About spinning rods
The spinning rod consists of a handle (butt), a reel holder, a blank, which is equipped with guide rings for guiding the cord or fishing line, the last ring at the tip is called a “tulip”.
Spinning rods are distinguished by the type of connection of the knees:
- Plug-in. The most popular among spinners. They have two, less often three, elbows that are inserted into each other. Lungs.
- Telescopic. Retractable, heavier, less durable and sensitive. Convenient to transport.
There are rods of one-piece designs on sale, usually short (up to two meters).
They are called one-part ones. Consist of one knee. The most “sensitive”, but often inconvenient to transport. The material used to make the form determines its weight and strength:
- Fiberglass.
- Carbon fiber (graphite, carbon).
- Composite (a mixture of fiberglass and carbon fiber in various proportions).
- With Kevlar admixtures (super strong material).
Pay attention to the material used to make the handle: smooth artificial polymers will slide in your hand, choose natural ones, for example: cork.
Rings are one of the most important elements; the reliability and sensitivity of spinning tackle depends on their quality. But it should be noted that expensive samples are not always necessary.
For example, when fishing exclusively with monofilament, it is not necessary to use expensive SIC ceramic inserts; they are necessary when fishing with braid, since it, like a saw, leaves deep cuts in conventional plastic ring inserts.
Accordingly, for a spinning rod on which it is possible to use braided wire, we check the quality and material of the inserts and the rings themselves; for a regular rod, more budget solutions are also suitable.
The test form indicates the weight of acceptable baits, divided into:
- Ultra-light (UL – Ultra-Light) – up to 6 gamma.
- Light (L – Light) – from 6 to 11 grams.
- Medium-light (ML – Moderate Light) – from 11 to 19 grams.
- Medium (M – Moderate) – from 19 to 23 grams.
- Moderate Heavy (MH – Moderate Heavy) – from 22 to 37 grams.
- Heavy (H – Heavy) – from 35 to 45 grams.
- Super heavy (XH – Extra Heavy) – over 45 grams.
Lures that are too light or too heavy and exceed the test limits can lead to loss of control when retrieving or damage to the rod when casting.
The structure of the form is an important characteristic that determines its flexibility.
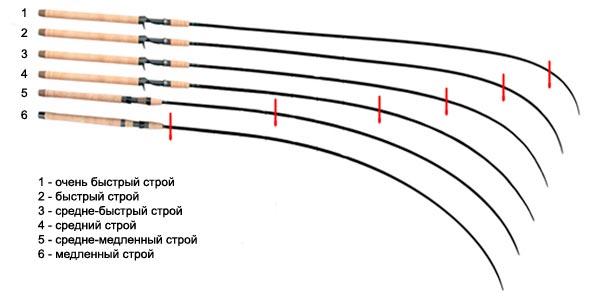
The play of the bait when retrieving and the casting distance depend on this:
- Extra Fast – when loaded, 1/5 of the form will bend.
- Fast – 1/4 part.
- Medium (Moderate) – 1/3 part.
- Slow – 1/2 part.
The length of the rod allows you to vary the casting distance:
- Long rods over three meters are used for sea fishing, on large rivers, and when fishing from the shore of large bodies of water.
- Medium length (2.10-3.00 m) - used on lakes, small rivers and rivers, canals, etc.
- Short (1.50-2.10 m) – when fishing from a boat.

Keep your spinning rod clean and transport it carefully. If the knee joint gets stuck, cool the rod and release it without sudden movements or force. Do not allow sand particles to get into the joints.
Casting technique

To cast from a boat, you need to stand facing the stern, spread your legs slightly, and make sure that the bait does not hit the boat and your comrade. And only after that they cast with great force.
Casts can be over the shoulder (side) or over the head.
Side casting (left or right) is the most convenient for a one-handed rod. At the same time, a slightly bent arm is swung forward from bottom to top, and at the end the arm is extended in line with the rod.
The overhead throw is done using a similar principle.
There is also a sitting cast; its techniques are similar to those mentioned earlier. If desired, brake the line with your finger when casting.
It may happen that you have to use a two-handed spinning rod when fishing from a boat. In this case, the initial position of the rod is 45° to the water and you need to make sure that the bait is outside the boat before casting.
If the spinner (wobbler) is heavy, then the distance from the top of the rod to the tackle should be at least one meter.
More details about how to properly cast a spinning rod, not only from a boat, as well as the secret of long-distance casting are discussed in this article.
Types of spinning fishing
Spinning rods are selected depending on:
- Weight and size of the desired catch.
- The baits used and the method of conducting them.
- Conditions of the planned fishing.
- Kind of like a pond.
Catching a predator with a spinning rod
Catching predatory fish with a spinning rod is carried out using artificial baits that imitate fry or insects on which the predator feeds.

The attractiveness of the bait is created by the wiring technique. And also using live bait - fish secured with hooks (single, double, treble) or special tackle.
Types of the most popular spinning baits.
Spoons
They are divided into two types: rotating and oscillating.
Rotating ones consist of a core, a hook (with or without “feathering”) and a petal; there are different types:
- Spoons are insects : the core of the spinner copies the larva or insect, the petal is its chitinous cover. Can be supplemented with hook feathering.
- Spoons are “condoms” : a heavy core dressed in a bright rubber cover with “tails”.
- Bell spinners : an acoustic spinner with a bell core, which is a resonator and a load at the same time.
- Container cargo . Installation of a container on the core of the turntable for aromatic gels or pastes that dissolve during the wiring process and create a “fragrant trail”.
- In combination with a system of changing hooks for additional equipment of the spoon with artificial bait.
- Spinner with natural bait.
- Two-leaf spinners in tandems on a rigid, composite rod, or on a flexible cable.
- Spoons with twin blades or screws.
- Spinnerbaits are a hybrid of a jig head and a rotating spoon mounted on one wire frame. The design is designed for fishing in snags.
By type of shipment they are divided into:
- Spinners without loading for fishing in the upper layers of water.
- Front-loaded spoons - the sinker is located in front of the blade. Sometimes such a load is called a head.
- Rear-loaded spoons - the sinker is located after the rotating blade.
The game can be divided into:
- with a narrow game;
- with a wide game;
- with a fixed blade deflection angle.
Petal shape:
- With a rounded petal - for fishing in reservoirs without current.
- With oval - for flow.
Oscillating spinners. In essence, it is a piece of metal of a special shape with a hook. Can be equipped with various additional elements.
Can be classified:
- in appearance: classic flat, stamped, three-dimensional, made by cutting or casting, with additional equipment;
- by weight: light, medium, heavy and extra heavy;
- by purpose: models for uniform, stepped, jumping or semi-plumb wiring;
- by relative width: narrow, medium and wide.
The shape of the spinner affects the game during the retrieve. The longer the spoon, the slower it oscillates in the water column (and is better suited to the current).
Some types:
- Spoon.
- Fish.
- Storling.
- Wave.
- Plate.
- Castmaster.
The thickness of the spinner also has a strong influence on the game: the thicker and heavier, the slower the game.
The depth of the stamping determines the nature of the game: flat ones play easier, but are more prone to spin; with increasing stamping depth, it is less active, but more stable during insertion.
The shape of the longitudinal bend most determines the nature of the movements of the bait and there are four options:
- arc;
- caterpillar;
- wave;
- snake
Jig head

It is an element of equipment designed to increase the weight of the hook and deliver the bait to a given depth. A distinctive feature is the location of the load in the head of the bait. They differ in weight, material of manufacture, shape, type of construction.
The weight of the jig head is selected depending on the depth and presence (speed) of current in the reservoir so that the duration of pauses between retrieves (the length of time during which the jig reaches the bottom after the completion of the retrieve) remains within 2-5 seconds. The casting distance depends on the weight of the equipment.
Some examples of choosing a sinker weight for different fishing conditions:
- Nanojig – up to 3 grams. Standing water and depth up to 2 meters;
- Microjig – from 3 to 7 grams. Depth up to 4 meters and current speed up to 2 m/s;
- Light - from 7 to 21 grams. Depth 4-6 meters, speed – 3 m/s;
- Average - from 21 to 42 grams. Depth – 4-6 meters, speed – more than 3 m/s;
- Heavy - from 42 grams or more. Great depths and/or high current speeds.
Jig heads are made from lead, tungsten alloy and brass. They vary in price, size and durability.
There are two types of jig head designs: cast and collapsible. The cast design involves the weight and the hook as a single unit, the collapsible design involves offset installation of the weight and the hook.

Offset installation involves the use of a weight with two fastenings (popularly called “Cheburashka”) and a hook (simple or offset). A hook is attached to one ring of the weight, a leash carabiner is attached to the other, or a cord is tied. A silicone bait is put on the hook.
In addition to jig heads, other weights are also used. Some are used as a “flexible”, “jointed” version of jig heads - these are “Cheburashkas”, “drops” and “sticks” with built-in swivels and hooks attached to them using a winding ring.
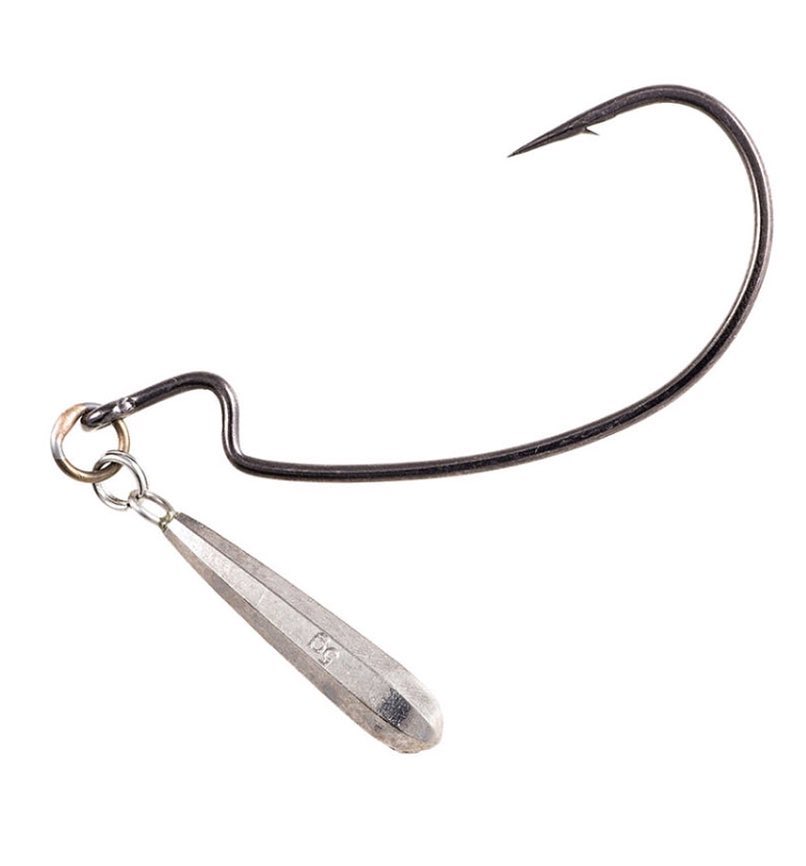

They can be of different shapes, with soldered “ears” or with collapsible ones.
Others are used in rigs with a “retractable leash” and the like. They have the shape of a bullet (in the case of the Texas rig), a ball, a drop, a stick, etc.
Types of fishing for predators: trolling, fly fishing, jig fishing, microjig, casting, etc.
Trolling fishing. This is spinning fishing from a boat with a motor. This type of fishing from a rowing boat is called “track”. The bottom line is that at low speed the fisherman lowers the bait into the water and, without using wiring, but only the movement of the boat, “combs” the reservoir in search of prey. The presence of an echo sounder optimizes the process.
Fly fishing. This is fishing for artificial or live insects using a spinning rod with special equipment and casting and retrieving techniques. With this type of fishing, floats and sinkers are not used; fishing takes place on the surface of the water or its upper layers. Casting is primarily carried out using a special cord, and not a spinning rod blank as in classical fishing.
Mormyshing. Jigs are traditionally a winter bait, but there are already exceptions. Spinning fishing with jigs is becoming increasingly popular. Refers to ultralight fishing. Jigs work more effectively in early spring and late autumn.
Microjig. A type of jig spinning fishing using light baits. These include marmodroch, nanojig, etc.
Casting. It is distinguished by the use of special gear: spinning rod and reel.
The rods are shorter, specialized, and have an inertial baitcasting reel – all this allows for more accurate and longer casts, more sensitive and smooth movements of baits.
Exploration and search for catchable fishing spots from a boat
The main task on an unfamiliar body of water is to find catchable fishing spots. Therefore, while we are sailing to the place, it is advisable to unobtrusively ask all the fishermen we meet: what kind of fish are they, what are they biting on, when and where? And so that they don’t think that we want to stand next to them and interfere with them, the question is formulated something like this: “Good morning. This is my first time here, swimming around that bend. Can you tell me what's interesting there? And how are you? And what kind of body of water is this anyway?”
The main task of reconnaissance is to determine an approximate picture of the depths. Therefore, if we have an echo sounder or an electronic depth gauge, we can immediately turn it on. In extreme cases, a regular depth gauge will do. It is enough to cross a body of water a couple of times and you will be able to imagine it “in cross-section.”
The next task: to determine the “working” depths - those at which the fish bite. There are several characteristic ranges: near the shore, up to 2 m, 3-4 m, 5-6 m and 7-10 m. We have already said that on certain days predators clearly adhere to certain depths. Therefore, it is advisable to consistently fish all ranges and determine which fish are located where. For example, perch stays at 2 meters, pike – at 3-4 m, pike perch – deeper than 6 m. All that remains is to choose who interests us most today, and in the future adhere to the desired depth.

Choosing the optimal bait and bait is in many ways similar to shore fishing. The only fundamental difference is that at a depth of over 3 m, due to its technical capabilities, it is difficult to find an alternative to jig baits. The only question is usually the choice between “rubber” and foam rubber, as well as the optimal load. Let me remind you that with active biting, a heavier head weight and faster retrieval are preferable. But for a passive predator, on the contrary, the lightest possible load and the slowest retrieve are better suited.
Catching peaceful fish with a spinning rod
Catching white fish with a spinning rod is carried out mainly with bottom gear: a feeder and a donka. These two species have their own equipment depending on the desired catch.
But both fly fishing and casting can also be classified as types of fishing for “white” fish using spinning rods. You can also catch peaceful fish while trolling, fishing with edible rubber, wobblers and other options for hunting predators, but this is mostly an accidental bycatch rather than the rule.
How to properly equip a spinning rod
The spinning rod is equipped with a reel on which a cord or fishing line is wound, passed through guide rings and the equipment is tied. Gear is selected according to the characteristics of the spinning rod.
If there is a pike in the reservoir, then a leash is used, which is tied to a cord, and the bait is attached to the carabiner of the leash.
Reels can be inertial, inertial-free, multiplier.
Multiplier rods are the most powerful, so they are equipped with spinning rods for trolling and for catching catfish and other large fish.
Inertial ones are used in fly fishing and in the bottom version of spinning fishing.
Inertia-free, as the main type used in hunting for predators, and in feeder fishing, in carp fishing, etc. They are popular due to the ability to fine-tune the friction brake, with the help of which you can bring out impressive trophies on delicate tackle. Because of such emotions, real fishermen go to the pond. The simplest reels, like the Nevskaya, are suitable for fish harvesters.
The choice of cord or monofilament depends on the fishing method and location.
For example, for jig fishing, the extreme sensitivity of the gear is important. The fisherman controls the movement of the bait and the bite tactilely - through the form and visually - along the tip of the rod. The cord has no stretch, which ensures the best signal transmission from the bait to the form and then into the angler’s hand.
The monofilament, in turn, has stretchability and thereby dampens sudden jerks of the fish. This property, coupled with the flexibility of the rod and a properly configured clutch, helps to bring out the trophy without annoying derailments.
Expert opinion
Vladimir Poltoranin
Fisherman - expert
What type of base to equip a fishing rod needs to be determined for each individual case. There can be many factors - this is a littered reservoir (braid collects garbage like a vacuum cleaner), the presence of a shell (monofilament is less susceptible to cuts on sharp edges), weak fish lips (the line is stretchable and handles jerks better), pike teeth cut braid perfectly and do not always cope with fluorocarbon (fluorocarbon fishing line).
Small in appearance, but not in importance, are the auxiliary equipment elements:
- swivels;
- carbines;
- winding rings;
- fasteners

The comfort and reliability of the gear depends on their quality and proper selection and installation. A poor-quality swivel will ultimately result in twisting of the fishing line, which will lead to its tangling, the so-called “beard”. And instead of enjoying fishing, you will waste time and nerves redoing the gear.
This also applies to other installation elements. High-quality fittings contribute to the overall balance of the gear; you should not skimp on these small things.
Collective fishing from a boat
Group fishing from boats is especially interesting. After all, here you can spread out in different directions and, without interfering with each other, fish for your pleasure. Thus, in a day, a large area of water is checked - both deep and coastal, all kinds of gear and bait are tried, and a wide variety of fish are caught.

The only thing that needs to be thoroughly discussed is the initial collective plan, which should take into account as much as possible the passions and capabilities of all participants. After all, among spinning anglers there can be convinced “coast fishermen”, experienced “deep fishers” and simply “generalists” - naturally, each of them prefers “their own” fishing.
The main difficulty is the current exchange of information. It would be nice to get everyone together in a couple of hours, but often this turns out to be unrealistic. The problem is solved through walkie-talkies and mobile phones - for those who have them. The rest have to collect useful information along the way and through third parties. Nevertheless, if not all the news, then most of it can be found out at the reservoir. The full picture becomes clear only in the evening at the base or on the way back. And all the same, this is very valuable information that shows the overall picture of the bite in the entire reservoir.
Fishing together from one boat can also be considered as an option for group fishing. After all, here, too, until the situation is completely clarified, different baits and different wiring are usually used. For example, both anglers prefer jigs: but one fishes with “rubber” with a long “step”, and the other fishes with foam rubber with a “short” one. Another method is often used: the first one throws towards the shore, the second - into the depths.
That is, together you can also fish a double area of water or “comb” any area twice as tightly. However, there are no longer opportunities for broad collective reconnaissance here. But you can immediately compare different baits and fishing options, and the exchange of information occurs instantly. The optimal fishing pattern is gradually determined, and then the gambling competition begins - who will win!
The only condition: to correctly arrange all the gear and agree on the sequence of casting and the order of fishing - in order to catch the fish, and not each other. Well, fishing together is doubly fun. And the total catch is always greater. And if you suddenly come across a “crocodile”, a friend will always help you pull it out.
Spinning fishing technique
Using artificial baits, the fisherman needs to “deceive” the predator and make him believe that in front of him is a living object of his diet. To do this, various wiring is used, forcing the bait to move in one or another amplitude, direction and speed.
Spinning wires
Basic wiring techniques:
- Uniform – suitable for spinners and silicone lures. It is carried out by uniformly winding the fishing line onto the reel. The closer the bait is to the surface of the water, the faster the retrieve rate. In the bottom layers, bait is carried out very slowly.
- Uneven - alternating bait movement and pauses. Suitable for fishing with oscillating spoons and silicone. A correctly selected ratio of the speed of posting and the duration of pauses gives excellent results.
- Stepped – for bottom baits. The bait sinks to the bottom, then sharply, by moving the tip of the rod, rises at an angle (at this time the cord is wound on the reel) and falls again. The secret of retrieving lies in the timing of the movement of the bait from the top point to the bottom - the predator often attacks at this moment.
- Twitching is a jerking drive that involves active movement of the form from side to side. The amplitude and depth of the bait's immersion varies, which presupposes the spinning angler's skills. Very good for wiring wobblers.
- Jig is a type of stepped wiring. The difference is that the movement of the bait is provided by the reel, without the participation of the blank. The speed of the drive and the duration of pauses change. Used for fishing with jig heads.
Different wiring techniques are used for different types of baits. But we must not forget that fishing is creativity, and this is projected onto the options and elements of wiring. You always need to improvise, look for the right technique right now. By mixing styles, changing established criteria, you will always find the key to the object of the hunt.
How to cast a spinning rod correctly
Spinning is a tackle that has its own characteristics. The casting is performed with a sharp throw without stopping. The casting technique depends on the reel that is installed. Let's consider a spinning coil.
Casting options:
- Vertical.
- Horizontal.
- Pendulum.
- Ejection.
Vertical cast.

The most common technique that allows you to deliver the bait to the designated place, applicable when there is no interference with the swing. Highest casting distance.
- We begin casting by searching the surface of the water for the bait delivery point.
- Using a reel, we wind the cord so that the bait is twenty centimeters from the tip.
- After this, the cord is pressed against the rod with the index finger, and the line-laying arc opens.
- The rod is thrown behind the back, a sharp movement of the hands so that the rod plays and a sharp feed forward of the bait, which “shoots” in the desired direction, at the same time the cord is released.
- While the bait is flying, the cord falls freely in rings from the spool, the tip of the rod points in the direction chosen for casting.
- When the bait touches the surface of the water, the line-laying arm is returned to its original position and they wait until the bait takes the desired position in the water column, then the retrieval is carried out.
Horizontal (side) cast.

It is used when tree branches are in the way above the spinner’s head and/or there is high overhanging vegetation at the casting point. The casting range is slightly less than in the previous case, but the accuracy is high.
The casting technique differs from the previous one in that the spinning rod is wound up to cast not behind the head, but to the side. The accuracy of the bait's flight directly depends on the moment when the cord is released.
Pendulum cast.
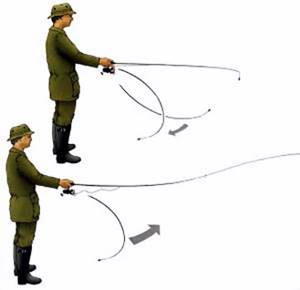
It is carried out when the branches are located very low above the water and the bait must be delivered as if from below, under the branches.
- We mark the point where we need to deliver the bait.
- We pull the bait to the tip of the rod by 20-30 cm.
- Fix the cord with your finger and open the line handle.
- We swing the bait and with a sharp movement “from under ourselves” we direct the bait to the desired point.
- We track the moment when you need to release the cord by the amplitude of the bait’s swing.
- We return the bow to its original position and carry out the wiring.
Catapult cast.
The cast is quite difficult to execute and unpredictable. Designed for hard to reach places. Reminds me of shooting with a slingshot. Requires high skill.
- The bait drops just below half the length of the rod,
- The line-laying bow is retracted and the cord is fixed with a finger.
- You need to grab the bait with your hand so as not to catch on the hook, pull the cord until the tip of the rod bends,
- First, release the bait with a throw, then release the line.
- Close the shackle and make the wiring.
Casting distance is affected by:
- Length and structure of the form;
- Size, type of reel and spool shape;
- The diameter of the cord and the quality of its winding;
- Diameter and location of passage rings;
- Casting technique, environmental and weather conditions.
When does the autumn pike zhor come?
It’s not enough to find a promising place; you also need to figure out the best time for pike activity. After a hot, sultry summer, pike begin to actively feed. When the water level in the river drops, the oxbow lakes dry up, the channels dry up, and the first cold snap sets in - this is the signal to start trophy hunting! In our region, this is usually the end of July - the beginning of August, but recently the calendar is increasingly moving closer to September.
Not only is a large pike more difficult to tease and provoke to bite, it also rarely goes out hunting. Its metabolism is slower, compared to 1-3 kg pullets, which are ready to attack anything that floats nearby. Large pike feed on kilogram-sized fish, after swallowing which they return to their stopping place and digest the prey for quite a long time, without reacting to anything else at this time.
You should know that maximum activity in pike occurs when the water temperature drops to approximately 15 degrees ; the fish's satiety instincts turn on before a long winter - this leads to real gluttony. The active phase of which continues as the water cools to 8 degrees . During this period, your chances of meeting a trophy crab increase.
In autumn, the predator feeds throughout the day. On clear days, it makes no sense to get up early and go to the reservoir at dusk, hoping for an early exit of the pike, it is reckless. Rather, the first exit begins when the sun has already illuminated the pond with its rays, the second - from about 10 to 12 noon. In the evening, the start of departure can be expected around 18:00 and just before sunset. For different bodies of water, and especially weather conditions, exit hours may vary.

Spinning fishing tactics
The tactics of spinning fishing are practically the same in any body of water: be it a large or small river, lake, reservoir, etc.; Whether you are fishing from the shore or from a boat, with an active spinning rod or feeder, with a donkey or a casting rod, you will be subject to the following components:
- Finding a fishing spot (choosing a fishing spot);
- Duration of reconnaissance (fishing) of an unfamiliar (or familiar) place;
- Variety in the choice of baits and complementary foods (selection);
- Varying the degree of immersion of baits (for active spinning);
- Animation of baits by combining the type of postings (for active spinning).
Finding a fishing spot

It involves choosing a place in the territory of which the fish you have chosen can stand (feed) or hunt.
If this is a predator, then we will choose dumps, edges, bottom holes, boundaries of vegetation and clean water, steep shore, etc., i.e. those places where it is convenient for a predator to make an ambush.
If we catch peaceful fish, then we choose places for active feeding (or we feed in places that are familiar to fish and convenient for fishing) depending on the time of day: if night fishing is in shallow water, daytime fishing is in deeper fishing areas.
Duration of the catch
The time you will spend searching for actively feeding fish or stimulating their activity.
This parameter depends on the time of year. In winter, late autumn, early spring - there is a greater dependence on weather conditions and seasonality of behavior: if you find a fish site and cannot catch it, then the fishing time will be quite long, because... All tactics will need to be tested.
In late spring, summer, early autumn, when the fish are active, the time for fishing is reduced significantly. To search for active fish, three or four casts to each promising place are enough.
Selection of baits
It all depends on the preferences of the fish at a particular moment.
For example, the choice of the size of a wobbler or silicone will depend on the length of the fry near the shore. This is the main food supply of the predator in the fishing area.
You will vary the bait on the hooks of the feeder or donkey, just like the complementary food in the feeders. Everything will depend on the gastronomic preferences of the selected fish.
Degree of immersion of baits
More relevant to active spinning fishing, since it is necessary to find fish sites in layers of water. We consistently study by varying the depth of the postings, experimenting with equipment (jig heads, wobblers, spinners, spoons). This is more about a predator than a peaceful fish. Her preferences will depend on weather conditions, time of year and day.
Lure animation
It is more important during the period of least fish activity, as is the choice of color, shape and size of baits. To stir up a sluggish predator, it needs to be qualitatively stimulated to attack the bait by changing or combining the methods of wiring to create a more attractive animation for the predator. It would be very appropriate to experiment here. This requires time and skill.
Fishing objects, their habitats
The species composition of fish caught with a spinning rod on the Oka and Moscow Rivers is common for central Russia: pike, pike perch, bersh, asp, perch. It is still too early for us to systematize catching chub and ide with jig baits: cases of their capture are relatively rare and mainly occur in shallow sections of rivers with fast currents and a hard bottom. Fishing for catfish and burbot in these sections of rivers has been mentioned only a few times by anglers over the past five years. Since we fish mainly in deep areas, we will try to talk about the predator’s attachments to these places. The main thing is the presence of a hard bottom: clay, small stone with sand. In silted areas there is either no predator at all, or very few. The location of a predator is influenced by many factors: time of year and day, weather, pressure, lighting, water and air temperature, water turbidity, but the main one is the food supply, which, in turn, is influenced by the same conditions. Pike rarely lives in areas with fast currents. It can be located and hunt in any part of a hole, riverbed edge or snag. Fish weighing from 1 to 3 kg especially prefer exits from pits. There is one more feature - the larger the fish, the deeper it is. On the Oka there are several creeks in which there is no current, and the depth there is up to 8 m; a sharp drop begins from the shore. Large specimens are found in these places. It has been noticed that sometimes, in early autumn, medium-sized individuals form small schools, and several pike can be caught from one point. At the same time, large specimens (from 2 kg) stay apart. Pike bites are usually clear and sharp. Pike perch and bersh on the Moscow River and Oka usually form joint schools of up to 10 individuals. Only in early spring and late autumn do they gather in groups of up to 50 individuals, and on the Oka River up to 30% of the flock are bershi. Specimens of pike perch - weighing from 400 g to 2 kg, bersha - from 300 g to 1 kg. These fish, on the contrary, love a fresh flow of water. Their favorite places are channel edges and sharp drops with a medium current. The pike perch bites are clear, but often it presses the bait to the bottom. Bersh rarely takes during a pause; he mostly grabs an already fallen bait, but more often he covers it with his lower jaw, pressing it to the bottom - apparently, this is due to the absence of fangs. Pike-perch weighing more than 3 kg always stay apart due to their weight and size, as they say, “they don’t take them into a flock - they’re too dangerous.” Perch stays separately or in small schools of up to 10 specimens on the upper sections of drop-offs and edges and on extensive plateaus with an average current and a depth of 4 meters. On September 12 last year, at one of these places, in the area where the Kashirka River flows into the Oka, we caught 56 perches weighing from 300 to 700 g using foam rubber fish. A large flock “occupied” the plateau for only one day, and there were bites on every retrieve . In the following days the situation was usual for this place - 5-10 fish caught. Favorite hunting spots for perch are various underwater mounds. The perch bites are sharp, but not strong. Very often, before he grabs the bait, he chases it for a long time and hits it several times. The asp feeds in open areas with strong currents and depths of up to 4 m; its flocks are few in number. He is shy, after catching one or two specimens, you can change the place. However, oddly enough, by boat you can approach it at a distance of up to 20 m, the main thing is to maintain silence. In summer, the asp’s main habitats are backwaters where his favorite delicacy, bleak, lives. The bites are so sharp that sometimes a predator can snatch the spinning rod out of their hands.
How to fish at night with a spinning rod

More comfortable night fishing in summer. Traditionally, this is fishing for pike perch, but in the July heat, catching pike can also be successful. You can also catch a good bite of asp, chub, ide, catfish and other fish.
At night, the fish more willingly goes into shallow water; you should look for it not far from the daytime anchorages. It is better to study promising places during the day for the presence of bottom snags, vegetation, and bottom topography. The bite can be good throughout the night, but the hours immediately after sunset and just before dawn stand out.
Illumination of the reservoir: on clear moonlit nights, the natural light of the moon is enough; in cloudy weather, you can use an electric flashlight.
Baits are chosen depending on the light level: on clear nights, use all types of silver-colored spinners of at least No. 5, jig baits from 3 to 7 cm; in cloudy weather - wobblers with a rattle, popping poppers; Glowing rubber is used when fishing for pike perch.
Placing baits at night forgives all mistakes; you can move any bait evenly and slowly - and this is the main advantage of night fishing.
Tackle
We fish from a boat with the same gear as from the shore on large rivers. Let's start describing them with baits. We prefer front loaded ones, of all types. The most catchy and most frequently used is the foam fish. We gave her first place because... it has proven itself well in almost all conditions. Depending on the time of year and the stability of the bite, we use fish of several sizes, colored like minnows: the smallest in winter and spring, medium in summer, large in autumn and summer with a stable bite. This bait is easy to make and inexpensive, even taking into account that the consumption of baits in some places, especially on the Moscow River, is very high, up to 20 pieces per day of fishing. In second place are twisters and vibrotails of various colors and sizes, depending on the object being fished. It is impossible to say for sure that in the Oka and Moscow rivers the fish have a preference for a certain color of twister or vibrotail. The most commonly used colors are white, yellow, bright green with glitter, orange, black or blue. The choice of bright colors is due to the fact that they are easier to provoke fish to bite. Black and blue, according to our observations, are more suitable for fishing in calm sunny weather. The choice of color also depends on the time of day and water transparency. Two-inch twisters are optimal for catching perch, and three- to four-inch twisters for other predators. Other baits are used purposefully: at certain times of the year and under specific conditions. Some of them are designed for only one type of fish. This group includes tail spinners with lurex, polyurethane foam fish, sometimes “decorated” with lurex, and loaded wabiki. Observations of their catchability over the past three years are shown in the table.
Choice of bait depending on the month
Separately, it is worth mentioning the well-known castmaster, which shows stable results with stepped or scratching retrieves at a slow pace near the bottom. However, it should be used only in clean areas of rivers where there is no risk of snags. A big fan of this bait is pike perch, but it is caught this way only in June and July, mainly in the evening hours. Depending on the depth and strength of the current, 21- and 28-gram spoons are used, in rare cases at a depth of two to three meters - 14 g. A boat with a hard bottom allows you to use rods with a length of 3 to 3.30 m. If you fish with a regular inflatable, then you should use shorter spinning rods, from 2.4 to 2.7 m - sitting on a “cushion”, it is more convenient to cast with rods of this length. The recommended action is fast or complex, the test is from 10 to 40 g, it is quite enough when fishing both on the Oka and on the Moscow River, since here it is not necessary to use sinkers lighter than 10 g and heavier than 32 g. One of us fishes with a rod 3.2 m long with a complex action, test 10-32 g, the other with a multiplier rod 3 m long with a fast action, test 10-40 g. It is better to fish at sub-zero temperatures with a carbon fiber rod. This is primarily necessary to ensure that the spinning rod does not break in the cold. In addition, in winter the bites are very weak, and carbon fiber transmits them well, unlike fiberglass or composite. The reel should preferably have 4-5 ball bearings, with a “thrust per handle” of at least 7-8 kg, and must match the rod both in weight and size, that is, the tackle must be balanced. A reel with a front drag is preferable, which is considered more reliable, with a Twist Buster device in the line roller that prevents the line from twisting - this will avoid the formation of loops and “beards”. Reel lubrication for winter fishing requires a special one, suitable for fishing at sub-zero temperatures. Of the multiplier reels, you can use any classic models from well-known companies, with a cast bait test from 10 to 40 g. “Soap dishes” are not suitable for this extreme type of fishing, but only 2-3 models, the rest quickly fail. In winter, fishing with baitcasting gear in temperatures exceeding -5°C is prohibited. Water freezes in the “eye” of the line guide and on the rod rings, since their diameter is smaller than on classic spinning rods. On the Moscow River, “rinsing” the rod helps, but on the Oka, where the water is much colder (less warm runoff), this procedure will only worsen the situation. Silicone or petroleum jelly can be used as a de-icer. Many anglers have a problem with ice particles freezing on the spool, especially when reeling in the last section of line. You can avoid this by passing it through your fingers, which will remove most of the water. Another disadvantage is considered to be the upper position of the multiplier reel on a spinning rod; because of this, water from the line guide and spool drips onto your hand. The solution is simple - wear gloves made of water-repellent material, they perfectly warm your hands and keep them dry. On one of the gloves, depending on whether you use a right-handed or left-handed reel, cut off the fingertips. This is necessary to slow down the spool when casting and control the retrieve when fishing “in one line”. It should be noted that if handled correctly, there are no malfunctions in the operation of the multipliers, and the casting range is the same as in the summer. All year round we use braided fishing line - the usual classic “pigtail” with a diameter of 0.15 mm with a breaking load of about 7 kg. At sub-zero temperatures, it can be soaked in Vaseline oil to prevent water droplets from freezing, but this cannot be done with a braided cord. Monofilament fishing line tends to stretch, as a result of which the sensitivity of the tackle decreases and the clarity of hooking at a long distance is lost. In addition to the “standard” ones, it is advisable to have other gear in the boat, for example, for catching chub and ide, but we hope you can read about this in our next materials.
Winter spinning fishing

With the advent of abnormally warm winters, spinning fishing in open water is becoming increasingly popular and has its advantages.










