Rod selection
The float fishing rod currently has 4 varieties - fly rod, match rod, Bolognese rod, and plug rod. Each of them has its pros and cons and is successfully used to catch bream in certain conditions.
Fly fishing rod
It is a telescopic rod without guide rings and a reel. All equipment is attached to the thin and sensitive tip using a special connector.
It is used most often when fishing from the shore in still water or slow currents.
Advantages:
Lightness of gear - when fishing with a fly rod, you can use fairly long rods, and their weight will be significantly less compared to analogues of other varieties.
The use of thin and strong fishing lines and sensitive equipment - when fishing on the fly, the fishing line does not pass through a series of guide rings, gradually wearing out from friction against their surface. In addition, when float fishing with the same Bolognese or match fishing rod, thin fishing lines are very damaged when repeatedly winding the reel onto the drum, which, due to the absence of such in the fly tackle, does not happen. Based on this, the swing allows you to fish with thin fishing lines with a cross-section of 0.12 mm, while equipping the fishing rod with a very sensitive float with low load and a small hook.
Quick change of equipment - fly gear allows you to very quickly change one equipment for another pre-prepared and wound on a reel.
Reasonable price - due to the absence of rings and a reel seat, such rods have a lower price than other varieties.
Flaws:
It unfolds and folds somewhat slower - winding the equipment from the reel when unfolding the fishing rod and winding it back when folding is much slower than in versions with a reel.
It is mandatory to use a landing net when float fishing for large fish - blind rigging does not make it possible, as in the case of Bolognese or match, to shorten the line by winding the reel when landing large fish, which dictates the need to use a landing net.
Match tackle
Match rods are durable plug-in rods, consisting of 3 elbows, with frequently spaced guide rings and a comfortable cork handle. This rod is equipped with a special high-speed spinning reel that has a shallow depth - this allows you to wind thin fishing line on it, filling the spool completely, which makes it easy to pull off when casting. This gear is used for fishing over long distances, both in still water and in weak currents.
Advantages:
- The ability to make long casts to places remote from the shore.
- Thanks to the rigid and durable rod with frequently spaced guides, it allows you to catch large fish.
Flaws:
Match fishing rods are quite expensive.
This type of tackle is not suitable for fishing on small rivers and small ponds, being inferior in lightness and sensitivity to a more compact and lightweight fly rod.
Bologna rod

The Bologna float fishing rod is the most common telescopic fishing rod with guide rings. Reels for such tackle can be installed both cheaply with a small drum and a simple stopper, and more reliable small inertia-free ones. This type of gear is used everywhere – it is used for fishing both on rivers and on lakes and reservoirs.
Advantages:
- Versatility - thanks to a fairly light rod and running equipment (the presence of guide rings and a reel), such tackle can be used when fishing with a float, both in still water and in the current during the retrieve.
- The ability to make fairly long casts when using heavy equipment.
- Quick disassembly and assembly of the tackle - when unrolling, a large amount of fishing line comes off the reel and the rod unclamps very quickly. When assembling the fishing line, the rod folds just as quickly, and the fishing line is quickly wound up with a reel.
Flaws:
- Compared to a light fly rod, a Bolognese fishing rod weighs more due to the presence of reel guide rings, which can tire the angler’s hand when fishing with a fly line.
- The reel and rings create additional load on the fishing line , which does not allow the use of thin monofilament fishing lines when fishing with a Bolognese fishing rod
Plug tackle

Plug tackle is a fishing rod consisting of a main part and end caps (whales) attached to it. The knees of the main rod are connected to each other in such a way that each subsequent knee fits onto the previous one; The lower part of the end cap also fits onto the last knee of the main form, while the larger part of the end cap has a more familiar telescopic connection of the knees.
The length of any individual plug rod, unlike Bolognese, fly and match rods, can increase with the number of ends and vary from 12 to 20 meters. All equipment of short length is fastened to the tip, as in the fly tackle. Plug tackle is used when fishing with a float, both in the current and in still water at distances determined by the total length of the assembled rod.
Advantages:
- The ability to fish promising places remote from the shore , measure the depth in them and, using a portable feeder, accurately feed this place.
- Using thin lines and light rigs.
- High sensitivity of the tackle - the equipment in the plug rod is short, thanks to this, a small piece of fishing line located on the surface sails weakly, without contact with water, and does not cling to aquatic vegetation
Flaws:
- The high cost of the gear and its low prevalence - plug rods are more expensive than all other types of float rods, and besides, you can’t find such gear in any fishing store.
- The need for a large number of devices - sliding racks, holders for limit switches, inconvenience in transporting them in the absence of a car
- Large weight – the mass of the assembled plug is quite sensitive.
- The fragility of the main rod and end rods - strong and flexible rods are often damaged by pinpoint impacts on branches or trunks of coastal trees.
- Inconveniences during transportation and fishing - long plug rods are very large and take up a lot of space when transporting them; When fishing with a float, very often this or that place turns out to be unsuitable due to the lack of space sufficient for maneuvering the rod.
Coil selection
For match and Bolognese float fishing rods, reliable and easy-to-use spinning reels are used. Among the huge variety of models of spinning reels, there are several that have a good reputation:
Shimano Rarenium 3000
Shimano Rarenium 3000.
A lightweight high-speed reel with a small-profile spool with a wear-resistant coating capable of holding up to 120-140 meters of thin fishing line with a cross-section of 0.27-0.25, a durable body made of composite material, 7 bearings making its rotation easy and silent. This model is one of the best for match gear
Mitchell EXX-S 4000.
A very high-speed reel (gear ratio 7.2:1) with a durable body and a spool capable of holding up to 150 meters of thin fishing line with a cross-section of 0.25 mm, equipped with 5 reliable ball bearings. Suitable for both match and Bolognese fishing.
Browning Xitan Master Match 930FD.
A high-speed reel with a capacious spool (up to 150 monofilaments with a cross-section of 0.18 mm) is capable of reeling out 110 cm of fishing line in one turn of the handle, equipped with a reliable carbon clutch, 9 ball bearings in the spool rotation mechanism and 1 in the line guide. The reel comes with two types of handles - double and single.
Equipment
In rigging for bream, each element, from line to hook, is of great importance. Properly assembled equipment is half the key to success when catching bream on a float.
Float selection
- Floats for crucian carp
When fishing with a fly rod and a plug rod, it is best to use light drop-shaped floats with a thin and long antenna with a weight of 0.5-1 grams. - For the Bolognese fishing rod, spindle-shaped floats with a long antenna float and a weight of 2 to 3.5-4 grams are suitable.
- For match gear, a variety of floats specially designed for it are used with a massive body, a length and an antenna clearly visible from a long distance, and its own weight attached to the bottom of the float body.
Loading
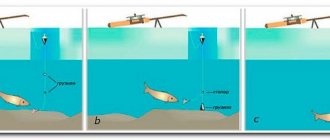
The load of floats when fishing for bream with a float rod varies depending on which of the varieties described above will be used.
Fly fishing rod
To load the small and sensitive floats of the fly tackle, small pellets are used, carefully attached to the fishing line. At the same time, the load is secured and divided into 3 parts:
- Podpodak - several small pellets weighing 0.1-0.3 grams located near the attachment of the leash to the main fishing line.
- Intermediate weight - a weight consisting of one pellet located at a distance of 15 cm from the under-grazing.
- The main weight - about 60% of the load required to load the float, is located 20-25 cm above the intermediate weight.
Match
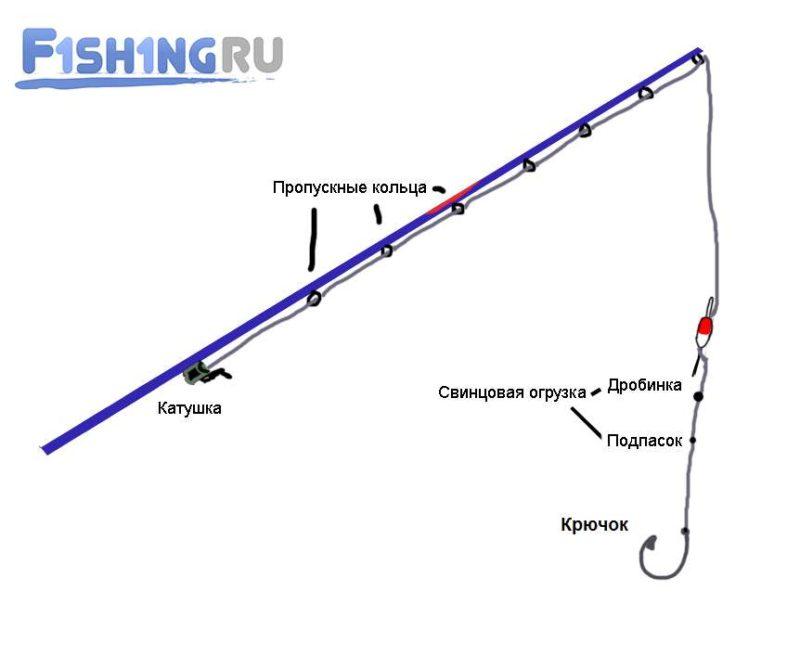
- The main sinker is an olive, the weight of which is selected taking into account the fact that match floats have their own weight built into the body. It is located at a distance equal to the length of the float multiplied by 1.5.
- A sub-shot is a pellet weighing 0.2 grams, located at the junction of the main line and the leash.
Bologna
- Podpodok - small pellets weighing 0.2 grams are placed near the loop for attaching the leash to the main fishing line.
- The intermediate part is several pellets of larger diameter located 20 cm above the under-grazing.
- The main load - 60% of the weight required for loading the float is located 20-25 cm above the intermediate load.
Plug
When fishing with a plug, light, sensitive floats are used. The load pattern for a plug fishing rod is generally similar to that of a fly fishing rod and consists of a main weight, a sub-weight and an intermediate one, which in the case of a plug is usually separated into several parts in order to increase the sensitivity of the tackle when fishing over long distances.
Hook selection
When fishing for bream, hooks are selected according to size, taking into account factors such as:
Weight of the expected fish to be caught - for catching bream and small bream weighing up to 1-1.5 kg, hooks No. 8-10 are used; When catching larger fish, use hooks No. 6-4.
Type of bait used for fishing - long shank hooks No. 10-6 are suitable for worms; when fishing with maggots - No. 10-14; small bloodworms – No. 14-16; when using vegetable baits (corn, dough, porridge), depending on the size of the bait, hooks from small No. 14 to larger No. 8 are used.
Of the hook manufacturers, the following brands are the most popular among bream fishermen:
- Owner
- Gamakatsu
- Drennan

Owner

Gamakatsu (Japan) Drennan
Features of the gear device
Float tackle when fishing for bream should be:
- Light;
- Sensitive;
- Unnoticeable;
- Durable;
- Adapted to certain fishing conditions.
Features of the gear device
Features of the gear design can be characterized by basic concepts that should be adhered to during assembly. These include: selecting the lightest possible version of the fishing rod in combination with its high strength, knitting a sensitive assembly with the smallest inclusions in its composition of elements that are ineffective and have little effect on the fishing process, the use of oversized, unobtrusive tackle, which is most adapted to certain conditions catching Following the above criteria, the fisherman will be able to independently develop a universal mechanism for assembling a bream fishing tool, rational and effective in all areas of its practical application.
Nozzles
Bream is a fish with very wide taste preferences. They catch it both with plant baits and all kinds of bait.
Vegetable origin

- Dough - prepared from loaf crumb, flour and eggs.
- Mastyrka is a porridge made from boiled peas and semolina; This attachment is universal not only for bream but also for all carp fish in freshwater bodies.
- Canned Corn – This attachment is easily available at any grocery store. It stays very firmly on the hook, attracting bream not only with its smell, but also with its golden color.
- Undercooked potatoes - the tubers are boiled to such an extent that they do not fall apart and can be cut into cubes, which are then placed on a hook.
Animal origin
- Worm - used as bait for large dung crawls.
- Bloodworm is the larva of the squeaking mosquito, used when catching bream on a float in early spring. Place bloodworms on small thin hooks, 2-3 pieces each.
- Maggot is the larva of a blowfly; maggots are baited across the body, 3-4 maggots per hook.
- Pearl barley meat is most often used when catching bream on rivers; the softest and most tender part is used in the shell.
Make your own nozzle
In addition to homogeneous baits, bream are often caught using homemade or purchased boilies.
Homemade boilies are prepared using the following technology:
- Grind 100 grams of sunflower seeds in a coffee grinder to a powder.
- Add 30-40 grams of egg powder, 10-15 grams of sugar and wheat flour to the resulting mass.
- Mix the mixture thoroughly.
- Add water to the resulting dry homogeneous powder and knead until it becomes a thick dough.
- Let the dough sit and thicken.
- Roll into balls, boil them in lightly salted water, and dry.
- Place the finished boilies in a plastic bag with sunflower cake and place in the refrigerator for 2-3 days.
Basic food and bait
Ready-made baits can be purchased in specialized stores, but since most people like to prepare them themselves, here is the basic recipe for the mixture: bulk (1 kg), slightly undercooked peas (1 kg), steamed millet (1 kg), dry Hercules flakes (1 cup). They also add additional earth to the mixture (if fishing in shallow waters and slow currents) or clay (if there is a strong current) from 1 to 3 kilograms. The first feeding should make up the majority of the total. After about 40 minutes, you can throw in a little more complementary food, gradually adding it after each fish caught. If possible, try to feed the fishing spot in the evening.
Pleasantly smelling bait will attract bream even more; for this purpose you can use vanilla, coriander or anise, but do not overdo it!
There is a large selection of different baits for catching bream.
All of them are divided depending on their origin into:
- vegetable (used only in summer). You can use barley, semolina with flavoring, mastyrka (corn with peas), steamed peas and canned corn;
- animal origin (used at any time of the year). They often use bloodworms (quickly removed with small change in the summer), maggots, and worms;
When fishing with bait of plant origin, use a leash less than 15 cm, otherwise it should be at least 30 cm.
Try to hold the bait on the bottom for a few seconds, so the bream will react faster.
So, how to catch and with what? Bloodworms, maggots, pearl barley and dough are what suit him best. They can be alternated depending on the bite.
orybalke.com
Lure
When fishing for bream, bait plays a huge role - it attracts cautious and often well-fed fish to the bait. Bait mixture can be bought at a fishing store, but many fishermen prefer homemade bait prepared according to their own proven recipes over commercial bait.
Purchased
Among the store-bought baits, the following mixtures have proven themselves well when catching bream:
Trapper “Leszcz” is a fairly effective and at the same time cheap bream bait used for catching bream and large bream in reservoirs with standing water, as well as in rivers with medium and fast currents.
Sensas 3000 Bremes is a specialized bait for catching bream. It is used in any conditions, both in mixture with other baits and with the addition of clay or sand.
Dunaev BREAM LAKE and Dunaev BREAM RIVER are well-known Russian baits used respectively for catching lake and river bream.

Dunaev BREAM RIVER

Sensas 3000 Bremes

Trapper "Leszcz"
Homemade
Making bait with your own hands is not difficult. Difficulties may arise only when finding some ingredients.
Recipe for fishing in cold water
- Breadcrumbs - 1 part.
- Makukha - 1 part.
- Unsalted fresh lard, cut into 5x5 mm cubes - 0.5 parts.
- Bran - 1 part.
- Boiled pearl barley – 1 part.
- Finely chopped worm or bloodworm - 0.5 parts
- Finely ground coriander - 5 grams.
- Finely sifted soil.
Recipe for bait in warm water
- Breadcrumbs – 1 part.
- Well-roasted sunflower seeds – 0.7 parts.
- Bran - 1 part.
- Millet porridge – 1 part.
- Coriander seeds – 1.5 grams (autumn and spring).
- Vanillin – 2 grams.
Description and food supply
Bream fish is distributed everywhere: from the center of Europe to the north of Russia. Bream leads a schooling lifestyle, living at depths from 2 to 15 m. This representative of the ichthyofauna occupies its niche in both standing and flowing water bodies.
Bream in rivers can be found up to four kilograms, and in large reservoirs this figure rises to five kilograms.
Individuals up to a kilogram are popularly called breams. As a rule, they are the ones present in a fisherman’s catch—small representatives of their species.
In the warm season, bream goes to small areas and feeds there until the onset of cold weather. From mid-October, flocks gradually begin to move to the pits, taking the predator with them. As usual, the shepherd of bream is pike perch. The reason for this amazing phenomenon is still unknown.
The food base of juvenile fish consists of bottom invertebrates, worms, bloodworms and other insect larvae. However, the bream is not averse to feasting on vegetation, in the form of young shoots of hornwort. Having reached a larger body weight, the fish remains faithful to its original diet, but now it includes snails and even juvenile fish.
Choosing a fishing spot
On the river, bream prefers deep-water areas with a slow current near steep banks, reaches with a clayey or sandy-silty hard bottom.
Fishing on the current

When catching bream in the current, it is most often caught from a boat. With this method of fishing, short side rods or a small Bologna 4 meters long with a reliable spinning reel are used. After the boat is anchored in a promising place, a capacious feeder with pre-prepared bait is lowered into the water to attract fish. They fish by retrieving along the stern path formed downstream from the boat. In the summer, pearl barley meat, peas, and canned corn are used as bait; in the spring and autumn, worms, maggots, and bunches of bloodworms are used.
Shore fishing in the current is carried out using long Bolognese or plug gear. The bait is placed in a fine mesh net and thrown from the fishing spot upstream. The baits used are the same as for boat fishing with a float.
Fishing in still water

In still water, catching bream using float gear from the shore is more productive than on the current. Bream are caught at night from bridges, in shallow places near reeds, using luminous attachments on floats and mandatory illumination with a flashlight; at sunset and dawn and during the day, fishing from a boat is more productive. Among the varieties of float fishing rods, when catching bream, light fly and Bolognese fishing rods, as well as long-range matches and plugs are used.
As in the current, a mandatory technique when fishing with a float in still water is the use of bait. But unlike the river, the bait is rolled into clay balls and 3-4 balls are thrown into the fishing spot.
Among the baits used for lake bream fishing on a float in the summer, peas, mastyrka, worms, and canned corn prevail. In spring and autumn, bream are more willing to take on worms, bloodworms, and maggots
Catching bream in March with a float rod

In early March, when the ice on rivers and lakes melts, fishermen rush for bream. At this time, he is more willing to take bait. On the last ice, white fish are caught using winter float tackle and a nod, as well as in open areas using a summer float rod. To attach a fishing rod use:
- large bloodworm;
- red worm;
- maggot;
- semolina mash.
Complementary feeding mixtures attract the attention of bream in March and force it to remain in place for a long time at a depth of two to four meters.
Read also: Everything about bream fishing from A to Z
It is better to fish early in the morning, as soon as the sun rises, because at dusk the fish move away from the shore. You can catch bream at night, but the bite later than eleven in the evening until two in the morning is not always stable. Tackle for bream is chosen with high-quality fishing line, since the fish uses remarkable force while fishing, trying to escape.
Going fishing with Normund. Fishing for bream with a fly rod in March video.
Time to bite
Bream prefers to actively feed at night - at this time, schools leave the depths and go to muddy shallows with rich aquatic vegetation.
At dawn, bream leaves the shallows and moves to the dumps; when the sun rises high, the water begins to warm up, schools of bream return back to the depth where they remain passive until sunset, when a new migration to the feeding place begins. Such movements are typical for sunny and hot days. In cloudy weather, bream can go out to feed in the middle of the day, and in windy weather, bream is often caught near the surf shore, where the fish come to feed on living creatures washed out of the ground by a strong wave. In autumn, when the water temperature drops, this cyclic schedule is disrupted and bream almost all the time stands and feeds at great depths.
Fishing in spring
March
In March, bream is caught from the ice using a jig and a winter float rod in the morning, 1-2 hours after sunrise.
Night fishing for bream in pits and on riverbed edges using float winter fishing rods is productive - fish take from midnight until 4 am. The main attachment at this time is the bloodworm. Feeding when fishing for bream at this time is mandatory.
April
In April, bream are caught on the edges of adjacent holes bordering extensive shallows.
The best tackle for catching bream on a float at this time is a match or plug tackle. Bream is caught in April using a worm, maggot, less actively, but it still takes bloodworms. They feed the fishing spots in small portions. The bait must contain chopped worms and bloodworms. Flavorings are used in small quantities due to the low water temperature.
May
In May, bream leaves for spring spawning in shallow floods, backwaters and old areas with flooded thickets of aquatic vegetation. Medium-sized individuals spawn first, then large breams and last - small breams.
Bream is caught at this time near spawning grounds in old fish and backwaters on shallows remote from the shore and extending into the depths with thickets of aquatic vegetation; at the mouths of rivers flowing into lakes, at reservoir dams. The best tackle in May are match and plug float rods. Among the baits, along with bloodworms, worms and maggots, bream begins to actively peck on mastyrka, canned corn, steamed pearl barley, and peas. Bait is a must; as the water temperature increases, you can add more flavorings and components of plant origin - bran, cake, finely ground sunflower seeds
Fishing in summer
June
In the post-spawning period, bream most often feeds for some time near the spawning grounds, and then rolls down to their summer camps - holes, riverbed ledges. In June, bream switches to its usual cyclical feeding, in which it spends most of the day at depth, and comes out to feed only at dusk. first on the edges of the pits, and then at nightfall on the shallows. On cloudy days, fish can come out to the shallows during the day. In June they catch bream not only with a plug and match rod, but also with a fly rod and a Bolognese rod.
They feed promising areas in small portions. The content of flavorings in the bait is increased, the content of ingredients of animal origin is reduced
The main baits at this time are mastyrka, steamed pearl barley, and undercooked new potatoes. On the rivers, bream takes well for pearl barley meat and dung worms.
July
In the hottest month of summer, bream becomes lethargic and inactive, stands in deep holes most of the day, and begins to come out to feed in the evening when the heat subsides.
The best bite in July occurs in the early morning, until the sun begins to heat the water that has cooled overnight. Bream is caught best in the morning near holes, in shallow waters; the evening and night bite is somewhat worse
The main baits are mastyrka, peas, canned corn, a sandwich of bloodworms and maggots. Groundbait is a standard mixture for warm water, consisting of plant ingredients.
August
In August, bream begins to feed heavily at night. The most promising places for night and morning fishing are the upper edges of the holes, bays with a depth of 2-3 meters with reed thickets and water lilies. Among the gear, the same variety remains - all types of float fishing rods are applicable.
Baiting tips: canned corn, pearl barley, peas. During this month, bream begins to fish more readily for worms, maggots, and barley meat.
Be sure to use bait.
Fishing in autumn
September
In September, bream begin to gather in large schools and actively feed, preparing for the winter. It is caught in the first autumn month in its feeding areas - on the upper edges of holes, grassy shallows.
Bream feeds at this time much longer than in summer - the morning bite usually lasts until noon. Among the baits, worms, maggots, and bloodworms begin to prevail.
They begin to use ingredients of animal origin in the bait, and as the water temperature drops, the content of flavors is reduced.
October
In mid-autumn, bream prefers to occupy areas of medium depth in schools, well warmed by the sun. When it gets colder, flocks immediately go to wintering pits, where they remain until freeze-up. Bream is caught in October close to the upper edges of the holes, in the above-described areas with medium depths. At this time, night bream fishing is most productive.
The main baits are worm, maggot, bloodworm.
November
In the last autumn month, the bream moves to deep wintering holes, where it stays until the onset of a steady cooling of the water. At this time, bream feeds near holes, at great depths, and does not go to the shallows.
Feeding time is from 10 am to 1 pm. It is caught exclusively with worms, maggots and bloodworms. Among the float tackles best suited for catching bream in November are match and plug fishing rods.
Where and when is the best time to fish?
Fish such as bream and bream live in reservoirs with a sandy or clay bottom. They hide mainly in quiet and deep places with sufficient oxygen content. Consequently, in muddy bodies of water, where there is a fast current and a rocky bottom, it is impossible to catch such representatives.
When the water warms up to 18-23 degrees, you can safely go for prey.
Therefore, catching bream in the summer with a float rod is the best time:
- bream fishing in June. Shallow spawning grounds make it possible to catch large fish in early summer. However, as the weather gets hotter, it becomes increasingly difficult to get a good bite on the shore;
- bream fishing in July. At this time, the fish hides in aquatic plants at great depths. She should be fed generously. With daily feeding, the bream remembers certain points in the reservoir and approaches such shores in the mornings and evenings; the rest of the time it hides in the depths.
Considering the weather, it is best to go fishing for bream on the eve of a thunderstorm. For example, when you fish for an hour before a thunderstorm, the catch will be more than what you can catch during the week in the same place.
If the reservoir is calm, fishing is unlikely to be successful, but the fish will be able to freely feast on your feeding.
Fishing process
IN
When fishing for bream, keep silence, do not re-cast the tackle unnecessarily, avoid sharp and loud claps of the rod on the water - bream is a sensitive and very cautious fish, noise scares it away.
The bait should be thrown exactly into the place where the fishing will be carried out and wait a while so that the fish begin to gather around the turbidity formed in the water from the collapsing bait ball.
Bream bites are neat and sometimes unnoticeable - you should hook only after the float confidently moves to the side or, having emerged, lies on its side.
The hook should be sharp, but not sweeping - a strong jerk can tear the fish’s lips.
Fishing technique
The hooked bream very actively resists for some time, not allowing the angler to pull itself to the shore or boat. This does not last, as a rule, very long, and the fatal mistake during this short onslaught of fish is the angler’s stubborn desire to pull out the hooked bream as soon as possible.
Pulling it too quickly towards the shore can lead to the fact that the weak lips of the fish cannot stand it and the bream gets away. Usually, large fish are allowed to “walk” on the line for some time, without allowing them to go into the thickets of water lilies, coastal snags, or under the boat when fishing from it, and then, when the pressure of the fish subsides, they begin to smoothly pull the fish towards them. Usually, even the largest bream, having appeared on the surface and taking a breath of air, lies on its side and goes into the fisherman’s hands without resistance. Large bream are removed from the water using a landing net.
Bream baits
Anglers do not have a consensus on the best bream bait. Picky fish often change their tastes depending on the season of the year, weather conditions and the food supply in the reservoir. When fishing, you need to take bait, both animal and plant origin.
- Bloodworms are considered a favorite treat for bream. The bait is especially effective in cool water in the spring and fall. In summer, bloodworms are quickly removed by small change.
- One of the universal baits is maggot. The bait is good because it does not lose its properties after biting small things.
- The classic animal bait for bream is a worm. It is used from spring to late autumn, bringing the angler trophy fish.
The vegetable menu of bream has a richer assortment. But these attachments only work in warm water.
- An effective bait for bream is steamed pearl barley. The grains hold well on the hook, allowing you to make long casts with a match fishing rod.
- Semolina is very popular among bream fishermen. The bait does not become limp in the water and stays securely on the hook. Various flavorings can be added to semolina.
- Of the numerous types of dough, mastyrka shows the best result. Bream are attracted to bait based on corn or peas.
- Steamed peas are good not only as bait, but also as bait or bait. Thanks to this bait, it is possible to cut off bites from small fish.
- You can hunt for trophy fish with canned corn. Bream are attracted to the bright color and sweet taste of the soft grains.