The common nastus (lat. Chondrostoma nasus) is a medium-sized representative of the carp family, leading a gregarious lifestyle on the rocky, sandy, hard clay bottom of large and small rivers. The fish has pronounced biological feeding activity during daylight hours, and at night it prefers to rest in pits, snags, stone ridges, and dense bottom vegetation. Despite the daily waking schedule, catching undermouth is not an easy task due to the specific characteristics of the habitat, lifestyle and diet.
Description of the species
The standard size of representatives of the genus Chondrostoma is 25-30 cm with a weight of 400-500 g. Trophy specimens reach 1.2-1.5 kg (40-45 cm). The largest podust weighs 1.8-2.0 kg with a height of over 50 cm. But such individuals are extremely rare, since they reach their maximum dimensions at the end of life, which is 10-12 years.
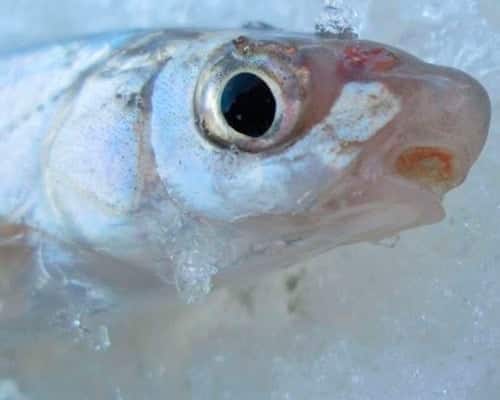
The fish got its name from the lower terminal mouth (old mouth), located under the elongated cartilaginous snout, like a sturgeon. Another common nickname is the black belly, due to the special dark film on the inner walls of the abdominal cavity.
The main distinctive characteristics of the appearance of the undermouth include:
- body flattened laterally in the shape of a pointed ellipse;
- yellowish-orange pectoral, pelvic and anal fins;
- medium, tightly fitting silvery scales with a rounded posterior edge (cycloid type);
- dark olive color of the back, on which a smoky-gray fin is located (3 unbranched and up to 10 branched rays);
- low head with a flat nose and large eyes;
- clearly visible lateral line of dark color;
- black rim on the tail.
The color pattern and tone depend on the genus taxon, specific habitat conditions in the river and the season: during the spawning period, all orange, yellow and red shades on the fins of males become an order of magnitude brighter.
Volzhsky Podust
Latin name: Chondrostoma variabile. Listed in the Red Book of the Saratov Region as a “vulnerable species.” It is distinguished by its more modest size (up to 1.4 kg) and shorter life expectancy (up to 8-9 years). The lower jaw has a sharp end. There are 52-62 scales in the lateral line. The dorsal fins are greenish in color. It lives in tributaries and rivers of the European part of Russia (Volga, Don, Ural), also found in the Sura, Moscow River, Oka and large reservoirs (Kuibyshev, Volgograd, Saratov).
To learn more:
Bream: description of fish, habitat and habits

Genoese (Western European) podust
The name in Latin is Chondrostoma genei. It lives in Italy, Slovenia, Austria, Belgium, France, Switzerland and in many rivers of the Adriatic and North Seas. The fish is distinguished by its yellow-green back and colorless fins. The lateral line runs through the entire strongly elongated body, but is poorly visible. Grows up to 35-40 cm (1.2-1.4 kg).
Dneprovsky Podust
The Latin name of the fish is Chondrostoma nasus nasus natio borysthenicum Berg. It has a moderately high body and a light, scaleless keel between the anal and ventral fins, colored red. Habitats are rivers, tributaries and reservoirs that form the basin of the Black and Azov Seas. Podust is especially numerous in the Dnieper and Southern Bug. Grows up to 1.5 kg (up to 45 cm).
Features of character and lifestyle

Photo: Podust in Belarus
Podusts prefer fast-moving plains in rivers and search for food in schools, in open areas, where they hunt small animals and eat algae on the ground. From March to May they appear in schools on flat and heavily crowded gravel areas. They often make extended spawning trips as so-called “mid-level tourists.” They need warmer, quieter areas for larval development and deep, quiet areas for sleep.
The species is relatively sessile, benthic and gregarious. Podust forms schools of varying sizes and ages, often associated with other rheophilic carp fungi. During the spawning season, they can migrate even several hundred kilometers to reach areas suitable for laying, often located in small tributaries where adults do not stop for the trophic phase.
From early spring to late autumn, schools are very active and move along the bottom of streams in search of food. During this period, they often congregate near obstacles that slow the water's speed, such as bridge abutments, large boulders, submerged tree roots, or submerged trunks. In winter they move into deep waters, hiding in crevices or under large boulders, protected from strong currents, where they remain latent or have reduced activity.
Habitats
The common podust has a rather limited range due to its attachment to warm, clean and oxygen-rich water, moderate currents and a hard bottom, near which it spends its entire life. That is why representatives of the carp family can only be found in lowland and mixed rivers with slow sections, large flowing reservoirs and lakes. In Russia, the black belly lives in the basins of the Caspian, Baltic and Azov seas, for example in the Western Dvina, Klyazma, Oka, Kama, Volga, Don, Kuban.
A school of fish usually consists of several dozen individuals of the same age and size, choosing a flowing area with depths of 1.5-3 meters as a permanent habitat. If there is a riffle on the river, the podust sites are located immediately above it and several tens of meters below, since there is the largest amount of the main food - periphyton fouling.
Periphyton organisms (obrogetes) are dense colonies of microscopic animals and plants (diatoms, green algae, bryozoans, insect larvae, rotifers, suctoria, ciliates, etc.), which require a solid substrate and a lot of sunlight for development. These circumstances determine the shallow depth of residence of the sub-dust and its attachment to the sandy-rocky bottom of the river.
The fish remains active from early morning until late evening. Even intense heat in August and frequent bad weather in September are not able to affect the usual schedule of the flock; it feels comfortable in the bottom layers regardless of any changes in the environment. Only in the cold autumn, when the volume of periphytic fouling decreases, does the undergrowth gradually slide down to the maximum depth in the river, where it overwinters in pits, next to other representatives of the cyprinid family.
To learn more:
White carp: description of the fish and methods of catching it
How to detect podust on a pond
Podusta, unlike other fish, can be tracked in a body of water, as it leaves traces of its presence. While feeding, they leave traces of eaten algae on stones and other objects. They are usually crescent-shaped, ranging from 10 to 30 mm wide. When feeding, they sometimes turn to the side to reach food in inconvenient places, at which point their silvery body reflects light and they are easy to see in the pond.
Their habitats are rivers with a strong current and a rocky bottom, but not with a rapid flow, as this prevents the growth of algae. Algae should grow on the rocks that lie at the bottom. Where the stones are clean, there will most likely be no dust.
Podust does not like very cold water, so there is no point in catching it at depths of more than two meters.
During the day they usually stay closer to the middle of the river and in deep places. In the evening they move to shallow water, but at this time they are very careful and are easily frightened. Closer to dawn they go deeper again.
The best time for fishing is the second half of the day.
Reproduction
Podust spawning occurs in the first half of spring, at a water temperature not lower than +8-10°C. Mature males, starting from 3-4 years of age, participate in the process of spawning. Females mature 1-2 years longer. Shallow water with a pebble or sandy bottom is chosen as a spawning ground.

Fish spawning is one-time and occurs in the morning or evening twilight. The clutch contains from 2 to 12 thousand large whitish eggs, the incubation period of development is 10-14 days. After hatching, they intensively feed on plankton in the water column for several months. Having become a fry, the podust switches to a bottom lifestyle and begins to eat detritus, benthos, and periphyton fouling, scraping them off stones, snags, and aquatic vegetation.
Natural enemies of podusts

Photo: What does podust look like?
Podust is the prey of fish and ichthyophages, aquatic reptiles and some species of mammals, such as otters. The submouth's preference for clean, well-oxygenated water streams makes it prey to large salmonids such as brown trout, marbled trout and Danube salmon. The species is susceptible to viral and bacterial diseases. Podust can host and transmit parasites, including various types of trematodes and cestodes, other helminths, protozoa, parasitic crustaceans and other invertebrates. Wounded and diseased specimens often become infected with deadly fungal infections.
Podust is considered a very important fish for the salmon life cycle. After the hatching of small pods, this fish feeds on them. Before spawning, pods migrate upstream, where they often encounter obstacles in the form of dams built on rivers, which reduces their numbers. Podust is extremely sensitive to pollution.
Interesting fact: Podust is not of much interest to the fisherman: its quality as a live fish is mediocre, in addition, its legal catch size is usually quite low.
This is a valuable sport fish that is blasted with explosives at depth. Podust is very suspicious, and his reaction to the capture is vivid. Algae in lumps, earthworms, insect larvae and other larvae are used as bait. Podust meat is valued, but only in the case of large specimens, otherwise the fish contains a large number of bones. Poor commercial fishing occurs only in states bordering the Black Sea. The species is used as feed fish in trout and salmon farms.
Fishing locations and biting times
Maximum food activity occurs in the morning and evening. During the day, the fish becomes calmer and more cautious, although it continues to feed.
When choosing a place for fishing underwater, you must immediately exclude sections of the river with a muddy bottom, too slow a flow and blooming water. The rapid proliferation of phytoplankton, which turns everything green, is a clear indicator of stagnant water with oxygen deficiency.
Promising places for catching podust are shallow riffles, sandy, pebble edges on the border of a fast current, shallow water near a steep bank, areas with stone ridges and piles of snags. Blackbelly often lives in close proximity to artificial structures installed in the water and bridge piles, where huge colonies of periphyton organisms live.
Nozzles, lures, groundbait
Podust is almost always hungry. His food is low calorie. Therefore he is omnivorous. He will greedily grab meat delicacies: maggots, dung worms, bloodworms, tubifex. Biting on larvae and water-dwelling insects will be successful. You can offer him a dragonfly. He knows her very well, because she spends part of her life under water. On hot days it can be caught using plant baits. You can use dough or potato balls. Loves podust and pea puree. It can be caught with an unpainted lead jig (pellet, uralka or drop). Can't be caught with lures.
There is no need to attach the fish to one place. The fisherman must know where the fish accumulate. And bait is definitely needed. This will keep the school in the fishing area. Lumps of dense clay with a worm mixed in it, small maggots, bloodworms or tubifex are suitable. In winter, you should not skimp on complementary foods. He loves not only protein foods, but also plant foods. Fish like steamed buckwheat porridge. Podust will be happy to approach the hole.
How and what to catch podust
Almost all methods of fishing for bottom fish in the current are suitable, but fishing with a float rod using the retrieving method is considered the most interesting and effective.
Despite its modest size, the podust is distinguished by great strength and endurance, so the equipment should be light, but withstand powerful jerks.
The optimal gear parameters look like this:
- a rod with a fast action, 3.0-3.5 meters long;
- inertial coil;
- main line – 0.22-0.25 mm (with breaking load from 3 kg);
- leashes – 0.16-0.2 mm;
- hooks with a short shank No. 10-5 (international numbering) or No. 5-8 (standardization of the Russian Federation).
To learn more:
What is bleak and where does it live?
Due to constant feeding at shallow depths, the blackbelly is quite bold and comes close to fishermen's boats. But noises from the shore alarm him; here it is better to use long-range gear.
Fishing on a feeder
Rods with a length of 3.5-3.9 m with a medium-fast action and a cast of up to 120 g are used. For long casts from 40-45 m, a braided cord of 0.12-0.15 mm is wound on a spinning reel with a spool capacity of 3000-4000. For fishing at a distance of up to 40 meters, you can use 0.22-0.25 mm monofilament.
For fishing undermouth in the spring and from September to October, it is wise to use an asymmetrical loop. It provides better visualization of the bite and free movement of the feeder at a distance of 30-60 cm, which allows cautious fish to swallow the bait deeper without any resistance from the gear. Fishing for subdust in June, July and August does not require complex equipment; either a symmetrical loop or any other feeder installation will do. In addition, you can use classic donks without a feeder.
Spinning fishing
Despite its herbivorous nature, podust responds well to artificial moving baits, especially in the fall. Small spoons, spinners, wobblers and silicone baits designed for catching chub, ide, asp are suitable - Blue Fox Super Vibrax, Forest Crystal, Strike Pro, BJ-Bug. In this case, the spinning retrieve must be slow enough so that the fish has time to grab it with its low mouth.

Volzhsky Podust
The most common type of podust is undoubtedly the Volzhsky podust.

Judging by its name, it is quite possible to guess that it lives on the territory of the Volgograd region and the Volga River. Its numbers in that area are quite large. The climate of the Volgograd region allows fish to grow up to 35 centimeters and weigh over 2 kilograms.

The Volga Podust has an oblong fin and conspicuous silver-colored scales. The life cycle of this fish is 9-10 years. During this time, the female can produce over 500 thousand eggs, from which small undergrowths will appear in the future.

Despite its large number, the Volzhsky Podust is constantly monitored and its population is controlled. This fish is very important for the ecology of reservoirs, which is why such close attention is paid to it.

If you want to take a closer look at this fish, then look at the photo of the fish on various Internet sources.

Baits and lures
The black belly has an excellent appetite; it readily eats animal and plant foods. The following can be used as a catch bait for the undermouth:
- dough, bread crumb, boiled peas;
- steamed grains, pearl barley, snail meat;
- mastyrka, bloodworms, maggots;
- earthworm and dungworm;
- honeydew, bark beetle larva, bunch of filamentous algae;
- caddisfly, a piece of crawling, large ant eggs.
It is not recommended to use hooks with a long shank for fishing, since then the fish cannot completely swallow the bait. At the moment of hooking, the sting of the hook simply slides off the hard lips of the undermouth or pierces only their edge, which is not enough for successful fishing.
To learn more:
Types of carp: mirror, koi and others
What does the podust eat?

Photo: Common Podust
The young podust is a carnivore that feeds on small invertebrates, while the adults are benthic herbivores. Larvae and juveniles feed on small invertebrates, while larger juveniles and adults feed on benthic diatoms and detritus.
Like other species of its genus, Podust uses its lips to scrape the surface of rocks for food, remove algae and encrustations rich in organic matter. With his upper lip he rocks the rocky bottom covered with his food. It feeds on both filamentous algae, which it scrapes from bottom rocks thanks to its horny lips, and invertebrates, which it finds in the same environment.
The Podust diet includes the following foods:
- aquatic insects;
- crustaceans;
- worms;
- shellfish;
- seaweed;
- mosses;
- protozoa;
- rotifers;
- nematodes;
- plant residues;
- minerals mixed with the algae cover;
- benthic diatoms.
An observer can detect the presence of pods due to traces of food left on the bottom. Juveniles have an elevated mouth, so they feed on microinvertebrates and plankton. As it grows, the mouth moves downwards and acquires proper feeding habits, like those of adults.
The importance of groundbait
The result of catching undermouth directly depends on the fisherman’s ability to form a stable cloud of food turbidity, as well as a fragrant trail spread by the river current. There is no need for culinary delights - the fish reacts to flour, crackers, bran, boiled peas, millet, crushed biscuits, cereals, and barley. One of the most attractive baits is buckwheat with the addition of garlic, coriander, and vanilla flavor enhancers.
Store-bought baits are widely used for other representatives of the carp family, for example, FISH DREAM “Universal”, DUNAEV “Feeder”. Crucian carp", "Volzhanka. Roach", GF "Feeder. Bream".

Before fishing, you need to feed the bait in advance or immediately after arriving at the reservoir. If the weather is cool, it is advisable to add additional ingredients of animal origin: chopped worms, bloodworms, maggots. In order not to scare away the fish, it is advisable to give the mixture a sandy-clay tint. You can use cinnamon or turmeric for this.
Description
Podust belongs to fish from the carp family. It prefers to live in cool rivers and is found in many regions of Europe and Russia. In a favorable environment, the fish can reach a length of 50 cm and a weight of more than 1 kg. But the arithmetic average readings of the sub-dust are more modest. Fishermen's catches most often contain fish up to 30 cm long and weighing 500 g. The body of the fish is runny, which is associated with the river way of life. Podust fishing is interesting because bites occur abruptly and unexpectedly, and when fished out, the fish puts up serious resistance. A distinctive feature of this representative of the ichthyofauna is the color of its fins. If the dorsal fin is gray, then the rest of the “plumage” is highlighted with a yellow-orange tint. The black back has a green tint, and the sides and belly are painted silver. Before spawning, all the colors of males become even richer and brighter. The name of the fish is largely determined by the structure of the mouth. “Mouths” are located under the conical cartilaginous nose; the head shape is similar in such species of fish as raw fish or vimbe. In some regions, podust is called blackbelly. So ordinary fishermen reflected another distinctive feature. When the fish is cut, black stripes are clearly visible in the walls of the abdomen. On average, the life expectancy of a podust is about 9 years. Some individuals are capable of reaching 15 years of age. When targeted fishing for subfish is carried out, anglers often come across similar types of fish such as vimba or syrty. How to identify these representatives of the ichthyofauna?
Hooking and landing
Podust is caught well from late spring to October, showing various types of bite. He can suck on the pearl barley for a long time and then smoothly lay out the float, sharply grab the worm and instantly drag the entire tackle under water. But no matter how the float antenna or the tip of the rod behaves, at the right moment it is necessary to perform a sharp and strong hook in order to reliably drive the hook into the hard lips of the fish.

During fishing, the undermouth actively resists, demonstrating a strength that is surprising for such small dimensions, which makes fishing interesting and tempting. Since this fish is often caught in places rich in snags and aquatic vegetation, it is important to constantly monitor the tension of the fishing line and not allow the trophy to hide in cover. In order not to be left without a catch at the last moment, you need to use a landing net.
Podust and rybets, the main differences
Some anglers don't think much about what type of fish they've hooked. Sometimes this happens due to excessive fishing excitement; often different species are so similar that even experts get confused. But the importance of identification will become clear the moment a fisheries inspector appears on the shore and begins drawing up a protocol for poaching. The fact is that in some regions one of these representatives of the ichthyofauna may be prohibited from fishing. And for every fish found in the cage, the inspectors will impose a substantial fine. But even government workers make mistakes when determining the species. To avoid getting into such a situation, you should clearly understand what kind of catch is stored in the cage. Both “nosed” representatives have a lower mouth position and a similar shape and color. But there are two characteristic features that make it possible not to confuse podust with vimba. 1. The mouth of the podust has no lips, its appearance resembles a slit. Only the lower lip can open slightly. The fisherman is distinguished by clearly defined sponges, and this feature becomes more and more pronounced as the fish ages. The fish is able to extend its mouth, turning it into a kind of vacuum cleaner.

2. The second difference should be sought in the shape of the anal fin. In the undermouth it is short, it has 8-9 rays, like in a chub or roach. The similar fin of the fish is approximately twice as large, it consists of 16 rays. The appearance of the anal fin resembles a smooth sinusoid. Attention! Some anglers identify these fish species by the shape of their nose. Podust has a pointed nose, and vimbe has a nose shape that resembles a potato.
Taste qualities of the podust
Blackbelly fish taken from natural conditions quickly die and deteriorate, so it is important to use a long cage and process the fish immediately.
In terms of consumer characteristics, nutritional value and culinary versatility, podust is inferior to carp, ide, bream and is quite bony. To prepare aromatic dishes, frying, baking in foil, hot and cold smoking are used. Due to its moderate calorie content (104 kcal per 100 g) and low fat content (4.3%), podust is well suited for dietary nutrition.
Fishing methods
Fishing for undermouth
When choosing a fishing method, you must take into account that undermouth can provide resistance. It will rush with the current and will be able to break the thin fishing line. For fishing it is recommended to use:
- float rod. This tackle is very convenient and effective. In winter, you can also catch fish with a nodding rod.
- float rod for line fishing. Usually they fish from a boat or shore. Using this tackle, you can place the bait where it is impossible to hold it with other tackle. The leash should have a cross-section two times smaller than that of the main line. When hooked, this is to save the tackle.
- in English. The method involves long-distance casting of the float. The leash should have a diameter of up to 0.1 mm. Small pellets can serve as loading. As they approach the hook, their weight should decrease.
Podust fishing is a very exciting activity. The fish does not immediately swallow the bait, but keeps it in its mouth for some time. This helps the pod to easily release from the hook. But even if the podust is hooked, don’t rush to consider it luck. He will resist quite strongly, making intricate jerks. But these movements will not last long.
Podust is most successfully caught from the end of May to the beginning of July from 9 a.m. to 7 p.m., using a float rod, wiring, a match rod (in English) or bottom tackle. In winter, use a regular winter fishing rod with a float or a nod to a jig. The gear must be durable. You need to fish 5-10 cm from the bottom, since the podust does not take bait above its mouth.
The bait can be steamed cereal (wheat, rye, oats), pieces of worms, maggots, bloodworms, dragonfly larva, a bunch of tubifex worms and other insect larvae, as well as green filamentous algae rolled into balls. In hot weather, you can fish with baits made from dough, peas and potatoes with flavors. Groundbait significantly improves the bite. It can be various porridges, breadcrumbs, cake, chopped worms and insect larvae mixed with clay or soil.
It is curious that the podust does not pay attention to the process of catching it, so the entire flock can become a fisherman’s catch. The bite from the pod is sharp and confident; it pulls the float to the side and hooks itself. When playing, he resists strongly, but gets tired quickly.
Where does it live?
This fish is found near the clayey, sandy or rocky river bottom and prefers warm, clean water and moderate currents. Therefore, its fishing is carried out in slow-flowing rivers, reservoirs, and lakes. The habitat of the black belly is the basins of the Baltic, Azov and Caspian seas: Oka, Western Dvina, Klyazma, Volga, Don, Kuban.
Podust is very brave, so it is not at all necessary to remain silent at the fishing site. A loud human voice will not scare the fish.
One flock consists of about 25-30 individuals. They usually have the same body size. The main diet of the podust is periphyton fouling, algae, plankton, and insect larvae. The activity of the fish continues throughout the daylight hours. Even if it is very hot or there is prolonged rain, the usual mode of the flock does not change, since external climatic conditions have virtually no effect on the water temperature at the very bottom; it remains stable throughout the season.
Catching
Fishing for podust is an interesting and exciting process. In some areas it is one of the main trophies, but its numbers have declined quite significantly in recent years. For this reason, it was listed in the Red Books of some regions, including Moscow. This must be taken into account when planning to catch it. Due to its relatively small population, even in those regions where its catch is permitted, it is only an object of recreational fishing, and not a commercial species.
There are several ways to catch podust, since it, like some other representatives of the carp family, can attack both plant and animal baits, as well as artificial baits. For this reason, it is better for an angler to understand the intricacies of fishing for it. Three types of gear can be used for catching podust:
- Float
- Bottom.
- Spinning.
Moreover, each method of fishing for podust has certain specifics.
Podust
WHERE IS THE PODUST FOUND? FISH PODUST: PHOTO, DESCRIPTION, RECIPES, TASTE. WHAT TO FISH WITH, HOW TO COOK?
You should not be upset if, instead of a bream or roach, an inexperienced fisherman caught this particular specimen while river fishing. Podust is a fish that deserves close attention.
And an avid fisherman will not be upset at all, because he knows that this species is very popular on the river and can be used to prepare many delicious dishes in the culinary arts!
Who it?
Podust is a fish, by the way, from the Karpov family. It is a typical representative of river cold-blooded fauna.
Mature specimens reach a length of up to fifty centimeters and a weight of up to 1.2 kilograms (rarely up to two kg). Average parameters – length 30 cm, weight – half a kilo.
Podust fish, description : the body is flattened, slightly slab-shaped, which provides it with good mobility and a fairly high speed of movement in the water element.
The dorsal fin is hazy gray, the rest are yellow-orange, the caudal fin has a black border. The back is black with a green tint. The belly and sides are silvery. During spawning season, the colors become brighter in males. This species lives up to 15 years.
Etymology of the name
Podust is a fish with a “speaking” name. It is used throughout most of the middle zone.
Most likely, this name indicates the structural features of the fish’s mouth. The “mouths” are located under the cartilaginous and conical nose (which makes its appearance slightly reminiscent of vimba or raw fish).
The second name popularly used is black belly. It reflects another feature of the fish: when the abdomen is cut along the walls, black stripes become visible in the lower part.
Podust (fish). Where is it found?
It is found in many European and Russian rivers, mostly navigable, if possible without dams, as they prevent its rise.
This fish does not like standing water, it sticks to the current more strongly, although it does not like shallow riffles as much as the chub, preferring places where the rapids end and a calm and deep current with small whirlpools begins.
It adheres to a rocky bottom, sometimes clayey, almost always uneven. This condition, as a rule, makes it difficult to catch undermouth with nets. He, like, for example, a gudgeon, also prefers to walk along the very bottom, almost touching it with his belly.
Although it can also come to the surface at certain times, but not for long.
Features of life activity and spawning
During high water, the fish is quite cautious and does not go into floods (like an ide), but from the sandbanks it rises up the rivers, sticking to the banks and the weakest currents.
Thus, starting to move while still under the ice, it can travel many tens of kilometers until the river enters the banks and favorable warm days arrive for spawning.
So, according to Sabaneev, in Moskvorechye the podust fish (photo above) spawns in late April - early May. Sometimes in several stages, releasing eggs on large stones, in a gentle current, on stilts, near dams.
After spawning, the fish remains in place for some time, feeding. And by mid-May, the podust fish slides down the river.
Dams become a significant obstacle to movement, where these fish accumulate, not daring to jump down, like pike perch and chub (data are given from Sabaneev’s book “Life and Catching of Freshwater Fish”).
gregarious and diurnal
Podust is a schooling fish. As a rule, they live in schools of several dozen, or even hundreds, mostly of the same age. Smaller fish are driven away.
As soon as the current intensifies, the flock comes out onto the stream. Podust is a resident of the world; it tends to feed mainly during the daytime.
Food and menu
The main food of this species, if we take the summer and autumn periods, is algae. The podust scrapes them off stones and piles with his lips.
But in the spring it feeds on the eggs of other fish species, for example, chub or ide, which causes (like gudgeon or burbot) quite a lot of harm. Since it mainly eats eggs that have already been fertilized, tearing them off from underwater clutches.
In the spring, in addition to caviar, worms, dung and earthworms, are also used, but then he completely switches to plant food. At this time, if you gut a caught underfish, you will notice that its stomach, like that of a roach, is filled with a greenish mush of algae that has not yet been digested.
They say that in the past, when barges with bread and grain sailed along the rivers, each ship had its own flock of podusts, which followed it relentlessly, feeding on the grain and bread that fell into the water.
At the very beginning of autumn, the fish eats bloodworms, but in October-November it finally moves to the pits for the winter, and you will no longer see it in strong currents until the ice breaks up.
Podust (fish). What to catch?
The commercial value of fish is zero. This happens due to the peculiarities of life: movement along the bottom, in places inconvenient for net fishing. Therefore, podust will most often be the prey of a fisherman with a simple fishing rod.
And catching it is quite an exciting and challenging activity. Since the bite of this fish is unstable, it requires the angler to quickly react and almost instantly hook.
The fish is lively and strong, and often breaks off the hook. True, which is typical, it will almost always return to the fishing site with appropriate bait. It happens that on the same day a fish that has recently fallen off the hook is caught in the same place.
Active fishing takes place from the end of May until the beginning of autumn, when the days are still warm. In early spring, it is quite difficult to catch a podust, unless you catch it by accident while trying to catch another fish.
At the beginning of May, this fish can be caught when catching ide on a donk. However, the crawler used as bait does not fit its small mouth. Therefore, if you have already begun to peck at the podust instead of the supposed ide, then it makes more sense to replace the hooks with smaller ones, and the earthworm with a dung worm, and continue fishing.
Fishing becomes more attractive in the hot season, in the middle of summer, when the time for catching other fish is the deadliest, when ide, for example, or other more powerful fish are rarely caught due to the heat.
Tackle set
Gear for podsta is practically no different from gear for roach, ide, dace, when fishing is carried out during the day on the current.
The rod is flexible, more than 3 meters. Line and floats, like for medium-sized bream or roach. The mouth of the undermouth is small, so many fishermen recommend using small hooks.
Fishing is carried out (if from a boat) best from a depth of 1.5 m, but sometimes deeper. You need to stand at the place where the rapids and waves decrease and the depth begins to increase. The podust will most likely be based there. And he takes it not far from the boat, since he has a certain courage of character.
But it is not at all recommended to catch this type of fish from the shore (with a fishing rod). Except for the donk. The bite is better in the early morning and in the evening, during the day, in the heat, it subsides.
Groundbait and bait
Some fishermen are convinced (and not without reason, based on their own experience) that without bait, fishing for podust will not be catchy. But there is no need to feed the fish too much!
The bait is thrown shortly before fishing or just before it. Buckwheat, which is mixed with clay and flavored with vegetable oil, goes well .
You can use other cereals, but less effectively. It’s good to add ant eggs and bran to the mixture - they will attract pods even from afar .
Bloodworms and pieces of worms are sometimes used as bait. At the end of spring, it is good to fish with large ant eggs, carefully placing several on the hook so that the milk does not come out. In summer, wheat, crumpled bread, and dough with added oils are used.
Taste qualities
It should be remembered that podust, like roach, is a perishable fish. Having fallen asleep, it disappears very quickly: if, for example, it is caught early in the morning, then by the evening it will rot without proper measures.
Therefore, when fishing, you need to be more careful about preserving your catch, either using traditional methods or using stored cooling agents.
Podust is a fish whose taste is inferior to ide or, for example, chub. But still, you can cook quite a lot of things from it. Here are some simple dishes.
How to prepare podust (fish)
1. How to cook it in the oven in foil? We will need thin food foil, three-four-five medium ones, half a kilo of podust, a couple of onions, carrots, herbal seasonings, salt, half a lemon. Lemon and onion - in half rings. Carrots – coarsely grated.
On a piece of foil the size of a saucer, place a little carrot, onion, lemon, and on top - a piece of peeled and rolled in herbs.
Add some salt and wrap it in the form of a bag (you need to leave a small hole on top for steam to escape. Place in the oven at 180 degrees for half an hour.
2. Podust is a fish whose frying recipes were previously considered the most acceptable . This is because the meat is quite bony. But with proper culinary execution, this drawback can be overcome.
Then the small bones seem to dissolve, become invisible, and only the large, spinal ones remain.
A similar effect is achieved by cutting cleaned fish crosswise. This procedure is done using a sharp knife. Shallow crosswise cuts are made slightly obliquely throughout the body (especially on the tail, where there are many small bones).
The distance between the stripes is approximately a centimeter. We do it on both sides. And then soak the fish for an hour in brine (a glass of hot water and a couple of tablespoons of salt, you can add herbs and lemon).
After that, remove the podusta and dry it from excess moisture, roll it in flour and fry it in a large amount of heated vegetable oil over medium heat.
The fish turns out crispy and not bony, contrary to its structure. By the way, if you get a large one, you can do the same, and then cut it into pieces before frying.
3. This type of river fish also turns out well in a home smokehouse - cold or hot smoked: you'll just lick your fingers!
Season
The behavior of the podust when fishing largely depends on the time of year. Often places and baits tested in the fall do not have the desired effect in the summer. Because of the love of this species for the current, the fact that it is caught exclusively on rivers remains unchanged all year round. But it’s worth familiarizing yourself with his other habits in more detail.
Spring
The time when this species is most active, and accordingly, bites quite consistently, occurs in the second half of April and May. Fishing for podust in the spring can be quite successful in all rivers in which it lives. The fact is that this season marks the period of spawning and preparation for it, which is why the fish actively feed before it begins. At this time, fishing for podmouth with all types of bait becomes relevant - it happily bites both on a worm or dough, and on micro-spinners.
Summer
Despite the fact that at this time most fish species become passive and suffer from the heat, the podust continues to bite quite well. After spawning, it returns to its usual habitats, where it feeds quite actively. In summer, the most successful tackle for catching this fish is a feeder. In this case, it is advisable to use a sufficiently large amount of bait. Porridges that contain crushed boiled peas and ground crackers perform well. Such mixtures are perfectly retained in the feeder even in fairly strong currents. Until August, podust sites are located at medium depths with moderate currents, mainly in areas with a clay bottom.
Autumn
After the end of the hot season, the pods roll down to deeper areas of the bottom, which means the use of gear for long-distance casting. The most effective is the use of float rods with a reel, since with their help the equipment can be delivered to the fishing point almost silently. It is best to look for undergrowth in the fall near deep drops and large holes, as well as in the lower part of the edges. It is better to fish at this time with animal bait - maggots, worms, amphipod larvae, since in the fall the fish prepares for winter and tends to look for more high-calorie food.
Winter
The cold season is not the easiest for fishing for this peaceful fish, but if you arm yourself with patience, it still makes sense. Fishing for podust in the winter on the current is carried out mainly in deep holes, where it stands for most of the season. For such fishing, classic fishing rods and lead jigs are most often used, but often the water flow does not allow the bait to be delivered to where it is needed. In this case, you can use a trick and equip the installation with a feeder. It will not only overcome the resistance of the current, but will also attract more passive fish to the fishing spot.

Bloodworms become an excellent bait in winter. Its bright color attracts fish in clear winter water, and its small size allows it to interest small individuals, which are mainly active in the cold season
It is also worth noting that during the cold season, Podust sometimes bites in creeks with a weak current, where at other times it practically does not enter. For this reason, winter fishing for this fish can be extremely unpredictable.