Features of Winter Perch Fishing
Firstly, we want to say right away that perch is not the kind of fish that needs to be guarded while sitting near one hole. Of course, sometimes you get lucky, and from the first drilled hole you come across a school of perch. But this is like pointing a finger at the sky.
Our article is not intended to encourage you to go fishing for perch, hoping for luck. And relying on knowledge and the ability to apply this knowledge.
As you already understand, the basis of winter perch fishing is its constant search. He constantly moves around the pond, and the saying “Legs feed the wolf” is right about him. Anyone who has ever caught an active perch in winter knows how cool it is, how much drive and adrenaline it gives. When the perch is active, it takes sharply and greedily, almost everything that you offer it.
But the Passive Perch, of course, needs to be slowed down:
First, pick up the bait;
Secondly, select the wiring;
Thirdly, you can play with the diameter of the fishing line, for example, instead of 0.14, put 0.12.
In any case, it is important to understand that winter fishing for perch involves dozens of holes drilled and kilometers of distance traveled on ice.
Finding shallow perch

The most rational option here is to search in the shallows, not far from the shore of the reservoir. This approach makes sense to use in winter on a lake, the shores of which are densely overgrown with grass in summer. Strands are often found in the coastal zone, but they can also be found in the wider area. Moreover, near the coast there is a greater chance of catching small fish. But shallows formed by underwater hills, especially near the depths, often attract commercial humpback whales.
Recommended reading: How to catch a loach
It is known that perch is not afraid of noise on ice, the only exception being sharp, strong sounds. Therefore, having found a promising area in shallow water, you can start fishing almost immediately after drilling holes. To verify the presence of a striped fish, it is enough to go through a dozen holes with a no-attachment jig.
When finding fish, you can use two tactics:
- We drill a successful hole in different directions, the distance between the holes can be 1–2 meters. Thus, the maximum concentration of perch is revealed. A flock can stand in a tiny area, most often becoming attached to bottom anomalies or snags.
- The second technique involves quickly catching striped predators from “lucky” holes and searching for new promising places. This option is more suitable for fishing with baitless gear. Although it is more difficult, it shows better results in terms of the number and size of perches.
In general, in shallow waters it is advisable to catch perch on the first ice. As the temperature drops and the ice thickness increases, the fish move into deeper places. For example, it is better to look for perch in December or January in deep snags or pools.
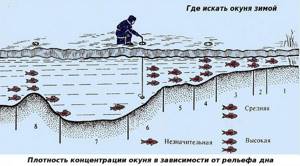
Where to Look for Perch in Winter?
Finding perch in winter is the most important task for a winter fisherman. And if for some reason the perch does not bite, then the first thought that arises in the fisherman’s head is: “Are there any perch here at all?”
Getting the perch to bite is the second task that the fisherman faces. The main thing is to find it, which in fact, in some cases is not so easy. The curiosity and aggression of the perch forces it to take even such bait that does not correspond to its food supply. It's all about the ability to provoke the perch to attack.
Many fishermen are of the opinion that all movements of perch in a body of water are random and chaotic. We fundamentally disagree with this. Like any living creature, perch has its favorite places where it likes to feed or just stand.
And also, his favorite paths along which he likes to move around the pond. We agree that he has many favorite places. And they change depending on the time of year, weather, and the topography of the reservoir itself.

Where to Look for Perch in Winter, We Identify 3 Periods:
- First ice;
- Deaf winter;
- The last ice.
But still, these periods have a general trend, and it’s worth sticking to it.
Tackle for catching perch in winter

In winter you can fish with jigs, balance beams and spoons, less often with jigs. Bloodworms, caddisfly larvae, and maggots are used as bait. If there is a good bite, then some anglers catch by eye a perch that has already been caught before. As for fishing with lures, in cloudy weather it is worth using silver and white colors, and in sunny weather - brass or copper.
The gear should be the following: a regular fishing rod, thin fishing line, no more than 0.2 mm, a silver or yellow jig and a winter float. For trolling, use a standard live bait fishing rod.
Fish promising places, watch the actions of other anglers, look for places where you have already fished and you will definitely end up with some catch.
Read! Tips for catching large roach in winter
Where does perch hiccup in winter when it migrates through a body of water?
In winter, the movements of perch can be divided into: Large migration and Daily migration. Throughout the winter, perch often changes its favorite stopping and feeding places, sometimes covering considerable distances. (This is called the great migration). Also, during the course of the day, perch can change its location many times.
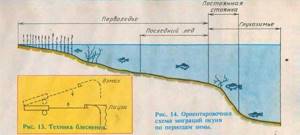
It Depends On Several Factors:
Oxygen saturation at a point;
Availability of natural food;
Weather.
This is what is called the daily fish migration. TIP : If you see snags sticking out of the water, be sure to fish this place!
Migration and Stay of Perch on the First Ice
According to the first ice, the places for catching perch are practically no different from summer ones. The most promising places at this time of year are coastal areas. Even at a depth of 0.5 meters, you can catch a trophy perch quite well, not to mention the standard of 200-300 grams.

What to Pay Attention to When Choosing a Location:
- In close proximity to the shore;
- Snags sticking out of the water, bushes, frozen, fallen trees, etc.;
- Driftwood at the bottom, grass;
- Steps and depth differences, no more than 0.5-1 meters, any bottom irregularities.
At this time of year, perch is most active and aggressive, constantly prowling in such places.
TIP : Don't spend more than 10 minutes on a hole. If within 10 minutes you are unable to catch a spot, move on to the next one. And so on until you come across a flock. If you find a perch, but you feel that it is somehow hesitant, weak, sluggish.
First Thing You Need:
Change the wiring technique (change the game with bait);
Reduce the weight of the bait (or increase, depending on the situation);
Think about the diameter of the fishing line. This also greatly affects the perch’s interest in your equipment.
Don't neglect old holes. For example, in the morning you were successfully fishing in one place, then the bite suddenly stopped, and you went to another place, it stopped in another place, you went to a third.
During all this time, the perch could very well return to your first place. Or vice versa, if the place is very promising, both visually and in terms of bottom topography, but the perch didn’t bite at all. It is advisable to check such a place a little later.
Tackle and fishing tactics
To hunt for perch in winter, you should prepare gear for winter fishing.
The most popular are:
- Tackle with jig.
- Fishing rods with spinners and balancers.
- Zherlitsy.
With the help of a fishing rod with a jig, which produces the necessary action, you can achieve a good bite. Many fishermen catch perch using a jig without a nozzle. The jig is attached to the fishing line at the desired angle. When using a nozzle, the jig should be mounted in a vertical position.
A jig that moves in leaps and bounds can attract fish. It is necessary to ensure that there are no deviations from the vertical. The bait should not glide or move smoothly. In this case, the predator will not react to it.
It is necessary to pull it, lifting it slightly up from the bottom level. You can place the jig on the bottom and then move it a little. If the bottom is covered with silt, the water will begin to become cloudy, which will attract the attention of the fish.
In winter, the lure must be held vertically, unlike summer fishing. This reduces the likelihood of catching aquatic vegetation hidden under the ice crust.
Because If fishing is carried out through a punched hole, it is necessary to avoid strong deviation of the spoon from the middle of the hole. It is necessary to select a spoon depending on the type of reservoir. If it is shallow, then light weight baits will be most suitable. If there is an underwater current, preference should be given to a weighted bait.
A balancer is a spoon that is shaped like a fish. It can move up and down, or it can be fixed in one position. It is attached to the tackle horizontally. There is a hook on the belly of such a balancer. To increase efficiency, treble hooks are used.
To attract fish, the balancer must move. Balancers come in a variety of colors and sizes. Often fishermen make homemade balancers for catching perch in winter.
The winter girder is slightly different from the standard one, which is used when fishing for pike.
Based on the size of the striped predator, it is necessary to use light equipment. It is more sensitive and less noticeable.
You should adhere to the necessary tactics during winter fishing:
- An important point is to choose a place with a suitable bottom topography.
- After a place has been found, you should punch several holes and feed them.
- After this, you need to make 8-12 holes, the distance between which should be from 4 to 6 m. They need to be fed.
- Then you should return to the first hole and start fishing, moving alternately from one hole to another.
If the oxygen level in the water decreases, the fish become less active. You need to know how to catch passive perch. For this purpose, you will need a bait that will make slow movements and stop from time to time.
Do you need bait?
If the fish bites weakly, then you need to feed it. To do this, they use feeders that sink to the bottom, where they open. Thus, a mound of food is formed at the bottom, near which the fish gather. This increases the bite many times over.
In some cases, this slide becomes food for the ruff, which can pay attention to it faster than the perch. To avoid this, you need to sprinkle it with sand.
It is best to place such slides near a school of fish. Then a large perch (which can be seen less frequently in winter) will be the first to notice the food and will not allow the ruffe to approach it. Thus, the chances of catching a huge perch in winter increase significantly.
During the cold season, the fish are actively looking for food, so there is a high probability that it will bite even without complementary food. But there are also times when you can’t do without it.
Where to Hiccup Perch in Glukhozimye
In January and February, the tactics of searching for perch change dramatically, as do its habitats. In the dead of winter, perch, like any other fish, is passive. It moves little, is found in deep places, with snags, grass, stones or any irregularities at the bottom.
If at any other time, perch can be lured by playing bait from a distance of tens of meters, then in the middle of winter such a trick will not work.

The search radius for perch in the wilderness is greatly reduced; holes are drilled from each other at a distance of no more than 2 meters. In a word, the bait must be placed right under the perch’s nose, only then can you count on results.
In addition, when you find a perch, it would be useful to feed it. Basically, a feed bloodworm or jig is used for this. Important: complementary foods of animal origin.
3 ways to improve your fish bite!

Over 15 years of active fishing, I have found many ways to improve the bite, and here are the most effective:
1. Bite activator . This pheromone additive attracts fish most strongly in cold and warm water. The Fish Hungry bite activator has proven itself to be excellent - Read more…
2. Tackle with increased sensitivity . You should first familiarize yourself with the features of using a particular type.
3. Pheromone baits . They attract the attention of fish, stimulate hunger and cause a schooling reflex, which allows you to collect a lot of fish in one place.
You can get the rest of the secrets of successful fishing for free by reading my other materials on the site.
3 ways to improve your fish bite!
Over 15 years of active fishing, I have found many ways to improve the bite, and here are the most effective:
1. Bite activator . This pheromone additive attracts fish most strongly in cold and warm water. The Fish Hungry bite activator has proven itself to be excellent - Read more…
2. Tackle with increased sensitivity . You should first familiarize yourself with the features of using a particular type.
3. Pheromone baits . They attract the attention of fish, stimulate hunger and cause a schooling reflex, which allows you to collect a lot of fish in one place.
You can get the rest of the secrets of successful fishing for free by reading my other materials on the site.
What do perch bite on?
Focusing on the predator’s propensity for the animal component of its diet, it is necessary to choose bait based on this position. The factor of high aggressiveness of fish makes it possible to successfully use artificial imitations of food, both visually similar to food items and causing vibration and sound vibrations that tempt the fish to attack. You can catch perch using inert baits of animal origin and live fry of various species of fish that live side by side with the predator. The use of artificial baits comes down to the use of spinners, wobblers and silicone. Let us take a closer look at the analysis of nozzles of various types and compositions.

Artificial baits
Artificial baits are mainly used in catching large perch. The primacy here is given to shallow-water wobblers such as minnows and crankbaits, with a high-frequency, not sweeping game. In areas free of underwater vegetation, small spinners are used, as well as silicone vibrating tails and twisters mounted on stationary jig heads. In currents, equipment for catching perch involves attaching silicone worms and imitations of insects and aquatic arthropods, which, from the strength of the current, receive animation that arouses the interest of striped fish. Fish are caught from the ice with all kinds of jigs and vertical spinners. In recent years, balancers and rattlins, which are equipped with winter spinning rods, have become especially popular in ice hunting.
Live baits
It is good to catch perch using small fish with a narrow body. These species include verkhovka, bleak, gudgeon, spined loach and loach. If the top and bleak are less resistant to injury to the fish and they are short-lived as bait, then the next three options can be confidently used for a day, without worrying about their survivability. More inert baits, but no less effective than live bait, include the dung worm, which, in a single specimen or in the form of a bunch, will always be a desirable delicacy for the striped fish.

Caddisfly larva, bloodworms, maggots and goose, both individually served and as a sandwich, are also among the most commonly used baits. Perch fishing in the summer is successful using seasonally emerging insects. In particular, dragonflies and grasshoppers are always in the diet of perches in the first half of summer. The predator does not hesitate to hunt for frog tadpoles. Well, in the fall, bait for perch in the form of a small frog mounted by the lip rarely remains unclaimed by the aggressive humpback whale.
In winter, fish are lured by baiting jigs and spoons with pieces of fish fillet cut into small strips, as well as perch eyes. The fragrant, protein-rich bait irritates the predator’s sense of smell and provokes it into frequent and confident bites.
Where to Look for Perch on the Last Ice?
The tactics for finding perch at the end of winter are practically no different from the first ice. As the ice melts, you should look for perch closer and closer to the shore. He is gradually returning to his usual habitats.
Every day the water becomes more and more saturated with oxygen, thereby increasing the activity of the perch. This means that the radius of drilling holes increases 10 times, and finding perch becomes many times easier than in the middle of winter.

Where to Look for Perch on Small Rivers and Lakes?
It is much easier to find perch on small rivers than in large reservoirs and rivers. First of all, you should orientate along the shore and coastal zones. All landmarks and signs of promising locations for perch are exactly the same as described above. Namely:
Driftwood. Both at the bottom and sticking out of the water. Fallen trees frozen in ice, bushes;
Any bottom irregularities. Depth differences from 0.5 to 1 meter, no more;
Steep banks, steep slopes, and so on.
The search for perch on small rivers begins from the very shore, starting with fishing at the coastal edges, gradually moving away towards the river bed. As for lakes and ponds, here the search for perch is carried out according to the same principle.
The same fish, the same favorite habitats. The only thing that may differ from river perch fishing is: the type, weight and color of the bait. In such places, the bait should be selected as closely as possible to the natural food of the perch.
Lures
All types of lures for catching large perch should not be small in size. The size of baits should be either medium or relatively large. Of course, you should not use giant-sized spoons, as when catching large pikes. But there is no need to install very small turntables or twisters. Small fish will peck at them and thereby distract you from catching perch of the desired size.
The spinner has always been considered a perch spoon. Such baits always work well for perch. And in a big way, too. You just need to choose larger baits. Otherwise, there is a chance of catching small fish instead of humpback whales.
Twisters and vibrotails are also good for catching large perch. Lure sizes are medium or large. A large perch will undoubtedly attack even a fairly large artificial fish, even when it seems that it will not fit into its mouth. In cluttered places, offset hooks work well, making these baits a kind of “unhooked hook”.
Wobblers always catch fish well and large perch too. It is preferable to use a medium wobbler size, 5-6 cm long. And you definitely need to select the depth if you plan to fish at depth. Topwater poppers work well when big bass come out to feed in the shallows and hunt small fish close to the surface of the water.
In thickets of grass and reeds, an ordinary medium-sized oscillating spoon in the “non-snag” design works very well. It is especially good at fishing in thick reeds, where most other baits cannot be properly passed through the grass thickets.
Natural fish attached to a tackle has always been and remains a good bait, often replacing all spinners. In addition to large perch, pike often take this bait.
Also in deep places it is practiced to catch perch using tackle with a retractable leash. A fairly heavy sinker is attached to the lead and slides along the bottom, while the main lead with the bait goes behind at a short distance from the bottom. The bait in this case is usually a small wobbler.
You can catch large perch with a balance beam and a vertical spoon all year round. Of course, it is preferable to fish from a boat and in deep places. In shallow waters, normal fishing with such gear will not work. It is especially good when the boat is carried by a slight breeze, and the fisherman has the opportunity to move in the boat across the pond, fishing all the necessary territory, without making any effort to row or touching the oars.
Read: Catching perch with live bait using a float rod
Where to Look for Perch on Big Rivers and Reservoirs?
Finding perch in such a huge water area is not easy. And if the reservoir is completely unfamiliar, then one might even say it’s unrealistic. You should go to such reservoirs prepared for perch.
Prepared in the sense of at least theoretically having an idea of the river’s topography, the presence of dumps and edges. It certainly wouldn’t hurt to ask local fishermen to find out what’s going on. Moreover, now all this is freely available: thematic forums, groups on social networks.
Of course, you can always find your way on ice even without special knowledge of the reservoir. It is enough just to stay close to the bulk of the fishermen. If you see a bunch of anglers, you can be sure there are fish there, or at least there were.
Just wandering around a pond and drilling holes anywhere is dooming yourself to failure in advance. The main thing is to find a slope, edge or ridge. And then it’s a matter of technique; we begin to drill in a checkerboard pattern in search of perch. It’s better, of course, to go fishing with a group of people, as many actually do. This way, finding a perch is much faster and easier than alone.

Winter search for promising perch fishing spots on the reservoir
Sergey Akulich | November 9, 2021
I remember that my father and older brother began to take me at the age of seven to the city reservoirs, where we hunted for ruff, perch and small roach in the coastal zone. What delight I felt as I watched numerous underwater inhabitants in the shallow water through the transparent, but already hardened first ice, while my family was drilling holes and preparing gear for fishing! The first fish I caught on my own was a small perch. Having pulled him out of the hole, I filled the surrounding area with a cry of jubilation. Since then, I have come a long way as an ice fisherman, and again I want to pay tribute to the perch.

And you need to start, of course, with a review of promising places in the reservoir where the likelihood of encountering a striped robber in winter is highest. All my conclusions and conclusions will be based solely on personal experience of ice fishing in reservoirs located near the Belarusian capital, as well as several reservoirs directly within the city.
1. Since freeze-up occurs unevenly across the vast expanses of the reservoir, and shallow water areas are the safest for fishing at the beginning of winter, I begin my search for perch in the reservoir at this time from the coastal zone. The most attractive places are located in close proximity to upright aquatic vegetation - reeds, cattails and reeds.
But it would be useful to remind you: move with caution in such areas of the reservoir. And it’s better not to walk through the thickets themselves, because... the ice here is less strong than at some, even a short distance from them.

The bases of aquatic vegetation, which are hidden under water, as well as the bottom surface in such places (Fig. 1) in winter serve as a home for a variety of aquatic insects and organisms. These, in turn, provide food for numerous species of fish that often visit these thickets, including small perch. A decent-sized striped robber comes here only occasionally to hunt at the border of plants and clean water for growing fry, but sometimes it does not disdain various bugs and boogers.
In reservoirs with poor oxygen conditions, places near thickets of aquatic vegetation for searching for perch are of interest only within one to two weeks after freeze-up. Then the perch and other underwater inhabitants leave them, because... This is where weird things start to happen.

2. In fairly deep-water reservoirs, relatively smooth decreases in depth from the shore into the depths of the reservoir are of interest for catching striped robber (Fig. 2) . An additional attractiveness of these areas is given by the presence of a moderately hard (hard) bottom structure, sandy, sand-pebble or rocky. On some reservoirs where I hunt for perch, such gentle edges are the favorite habitat of the large striped robber.
Thanks to the acceptable oxygen regime, relatively shallow depth and rich food supply, these places are almost always inhabited by growing juveniles of all kinds of “leucorrhoea” (and not only), which serves as the main food item for a decent-sized predator. In turn, a number of favorable factors contribute to the presence of perch here throughout the entire season of “hard” water, be it the first ice, the middle of winter or the last ice.

3. A few words about steeper edges and sharp drops into depth. In such places, the striped robber is almost always present. True, the size of the perch caught here leaves much to be desired; most of the fish caught are small predators. But I note that some features of the change in the relief of such steep edges and slopes make them attractive for large predators.
These are places where a rather sharp decrease in depth from the shore into the depths of the reservoir occurs in ledges (Fig. 3) - so-called local tables with slightly different depths are formed. It is on such small underwater plateaus that you can count on catching a winter humpback whale.
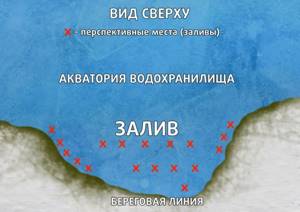
4. On many reservoirs bays of different sizes are formed. Such formations, as a rule, differ significantly in depth values. Sometimes you have to catch perch in bays where these values do not exceed a meter, and somewhere the depth sometimes reaches three to five meters. Depending on the area of such places, as well as the bottom topography, its composition, depth values and some other factors, bays may have different local attractiveness for perch (Fig. 4) .
And it is very important to know that the predator can be (and is) in the bays irregularly, visiting them only during certain periods of the winter season. I would venture to suggest that the striped robber moves into them, following the food object, or due to the more acceptable oxygen regime established here than in the main water area.
To support my words, I will give an example from personal practice. Once at the end of March, my friends and I went to the Minsk Sea for perch. The winter that year was good, the ice grew up to half a meter, and in some places even more. But at almost all the checked points there was a “sailor” the size of a little finger, and in a few hours we managed to catch only a couple of qualifying perches and one large roach. We moved to the exit from a bay of a decent size, the depths here were somewhere around 2 - 3 m. But the situation repeated itself - the spinner was generally “silent”, and the jig with bloodworms, as well as the “reelless” one, was only annoyed by microperch.

Meanwhile, the clock hands already showed two in the afternoon. And I decided to check the places near the reed thickets in the bay itself. Under the influence of air temperatures with a decent plus, which established several days ago, the ice around the stems of aquatic plants melted rapidly. And the oxygen regime here began to undergo significant changes for the better; this definitely gave us hope for meeting an active predator.
Having drilled a dozen and a half holes (the depth in them was about 60 - 80 cm) along the reed wall at a distance of no more than half a meter from it, I began fishing. And already on the first hole, after another swing of the fishing rod during a pause, a powerful blow to the spoon followed. A short hook and the plump perch ended up on the ice. Further bites from decent-sized perch occurred in series - three to five, then there was a lull for 15 - 20 minutes. I called my comrades and invited them to join. In the next two hours, we managed to catch more than three dozen well-fed predators in this place.
A small fish no larger than 3-4 cm in size fell out of the mouth of each of them. This means that with the warming and melting of the ice, small fish moved towards the thickets of aquatic vegetation, followed by large perch. By dusk, my lure was seduced by a mega-predator - a kilogram humpback whale, which after several minutes of extreme fishing was safely pulled onto the ice! A few days later we checked this bay again, but the big bass had already left it. Near the reeds at this time, only occasionally a very small perch was caught on a small spoon, and the ubiquitous ruff did not allow the jig to pass.

5. Most of the reservoirs I visit have fairly uneven shorelines. In areas where its break occurs more sharply and steeply, capes are formed (Fig. 5) . And this coastal formation, as a rule, undergoes a significant change in the bottom topography. Many capes are characterized by the presence of sandy, sandy-pebble and stone ridges near them, which sometimes extend a considerable distance from the shore and near which perch loves to stay in winter (as well as in summer).
Near the capes, shallow areas of the reservoir (in summer they are significantly overgrown with aquatic vegetation) are often adjacent to deeper water areas. Often here you can find piles of stones of various sizes, and even huge boulders, located both at depth and near the shore. They serve as shelter for different species of fish and their young, and among predators, perch is always in the numerical majority.
An additional attractiveness to these coastal anomalies is given by the fact that near them the current is always somewhat stronger than near relatively flat sections of the coastline. Which in turn contributes to the presence of a very good oxygen regime here, even during periods of deep winter and oxygen starvation observed in other parts of the reservoir.
6. Islands are next in the review of promising fishing spots. They attract a wide variety of underwater inhabitants like a magnet throughout the calendar year. Depending on the size and on what part of the reservoir they are located, the bottom elevations near the islands serve as shelter and a transit point on the migration route of schools of many species of fish of varying numbers.
Well, if the islands are adjacent to the deep-sea waters of the reservoir, and even if there is an acceptable oxygen regime here (Fig. 6) , then different quantitative populations of some underwater inhabitants will live near them on a permanent basis.

The most popular species here in winter is, of course, the striped robber. The area adjacent to these bottom anomalies is particularly attractive due to its moderately hard bottom structure with abundant shell rock, occasionally alternating with muddy areas. And the rather rugged bottom topography here allows perch to camouflage perfectly when hunting for young fish. Also, in the winter, the remains of aquatic vegetation, of which there is quite a lot on the islands, are always full of various insects and microorganisms. Various small creatures feed on them, including small perch, and they, in turn, are often eaten by well-fed humpback whales.
7. In winter, you have to catch perch in relatively shallow reservoirs with a fairly flat bottom topography. These reservoirs, as a rule, do not have a clearly defined channel - and they can rightfully be classified as lake-type reservoirs. Working depths here hardly exceed 2 - 3 m. The slightest changes in the bottom topography in certain places, sometimes only 10 - 20 cm (Fig. 7) , make them very attractive for this predator, which uses such local areas for shelter while hunting.
Also, piles of stones varying in area and size, all kinds of sand deposits in the form of dunes and ridges, washed up by wind currents, can be confidently attributed to quite promising places for catching striped robber in such relatively shallow reservoirs. Often in reservoirs of this type there are local islands of aquatic vegetation, sometimes reaching only a few meters in diameter, mainly reeds, which are clearly visible on the frozen water area of the reservoir. The bases of this aquatic vegetation attract various species of fish and their juveniles, which serve as food for perch of various sizes that visit here at certain times.

The winter angler needs to pay close attention to the snagged areas of the reservoir, where the striped robber is almost always present. By the way, I was often able to achieve better results by fishing not for abundant piles of snags, but for separately flooded trees and shrubs. And the size of the predator caught near single obstacles is larger than in a dense snag. This applies to reservoirs, both with shallow depth and to deeper water bodies.
But you should understand that hunting for a striped robber in snags always involves some consumption of bait (jigs and spinners), which the angler will lose here on the hooks.
8. One of the most promising places for catching perch in winter, undoubtedly, are all kinds of underwater banks and slides. Located in the rather deep waters of the reservoir, they serve as a real island of salvation for peaceful underwater inhabitants who find shelter here from various predators. Of course, predatory fish cannot help but take advantage of this by hunting on these bottom anomalies, and the most numerous of the hunters, of course, is the striped robber.
Underwater slides, depending on their size and location in the reservoir, can host different populations of perch, both in number and size. Based on the period under consideration - first ice, deep winter or last ice, as well as due to the presence or relative absence of food, the values of these indicators (the number and size of the predator) at a particular bottom elevation are in constant dynamics.
It should be borne in mind that in order to search for the striped robber in such places, it is their slopes or the bases of these bottom anomalies that are of greatest interest (Fig

To summarize, I would like to note that, on the one hand, the fisherman’s ability to find promising places on the reservoir both in winter and in summer is facilitated, first of all, by his ability to correctly read the shoreline of the reservoir. On the other hand, in discovering interesting points with a changeable bottom topography, sometimes located at a decent distance from the shore, the winter angler receives invaluable help from his summer and autumn fishing practice, when, as a spinning fisherman on a boat, he finds promising places using an echo sounder and records them in your navigator.
Good luck, and see you again!
The Influence of Weather on Perch Behavior
The bite and activity of perch can be influenced not only by the periods of winter: first ice, deep winter, last ice, but also by the weather. Let's take a closer look at how weather affects perch activity. When is it worth going fishing for perch, and when not?
In general, the best time for fishing has always been considered when the weather has been the same for a long time, without sudden changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature. But what to do when the weather is constantly changing, calm gives way to wind, atmospheric pressure fluctuates: sometimes low, sometimes high, air temperature sometimes plus, sometimes minus?

Things to Consider When Planning a Fishing Trip:
Full moon. It has been noticed more than once that when the moon is full, the bite is simply disgusting;
The predator is most active at low atmospheric pressure, and passive at high;
During the thaw the bite is always good. But you probably already know this very well;
The best air temperature for catching perch in winter is up to -15°C. When the thermometer drops below -15°C, catching perch will be more difficult.
No one has been able to prove with certainty that this is indeed the case. They seem to be experienced fishermen, they all say the right thing, but everyone is different. Of course, you should focus on the weather, but not always and not everywhere. For each body of water and its inhabitants, changes in weather and pressure act in their own way.
Tactics for Searching for Active Perch
Constant search and fishing of all promising places is what awaits every angler hunting for perch. When a promising location is found, 10 holes are drilled at once, at a distance of approximately 15 meters.
The holes need to be drilled in a checkerboard pattern. After we have drilled 10 holes, we begin to fish them, spending no more than 10 minutes per hole.
We would also like to point out that when searching for active perch, the distance between holes should be 10-15 meters. Since active perch can be lured by playing bait from longer distances.

If the search begins from the coastal zone, then in the absence of a bite, they begin to shift towards the river bed. Also drilling holes in a checkerboard pattern, and at a distance of 10-15 meters.
If you finally find a perch, but for some reason it doesn’t take it, but simply pokes at the bait. This is already good, since we completed the first task facing us - we found a perch. Then we simply select the desired bait, balancer, jig or spinner.
And if the bite starts, we fish until it stops. When the bite stops, we move on again to the first task - finding the perch. Moreover, periodically returning to their old holes, therefore, as practice shows, in most cases they work.
To fish holes, a balancer is most often used. It attracts perch from as far away as possible. And when the perch approaches, we act according to the situation depending on the bite. If there is no bite or frequent, idle bites, we change the bait to a lighter one.
Perch fishing in January
Everyone has long known that in the winter months, perch acts as a kind of lifesaver for many fishermen, since its gluttony and sufficient abundance always affects the catch. But with the arrival of January, the oxygen level in the reservoir drops to a minimum, and even the perch experiences this, which in turn affects the bite. But still, catching perch in January with the right approach can bring positive results.
Where to look for perch in January?
These are primarily places that, despite a thick layer of ice, still remain sufficiently saturated with oxygen. Namely: in places where streams flow into a lake or river; in places where there are warm springs; in deep holes where the water temperature does not drop below 4 degrees; wide reaches with strong currents. It must be remembered that the success of an angler directly depends on knowledge of the reservoir. Bass are very unpredictable in January and the more holes you drill, the more likely you are to find a striper site.
Finding a perch is, of course, a great achievement, but you also need to catch it.
How to catch perch in January?
To do this, it is enough to have in your arsenal a regular winter fishing rod and a fishing rod for winter lure. The diameter of the fishing line should be around 0.15 mm, but no more. A prerequisite is the presence of a nod, but not more than 10 cm.
As for baits, at this time baitless jigs perform best at this time, as they so well imitate the usual food of January perch, namely underwater insects. The most commonly used baits are bloodworms, small perch eyes, maggots, etc. But they usually attract the smallest things, so there’s no need to rush to catch them with baits. Spinner fishing in January shows itself to be much worse than jig fishing, but is still used.
The best weather for perch fishing in January is, of course, the thaw periods. On such days, it is not uncommon for anglers to completely forget their striped boxes.
Tactics for Searching for Passive Perch
The tactics for searching for passive perch are very different from the tactics for searching for active perch. Although the basic principles are the same, there are still a few nuances.
The fact is that a passive perch moves little and mostly stands in one place. And it will no longer be possible to lure him with bait from a distance of 10-15 meters. Although the principle of drilling holes is the same, we make the distance between holes no more than 2 meters. As soon as you present the bait under the perch’s nose, you can count on a bite.

Winter perch tackle

Various types of reelless jigs are best suited for actively searching for fish. Not everyone finds nozzles easy to learn, but it is accessible and effective. The main problem that beginners without attachments face is the fight against their own stereotypes. For example, people simply cannot believe that a perch can bite on a bare hook. Maybe even so!
Recommended reading: How and what to catch minnows with
The fact is that the fish does not consider the hook as a separate, dangerous element. She sees the entire jig as a whole. The selected animation and shape of the bait make it very similar to a small larva or bug. There is no need to be rude with the thickness of the fishing line. A diameter of 0.08-0.12 will be preferable; on a thick, strong fishing line, the jig will simply lose its attractive game.
The nod should be sensitive, but at the same time it should be elastic. Elasticity is needed to give high-frequency play, which perches really like. The length of the nod should not be long, again to give the desired frequency.
A nod for catching perch should not have weighting elements at the tip. Various rings and cambrics can give the nod parasitic vibrations that worsen the natural play of the jig in the water. In my opinion, lavsan nods in the form of a plate, slightly tapering at the end, work great. The angle of the nod loaded with the mass of the jig should not be more than 30 degrees.
Jigs like goat are painted in dark colors and have large beads on the hooks. These baits are especially good when fishing in deep water or currents. To animate a goat, lavsan and metal nods made from a clock spring are suitable.











