Promising places for catching rudd in autumn
Perhaps the most important aspect of fall rudd fishing is choosing the right location. In summer, it is enough to find an area near the reeds where there is algae at the bottom, and you can lay out your fishing rods and start feeding.
In the fall, it is necessary to find areas where, on the one hand, the water has not had time to cool too much, and on the other hand, so that there is vegetation in this place. It is best to find some creek where there is a coastal drop with a sharp change in depth. The ideal option would be to have a shell and some algae at the bottom. The depth in such a place should be 2-2.5 meters. Here you can catch rudd with a fishing rod throughout October and a little in November, until the first morning frost.
Autumn sometimes brings many sunny and relatively warm days. If the wind is still slightly southerly, then you can safely go fishing for rudd. Another promising place would be a quiet section of the river, along the banks of which reeds grow. Casts should be made close to the reed wall or a little further, to a deeper area.
Rudd loves places with little or no current. Therefore, you should not even try to catch it in areas with medium and fast currents, especially in the fall. When scanning the bottom, it is better to find the boundary between vegetation and a clear area. If you feed this place a little, you can count on a good, by autumn standards, bite.
If pondweed or cattail grows in the selected area, then with a high degree of probability we can say that our target lives here. It is well known that the rudd does not like long journeys. She prefers to stay in the same area for a long time. If the food supply in the form of underwater plants and larvae is in sufficient quantity, then this type of fish will be constantly near such food.

On cloudy and fairly cool days, rudd are better caught from the bottom. On sunny and calm pleasant days it can be caught in the water column. Here you can experiment by changing the depth. Sometimes such techniques bring good and even unexpected positive results. If you catch rudd in the water column, then the most promising way is to lower the bait into the middle horizon. As a rule, there are the most bites here in the fall.
You should never forget that rudd often coexist with perch. These fish have almost the same food supply. Therefore, if you manage to catch a perch, then, most likely, there should also be rudd in this place. The truth is that sometimes it happens the other way around, when the perch displaces the rudd. If only striped robbers are hooked, then it is better to move a little to the side and try to fish there.
Habitats and habits
Both in appearance and behavior, the rudd resembles a roach. For example, both of them avoid areas of the reservoir with fast currents. But if the roach is not afraid to go out into clean water, then its red-feathered neighbor prefers to stay in the most remote places, densely overgrown with reeds, reeds, arrowheads, water lilies and other plants. This may be a partially separated old river bed or a small bay, flowing lake, or reservoir. Here she has everything she needs for life: an abundance of food, reliable shelter from predators, a suitable oxygen regime.
There are a lot of snags and grass in the coastal zone, so the concentration of rudd is maximum here. True, more often these are small and medium-sized individuals living in flocks. But large specimens love space. They spend most of their time away from the coast, in places with overgrown underwater hills. They enter the thickets of coastal vegetation only occasionally to feed themselves.
Rudd is a sedentary fish. She always stays in the area she likes, where she often walks in mid-water, and in extreme heat she rises to the surface to bask in the sun. In calm, warm weather, this fish makes its presence known with splashes and a characteristic smacking sound. This is how she hunts midges and other small insects in thickets of pondweed and egg capsules. Late in the evening, she likes to “keep vigil” under the branches hanging over the water in the hope that the wind will blow away some living creatures from the trees.

Fishing rod equipment for autumn catching rudd
Depending on which place is chosen, one or another version of the float rod is used. For example, if the area is densely surrounded by reeds, then it is better to use a longer Bolognese rod of 6-7 meters. With its help, you can easily cast the equipment to the desired point. It is only necessary to remove the reeds a little on the sides so that there are no obstacles when casting.
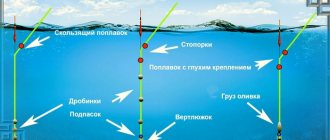
To ensure that the tackle flies well and accurately, you can use a self-loading float when fishing in such conditions. It can be sliding. In this case, loading is performed as follows:

If you fish with a rig with a blind type of float attachment, then the loading is performed in the lower part of the keel:

If you manage to find an area without a current among the water lilies, located not far from the shore, then you can try fishing with a rig without a sinker. Its advantage is that the bait will slowly sink, thereby attracting fish in the water column. On sunny and calm days, this method of presenting baits can lead to good results. The result will be a plausible imitation of a slowly falling larva.
Naturally, with the appearance and strengthening of wind, it will become impossible to fish with a rig without a sinker. Therefore, in this case, you should attach the weights to the fishing line. To make the bait float in the water column, you can attach a foam ball to the hook and change the leash to a longer one. We choose the length experimentally.
We attach an inertia-free reel with a fishing line with a cross-section of 0.18 mm to the Bolognese fishing rod. Special requirement for fishing line. It must be quite rigid and have no memory. It is not always possible to find thin line that remains level when fishing using a reel. Therefore, preference in such cases should be given to high-quality and branded fishing lines that have been repeatedly tested on the pond.
As for the methods of attaching weights, if we use ordinary floats, without self-loading, then the best option would be one olive, which is limited by stoppers on the sides. Using the stoppers, you can adjust the distance from the weight to the leash. If you need to move the equipment so that it sinks smoothly, then raise the stops higher. If we want the rig to quickly fall to the bottom, then we lower the lower limiter all the way to the leash loop.
It is advisable to use 3-5 pellets rigidly attached to the fishing line in cases where the rudd is active and is not afraid of the resistance of the equipment when biting. This option for attaching weights is most often used in warm weather in the first half of September.
We pay special attention to hooks. In the autumn, rudd is most often caught on maggots and less often on bread and bloodworms. Therefore, priority is given to hooks made of thin wire No. 14-16 according to the international classification.
Features of fishing by season
Despite the fact that rudd actively moves around the reservoir throughout the open water season, there are still certain features when catching it in spring, summer and autumn.
Spring fishing for rudd on a float
To catch rudd in early spring, a fly rod 5–6 meters long is used. This applies to both fishing from the shore and from a boat, because long casts are not needed. When the first vegetation appears on reservoirs, rudd looks for places where it is easy to camouflage and where there is abundant food.
On rivers with a current they fish with a wire and use 3–5 gram floats with thin antennas. The color of the float should be dim, especially in the lower part, which is visible to the fish. At the beginning of spring, warm layers of water are in the upper part, so equipment is set up for fishing at shallow depths.
From the baits we select maggots and casters; the bark beetle larva also shows good results. Hooks 20–22 numbers for medium-sized dark-colored baits and long leaders are the most catchy. The larvae are put on along the tip of the hook “stocking”, or across, but so that the liquid does not leak out.
The place is chosen where there is aquatic vegetation or algae and fishing is carried out on its upper edge. There should be very little bait, rather to mark the spot than to saturate the fish.
Catching rudd on a float in summer
During the summer heat, the fish stands under trees or in close proximity to reed thickets and does not show much activity during the day. Therefore, you need to catch rudd in the summer in the morning, or in the evening, when the sun begins to set below the horizon. During such hours, the fish are most active and move around in search of larvae, insects and other attractive food.
An excellent place for catching rudd near thickets of water lilies, because this is also good protection for the fish, including from predators. Fishing from a boat or shore with a fly rod is very interesting, but you need to guess the depth, and it is better to choose it experimentally. Fishing with a match rod requires precision when casting, and such gear is used in still water.
The bait is fed in the form of balls manually or from a slingshot, it all depends on the distance at which the fishing point is located. In summer, plant and artificial baits work well and these are:
- pearl barley;
- bread crumb;
- hominy;
- boiled corn.
When biting activity decreases, try placing maggots and worms, burdock larva, or the same caster, this will help activate the biting. Due to the fact that in summer the fish is less timid, it is most convenient to catch it while fishing from a boat, placing it near the thickets or tying it to the reeds.
If underwater vegetation interferes with the movement of the hook and sinker in the current, look for “windows” in the grass and, increasing the weight of the equipment, throw it exactly at the same baited point. Often they feed two or three “windows” at once and, when biting activity decreases, they move from place to place in search of fish.
A good catch can also be made when using a grasshopper or a fly as bait, but larger hooks are chosen for them, so that the bait does not look bulky and does not hang from the hook tip. With quick bites, the rudd pulls the bait from the small hook, and the tackle has to be re-baited again.
Baits for fall fishing for rudd
With the onset of cold weather, the number of baits on which you can catch rudd decreases. If in the summer it was well caught using pearl barley, dough, semolina, wheat grains and other vegetable baits, now it is better to use maggot, in some cases dough or bread, a small worm and bloodworms.
Experience has shown that maggots work best in cold water. One or two larvae are placed on the hook, depending on the size. It is impossible to say for sure how many maggots the rudd will peck more actively. Sometimes only one small larva on a small thin hook tempts the fish, and it bites only in this way of presenting the bait.
In some cases, it is necessary to plant clusters of 3-4 larvae. It is very useful to have not only white, but also red and yellow maggots, as well as casters. It happens that rudd only bite on caster or red maggot. This point must be taken into account when preparing for fishing. If you forget something, you will only regret later that you don’t have a complete set of attachments.
It is important that the maggot remains active throughout the entire time it is in the water. If a maggot on a hook quickly loses its mobility, then it is unsuitable for further fishing. The bait should be lively and constantly attract the attention of fish.
It is also important to place the maggot on the hook correctly. Often anglers pierce the end of the larva and thread it through. This is not always justified, especially when the bite is sluggish. In this case, it is better to plant the maggot like a worm in order to hide the hook as much as possible, exposing the sting a little.
One thing to take into account is that thicker maggots fall more slowly, and casters generally have positive buoyancy. Be sure to have foam balls with you so that you can apply bait to different water horizons.
When casters are planted, a juice with a characteristic odor is released from them. This juice will be the best flavoring agent when fishing for rudd. Casters are often used in combination with live maggots. Some fishermen specifically press on the dark pupa so that more liquid comes out of it.
Dung worms can be effective bait on warm days. It has been noticed more than once that on sunny days with a calm wind, rudds bite well on the worm. Small specimens should be selected so that they sit neatly on a small hook. If the rudds only eat the worms, but are not spotted, then we attach them in such a way that they are entirely on the fore-end, and the sting sticks out a little. Combining worms with maggots also helps to increase the percentage of successful strikes very well. In this case, the worm is first threaded through, and it is closed with maggots, leaving the sting open.
When fishing in mid and late autumn, bloodworms are increasingly used. It can be used as a stand-alone attachment or paired with maggot or caster. It is very important here that the hook is thin and very sharp throughout the fishing. The easier it passes through the bloodworm's body, the longer it will remain alive and active.
Features of autumn behavior
With the arrival of autumn, radical changes occur in the life of the fish kingdom. This is facilitated by changes in nature itself. Cold mornings and shortening daylight hours, gradually dying algae and clear water make the fish more careful, forcing them to change their usual camping and hunting places. Breaking up into small schools, rudd retreat to the lower layers of reservoirs.
On warm days, the diet of this fish consists mainly of a variety of insects that fall into the water. It happily eats mollusk eggs deposited on the leaves and stems of aquatic plants, characteristically slurping as it does so.
If we draw further parallels with roaches, then with the onset of autumn, rudds turn from a completely peaceful fish into notorious predators. Their prey is leeches and tadpoles. With great passion they attack small frogs, flocks of fry, and spinning baits.
Feeding rudds in autumn
To catch good autumn rudd, you should feed it correctly. The best baiting tactic is to fish one or more selected areas first. We are waiting for the first individuals to bite. If there are rudd in a given place, then we proceed to the starting feeding.
We use a fine mixture for cold water. Roach or universal bait with a not very strong aroma is suitable. The main thing is to properly moisten it and roll it into balls. These balls must then be accurately thrown to the fishing point. After landing, they should crumble evenly.
It is very effective to add maggots and chopped worms or bloodworms to the mixture. In this case, you can count on larger individuals being suitable. You also need to take into account that there may be perches in this place. If they are in large quantities, then it is better to change the location.
The number of balls for starting feeding is 3-4 pcs. the size of a tangerine. Next, we feed the fish depending on its activity. On average, we throw 1 ball every half hour. This will be quite enough for autumn fishing. Add the animal component to the balls in pinches. It is not necessary to fill each ball with bloodworms or maggots. Here we look at the situation.
If we catch fish from the bottom, then we make the “tangerines” more dense so that they crumble only when they touch the bottom, and not on the water. When fishing in thick water, it is better to make the balls more loose so that they disintegrate before they touch the bottom.
Tackle and bait
For autumn fishing “from the shore” the most popular rods will be:
- Bolognese - suitable for accurate and silent casting into coastal windows free from aquatic vegetation;
- match - will allow you to fish promising points of the reservoir remote from the shore;
- light spinning rod - will allow you to use a variety of baits.
The equipment for the “lapdog” is made sliding, using a float with two rings for the free passage of the fishing line. Splashdown occurs almost silently, and the line, under the weight of the sinker, smoothly falls down.
Photo 1. Sensitive float for cautious fish.
Classic sliding type floats are successfully used for match fishing. They have high sensitivity and excellent flight qualities.
When going to a pond, you need to take into account that catching rudd in the fall involves the possibility of catching “test” specimens weighing 1 kg. Therefore, the equipment must be ready for this. In addition, inevitable hooks with an abundance of “green stuff” force the use of a main line of a larger cross-section.
To load the equipment, one “olive” and a swivel that performs the function of a shed will be enough. To reduce the risk of equipment overlapping when casting, it is enough to install the shot higher than the swivel. Hooks suitable for sizes 10 – 16, thin, perfectly sharp.
If the beginning of autumn pleases with warm days, then you need to use summer baits of plant origin (crumbs, peas, pearl barley, corn). But, as the water cools, they cease to give the same effect. Therefore, the eternal question – what to fish for – loses its relevance. The bait comes out in the fall to play the main roles.
- Maggot is considered the most versatile seducer in the off-season. There is an opinion that the more of its larvae you put on the hook, the larger the fish you will catch.
- Red worms are another fall classic. Preferably a small size to fully bait the hook. For rudd, especially small ones, it will be somewhat more difficult to eat or pick it.
- The bloodworm is inferior to both in popularity due to its vulnerability, although it can attract the attention of the roach, the faithful companion of the rudd.
- Sandwich is the name of mixed bait in various combinations: worm - maggot, maggot - bloodworm.
Photo 2. Maggot sandwich with bloodworms.
Both homemade and ready-made dry mixtures are suitable for bait. It is important to achieve the correct consistency, especially when fishing “half-water”. The balls should break as soon as they touch the water. Therefore, when forming them, it is very important not to over-moisten the mixture.
If fishing is carried out from the bottom, the balls with bait should crumble as soon as they reach it. To do this, you need to prepare a slightly more viscous mixture, with the obligatory addition of fragments of the bait used.
Bites are most often observed either during the process of lowering the bait, or during a leisurely, short-term pulling of the equipment, that is, when some kind of dynamics is present. The static position of the bait is much less likely to tempt the fish.
The process of fishing rudd on a float
If you manage to find a more or less spacious place where the reeds do not interfere, then you can use two fishing rods. If casting is inconvenient and you constantly have to strain so as not to catch the neighboring equipment or reeds, then it is better not to torture yourself, but to fish with one fishing rod.

After the starting feeding, we begin fishing. Rudd bites most often occur when the bait sinks to the bottom and when you play along a little with a nod. Another option is to throw a small piece of bait at the fishing spot.
When fishing, it is very important to monitor the preferences of the rudd. In autumn, you should actively experiment with baits and fishing techniques. Sitting and just waiting for bites is not the best tactic. It is better to try changing leashes to longer or thinner ones. Changing the fishing point helps if the limit of rudd caught at the previous one has been exhausted.
Changing the fishing horizon often helps, especially in sunny weather. Therefore, it is important to use foam and caster to lift the bait to the upper horizons.

It happens that rudd is caught only near reeds or near algae. In such cases, you can throw one fishing rod on the left side, under the reeds, and the second in the opposite direction, also under the reeds.
It is very important that the tackle enters the water as quietly as possible, so that there are no loud splashes. In autumn, the fish becomes more cautious and will avoid such baits.
Another useful method when fishing for rudd in cold weather is to slightly pull the tackle towards the shore. We made 1-2 turns of the coil and stopped the movement. After a pause of 5-7 seconds, we continue to pull the rig to the shore. Sometimes this non-standard fishing method leads to bites. It is known that the rudd is still a bit of a predator. It is caught well with small silicone baits and small spoons. We will do a kind of dragging along the bottom. Such a presentation of baits may interest fish. In this case, it is better to use small worms and maggots as bait, which remain mobile after such postings.
☸ Fishing technique
If a rudd lives in a pond, it will definitely be caught with a spinning rod. Moreover, spinning baits are more interesting for large individuals, whereas when fishing with fly or float rods, such baits are only rarely encountered. This can be explained by the fact that the great rudd requires a lot of food. Small living creatures (insects, worms) cannot satisfy large fish, so they switch to fry.
In the theory of spinning fishing for rudd, everything seems to be simple. If it feeds on small fish like pike or perch, then take some tackle, several different types of bait, select the catchy one and enjoy fishing. However, in practice this is far from the case. Catching a rudd on a spinning rod is many times more difficult than any other predator. Before you start selecting the key to it (experimenting with baits and baits), you need to find an area with a high concentration of this fish. The larger the crowd, the stronger the competition, the fight for food. That is, for the same artificial fish that the spinning angler will offer.
It is better to make two small fishing rods for this fish. After feeding, place one on the bottom so that the float tilts slightly. Place a large pea of bread bait on the hook. Bites from the bottom are quite rare, but there are decent specimens there. But with the second one you can start the fun. To begin with, the depth needs to be set so that the bait is approximately in the middle of the depth, at “half water” as fishermen say.
The dance of the float begins. It submerges a little, jumps back out, rushes from side to side. These are small fish chasing the bait. Until one comes along that can grab the whole ball. In this case, the float suddenly suddenly goes completely away from the supply, or quickly runs to the side without stopping. It's not so easy to catch this moment. This is what gives catching rudd a special thrill and brings great pleasure.