Probably, any experienced aquarist will agree with the opinion that it is best to feed the fish with bloodworms or other live food. This ensures excellent health and well-being of the aquarium inhabitants. But here a problem arises. In the warm season, bloodworms can be washed in many reservoirs with standing water. But what about in winter? Fortunately, knowing how to breed bloodworms at home, you can provide the inhabitants of the aquarium with almost any amount of food, and also sell the excess, making a significant profit.
Why do you need bloodworms?
Of course, the most obvious use of mosquito larvae is feeding aquarium fish. Bloodworms contain all the substances necessary for successful and rapid development. Depending on the size, you can feed it to both juvenile and adult fish. With the constant presence of live food in the diet, the fish become larger and the color becomes more saturated. Various diseases, including curvature of the spine in females of viviparous breeds after childbirth, if not completely excluded, are at least reduced in number.
However, breeding worms and bloodworms at home can also be useful for fishing. Mosquito larvae are an excellent bait for many types of fish: roach, bream, perch, bleak and a number of others. However, only large bloodworms are suitable for this. Small ones can be used for feeding - just throw a pinch of larvae into the hole when ice fishing to ensure maximum attention from the fish.
Fishing for bloodworms, how to bait correctly
For ease of installation, the thinnest hook is used. On the other hand, the barb of the hook should not be too sharp to prevent the caught fish from falling off and losing the bait. A large point will severely injure live bait, which can leak out before it hits the ice hole. For a good bite and successful fishing, you need to master the technique of hooking bloodworms.
Standard method
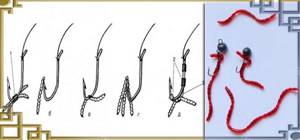
Experienced fishermen know how to properly put a bloodworm on a jig. The simplest method is to place a mosquito larva on the point of a hook between the head and another part of the body. This technique allows you to attach not only one bait, but also a whole garland. Preferred for catching fish that hunt dangling bait. When the bite is sluggish, it is advisable to mask the tip of the hook.

Bundle attachment
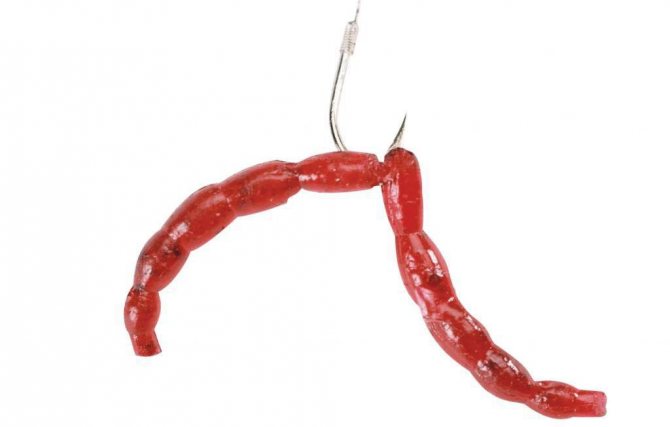
Used for catching large predatory fish. What is the most convenient way to attach a bloodworm to a jig? To do this, take a whole bunch of red worms, in the amount of 3-5 pieces, and tighten them with a rubber ring cut from the bicycle nipple. After this, all this “offal” is easily attached to a hook of any size.
Predatory fish, like bream, readily bite on this bait, which is easily replaced with a new bunch. The gum, after removing the fish, is usually preserved. You can even prepare the simplest devices for assembling beams.
The device consists of a transparent cylindrical body of a ballpoint pen. One edge of it is cut at an angle, creating a kind of small scoop. A rubber ring is placed above the cut. After this, a bunch of bloodworms is inserted into the cut, onto which a rubber ring is rolled. The result is a quick and high-quality bait that is ready for use.
Stocking
This baiting method is used for catching small fish. In this case, the body of the bloodworm is placed near the head on the hook of the jig, and carefully strung towards the tail, not reaching the end.
The hanging body must be of minimal size. It should not be pierced with a point. Experience shows that during the bite, the fish has no choice but to swallow the bait whole with the hook.
Sports
The method of attaching bloodworms to a jig is used in sport fishing for quick bait. Brings good results when catching fish of any size. The larva needs to be planted approximately in the middle of the body, at the level of 5-6 segments, but not pierced through. Then move the sting inside the body, shallowly towards the head or tail.

Per head
A bait mounted on a jig behind the head is used most effectively for fishing. To do this, the hook is clamped between the thumb and index fingers, with the tip facing upward. Using the fingers of the other hand, the bloodworm is placed just below the head. In this case, the hook's tip moves into the head, but does not pierce it. The method is effective and suitable for ordinary bait.
ring
How to put bloodworms on a jig when the bite is bad? In this case, it is recommended to bait the larva using the “ring” method. The hook pierces the body of the worm right through the neck area. After this, the tail is threaded onto the sting, starting from the tip. The result is a ring-shaped bait, useful for sluggish biting.
By the belt
To catch perch, roach or bleak, a method of baiting a jig for bloodworms, called “by the belt,” is used. In this case, the red mosquito larva is pierced through the middle with the hook. The head and tail hang down at the edges. For some reason, this combination causes an increased appetite of the prey even with a poor bite.
Bloodworm species
Before figuring out how to breed bloodworms at home, it will be useful to know what they can be like. Usually the species is determined by the size of the larvae - otherwise you need to study them for a long time and painstakingly under a microscope, looking for differences known only to highly specialized experts.
Let's start small - the larvae grow no more than 10 millimeters. They usually live at the bottom of rivers with weak currents, in backwaters.

Estuary – larger. It is found in shallow bays, mainly in the southern regions of our country. The sludge here contains a large amount of organic substances necessary for the nutrition of large larvae.
Large (also known as attachment) – larvae of the mosquito-jerk. It is almost never found in rivers and other bodies of water with flowing currents. It usually lives in the mud of ponds, lakes and long-standing puddles. An excellent choice not only for large and aggressive aquarium fish, but also for fishing.
What is a bloodworm?
Many fishermen and nature lovers know that bloodworms are mosquito larvae. Just not that biting insect that spoils a person’s outdoor recreation in the summer, but the harmless jerk mosquito of the chironomidae family. These mosquitoes always live close to water, where they lay eggs, from which one day red larvae look like small worms.
Variety of larvae
In general, there are more than five hundred species of mosquito larvae in nature. Mainly three types are used as bait and groundbait: small bloodworms, large ones and estuary ones.
Small and large bloodworms live everywhere in freshwater bodies. Large larvae can be somewhat more difficult to obtain; they live in heavily swampy rivers and lakes.
Limannik does not have a fixed size; there are both small individuals with a size of 2-3 mm, and quite large ones. It differs from other species in its saltiness, as it lives in the estuaries of the seas. The larvae got their name from their place of residence.
Bloodworms feed on small organic matter. Eats food of plant and animal origin, willingly gathers for carrion.
Fishing use
You can catch almost any freshwater fish with bloodworms that is at least somehow interested in animal food.
Recommended reading: Baits for carp
The best time to fish for bloodworms is autumn, winter and spring. Even in summer, especially on cool days, roach, small bream, crucian carp and many other fish bite well on such a bait. Bloodworms are often used in fishing methods such as feeder fishing, summer and winter fishing rods.
Creating optimal conditions
Before you start breeding bloodworms at home, you need to make sure that the living conditions are normal. Otherwise, all your efforts may be wasted.
You should start with temperature. The optimal range is considered to be from 13 to 20 degrees Celsius. In such conditions, the larvae develop most intensively and retain their beautiful appearance, which is especially important in cases where bloodworms are raised for sale.
It can be grown at other temperatures, but this will have negative consequences. For example, if the room is colder, the development of the larvae is much slower (in general, bloodworms can withstand even short-term freezing without harm to themselves). And if the room is too warm, the bloodworm gets a thin, delicate shell. This not only makes the hooking process more difficult, but also reduces shelf life.

The next important factor is humidity. Some experts believe that this is not an important circumstance and can be ignored. But others claim that bloodworms develop better if the air humidity in the room is about 70%.
Technique for planting bloodworms
Insect larvae are a rather delicate product, sometimes they are smeared directly on the fingers. To keep the bait intact on the hook and make it appetizing to the fish, you should attach it correctly. There are the following options for placing bait:
- Hanging fresh bloodworm.
- Dressing the larva across.
- Impaling with a stocking or ring.
- Engaging baits with a beam.
The first method is used when fishing for medium-sized perches. The nozzle is placed on the finger and pierced with your free hand near the head so that the bloodworm hangs from the hook tip in the form of a thread. There is no need to hide the point, since it does not interfere with the fish. A correctly hooked larva remains viable in water for 8-10 minutes, after which it is advisable to replace it.
When fishing for roach, the bait is hooked across the sting. To do this, the bait is pierced not near the head, but in the middle. In the water column, a bait placed in this way makes oscillatory movements with both ends, attracting hungry fish.
In its natural environment, the bloodworm curls up into a ring. In this position, the inhabitants of the underwater world find him. To make the bait on the hook look just as natural, it is taken by the back and pierced with a sting, forming a small ring. In a reservoir, such bait moves well, and it is more difficult for fish to pick it off.
The method of putting on a stocking is that the tip is inserted in the area of the head, but is not pushed out, but is pushed onto the sting with light turns until the end of the tail. The advantage of this method is that the fish will not be able to pull the bloodworm with impunity.
To learn more:
Shitik in the house: caddis larvae as catchable bait
The technique of putting on larvae in a bunch is used in cases where bites from large individuals are expected. Several bloodworms are taken out of the bait storage container (for perch and roach 2-3 are enough, in the hope of catching bream you can use up to a dozen) and put them on the hook by the head. The advantage of this method is that a bunch of larvae release more juice and attract bottom inhabitants faster.

We receive the first batch of bloodworms
First you need to take a sufficient amount of sludge. This is done simply - dirt from the bottom is collected from the nearest body of water (lake or river), which is washed through a fine sieve. As a result, the smallest particles of sludge pass through, while large debris remains in the sieve. The sludge is drained into suitable containers and the garbage is thrown away. The more sludge there is, the better.

The best containers for growing are baking trays about 5-7 centimeters high. Moreover, experts recommend painting them yellow - for some reason it attracts mosquitoes. The sludge is placed in baking trays in a layer of about 2 centimeters. Water is also poured here - no more than 3 centimeters. These baking sheets are left outside (in the warm season, of course) in a place where mosquitoes live. Ideally, the cottage is located near slow-flowing rivers, ponds or even swamps. In a word, the place should be mosquito-proof. The main thing is to place the baking sheets in such a way that they are in the shade at all times. In the sun they will overheat, which will lead to the death of the larvae.
After 3-4 days, there will be a sufficient number of clutches of mosquito eggs in the water. You can continue working.
How to get bloodworms
The largest number of mosquito larvae in the natural environment can be found in the silt of lakes and ponds, abundantly overgrown with bottom vegetation. They are also found in flowing bodies of water. Having determined the habitat, it is easy to wash bait for fish yourself.
The easiest way to do this is to use a fine sieve in which the bottom silt is rinsed. The soil is carried away with the water, and the larvae remain on the sieve. They are easy to collect with a fine-mesh net. Getting bloodworms will not be an insurmountable problem if you use a fork with a long handle and a thin metal wire wound around the teeth. It is tied with horizontal lines at intervals of 6-7 centimeters. By raking the constructed device along the bottom of the reservoir, you can easily catch mosquito larvae.
To learn more:
Vobla - what kind of fish, description and way of life
The third method of extraction is even simpler - the silt is scooped up with a bucket and placed near a hot fire. Feeling the warmth, the bloodworm will float to the surface from which it is collected with a net.
The slowest, but quite effective method of obtaining larvae is to lower pieces of meat or fish wrapped in a gauze bag and loaded with heavy cobblestones to the bottom of the reservoir. In about a day, the trap will have a lot of bait.
How to wash bloodworms is up to each hunter to decide for himself. And to separate small specimens from large ones, just put them in a fine sieve and lower them into a container of water. Large prey will remain on the mesh, and small fry will leak out along with the liquid.
Growing bloodworms from eggs
In general, the technology for breeding bloodworms is very simple. The baking sheets are carefully transferred indoors so as not to spill. Now you need to wait about 2 days and you can carefully examine the silt. Most likely, you will notice tiny worms moving in the mud. This is the bloodworm. True, it is very small, this is suitable only for the smallest aquarium fish or juveniles. But it's better to wait.

In total, the bloodworm grows for about 3 weeks. At any stage, you may decide that he has already grown up enough. There is no point in delaying it any longer - the larvae will hatch into adults. However, this option is also acceptable - we’ll talk about it a little later.
Tackle for fishing with jig and bloodworm
In ice fishing, everything is important - a comfortable rod, the thickness of the fishing line, the required elasticity of the nod, the weight of the jig, and even the number of bloodworms on the hook. Experienced fishermen advise using the following set of gear:
- a comfortable fishing rod that fits well in the hand - it can be a “balalaika” with a whip length of about 15 cm;
- choose a fishing line that is strong, but not thick - for catching small fish (up to 200 grams), a fishing line with a diameter of 0.1 mm is suitable;
- a sensitive nod is usually 3-6 cm long, always suitable for a specific jig;
- a jig weighing 0.2-0.4 g, which allows you to quite quickly lower the bloodworm to the bottom -
What should I feed him?
In the first stages, the bloodworm will have enough nutrients contained in the sludge. However, not for long. Therefore, over time you will have to feed it. Yeast is best suited for this. They need to be diluted with water, then mixed with sludge and added to the trays at the rate of about 100 grams of yeast per square meter of area. This feeding is enough for 2 weeks. Then you can fertilize again - now dry yeast is used. It is enough to simply pour them out in an even layer over the entire area of the pallet.

Here it is very important not to overdo it - it is better to underfeed the bloodworms, even if this leads to the death of some of the larvae. After all, if you give too much yeast, the water will begin to rot, which will cause the death of all the bloodworms.
Catching bloodworms
When you decide that the larvae have grown enough to be used as food or bait, you can trap them. The process is quite simple. The water in the pan is carefully removed - only sludge remains. It must be carefully transferred to a sieve. The sieve is then lowered into a large basin or small tub and a circular motion is made. The silt, washed away by water, is simply decanted into the water - the selected larvae remain in the sieve. It was for this purpose that the sludge was washed when it was collected from reservoirs - so that the sludge would not have to be dealt with again with excess garbage. The sludge can be returned back to the baking sheets - it will still serve for further cultivation. After all, if you are interested in bloodworm breeding as a business, the flow of production must be continuous.
In such a case, there is no need to remove all the bloodworms from the baking sheets. But you need to cover them on top with gauze or other dense material that allows air to pass through. But you need to provide a certain space, for example, build a small wire frame. Mosquitoes, having emerged from the larvae, fly for a while and, since they cannot fly away, they deposit the larvae directly in the same pans from which they emerged. After this, the process begins again.
Storage
Now you know how to breed bloodworms at home. But you also need to store it correctly, regardless of whether you are going to sell the larvae or keep it for your own needs. This product is perishable - it cannot be stored for a long time, at best a couple of weeks.

Young bloodworms can be stored in a nylon stocking, tightly tied and suspended in a toilet tank - cold running water will ensure good preservation. But make sure that it does not “overripe” and begin to hatch.
Bloodworms can be stored in the refrigerator for some time - only on the bottom shelf, where the temperature is definitely above zero. Place it on wet newspaper and wrap it up. Wrap the resulting package in another 3-5 layers of newspaper to prevent drying out.
If you plan to store bloodworms for a month or more, the only way is freezing. Yes, in this case it will not be possible to keep him alive. But it is still better to feed aquarium fish with dead bloodworms than with dry food.