water decrease occurs very slowly, then the fish may not respond to such conditions. She settles into her usual places and actively feeds at the same time. During this period, you can catch both small and trophy fish.
Bottom and shore
It is necessary to decide on the nature of the bottom and shore: is the shore overgrown or clean, rocky, muddy or sandy bottom, is there algae, etc. So, if the shore is overgrown with grass (sedge, for example), then we can assume that it is in the grass or on the border of grass and clear water there is a predator and peaceful fish species. In addition, if you plan to fish for crucian carp or crucian carp, then such areas will be the areas of choice.

The influence of weather on fish aggregations

Ambient temperature, atmospheric pressure, at a constant water level, significantly affect the effectiveness of fishing. When the weather changes, as well as when the weather is stable, the fish may bite differently. It was noticed that the fish began to actively feed before a thunderstorm or during rain, and after the rain and thunderstorm stopped, they also stopped pecking. Changing natural conditions affect fishing performance not only in summer, but also in spring, autumn and winter. Even with changes in wind direction, fish activity changes.
Experienced anglers use the wind to find fishing spots. For those who hunt bream, silver bream, crucian carp and carp, it is important to know that the wind, directing waves to the shores, brings these fish to the feeding area. The fact is that waves select various living creatures from the coastal zone and carry them from the shores to the depths. In such places you should use feeder gear or simple “donks”. Effective places in this case are on capes located parallel to the surf.











