Description and behavior characteristics
Tench belongs to the carp family; it is sedentary and calm. Undemanding to water quality, tolerates lack of oxygen well. It does not like bright light, and therefore prefers to stay near the very bottom. The body of the tench is multi-colored, the back is green-yellow, and the barrel is olive.
The scales are small, covered with viscous mucus on top. The fins are dark purple, rounded, and the eyes are small, bright red. It feeds mainly on green reeds, reeds, duckweed, and finds food in the bottom silt. It also eagerly eats: aquatic insects, worms, leeches, larvae, mollusks, crustaceans, and fry.
In summer it feeds only at dusk and at night.
Average weight from 300 gr. up to 2 kg, but there are also 7 kg individuals. When the water warms up to 14° C, spawning begins, somewhere from May to July, it does not migrate. It accumulates in small groups only in wintering areas or during the spawning period.
When the reservoir freezes and the summer drought occurs, the tench buries itself in the silt and falls into a long-term torpor. It can only be detected by air bubbles on the surface of the water, at dawn or in the evening. With the onset of persistent frosts, they stop feeding and freeze in mud pits until it warms up. It is preferable to hunt for it in the warm season; at other times there will be no bite.
Habitats
Inhabits: Eurasia, lakes and rivers of the Baltic, Black, Caspian and Azov seas. Found in the Baikal basin, in its western part. In the upper reaches of the Yenisei and Ob. Lives: lakes, ponds, river bays, channels, reservoirs, etc.
It prefers a silt-clay bottom, and an abundance of underwater and aquatic vegetation: water lilies, duckweed, egg capsule, reeds, pondweed, reeds, cattails, etc. It prefers reservoirs with standing water or weak currents.
Tench never changes its habitat , but has its own areas known only to it, to which it always returns. An observant fisherman can detect it: by the swaying of the stems on the water, air bubbles, cloudiness of the water, etc.
Varieties of tench
Depending on the tench’s habitat, this species is divided into four ecological variations. Their representatives differ slightly in body features and slightly less shade of scales. There are such varieties of tench:
- Dwarf. The reason for this name is the small growth of the tench - no more than 12 centimeters in length. This is due to the fact that tench live in places inhabited by fish, which leads to a sharp slowdown in growth. Dwarf tench is more common than other varieties. It settles in almost any freshwater body of water.
- Ozerny. The fish is similar in appearance to river tench, but is larger in size. This species prefers to settle in large lakes and reservoirs.
- River. Tench is found in creeks or bays of rivers, branches or channels with a slow flow. It differs from lake and pond lines in its significant thinness. Also, river lines may have a slightly curved mouth towards the top.
- Prudovaya. The habitat of tench is small artificial or natural reservoirs. Slightly thinner and thinner than lake fish. But when a pond tench is introduced into a lake, it will begin to gain weight as quickly as possible and will become outwardly similar to lake tenches.
Peculiarities of tench biting by season
- Winter. In winter, she does not feed, but is in deep hibernation. Therefore, it is not possible to catch it at this time.
- Spring . With the arrival of spring, he will come to life and, when hungry, will rush to any food offered to him. But a particularly favorite delicacy for him: bloodworms, bell larvae, and red worms. By mid-May, the bite will subside, and then stop completely before spawning. It will resume in 2 weeks because summer is starting.
- Summer. A favorite time for fishermen, because the catches are stable and it’s warm. On particularly hot days, the bite will only be after sunrise, or late in the evening. But only night fishing can be especially catchy. For bait, various baits are used: vegetable, animal. Which ones exactly will depend on the taste preferences of aquatic inhabitants.
- Autumn. You can fish throughout the entire fall with varying success, right up until the leaves fall. A good bite occurs in cloudy but warm weather with drizzling rain. But when incessant rains begin, not even the most attractive bait will be able to lure the tench out of the depths. At the beginning of autumn it is better to use plant baits, but in October switch to animals: bloodworms, worms, slugs, snails, maggots, etc.
How does tench taste?

In gastronomic terms, tench is considered a royal fish with excellent taste. Especially when it is served fried. Some people say that tench meat tastes like mud, and these accusations are partly true. To avoid this, before cooking, rub the tench with coarse salt or pour boiling water over it. If you are going to cook fish soup from this fish, then the first water should be drained immediately after it boils. Wash the pieces of fish, and you can start preparing the fish soup according to the traditional recipe, the taste of which you will remember for a long time.
Thank you for fishing with us! Or not yet? Yandex.Zen Facebook
Tags
: how to catch tench
Tench fishing methods
There are many ways to catch this difficult fish, but the two most popular are: a float rod and a feeder tackle. You can fish from a boat or shore, but it is more comfortable from a boat. And it will be easier to change the place if necessary.
Float rod
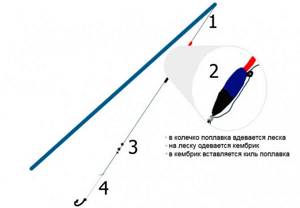
Fly tackle
It is necessary to choose a place for future fishing, and based on the characteristics of the reservoir, we begin to equip the fishing rod. For fishing from a boat, from the shore, in an overgrown reservoir, use fly tackle :
- rod—4–7 m;
- high-quality monofilament line - 5.5–6.5 m, Ø 0.21–0.30 mm;
- hook - N°7–10;
- float load capacity - 2–2.5 g;
- subpastor - 0.5 g;
- nylon leash - Ø 0.16–0.20;
- 2-3 pellets - 1 g each.
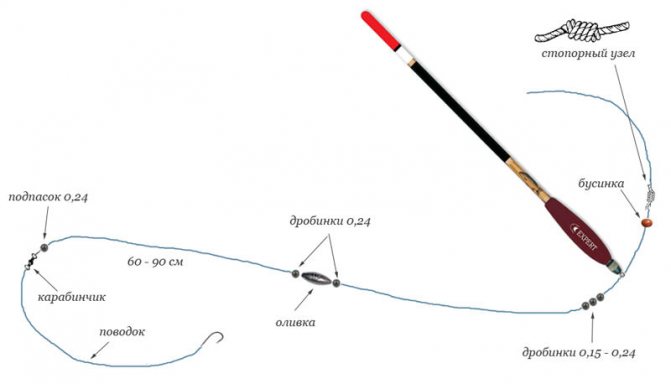
Match equipment
A match fishing rod is used in unpolluted reservoirs, its equipment:
- rod with rings - 3.4–4.5 m;
- spinning reel - 2000–3000;
- monofilament - Ø 0.20–0.27 mm;
- hook - N°6–10;
- sliding olive, made of lead -2–4 g;
- fluorocarbon leash - Ø 0.13–0.18 mm, length 20–30 cm;
- subpastor - 0.5 g;
- float of bright colors - 4–5 g.
Feeder tackle
It is assembled from the following components: feeder, rod, fishing line, reel and leash with hook. The set always begins with choosing a feeder.
It is better to acquire several models at once, of different weights and sizes:
- For the current you will need weighted ones, preferably triangular or square in shape. To cast the equipment 60–80 m, you will need 80–100 g of feeder.
- Without current - light, round or oval, for distant casting you will need a 60-80 g structure.
The rod is selected for fishing conditions, the test load should be in the following range: the total weight of the feeder plus bait should not exceed the upper permissible threshold, if the weight of the feeder is 40–50 g, plus 20–30 g of bait, then the test is in the range of 50–110 G.
We select the length based on the casting distance and the activity of the water flow:
- calm waters - 3.3 m;
- leisurely waters - 3.6–4 m.
Equipment:
- reel 3000, gear ratio 1:5, 1:6;
- fishing line (braid) Ø 0.13 mm;
- leash - a piece of monofilament Ø 0.19 mm;
- hooks - No. 5-6 for small bait for grains, etc., and No. 7-10 for larger bait: maggots, worms, worms, corn, etc.
To make the feeder equipment more sensitive, it is necessary to combine the feeder with the main fishing line. This can be done in different ways: anti-twist tube, Gardner equipment, loop equipment, etc.
Baits and lures
Baits and lures are used to attract fish to the hook. This can be food: animal, plant origin, or imitation food.
The choice will depend on:
- features of the reservoir;
- season;
- fishing place;
- type of fish;
- depths;
- indicators of atmospheric pressure, etc.
The main condition is that the bait should look tempting, and the tench should not notice any catch. Now let's take a closer look.
Animal origin
When choosing, take into account the tastes of the fish, and it prefers animal bait most of all. Those that can be found during this period of time are especially valuable. In summer, for example, worms will be very good, just drip them near the river. It can be extremely difficult to please this fish; you only need to adhere to the naturalness of the diet:
- Various worms (earthworms, dung worms, etc.) are best, especially in a bunch of 2-4 pieces, the hook point should be completely covered.
- Maggots are small, grown on vegetables or meat. 1–7 pieces are pinned onto the hook at once, depending on the fishing method. The sting should not protrude too much, otherwise the tench may refuse the treat after being pricked.
- Shitik - if there are flowing streams, then there are shitiks. Put on 1-3 pieces so that the sting is not visible. His only drawback is his quickly deteriorating body, and the other fish lads adore him, so they quickly eat him up.

Bark beetle larva
Muckworm
Maggots (attachment options)
Dragonfly larva Ant eggs
Shell meat - In the green reeds there lives a green soft larva , reaching up to 4–5 cm; moults simply adore it.
- The larva of a dragonfly - but only a large tench can encroach on it. They are inserted between the skull-shaped jaws, and the sting is brought out from the bottom of the abdomen. It should not stick out much, but when touched, it should be slightly felt with your finger.
- Shellfish meat (shells, pond snails, pearl barley, etc.) - is caught in places where mollusks accumulate, the hook tip must be completely drowned in the fleshy part.
- Larvae of bark beetles - in fallen trees flooded by spring waters, beetles lay larvae, which are an excellent bait. They string 2–4 pieces, the sting is masked.
- Ant eggs - put on 5-7 eggs, pressing down the sting.
- «Sandwiches» - combinations of attachments:
- bloodworm - mollusk;
- maggot – worm;
- shitik - ant eggs, etc.
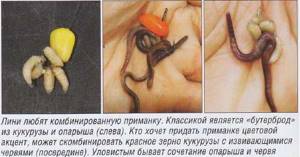
Curd bait
If you have cottage cheese in the refrigerator, then prepare a cottage cheese bait:
- missing cottage cheese 300 gr.;
- sunflower cake 600 gr.;
- breadcrumbs 500 gr.;
- a handful of peat;
- flavorings (any of your choice).
Mix all the ingredients well, then form small balls.
Plant-based: recipes
1 recipe:
- canned corn – 0.5 cans;
- breadcrumbs – 1–1.5 kg;
- hemp seeds – 200 gr.;
- cocoa powder – 40 gr.;
- sugar – 3 tbsp. l.;
Mix the dry ingredients, then the rest, bring to the desired consistency with water.
Recipe 2:
- semolina – 0.5 kg;
- corn grits – 0.5 kg;
- cake – 0.5 kg;
- oat flakes – 0.5 kg.
Mix and let it brew for half an hour; upon arrival, add a little water from the reservoir.
Recipe 3:
- pearl barley;
- peas;
- millet;
- some homemade butter;
- 1 tbsp. l. honey.
Cook porridge from cereals, the main thing is to make sure it doesn’t burn, then add butter and honey.
Bait for tench
Fishing for tench is much more productive with attachment and bait. As a rule, it is effective to set bait two days before fishing, and start complementary feeding at night, planning to fish from early morning. Tenches are voracious, and to collect them at a promising point you need to stock up on a sufficient amount of complementary food, in addition to diluting the main mixture with soil. The bait mixtures themselves are prepared on a base of boiled pearl barley porridge with the addition of fish feed and curd mass.
Important! The sour smell of bait with cottage cheese discourages all other fish from fishing areas, but for tench this smell is one of the components of attractiveness to the fishing zone.
For a kilogram of boiled and unstrained pearl barley you will need the same amount of fish feed with the addition of two hundred grams of grainy low-fat cottage cheese to the mixture. Ground cumin, coriander or cocoa powder are added as an attractant.
Important! As an animal component, the mixture is richly seasoned with chopped worms or crushed bloodworms.
The resulting complementary food is mixed with exactly the same amount of soil sifted through a sieve and moistened to a state that makes the balls crumbly when they hit the water, which makes it possible to cover the surface of the sludge with the feeding mixture.
Nuances of bait
In order for the tench to peck well, you need to feed the same place for several days. Only in small water areas, this fish can bite after the first bait. Much will depend on the time of year, day, and weather conditions. Shallow water areas, at the edge of reed thickets, in a “window”, etc., are most suitable for feeding.
You cannot feed with heavy balls, because the bottom is usually covered with a layer of silt or greenery, and when they sink into them, they become invisible. It is more advisable to prepare a loose mixture from crushed components, but it should consist of large fractions. Its slow immersion promotes attachment, and the fry will not be able to eat it.
It is better to introduce a little, but with nutritious bait, than a lot, but “empty”. Only targeted feeding can give the best results. It is advisable to enrich plant baits with a “meat” additive: maggots, worms, crawlers, pupae, etc.
Places of attachment must be inspected regularly. Approach the shore or swim up on a boat and see whether the bait has disappeared or not. If it is shallow and the water is clear, it will be clearly visible. If the water is deep and opaque, then only by the characteristic air bubbles can one find out whether the tench is feeding or not.
With your own hands
Recipe No. 1:
- any bran 1 kg;
- boiled semolina, a little;
- boiled or steamed millet 0.5 kg;
- a handful of chopped worms.
Recipe No. 2:
- sunflower cake;
- breadcrumbs;
- hemp oil 2-3 drops;
- grains, any (steamed).
Mix everything in equal proportions and leave for 1-2 hours.
Recipe No. 3:
- fry rolled oats;
- boiled potatoes;
- White bread;
- peas (steamed).
The proportions are arbitrary, soak the bread and mix with all the ingredients.
Shop
In fishing stores you can always buy ready-made baits suitable for all types of fishing.
If you don’t find a molt, use another: carp, crucian carp. The main thing is that the bait is suitable for standing water; read the information on the pack.
A spring or method feeder is often depicted on the packs. You need to choose only dark baits so that they blend in with the muddy bottom. Contains: rich in proteins and betaine, and many other nutrients.
Where to start catching tench
As I mentioned above, line fishing has its own tricky nuances, and therefore, before you get into it in earnest, you need to be well prepared for it. First, make inquiries about nearby bodies of water. Listen to what fellow fishermen say about them, analyze local fishing forums. You can even travel around villages near ponds and ask around the locals - it’s not a fact that they will “split,” however, and this sometimes works. As a rule, this is quite enough to identify a promising pond where it is known for sure that there is tench.
If there is already an interesting reservoir, but it is not clear whether tench are found in it or not, you will have to clarify this yourself.
How do you know if a body of water is “lined”?
All bodies of water in which the coveted fish live have a certain set of common features. The first (and obligatory) signs:
- Flow. The reservoir must have an influx of fresh water, no matter in what form - streams or underground springs. But the oxygen regime must be in order - this is necessary not so much for the tench itself, but for the survival of its eggs.
- Muddy bottom. If there are silted areas in the pond, then most likely there will be tench there, but only if the following point is fulfilled.
- Well-developed aquatic and semi-aquatic vegetation. The reservoir should quickly become overgrown along the banks and in the coastal zone, but for all that, not with just any plants. Lin, it turns out, doesn’t like all algae. This is a very important nuance in catching it, and it is worth dwelling on it in more detail. But for this you will have to delve into botany.
Plants - companions of tench
There aren't many of them. It's funny, but some of them are known for their edibility and appear in pictures of survival books.
Let's consider all the plants that tench loves. Let's start with near-water ones, since they are closest to the fisherman and their presence can be determined from the shore.

Photo 3. Broadleaf cattail. It is popularly known as “reed,” although it is not actually one (reed is a completely different plant, in appearance more reminiscent of an overgrown onion). It is very recognizable by its characteristic thick brown ears, which are often used to make bouquets and dried flower arrangements. Young, still tender and easy to gnaw shoots of broadleaf cattail contain a decent amount of starch, sugar and other nutrients, and therefore are very adored by tench.

Photo 4. Here are the ones! It turns out that not one, but two types of “reeds” grow here. Cattail angustifolia. Like the previous plant, it forms the food base for tench. The main difference is narrower leaves, as well as thinner and longer ears.

Photo 5. The well-known common reed is a lover of wetlands along the shores of lakes and in river deltas. Everything is also edible, rich in starch and sugars. When young, we adore tench no less than cattails.

Photo 6. Sedge, but not just any kind, but growing “with its feet in the water.” There are several types of it, and they are all, in principle, quite similar to each other. In the spring, tench eat well the basal shoots of sedge that have not yet hardened, especially those that have been flooded with flood waters.
But these were higher semi-aquatic plants. And behind them come the more ancient and primitive ones - horsetails. By the way, there is one interesting thing connected with them. As hydrobiologists report, these plants tend to increase the pH of water, that is, to make it more alkaline. For fish, this is akin to ozonation and ionization of air, that is, it has a beneficial effect on its health. Therefore, not only tench like to stand in horsetails, but also other scaly-tailed inhabitants of the reservoir.

Photo 7. Riverside horsetail, also known as marsh horsetail. A characteristic feature of this plant is the relative hardness of the stem and the presence of small notches on it. It feels like a manicure file and can even scratch not very hard materials. Lin is absolutely indifferent to this circumstance; he chomps the young shoots of this plant by both gill covers.

Photo 8. Another variety of our semi-aquatic horsetails. Swamp horsetail. It differs from the previous plant in its noticeable branching. Poisonous. However, this does not bother the tench at all. It is possible that he does not feed on horsetail, but collects boogers that are found in the thickets of this plant.
All six plants described above are familiar to every angler. They are regulars on the shores (especially closer to the upper reaches) of almost any small pond.
Next come those “algae” loved by tench, for which you will have to go into the water.

Photo 9. Floating pondweed, also known as “water cabbage”. A very important representative of the flora of our reservoirs, because in its thickets all kinds of invertebrates live that feed fish (including tench) - like the young shoots of this plant, the fry also hide here from predators. In addition, pondweed works like an “umbrella”, providing shade under water - the fish also like it. Fishing for tench in pondweed thickets is possible in “windows” (both natural and made by a fisherman), and it is often most convenient to do this from a boat.

Photo 10. Yellow egg capsule. Grows in deep places. Tench loves the pulp, which is hidden under the skin of its stems. Well, the shadow under the continuous carpets of water lily leaves also attracts him.

Photo 11. Urut. Another delicacy of tench, which other fish do not disdain.
All of the above herbs for tench are not only a feeding place and shelter, but also a spawning ground - this is their special importance.
Now is the time to study the plants from which tench shy away like the Japanese plague. And the reason for this behavior is the repellents with which these plants generously flavor the water around them. It seems to be for protective purposes. But in reality - probably to leave the fisherman without a catch.
Plants that repel tench

Photo 12. Common arrowhead. In places where it grows massively, catching tench will most likely be a waste of time. And all because arrowhead releases tannins into the water. It’s better to walk further along the bank and look for more promising areas where this grass is not present.

Photo 13. Canadian Elodea. She is also the “plague”, she is also “infection”, she is also “American gift”. Originally from North America. Previously, it did not exist, but now thickets of this rapidly growing rubbish clog rivers and ponds, disturbing rafters and fishermen. Say thank you to the fool who released it on our territory. Lin apparently already said it. Avoids elodea thickets in every possible way. Just like other fish.

Photo 14. And here is finally the hornwort. The third plant from the “black list”. Produces tannins that are extremely unpleasant for fish. Well, at least it doesn’t seem like it’s making horns out of the water...
In stagnant reservoirs, the presence of repellent plants clearly indicates that there is no tench in the places where they grow, but this is not yet a sign of its complete absence in these reservoirs. For even in the most remote pond there will probably be a place quite suitable for tench to live - that’s where it will be.
Other signs
There are fish that, in their preferences, have a lot in common with tench - based on their presence, one can assume whether it is found in a reservoir or not. Based on how close they are to it, they should be ranked on the following scale:
- Golden carp;
- Goldfish;
- Carp;
- Roach;
- Ide (especially on rivers);
- Bream;
- Rudd;
- Perch.
The presence of any of these fish already indicates the likelihood of a tench nearby. But the higher the fish is on the list, the higher this probability is. For example, if crucian carp is caught in a pond (no matter how), then there is also a chance of successfully catching tench.
Now all we have left is field observations. Or even “reconnaissance in force”, during which you can accurately determine whether there is a tench in the reservoir or not.
By the way, when our object of fishing digs into the detritus, it produces characteristic bubbles that are not similar to the bubbles from bream, roach and other fish. They differ primarily in their small size. They usually go in a chain. You can see them near the shore in the evening and morning, and from them you can determine the “fish path”, because the molting feeds, adhering to the “route” it has long chosen.
"Line" river

Photo 15. A leisurely lowland river is one of the places for tench fishing. A sign of a promising place is thickets of semi-aquatic plants along the banks. Author of the photo: Irina Starkova.
In principle, everything that was said for reservoirs is also relevant for rivers. In them, tench also stays in muddy, overgrown areas. These can be quiet and stagnant creeks, branches, bays, even stretches - but with a very slow, barely noticeable current, for example, on leisurely lowland rivers, or where you can feel the pressure from ponds and reservoirs. By the way, the size of the watercourse does not really matter. Tench can be found in both large and small rivers. The main thing is that the depth is at least one and a half to two meters. In general, as fishermen say, tench fishing in pits is very successful.
Another funny nuance is related to the fact that in the river the tench has the opportunity to choose its place, because it can easily move along the riverbed and is not limited by the banks, as in a closed reservoir. It often happens that out of all the typical “linear” areas, it occupies only a couple of the best ones - where the conditions (composition of thickets, influx of fresh water, degree of siltation) are as favorable as possible.
This selectivity of tench is confirmed by one remarkable case, well described in the fishing literature. On one river there were two completely identical, typically “linear” sections. But tench were found in only one of them. As it turned out later, a stream flowed into it, that is, the oxygen regime was a little better. Draw conclusions.
Preparing gear
There is no special gear for catching tench. An ordinary float rod or donkey is enough. The first of them is subject to the same requirements as when catching crucian carp, that is, increased sensitivity. One small “but”: tench by nature is a calm fish, but until it is hooked. Once hooked, it becomes violent and unpredictable, so much so that the carp rests. Therefore, the strength of the tackle , and it should be estimated “with a margin.”
Float rod
The most optimal option, in my opinion, is a relatively long (at least 5 meters) rod with a flexible tip that can absorb the jerks of large fish. The fishing line is at least 0.18 mm. But keep in mind: if a good molt comes down - about 2-4 kilos - it won’t seem like much. And the point here is not even in weight, but in those power jerks with which he will “reward” your tackle and thoroughly test it for strength. Therefore, it is better to take a thicker forest. It is also worth considering the fact that fishing will most likely be carried out in the grass, which means that the probability of a hook increases, as does the probability of pulling out a fish with a “beard” from the “green stuff”.
A light float is desirable, the best options are the time-tested “goose feather”, a bream one is also suitable. Well, of course, you need to properly configure the equipment, ensuring its maximum sensitivity.
Just as in the case of crucian carp, we will have to catch from the bottom. This means that we surround the rig so that it slowly sinks, and the lowest sinker lies at the bottom. The weight of the pod is selected so that if it is torn off from the bottom - the float, which was previously only sticking out of the water a couple of centimeters - will noticeably rise.
It is possible - and works very well - to use a rig with one sinker, if the float's carrying capacity allows it.
As for the hook, a small carp hook will do (like the one used to catch good crucian carp).
Donka or feeder
Bottom tackle is not as sensitive as float tackle, but it is still used for catching tench, and often shows good results. Although, most often, tench is caught on the bottom or feeder as bycatch. For example, none of my acquaintances who are adherents of this method were engaged in special hunting for tench, but floaters did. This is not surprising, given the fact that tench do not hesitate to come close to the shore when feeding. Here it’s really easier to use a “float” than a donkey, which by definition is designed for long casts.
A feeder is still preferable to a donkey hastily constructed from a spinning rod. Firstly, because of the good shock-absorbing characteristics of the rod and better sensitivity, and secondly, because of the feeder, which is an additional attractive factor. What to fill it with will be discussed below when it comes to bait.
A small nuance associated with using a reel with a friction clutch. If there is strong aquatic vegetation in the fishing area, or there are snags, then it is better to tighten the nut so that the line cannot pull the line at all, or can barely release it, and then only at the very peaks of its jerks. Otherwise, the fish will definitely go to strong places and get entangled there.
Side nod (summer jig)
The well-known summer jig tackle (a fishing rod with a side nod) can well be used for catching tench; moreover, it can show very interesting results, because it attracts fish not only with the smell of the bait, but also with the play of the jig.
You can use any jig - from a banal “pellet” to an “ant”. Preferably a dull color. The game is played at the bottom - no higher than 5-10 cm from it - in gaps of aquatic vegetation. The movements of the jig are smooth, slow, and don’t forget about good pauses. Pieces of worms, bloodworms or maggots are used as bait.
Is it possible to catch tench using a classic baitless bait with beads? I believe that quite well, because the same crucian carp takes it very well. Why is his tench worse?
As for jig fishing, it’s very tempting in theory, but in practice it’s quite difficult because of the thickets of grass.
Other equipment
a landing net , but not at all because tench is a fish of “increased sliminess.” At the end of fishing - when the fisherman begins to pick it up - he can suddenly “jump” and get off, or even break the line altogether. There are many such cases known.
It’s funny: the moulting grandfather I mentioned at the beginning of this story did not use a landing net. But his hand was full of many decades of fishing experience - the fish “stuck to it.”
Next come useful, but perhaps not entirely necessary elements.
Rake. They are useful for clearing fishing spots from underwater vegetation, but this is for the case if fishing in a reservoir is expected to be regular.
Boat. It will significantly increase the mobility of the fisherman; it will also make it easier to clear a window in the thickets.
The rest - a seat , " fishing rods ", a fish tank , etc. - is at the choice of the fisherman.
Tench fishing techniques and tactics
- To begin with, it is advisable to locate the place of fatting; if clusters of small bubbles appear on the surface of the water, it means that tench has arrived.
- Its location can also be determined by ear; when it licks larvae from algae, a characteristic smacking sound is heard.
- The most popular baits: crawlers, shell meat, worms, maggots, bloodworms, chafer larvae. Vegetable: peas, semolina porridge, corn. Don't forget the bait: chopped worms, shell meat, crackers or bran.
- You can’t talk loudly on the shore, stomp, cast a shadow on the water, or noisily struggle with hooks.
- The bite can sometimes last up to 10 minutes. At first, the float simply twitches and it seems that it is about to go under water. But this doesn’t happen, he just tries it out. Then everything calms down, and after 30–40 seconds it repeats again, and so on several times in a row. When the tench finally decides to grab the bait, you need not to yawn and make a sharp hook.
- If hunting is carried out from the shore, clear a path in the seaweed for fishing in advance.
Selection of baits depending on the season
Seasonal characteristics of tench should be taken into account when choosing bait:
- spring. You will have to determine whether tench bite in April in your region experimentally, using animal bait. If the period when tench bite in the spring falls in April (typical for an average climate), it is better to use all kinds of insects, snails, worms and leeches. After a series of unsuccessful fishing trips, the angler has a question about what tench bites in May, it’s all about including plant foods in the diet;
- summer. It’s easy to find out what tench bite on in the summer, just by taking with you several different baits: peas, dough, potatoes, worms, leeches. Sometimes prey bites exclusively on plant baits. In reservoirs crowded by fishermen, tench tend to feed on only one bait and may not respond to others at all;
- autumn. As it gets colder, the fish go to a depth of about 3-4 m. There are practically no temperature fluctuations in the water column. Now fishing is less effective, but still possible using leeches, worms, maggots and various artificial baits with flavors. The bite is more likely to be successful during warmer weather. It is impossible to catch the desired prey when the temperature drops to 10°C or on days with strong winds;
- winter. In winter, the tench sleeps; the only chance to catch it is to wait for a thaw. In warm winters, fishing is possible with autumn baits; bloodworms are best.
Read more
How and what to catch rudd?
Catching tench in the spring with a float rod is the most promising and easiest way of fishing.
Tips and tricks
Basic recommendations and useful tips:
- If there is no bite for a long time, try an effective remedy : cut out a small piece of grass along with the turf, put 3-4 worms or maggots there, wait until they dig in there and use the bait for its intended purpose.
- To prevent maggots from turning into pupae in hot weather , wrap the container with wet rags.
- If you plan to fish on a sticky, swampy bottom , where the hook and bait can be immediately absorbed by quagmire or silt, we recommend attaching a small piece of foam plastic painted in any dark color 3–5 cm from the hook.
- At first, you can feed in large portions so as not to make any more noise.
- Tench never stay in one place for a long time; even a small pressure drop or a change in wind leads to the cessation of fishing, even in a place that has been fed for a long time.
Making lures for tench
Fishing stores have a large number of different baits for tench, but they are not suitable for every fish. Self-made bait has a number of advantages:
- meets the individual requirements of a line or pond;
- does not contain an unpleasant odor or color for tench.
Bait composition:
- plant and animal additives;
- flavorings, preferably natural ones.
Important advice: bait for tench should only be fresh, otherwise there will be no fishing.
Methods for making bait:
- mix boiled millet, bran and worms;
- mix sunflower cake with dung worms;
- mix sunflower cake, crackers and maggots or bloodworms;
- mix fish and bread flour, hemp oil and red worms (you can use yellow or maggots). An important point is that you need to fry this flour a little in advance in a dry frying pan until it turns brownish.
To flavor baits, it is more advisable to use natural animal and plant odors.
The best flavors for tench:
- cumin seeds;
- coriander;
- cocoa powder.
Important advice: you must first fry the plant seeds and then grind them.
Extensive use of aromatization is not required, since tench are a finicky nature and too much aromas can have the opposite effect.











