Red fish in nutrition
Fish is generally good for health, especially red fish. Representatives of the salmon family are called this because of the color of their meat. People who eat red fish get sick less. It has long been considered a valuable dietary product.
About 80% of the salmon family fish on sale are chum salmon, coho salmon, and pink salmon. Which one is better is difficult to determine, since the differences are usually subtle. Although there is a slight difference in the composition, calorie content and density of meat. In addition, salmon include salmon, sockeye salmon, chinook salmon, whitefish, omul and others, but they are less common and have no commercial significance.
Balyk is prepared from red fish, it is salted and smoked. It is often sold frozen. This is a universal product from which you can prepare many tasty and healthy dishes. In addition to meat, salmon caviar is highly valued.
Salmon family

Scientists have identified 3 main subspecies of this family:
- Salmon.
- Sigov.
- Graylings.
Description

Representatives of this family are distinguished by an elongated body shape, compressed on both sides, with a gray-blue color. Numerous dark spots can be seen on the back, and the abdomen has a silvery tint. Depending on the living conditions, as well as the age of the fish, its color may differ, although slightly.
For example, salmon, as one of the brightest representatives of this family, changes its color to dark before spawning, and the males acquire red spots.
Where do salmon live?
Salmon lives both in the White and Baltic Seas, and in the rivers included in the basins of these seas. More recently it has been found in areas of Siberia. Closer to the northern part of the Pacific Ocean there are numerous schools of this fish.
Reproduction method

As a rule, salmon spawn from year to year in the same places in late summer or early autumn. To spawn, they enter rivers.
The fish becomes sexually mature when they reach 2 or 3 years of age, depending on their habitat. The older the fish, the higher in the rivers it goes to spawn.
After spawning, the fish returns back to its natural habitat in late autumn. They often remain in spawning areas until spring, depending on weather conditions. This applies to those areas that are located closer to northern latitudes.
The caviar of this fish is large, and the older the individuals, the more caviar they have. After the fry are born, they live in spawning areas for up to 3 years, until they reach adulthood, after which they migrate to the seas, where they form numerous schools.
Types of salmon with photos and names
Trout

It is considered one of the most prominent representatives of this family. It is also called the “pied fish” due to the presence of numerous dark spots located on the body.
This fish is found in reservoirs of the western part of Europe, as well as in the southern reservoirs of Russia. Trout prefer to live in cold, crystal clear water that is not covered with ice all year round. In summer, when the water temperature rises, trout prefer to stay in the shade, in close proximity to springs, without showing any activity.
Trout is a predatory fish that can feed on eggs while they are still small, as well as small fish and other underwater creatures when they become adults.
Salmon

It is considered one of the most valuable species of the salmon family. This fish can grow up to one and a half meters in length, weighing about 40 kilograms. Its usual habitat is the northern waters of the Atlantic, although it prefers to go into rivers to spawn.
The fish is carnivorous and feeds mainly on small fish such as herring or sand lance. It is found, as a rule, in lakes such as Ladoga and Onega.
Pink salmon

This is the most numerous species of the salmon family inhabiting the waters of the Pacific Ocean. Pink salmon grow up to 70 cm in length, no more, and reach a weight of about 3 kilograms.
In the second or third year of life, the fish becomes an adult and is ready to reproduce. Pink salmon spawn at the end of summer or with the arrival of autumn. The peculiarity is that all the fry born from her eggs are female. After some time, some of them acquire the characteristics of males.
Omul

This is an anadromous fish, which, like pink salmon, is not large in size, growing in length only up to 60 cm, while gaining weight no more than 3 kilograms.
It lives in the Arctic Ocean, but moves to rivers to spawn. There is also the Baikal omul, which belongs to one of the subspecies of this fish. The omul feeds on plankton or small fish. It is of commercial interest and is therefore caught on a large scale.
Chum salmon

It lives in the northern latitudes of the Pacific Ocean, but to continue its species it goes to rivers. The body of chum salmon has a silvery tint, without any spots or stripes, but before spawning its color changes greatly and its sides acquire a crimson hue.
Chum salmon can be found in summer and autumn. They differ from each other, both in behavior and in their appearance.
Far Eastern salmon

This salmon is also called Pacific salmon. This is a migratory species of fish that grows and develops in the seas and oceans, and comes to spawn in rivers. At the same time, she spawns in the same places where she was born.
All types of salmon differ in that they have different periods of maturation. Coho salmon and chinook salmon are among the most prominent representatives of Far Eastern salmon.
The benefits of red fish
Red fish is useful for the prevention of diseases of the cardiovascular system. Due to the presence of a large number of useful microelements, amino acids and fatty acids, it prevents disturbances in the functioning of the nervous system, normalizes hormonal levels and the functions of the endocrine glands.

Red fish is useful for maintaining good vision and preventing dysbacteriosis. Eating it helps maintain healthy hair, nails and skin. Red fish contains microelements that are not found in other foods, so it is recommended to include it in your food. For example, it contains a lot of Omega-6 fatty acids, vitamins A and D.
Subfamily whitefish
Included in the order Salmonidae. A group of whitefishes is united by appearance. Includes the genus whitefish, whitefish and valka.
Muksun
Individuals reach a weight of up to 8 kg and a length of up to 70 cm. Muksun lives in Siberian rivers. It has a small head with a high transition into a long body. The color is light gray on the sides with a dark back. The average price is 700 rubles per 1 kg. Fatty meat with a small number of bones is considered a delicacy.

Omul
Freshwater fish, gaining weight up to 3 kg, swimming in the northern waters of the ocean. The photo shows an elongated body with silvery scales. The fins are dark gray. Tail with sharp corners. The average cost for omul is 550 rubles per 1 kg. Protein makes up 80% of the total calorie content of meat and is a quickly digestible product.

Peled
It grows up to half a meter and weighs up to 5 kg. Peled can be found in rivers and lakes. The body is tall, the caudal fin and the head are covered with black speckles. For the sake of tender meat, rich in phosphorus and vitamin PP, it is bred artificially. Meat costs 160 rubles.

vendace
Fish up to 20 cm long. The body has large scales, the sides are flat. The lower jaw is pushed forward. Lives in lakes. The back is a dull blue color, with silvery scales on the sides. Siberian vendaces are semi-anadromous individuals. The taste is high; 1 kg of fresh frozen fish costs about 300 rubles.

Passable whitefish
Representatives of the group are endangered. All whitefish share common characteristics: protruding lips, smooth head. The meat contains a fat-soluble form of vitamin A. Whitefish fillets contain more fatty acids than any other freshwater fish.
Whitefish is a species of salmon fish. The rounded back and sides are strewn with small spots only in young individuals. Grows up to 40 cm, weighing 300 g. Distributed in Siberian and American rivers.

The Ussuri whitefish has a length of up to half a meter and a maximum weight of 2 kg. The tall body is silver in color with a dark gray back and gray transparent fins. After catching, delicacies are prepared. They are purchased for an average of 300 rubles.
Tugun
Freshwater individuals of the whitefish family. Lives in Siberian rivers. Size up to 20 cm in length and weight 100 g. The high nutritional value of the salmon breed and excellent taste affect the tugun fishery. Rare specimens are caught once a year; the price for 1 kg of lightly salted products is more than 2,000 rubles.

Chir
On average, they gain weight up to 4 kg. Large individuals are found weighing up to 16 kg. They live in northern fresh water bodies. They have a small head and a tall body with light scales. They are considered dietary products and contain a lot of protein. The price of chili is at least 500 rubles per 1 kg.

Belorybitsy
Fish of the salmon family with white meat. There are two similar varieties - nelma and white fish. They have a high curve from the head to the back. The lower jaw protrudes forward. Reaches a length of up to 120 cm and weighs up to 14 kg. Silver color, blue back, gray fins. Representatives of the group are second only to noble sturgeon in the ranking of valuable fish. Cost from 1500 rubles per 1 kg.

Valki
A species of river salmon. Several species live in a limited range. All valks are a source of valuable meat.

Features of pink salmon
This is the most common type of red fish. It is quite inexpensive, so it is accessible to many. This is a small fish, its weight does not exceed 5.5 kg. She eats only high-calorie foods. Therefore, pink salmon meat is fattier and denser. It has a richer mineral composition than chum salmon and a higher calorie content.

Distinctive features of pink salmon are dark spots on the back. It has smaller scales. Male pink salmon have a noticeable hump on their back, which is why the fish got its name.
What are chum salmon and pink salmon?
Both species belong to the salmon family and have some similarities. The meat of these species is very healthy and its consumption is an excellent prevention against certain diseases. The production of these species accounts for 80% of all salmon and is in great demand among consumers.
Is chum salmon a sea or river fish?
Chum salmon has a very wide habitat. The fish can be found in the Arctic and Pacific oceans, various seas and rivers. Chum salmon begins to enter rivers during spawning, and its color changes depending on its habitat.
To spawn, chum salmon prefers to enter the following Siberian rivers:
- Lena;
- Kolyma;
- Yana;
- Inligirka.
Features of chum salmon
Chum salmon is a fairly large representative of the salmon family; its weight can reach 14 kg. It is widely available and popular among buyers. Its meat is soft and tender, not very fatty. Chum salmon does not live in captivity; it eats only natural food, so its meat does not contain artificial additives. If we compare the composition of which is better - chum salmon or pink salmon, then chum salmon meat contains more vitamins. This fish is considered a dietary food because it is low in calories.

Chum salmon is larger than pink salmon, but lighter in color. It has a light silver color and fairly large scales. Chum salmon has a characteristic elongated body shape and a massive tail.
Sturgeon family

Representatives of this family appeared on our planet about 70 million years ago, so they can safely be considered old-timers on our land. These fish prefer fresh water bodies and are considered the largest representatives of their kind.
Description of fish and habitat

Fish of this family are distinguished by their elongated body shape and the presence of bone formations on the back and head. As a rule, these fish lead a benthic lifestyle, feeding on various underwater representatives of small sizes, so we can say that these are mainly predatory fish.
Interesting fact! As a rule, these fish are considered long-lived fish, and spawn only once every 2-3 years. To spawn, individuals leave the seas for rivers, where they rise upstream to their usual spawning grounds.
Features of sturgeon

The value of this fish lies in its black caviar, which was considered, and even more so, today is considered an exquisite and expensive food product that is not so easy to find on the market. In this regard, sturgeon are exterminated in large quantities by poachers. Therefore, recently the number of this fish is small and its fishing has been banned.
Artificial breeding

Due to the fact that the sturgeon population in nature decreases from year to year, sturgeon are bred artificially in special nurseries. As a rule, Russian and Siberian sturgeon, sterlet, bester and beluga are bred. They are bred both for industrial purposes and to increase their numbers in the natural environment, releasing fry, which are also raised.
Types of sturgeon with photos and names
Famous fish of this family include:
Sturgeon

The family includes up to 20 species of fish inhabiting both seas and bodies of fresh water, mainly lakes. As far as we know, up to 90% of all sturgeon species are found in the Caspian Sea.
Some sturgeon grow to impressive sizes. Atlantic and white sturgeon are capable of growing up to 6 meters in length, while gaining weight of several centners. These giants inhabit the seas, but in order to spawn or wait out the winter, they move to rivers.
Some sturgeon prefer exclusively fresh water bodies and do not grow to gigantic sizes. These small fish also stay close to the bottom, feeding on small fish and shellfish. Sturgeon are quite prolific and can lay up to several million eggs during the spawning period, so their mass before spawning increases to 20%, or even more.
It is important to know! Sturgeon are valued due to the high taste characteristics of both meat and caviar. In this regard, sturgeon were caught at a huge rate, which was the reason for the inclusion of various species in the Red Book. Currently, sturgeon fishing is prohibited.
Sterlet
Although sterlet is a smaller representative of this family, some individuals gain weight up to 15 kilograms, no less. The sterlet lives for about 30 years.
This fish feeds mainly on invertebrates, but if it encounters alien eggs on its way, it will not refuse it. Sterlet spawns in the upper reaches of rivers at the end of spring. With the arrival of autumn, it sinks to the bottom, where it remains there all winter, not showing any activity. This fish is often bred artificially, as it is considered a very valuable and sought-after fish.
Stellate sturgeon

It inhabits mainly the Black, Azov and Caspian seas, although it is also found in the Adriatic and Aegean seas. Spawns in rivers. Life expectancy is about 30 years. Its diet includes small fish and invertebrates.
Fish is caught very actively on an industrial scale. Mostly individuals are caught weighing from 5 to 10 kg, although the fish can gain weight up to 70 kilograms.
Beluga

It is listed in the Red Book and is considered both the largest freshwater fish and an endangered species. Beluga can weigh about 1 thousand kilograms, with a length of 4 meters or more. At the same time, a beluga can live 100 years, no less. It begins to spawn on average at 15 years of age, although it spawns only a few times in its life and with a large number of eggs.
The diet of this giant fish includes small fish, shellfish, and often seal pups.
Thorn

It is considered a semi-anadromous fish that lives in the Caspian, Aral, Azov and Black Seas. The thorn overwinters in rivers such as the Ural or Volga.
The fish lives up to 30 years and grows up to 2 meters in length, weighing 30 kilograms.
Which caviar is better
Sockeye salmon, chum salmon or pink salmon are those types of red fish whose caviar is common on store shelves. It is slightly different in appearance. But all red caviar is a very valuable nutritional product. Both chum and pink salmon are tasty and contain many useful microelements. But people who are wondering which red fish is better - chum or pink salmon, often also try to choose a certain type of caviar.
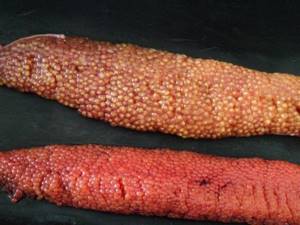
To do this you need to know its differences:
- Chum salmon caviar is large, with a dense shell, bright orange in color. It contains more protein and beneficial microelements. This caviar is the fattest and has a delicate taste.
- Pink salmon eggs are smaller and lighter in color. The taste of the product is lightly salted and not bitter.
- Sockeye salmon has small, bright red caviar. It may have a bitter taste.
- Coho salmon caviar is dark and medium in size. The taste is bitter.
Subfamily Salmonidae
The classification of the subfamily from the order Salmonidae includes seven genera. Distinctive features are a developed jaw with sharp teeth and the size of the body covered with small scales.
Brown trout
The average dimensions common to all species are 30-70 cm in length and weight up to 5 kg. Rounded dark back. Light gray oval body with shiny scales, covered with black specks. The lower jaw is pushed forward.

All forms have significant commercial value and are artificially bred. The average cost for 1 kg of red fish meat is 450 rubles.
The classification includes the following subspecies:
- Caspian trout, the largest fish of the salmon family. Weight reaches 7 kg, length 1 meter. Some representatives weigh up to 50 kg. The noble fish is listed in the Red Book.
- Black Sea trout, gaining weight in the sea, reaches a length of 50 cm. Brook trout grows up to 25 cm.
- Cis-Caucasian trout are gray-green in color with colored spots. Weight up to 500 g. Lives only in clean and cold water. Classified as an endangered species.
- Eisenam trout. They are a species of salmon fish that live in a limited area. They don't sell it en masse. There are large forms up to 1 meter long.
Atlantic salmon
Fish of the salmon family grow up to 1.5 m in length and weigh up to 40 kg. Spotted bodies with silvery scales and white belly. Lake salmon are in danger of extinction. Red meat and salmon caviar are high in the ranking of gourmet foods. Price on average from 750 rubles.

Adriatic trout
It lives in fast-flowing rivers and stays at depth. Grows up to 70 cm.

Italian trout
The fish lives in an Italian lake. The average length is 35 cm. It leads a bottom-dwelling lifestyle. Trout is listed in the Red Book.

Marbled trout
Fish of the salmon family, widespread within the range of Italian, Bosnian, and Montenegrin rivers. They grow up to 70 cm in length. A distinctive feature is the large head. The color is gray-green or silver. The photo shows that the brown stripes on the body create a characteristic pattern. The meat is valued for its unique taste and tenderness. On sale in the regions where they live.

Flathead trout
Salmon species reach a length of 50 cm. They hunt bottom. Individuals are at risk of extinction and have protected status. Fishing is prohibited.

Ohrid trout
Found only in Lake Ohrid and its tributaries. The fish, similar to rainbow trout, grows up to 70 cm. The long body is covered with silvery scales with colored specks. Available in the region where it lives.

Sevan trout
Lives in the Armenian Lake Sevan. There is a walk-through form. Large specimens reach 90 cm and weigh up to 17 kg. The price for 1 kg starts from 750 rubles.

Char
All species are valuable commercial fish, containing minerals and having high taste. The representatives are large, up to 90 cm long, and live in cold waters. The lower price level is 300 rubles. The list of representatives includes:
- Arctic. The body is gray with a dark blue back, covered with spots. Color changes during the breeding season.
- White. Found in Far Eastern fresh water bodies. The color is light shades of green or brown, with small spots. The snout is short, the cavity is green.
- Boganidsky. The content of polyunsaturated fatty acids is higher than in other marine fish. “Charr grows slowly, so fishing is legally limited.”
- Lake char. The largest group among the loaches. The maximum size recorded was 33 kg, 1.5 m in length.
- Chukotka. Far Eastern specimens with a cylindrical body of silvery-white color and red fins.
- Yakut. Individuals with a dark color and stripes on the sides. Has a narrow body.

American palia
Included in the species of salmon fish resettled in natural reservoirs. Palia has a rounded body. Brown back with light speckles. The size exceeds 30 cm. It is in demand in cooking. The cost is about 400 rubles.

Kunja
Dimensions up to 60 cm, weight up to 3 kg. Refers to the commercial species of migratory char. You can buy white kunja meat for a price starting from 400 rubles.

Malma
Salmon fish are up to 75 cm long and gain weight up to 3.5 kg. They swim in the northern waters of the Pacific Ocean.

Neiva
Lake fish with a long body and silvery color. During the spawning period, it acquires a yellow or red-brown color with crimson spots. Reaches a size of 40 cm in length. Has no commercial significance.

Svetovidova's longfinned palia
Small individuals up to 33 cm, listed in the Red Book. They have a short snout with a protruding lower jaw and long teeth. The body is dark gray with a golden tint.

Lenok
There are river and lake forms. They have a round body with small scales. The color camouflages the salmon fish in its habitat. Lenok grows up to 70 cm weighing up to 6 kg. Refers to sport fishing objects.

Sakhalin taimen
Individuals are large in size, growing up to 2 m, weighing up to 24 kg. Distinctive features are large scales. Taimen is included in the Red Book.

Pink salmon
Saltwater fish live in cold ocean waters. Distinctive features of the individual are the absence of teeth on the tongue and a white mouth. Commercial fish, reaches a weight of 2 kg. The color is silver with a dark blue or greenish back. Price from 250 rubles.

Chum salmon
Large individuals reach 1 meter in length, weighing up to 16 kg. Lives in Pacific waters. The body is light gray with dark fins. In second place after pink salmon as a mass-sold fish, with dietary meat and caviar, costing from 450 rubles. Find out how chum salmon differs from pink salmon.

Coho salmon
The body is covered with bright silvery scales, distinguishing it from other species. Grows up to 108 cm with a weight of up to 15 kg. The meat has a healthy composition and excellent taste, increasing its commercial value. Cost from 460 rubles.

Clark's Salmon
Has red or orange lines along the lower jaw. The body is gray or yellow-green. Grows up to 75 cm. Popular for fishermen.

Mexican golden trout
Freshwater salmon with a golden color. Fishing rules have been established.

Red salmon
A fish with a red body during the breeding season and a large jaw. Grows up to 80 cm and weighs from 1.5 kg. “An interesting fact: the brightly colored fillet is colored by carotenes from crustaceans that are part of the predator’s diet.” Sockeye salmon contains a large amount of fat. Price from 650 rubles.

Rainbow trout
The coloring corresponds to the habitat, with a longitudinal line of bright color. Size up to 50 cm, weight up to 1.5 kg. Artificially bred, the meat contains easily digestible protein. Sold in stores at a price of 800 rubles.

Sima
Lives in coastal Pacific waters. Size up to 80 cm and weight up to 10 kg. The Sim's walk-through form is larger. Bred in fish factories. The oval body is covered with black spots. The cost is on average 500 rubles.

Trout Gil
It has a yellow body with spots, up to 50 cm long. Sport fishing is permitted with restrictions.

Chinook
Representatives differ in length 90 cm. Black spots cover the entire body with fins. The gums on the lower jaw are black. Commercial fishing for Chinook salmon is prohibited. It has high taste qualities.

Taimen
The fish has an elongated body, with dark spots. The head is pressed from above. Wide jaw with curved teeth. The color is dull gray or green. The taimen genus includes individuals up to 2 m long and weighing up to 80 kg. They are a valuable fish and fishing is prohibited. The name is taken from its habitat. The list includes:
- Danube
- Korean
- Sichuan
- The common species lives in cold fresh water bodies from the Urals to the Far East.

How to choose
Some sellers sometimes replace chum salmon with pink salmon, since it is cheaper and chum salmon meat is more valuable. Therefore, it is important to know how they differ. When buying a whole fish, you can pay attention to its characteristic features: pink salmon has dark spots on the back and a hump, while chum salmon has a lighter color and a large tail.
But most often fillets of this fish are substituted for sale. People who know what is better - chum salmon or pink salmon - understand such features. Pink salmon meat is pale pink in color, so it is easy to identify. But when processing fish, for example, when canning or even freezing, it can be treated with dyes. And then pink salmon acquires a bright pink, juicy color, the same as that of chum salmon. Therefore, it is recommended to buy chilled, fresh fish.

When buying red fish you need to pay attention to some signs:
- the surface of fresh fish should be shiny and clean, without mucus;
- scales and fins should fit tightly to the skin;
- eyes should be clear, prominent and shiny;
- gills - pink or red;
- canned or salted fish should contain as little dyes, preservatives and flavor enhancers as possible, the color should not be bright, with pale veins;
- the fillet should be of uniform color, the meat should be dense and hold its shape well.
Use in cooking
Salmon meat is considered a valuable and tasty product; it is most often eaten after heat treatment, but certain fish species can also be salted and dried. The meat has a beautiful red-pink hue, and the presence of beneficial fatty acids is greater in those species that lived in cold waters.
The best side dishes are potatoes, boiled rice, and vegetables. Sweet and sour sauces perfectly highlight the taste.
Fresh fish should be scaled, gutted, washed, and then dried with a towel. Frozen food should be left in cold salted water to defrost.
Suitable seasonings for salmon are:
- dill (fresh, frozen);
- thyme;
- basil;
- pink pepper
Before cooking the fillets, it is recommended to sprinkle with lemon juice, but it is important not to overdo it, otherwise the taste will be reduced.
Frying
A simple but very tasty recipe for cooking red fish in a frying pan.
- Cut the carcass into pieces, salt and season. You can roll it in flour.
- Fry in a preheated frying pan for 5 minutes on each side.
Serve with potatoes and vegetables.

Baking in foil
This method of preparation allows you to preserve maximum beneficial properties.
- Prepare the carcass (clean, rinse, salt, season).
- Place foil on a baking sheet.
- Place a layer of onion sliced into rings.
- Place the fish.
- Cover with foil.
- Place in the oven. Temperature 210°, cooking time - 20 minutes.
- Open the foil, this will help get a crispy crust, then bake for another 5 minutes.
A tasty and healthy dish is ready.

Pickling
Both fresh and frozen fish are suitable for this option.
- Prepare the carcass, cut it into pieces of the required size.
- Rub the fish with a mixture of salt and sugar.
- Place the fillet in a glass container under pressure.
- Place in the refrigerator, in the freshness zone, for a day. After this, the product is ready for use.
For 1 kg of fish you will need 3 tbsp. salt and 2 tbsp. Sahara.
Arctic char (lat. Salvelinus alpinus) - this fish belongs to the salmon family and forms many forms (anadromous, lake-river and lacustrine), which often confuses ichthyologists, because very often it is almost impossible to determine which species a particular char belongs to. Char is widespread in the Arctic Ocean: it lives off the coast of Spitsbergen, Novaya Zemlya, off the coast of Siberia and in the North Pacific Ocean. Char is the most northern fish of all salmonids.

Char is one of the most beautiful fish. The body color of a loach depends both on its age and on its habitat. Migratory loaches that roll into the sea have a dark green back with small spots, silvery sides (sometimes with pink spots), a white belly, and gray-white fins. In the river, during spawning, the color of the fish changes: the back becomes green-brown with a silvery tint and bright red spots, the fins become grayish-pink, and the color of the belly remains gray-white; Young individuals of loaches differ from adults in being more variegated. Char is a fairly large fish. Sometimes you come across fish longer than 80 cm and weighing up to 15 kilograms. The body of the loach is not covered with scales (obviously, this is what gave it its name), only the sides are covered with small, small scales, and even these do not cover each other, but are simply located next to each other. The body height of the loach is not much greater than its thickness. Ichthyologists call migratory fish those fish that migrate or move from rivers to seas and from seas to rivers. Char is one of these fish. The need for such migrations is due to the fact that these fish prefer to spawn from the place where they usually live, say, from a river to the sea, or vice versa.

Char spends the winter in the river, and in June or early July (sometimes still under the ice) leaves the rivers for the sea. Returns to spawn in the river in early September and late autumn or even early winter. Char spawns several times throughout its life, but many individuals die after spawning. The loach is a typical predator and feeds only on fish. That is why it is good to catch char with a spoon, which it always grabs greedily. You can also catch it with great success using a piece of fish meat attached to the hook of a simple float rod.

In addition to the migratory (actually Arctic) char, lake-river and lacustrine char are found in the reservoirs of the Urals and Siberia (for example, in the Paga River and lakes Kybanty and Pagaty). Both types are smaller in size. Lake-river char (palia char) at best reaches a length of 25-35 cm. The color is the same as that of anadromous char in fresh water. Lake-river char feeds on insects and, in summer, mosquitoes and midges that have fallen on the water. It feeds in lakes and goes to tributaries to spawn in September-October. Pure lake char is found in the lakes of the Kola Peninsula and in the northern part of Siberia. It is larger than lake-river char (pali char) - it reaches a length of 60-70 cm. This type of char spends its entire life in lakes and does not rise into rivers. Like the migratory char, it feeds on fish. Its back is greenish-black, its sides are silver or silver-pink. The belly is white or pinkish-white, the fins are pink or red, sometimes gray. Both in stagnant waters, silted or with mud, and in clean mountain waters, the char usually stays deep, close to the bottom. It prefers to lie motionless and hide between stones and snags, and sometimes even buries itself in silt or sand (it makes holes for itself in the shore or climbs into cracks). Although, if necessary, the char can swim very quickly, which is facilitated by powerful muscles and body morphology. This fish is very demanding on the purity of water and the high oxygen content in it.

In small rivers (such as Talatayakha in the Polar Urals), char can rarely be found in schools. In this case, he prefers to live alone (in bays, near rifts, at shallow depths). In larger bodies of water (lakes and ponds) it gathers in flocks and stays at great depths. Often, especially in winter, it buries itself in the mud and comes out only in the spring, before the ice breaks up. If the reservoir freezes completely, to the bottom, but has a muddy bottom, then the char will overwinter very well in such conditions. In this it is very similar to crucian carp. It is distinguished by its vitality even when swampy streams dry up and can live in damp soil for quite a long time. You can catch char with a float rod using a worm and a fly, in the upper layers of the water, and especially during sunrise and sunset, when the fish rises to feast on midges falling into the water (this only applies to lake-river char). You can also fish with a small spoon, placing it quietly on the water so as not to scare the char, because this fish is very careful. Having swallowed the spoon, he immediately tries to get rid of it and fiercely resists. In winter, char should be caught at depth, at the very bottom, where it sinks, in order to look for insect larvae in the mud.