What do you know about acne? You will probably answer that they look like snakes and are a delicacy. However, not everything is so simple – exciting discoveries await those who want to get to know each other better. They can travel overland, even up to several kilometers. There is also a certain stage in their life - spawning, which leads to the death of the individual. In this article we will look at the most interesting and mysterious facts from the life of these amazing creatures.
| Class | Ray-finned fish |
| Squad | Eels |
| Family | Acne |
| Genus | Acne |
| View | River, Sea |
| Security status | Threatened |
| The average size | Up to 2 meters in length, up to 4 kg |
| Lifespan | Up to 85 years old. The famous record-breaking eel lived 155 years. |
| What does it eat? | Insect larvae, mollusks, frogs, small fish |
| Optimal feeding time | Mostly at night, sometimes during the day |
| Enemies | During the passage of the Gulf Stream, they are numerous. |
| What do they bite on? | Worm, small doubles. |
A little history
Development began more than 50 million years ago. At the same time, there was a division into 4 genera, 20 families, 111 species and about 800 subspecies. Like all underwater inhabitants, they are grouped into different scientific classifications. One of the most common species is a subspecies called Anguilliformes (river Anguillaanguilla species).
These radiant fish are classified as bony vertebrates. They include all the popular families such as moray, spaghetti, American, European and others.
Photo of river eel:
They spawn and migrate to fresh water. This movement is temporary - they remain marine in nature and require salinity. At maturity they return to the ocean to breed.
Salinity is essential for healthy individuals. Therefore, there are no real freshwater families in nature.
The name is also used to refer to other types such as electrophorus, spiny (family Mastacembelidae) and deep-sea slant-headed (family Łauraczowate). However, other genetically related individuals have developed an elliptical body shape during evolution, and this is their main difference.
More than 100 kilograms of eels detained in Hong Kong, Spain
What does an eel eat?
Eels are nocturnal and prefer to sleep in a secluded place during the day. By nature, they are voracious predators with powerful teeth. The diet is based on small fish, crustaceans and mollusks. They will not miss the catch caught in fishing nets. Lacking good eyesight, eel fish prefer to ambush prey, because thanks to their excellent sense of smell, they sense it from afar. There are species of eels that camouflage themselves with bottom vegetation. Digging a vertical hole in the ground with the help of a strong tail and leaning halfway out of it, sea eels wait for prey. In case of danger, they hide completely in the hole with lightning speed.
Emergence
The main habitat is the lakes of Western and Central Europe, as well as the southeastern and central Atlantic Ocean and all European seas. Representatives prefer warm and heavily vegetated places with a muddy bottom, although it can also be found in fast rivers with a rocky bottom, especially if it finds eroded banks, tree roots and other shelters there. He lives at the bottom. He spends the winter buried in a mule.
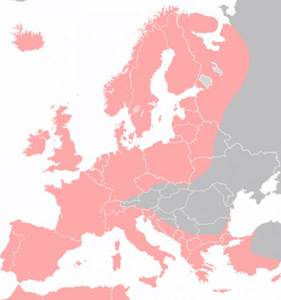
Eel habitats
Until they reach sexual maturity, they live in inland waters - females inland, males in the brackish water range. Adults migrate from fresh water to the sea (catadromous migration).
physical characteristics
Freshwater representatives are very similar to snakes, but this is only a superficial resemblance. Their exterior is amazing. The bodies are covered with a thick layer of mucus. They lack pelvic ribs, and many species also lack pectoral fins. The dorsal and anal fins are connected to the caudal fin, forming a single stripe running along a large part of the body.
The female reaches up to 200 cm in length and weighs up to 9 kg.
Males are smaller than females and reach a length of up to 60 cm (the so-called lace) and a weight of up to 0.35 kg.
The general characteristics are as follows:
- The body is elongated, 5 cm long. Depending on the species, they can grow from 1.2 to 4 m in length. The length of the record individual was 6 meters, and its weight was 72 kg.
- Adults weigh from 1.1 kg to over 25 kg.
- They usually have pointed heads with sharp teeth. Individuals that live deep in the sea are usually gray or black. Individuals that live in tropical areas have bright patterns and colors.
- They swim by generating body waves that travel along the length of their bodies. They can flow backward, inverting the direction of the wave.
Depending on the environment in which they live, their bodies acquire a lighter or darker color. Some individuals can be almost black, while others have an olive tint. In addition, the shape and size of the snout depend on the ecosystem in which the fish is found. First of all, it depends on food.

And therefore, individuals with a narrow head are found where they have the opportunity to feed on small crustaceans, larvae and worms. In places where fish and larger amphibians predominate, it adapts its mouth to this type of food, due to which the muzzle becomes many times wider.
The appearance of the larvae was so different from the adults that for a long time the leptocephala (as it is technically called) was considered a separate group. The larvae have a smooth, transparent, highly flattened lateral and elongated body with micro internal organs. They are also an exception among vertebrates because they have no red blood cells or hemoglobin in their blood.
Where do the largest eels live?
The largest specimens of conger are found annually over sunken ships in the English Channel. Fish up to 35 kg are caught from reefs in the western part of the English Channel. Reef conger eels are not always smaller than their counterparts caught over shipwrecks. However, due to their large extent, underwater reefs cannot be fished as effectively as the area of a sunken ship where fish are concentrated.

Lost ships in the English Channel
Some wrecks in less accessible areas of the sea have become home to numerous small congers weighing from 7.5 to 20 kg. On some days, a catch of 20 or 30 eels per angler is considered normal. There are not as many eels living above the sunken ships, where intensive fishing is carried out, but they are larger. If trophy eel hunters fish around heavily fished wrecks, they may only be able to settle for one or two fish per angler. But these will be specimens weighing more than 25 kg.
This is interesting! Vic Evans' record conger, like all the biggest conger eels of the last 30 years, was caught off a wreck that lies no more than 10 miles off the coast.
The most common marine species
Some of the most common species are sea eels and moray eels. They live only in salty oceans and seas. There are over 100 different types and they are primarily found around the Atlantic coasts of North America and Europe. Congeras can be up to 1.8 m long and weigh more than 45 kg. They prefer to live in deep water and are blackish or grayish in color.
Photo of conger eel:

Moray eels are the most popular species in the world. They live in tropical seas, in shallow waters and can be found in crevices among rocks or coral reefs. They are predators. When they are not hunting, they hide in rock crevices or, in the case of some individuals, in burrows, sand or mud.
They have bright colors and skin patterns. They are about 1.5 m long, with the exception of one species that reaches 3.5 m in length.

Natural enemies
In the aquatic environment, it is difficult to express the specific type of predators that prefer to hunt eels. There is absolutely no threat to adult fish in rivers. Due to their size and habits, no one can threaten these aquatic individuals. But the inhabitants of the seas have something to fear. Eels are a delicious delicacy for shark or tuna.
If we consider younger fish, then predators such as pike, cormorants, seagulls and others would not mind considering them as prey. But even these representatives cannot be considered serious hunters.
The main enemies of eels have always been, are and will always be people. Since it is an exquisite delicacy due to its tender meat, hunting it is very common.
Life style
Most species are nocturnal, so they are rare. Sometimes they are seen living together in holes or "bottoms". Some also live in deeper waters on the continental shelf and on deep slopes up to 4000 m. Only members of the Anguilla live regularly in fresh water, but also return to the sea to breed.
It usually lives in water, but during the migration period it can also move on land, crawling at a speed of about 3 km/h on wet soil covered with grass and mosses. Diffusion of gases through the skin is of great importance during breathing. This is a long-lived fish - up to 85 years.
Image of a fish
It is extremely difficult to say what an eel fish looks like, since taking a photo of an eel fish is not easy, since in principle it cannot be caught with simple gear, and even the greatest trickster cannot catch it in his hands. The reason for this is his uncomfortable body. The eel wriggles like a snake, crawling across land over short distances.

Some people enthusiastically interpreted that the river eel fish is different from others in that it can crawl from one end of the river to another if there is a small distance of land.

Habitats
Some families live in places with fresh water, such as ponds, rivers and lakes. When they are ready to breed, they travel or migrate to the salty waters of oceans and seas. However, many eels always live in salt water. Eels are found throughout the world.
In the spring they enter our ponds from the Baltic Sea and settle in river systems and lakes, where they usually live for six to ten years. They are bottom dwellers, meaning they are usually found on the muddy or sandy bottom of a body of water.
Another feature is the ability to sense temperature changes as low as 0.03°C.
Reproduction
Reproduction in captivity is impossible. It should be remembered that this fish lives in European rivers, lakes and ponds only at the juvenile stage. When individuals reach sexual maturity (from 6 to 12 years for males and from 9 to 18 years for females), they return to their place of birth: in the Sargasso Sea, to the Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Florida (USA), where they breed and where they come from do not return.

The larvae remain there for up to two years and then migrate to European shores. Their journey lasts from 200 to 300 days. Eels arrive in southern Europe at the beginning of winter, and regions further north reach later, until early next summer. They develop into shapes called glass or river eels.
These are small transparent fish ranging in size from 6 to 12 cm. They remain in the mouths of rivers, where they feed on plankton. Then they gradually colonize rivers, lakes and ponds in lowland areas, where they transform into yellow eels.
Most migratory fish, such as salmon, are anadromous - spawning in fresh water and spawning as adults in salt water. Meanwhile, the species in question does the opposite: it breeds in the ocean and spends its adult life in lakes, rivers and estuaries. Life according to this scheme is called catadromic.
Female eels are found in the upper reaches of rivers, while males remain near the mouth. These fish can spend up to 20 years in inland waters before returning to the ocean to spawn, after which they die. No one has ever observed this process.
For biologists dealing with this, solving the species' reproduction puzzle is something of a Holy Grail.
Eel farming
Sea eel, as well as river eel, is a very valuable food product. Its cost is high, and if one could learn how to breed them, or at least grow glass eels to marketable standards, this would have a huge economic effect. Naturally, the thought of this prompts experiments on the artificial cultivation of eels. In Japan, similar experiments have been going on since 1950. Then the Japanese started by trying to grow Japanese eels.

Here is a description of the experiments conducted by the Japanese scientist Takahashi in 1972. He took a shipment of glass eels received from England. In total, the batch contained about two thousand eels, the average weight of which was 20.4 grams. The fish were given a combination feed once a day in such a way that the weight of the feed was approximately two to three percent of the weight of the fish. Once a month, the water was drained and all the fish in a row were weighed, determining their total and average weight. A weight of 150 grams was taken as the control limit, and every month it was recorded how many fish reached this weight.
The main result can be summarized as follows: the eel grew very poorly. The number of fish reaching the target weight was only two to three dozen per month. Ten fish were taken from these specimens to study their sex. The vast majority of fish that outgrew the 150-gram mark were males. However, a more detailed analysis reveals very surprising dynamics of sex distribution: in the first, August batch, ten fish studied turned out to be females. Then the picture changed sharply: in September there were two females and eight males, in October - one and nine, respectively, in November two and eight, in December - all males. The experiment ended in December. Each fish was weighed again, and they were all divided by weight into three groups, 50 fish were taken at random from each and their sex was determined. Again an amazing result was obtained: there were always ten times more males than females!
Competent fishing
Eels can be found in almost every larger body of water, but they are not an easy catch. With the right equipment, determination and knowledge of habits, it is possible to catch one with a hook.

When searching for a place, special attention should be paid to the type of bottom and the amount of food. Fish don't like noise, so secluded bays with lots of plants are the place to find them. In rivers, it can be found at the mouths near calmer waters in close proximity to spurs and other obstacles. It feeds mainly at night, so this is the best time for fishing.
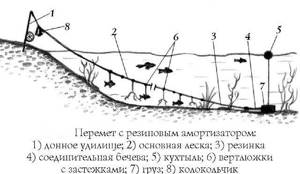
How to install fishing rods
Groundbaits
A highly developed sense of smell is the main advantage of the species. Attractive aromatic bait attracts them even from a very long distance.
A good bait is sand and silt balls mined from the shore in combination with crushed fish, earthworms, snails and other invertebrates. The most popular baits are red or white earthworms and fish pieces.
.Sea fishing .Tackle “SNIZH-CHUGH”
Equipment
It is almost impossible to catch with bare hands. It is covered in thick mucus and slithers like a snake. Since fish are most often found in the lower zone, anglers usually use the land-based method. Success will be guaranteed by a good, durable fishing rod equipped with a special set:
- reel - preferably a spinning reel, with a large amount of wound line (0.3 mm);
- hook with eye No. 6 or 4; the hooks used to catch these fish are 1/0, 2/0, 4/0, depending on the bait used;
- leading - from 70 cm to 1 m, made of thinner monofilament (0.25 mm);
- ground weight - in the form of olives or tears 20-30 g (maybe weight with anti-ball tube);
- swivel - located between the main line and the leader.
Since underwater fishing often traps specimens in underwater roots, it is not recommended to use side weights or bait baskets.
If we use the float method, the best would be 25mm fishing line, 0.20mm line up to 0.5m long, No. 6 eye hook, weights, depending on the float offset, 3-4 meter fishing rod. When fishing with a float, we need to place the bait just above the bottom or above the vegetation.

A well-chosen location, a favorable aura, patience and well-prepared equipment will guarantee a catch.
Use in cooking
Eel is present in the culinary traditions of all European countries. It is eaten in many ways and there are countless recipes to prepare it. It is sold fresh or processed (smoked, pickled, boiled, sliced, filleted, canned or frozen).

It has tasty, fatty, white, tender meat with few bones, rich in omega-3 acids, highly digestible protein, vitamins A, B1 and B2, vitamins C and E, as well as minerals: calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium and sodium.
Its useful value is really high - it is 75%!
This is a real delicacy on our tables, it tastes great in a stuffed or fried version, and also - with a lot of fat - smoked, grilled or deep-fried.
This heat treatment of meat gives it a juicy taste, durability and amazing aroma. Sensational flavors with the addition of Provençal herbs, lemon juice or dill.











