Area
The homeland of this population is the reservoirs of North America, located between southern Canada and Mexico. It is widespread in the North Caucasus, Central Asia, and is found in water bodies of Transcaucasia, Ukraine and Moldova.
In 1971, the fish was brought to the Krasnodar region. Now the population is widespread in many Russian regions. It is inhabited by the Volga, Akhtuba and other rivers with suitable water temperatures. Where is buffalo fish found? It is found in many reservoirs of the Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories. It is bred in reservoirs and lakes of the Urals.
Ictibus are heat-loving; reservoirs in which the water warms up well are suitable for their habitat. In cold ponds and lakes the population practically does not occur. Individuals feel great in muddy waters. In ponds and lakes where bighead carp and carp live, buffalo fish are uncomfortable. She is often affected by lerneosis.
Description of the species, habitat and characteristics
To an inexperienced angler, these representatives of the species may seem very similar. In fact, there are significant differences in the appearance, habits and lifestyle of fish.
Golden carp
Common crucian carp (golden) received its name for the characteristic color of its scales, which have a golden tint. The back of the fish is dark, gray or brownish. The belly is always light, although depending on the situation, it can also have a different shade.
This species lives in overgrown reservoirs of Europe and Siberia, and is almost never found in rivers. He can be called a real swamp inhabitant. He is able to survive in truly extreme conditions. In dry summers, when the reservoir dries out greatly, crucian carp burrow deep into the silt, waiting out the drought there. In the same way, it tolerates severe freezing of small lakes in winter, burrowing to a depth of about half a meter. The crucian carp hibernates in this way until the ice melts. For this reason, there are many shallow water bodies where only crucian carp live.
Other types of fish, even if they get into ponds in different ways, alas, will not be able to survive the winter. Even if the water does not freeze to the very bottom, there simply will not be enough oxygen.

Dense thickets of grass or reeds are the home of this swamp inhabitant. The favorite habitats of crucian carp are the border between the grass and the deep slope. It is often found in “windows” among dense thickets of algae. In the thickets, fish find food, a comfortable temperature and shelter from the sun's rays.
Goldfish
Silver crucian carp has spread even wider on the planet. It is found in most of Europe, Asia, and is especially common in China and Japan. It differs from the golden one by having a silvery color on the belly and sides. Currently introduced to India and some countries in North America. Unlike golden crucian carp, it is often found in rivers, where it prefers places without fast currents. For this difference, some fishermen received the name river crucian carp.
In bodies of water with flow, fish feed on caddis flies, worms, mollusks, crustaceans and insects. This species does not like strong thickets, but if vegetation is present, it often stays near it. The color greatly depends on the type of reservoir, the color of the bottom, the transparency and shade of the water. There are individuals of a dark gray color, and in some reservoirs, on the contrary, almost white.
Recommended reading: Perch in winter on a balancer
This species often does not burrow into the silt, but continues to live throughout the winter. This phenomenon usually occurs in reservoirs with a hard, sandy or clay bottom. This is explained by the fact that a lot of methane is formed in silted lakes during the winter. The gas does not have time to pass through thick ice, remaining in the water, making it difficult for fish to breathe. Having buried themselves in the mud, crucian carp fall into sleep, during which all vital processes are greatly inhibited.
Reservoirs with a hard bottom in winter remain quite comfortable for underwater inhabitants. The depth of the reservoir is perhaps of decisive importance. In shallow waters, a lot of greenery always grows during the summer. Dead algae under the ice consume a significant amount of oxygen, while releasing the same methane.
Fish growth rate
Silver crucian carp grows much faster than its counterpart and is a valuable object in fish farms. Having reached the age of two years, the fish weigh up to 400 grams, especially in the southern regions. With age, the weight of individual fish can exceed 2 kg. The whitebait feeds mainly on zooplankton and phytoplankton. The large one eats animal and plant food, and at times does not disdain carrion.
Silver and golden carp have much in common, but there are also significant differences between them. The mass of common crucian carp reaches two kilograms, according to some sources, more. But for the most part, specimens weighing 0.5 kg are considered a serious trophy among fishermen. Despite its extraordinary vitality, this fish grows slowly. On average, at the age of two years, crucian carp weighs about 100 grams. This is a rather small increase compared to other species of the carp family. After another year or two, he reaches sexual maturity.
It often happens that in small ponds with a poor food supply, only small crucian carp live. Moreover, its size seems to be calibrated. The presence of other fish species in the neighborhood can greatly influence the size and abundance of a species. It is known that rotan is a dangerous enemy of crucian carp, actively eating away the young. They hunt for juvenile crucian carp and perch and pike.
Features of reproduction

Crucian carp spawns in water heated to 14-16 degrees, at a depth of about half a meter. The fish rub against various branches of bushes and stems of aquatic vegetation, to which the eggs adhere in strips. The process can take place several times during the summer, or more precisely, during the time when the water is warm enough. At times, crucian carp can spawn even in August or September. This is especially observed in the southern regions, at a water temperature of 15-20 degrees.
We recommend reading: Catching rotan on the last ice
There is an interesting feature in the reproduction of silver crucian carp: predominantly females participate in the process. Of the emerging fry, females again predominate. In some reservoirs, only females spawn. In this case, the eggs are fertilized by other fish, mainly carp fish. These can be bream, roach, carp, carp, tench and others. The egg of a crucian carp carries a double set of chromosomes and does not need to merge its nucleus with the nucleus of the sperm. For the development of the egg, penetration of any sperm into it is required, which is subsequently resorbed.
As a result of such unusual fertilization, hybrid forms of crucian carp appear from time to time. Unfortunately, hybrids cannot continue the race as an independent species due to infertility. In addition, they are limited in growth and life expectancy.
Waterfowl often become carriers of eggs to neighboring ponds and lakes. Thus, they contribute to the natural stocking of even the smallest and most inaccessible reservoirs with fish.
Indeed, how else can one explain the appearance of crucian carp in forest ponds, the size of which can be several meters. In such “puddles” one of the minnow species often lives next to them.
Description
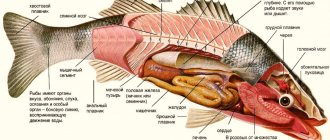
The buffalo fish has a relatively tall body covered with scales. The description emphasizes that the body has a valval shape. The outline of a buffalo resembles that of a goldfish. The back is decorated with a long fin. Its first rays are higher than the subsequent ones. The head of individuals is moderately long. Its shape is similar to the heads of silver carp.
The backs are painted in dull brown shades, the fins are gray, and the sides are light tones. Buffalo river fish is close in color to carp. A photo of these fish species allows you to verify the similarity of their coloring.
The difference between crucian carp and carp

There is no doubt that an experienced fisherman will be able to distinguish these fish without any problems. But some difficulties may arise for beginner fishermen. Let's try to understand the similarities and differences.
Both types of fish belong to the same family and have similarities, for example:
- Colors,
- Massive body;
- Large scales;
- Fin color and size.
All these similarities can be identified, rather at a superficial glance. If you look more closely, the differences become more obvious.
The main differences between these fish include the following:
- The dorsal fin of the carp is noticeably longer, but less in height.
- The body of the carp is somewhat elongated, while the crucian carp, especially the golden one, is more round in shape.
- The presence of mustaches in carp
- The weight of an adult carp is several times greater
Additional differences:
Carp Crucian carp
Hump on the nose Straight contours of the head Fleshy lips Thin lips The body is full, elongated, flexible The body is tall, compressed Dark, large scales The scales are lighter, smaller, harder Notch on the fin Smooth fin Larger and heavier Smaller, lighter
We recommend reading: Burbot: what kind of fish is it
smallmouth buffalo
This variety of buffalo has the highest nutritional value. The fish grows much slower than its largemouth counterpart. She reaches sexual maturity at 3-4 years of age. The gill apparatus, due to the short and sparse rakers of the smallmouth ictibus, is not capable of filtering plankton. His mouth is lower.
Zoobenthos is the food of young of the year. In individuals weighing 60-70 grams, it makes up half of the diet. The food of two-year-olds consists of 2/3 chironomid larvae and other bottom inhabitants. Buffalo fish happily consume detritus, photos of which are presented in many sources and in our article. She also does not refuse carp feed.

Buffalo and crucian carp: what is the difference
The United States is considered the birthplace of the buffalo. Fish appeared in Russia in the late 70s. A few years later, it successfully spread throughout the European part of the Russian Federation.
This is interesting! A hybrid of crucian carp and crucian carp does exist. It was bred in 1976 by breeders. The males of these hybrids are not capable of reproduction, and the females reproduce by gynogenesis.
Characteristic features of an “American”:
- body length varies from 35 to 120 cm;
- body weight can reach 35 kg;
- life expectancy is 14-20 years;
- medium or large head;
- large, pronounced eyes;
- the mouth is small with a horizontal slit;
- the dorsal fin has 6-7 rays (if viewed in profile, the fin is crescent-shaped);
- the tail is short with rounded ends.
The Chukuchan family prefers bodies of water with warm and turbid water. The ideal place is silted areas. Compared to cyprinids, chukuchanovs require warmer water for spawning. In the warm season, the buffalo goes to places with a lot of underwater vegetation. Icthyobus meat is much tastier and fattier than that of crucian carp or crucian carp. Plus, he's not that bony. “Sazanya Bay” is a fishing base with comfortable living conditions and affordable prices. Experienced huntsmen are ready to show you promising fishing spots and also tell you a few secrets of successful fishing.
TAGS:
Large Mouth Buffalo
Largemouth buffalos grow faster than other species. They have the gill apparatus of a planktivore. They have no antennae. Buffalo fish are completely covered with scales. The photo allows you to see large scales on her body. The mouth of individuals is upper and quite large. The surface of the thick lips is covered with villi.
This variety of ictibus prefers rivers and ponds. You won't find it in salty bodies of water. In the USA, the population is grown in ponds located among rice fields. Individuals reach marketable weight in 1-2 years. The average weight of fish is 15 kilograms. Sometimes there are specimens weighing 35-45 kilograms.

The population begins to spawn in March and ends at the end of summer, when the water cools to 14-16 ˚C. Females lay small sticky eggs, laying them on plants.
The diet of juveniles consists of lower crustaceans. One-year-old fish feed on water beetles, ostracods and occasionally phytoplankton. Adults prefer zooplankton and eat crustacean larvae. In artificial reservoirs they actively feed on mixed feed.
Commercial value
Icthyobus is a schooling fish and, depending on the water temperature, can live both at the bottom and in the middle layers. This breed is quite unpretentious and can be used for several purposes:
- industrial breeding;
- stocking ponds where paid fishing is carried out;
- as a decorative object.
With proper feeding and warm water, by the age of two years a buffalo reaches half a kilogram in weight. Such growth rates make breeding this fish a very profitable activity. The maximum weight of an adult can be more than 18 kg. Catching such a trophy will be of interest to any fisherman.

The largemouth variety of buffalo can reach very impressive sizes.
The taste of this fish is at a fairly high level. Its meat has a high fat content and, unlike carp and crucian carp, does not have a grassy smell. The absence of small bones is also highly valued by gourmets. In addition, ictiobus is easily subjected to primary processing.
The subtleties of fishing for buffalo
Buffalo is caught in almost the same way as crucian carp. Fish are usually caught from the bottom. The best bite happens during summer fishing with the onset of dawn or evening sunset. For fishing they use donks, fishing rods and feeders.

For winter fishing, a simple fishing rod designed for this season is suitable. A jig is suitable as bait. To fish with it, the method of vertical trolling is used.
For a successful catch, the fish should be fed. For each season they use their own bait designed for crucian carp. In addition, universal feed is used. Effective biting is achieved by using ready-made flavored baits.
Sometimes baits are scented independently at home. They are enriched with hemp and caraway seeds. A variety of oils and cakes are used for this purpose. Fish love baits with the aroma of anise, coriander and garlic. Suitable baits for fishing these fish include worms and maggots, corn and bloodworms, bread crumbs and pieces of dough, cereals (pearl barley, semolina or rolled oatmeal) and, of course, boilies.