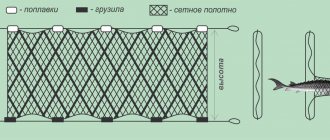
Types of artificial flies
Fishing flies are divided into several main types and can differ in the following parameters:
- size;
- modifications;
- degree of buoyancy;
- used manufacturing materials.
The final result of fishing often depends on the choice of fly.
When choosing a specific fly model, the angler must focus on the type of reservoir and the type of fish that is intended to be caught.
Dry flies
Dry flies are located on the surface film of water during fishing. They are designed to imitate insects that have fallen into the water:
- Zhukov;
- dragonflies;
- horseflies;
- os;
- caterpillars;
- ants;
- adult caddisflies and mayflies.
Materials with positive buoyancy are used to make dry flies. When assembling such baits, small hooks made of thin wire are used.

To increase buoyancy, the imitations are treated with a special spray or liquid (flotant). Use dry flies to catch:
- chub;
- rudd;
- ide;
- bleak;
- trout;
- grayling
Large floating imitations of the “mouse” type are used for fishing lenok and taimen. The fish attacks the dry fly, moving from bottom to top, while seeing only its silhouette. This relieves the fly fisherman of the need to accurately copy the smallest details of the prototype. Much more important is the natural presentation of the bait, which is ensured by correct manipulation of the cord and rod.
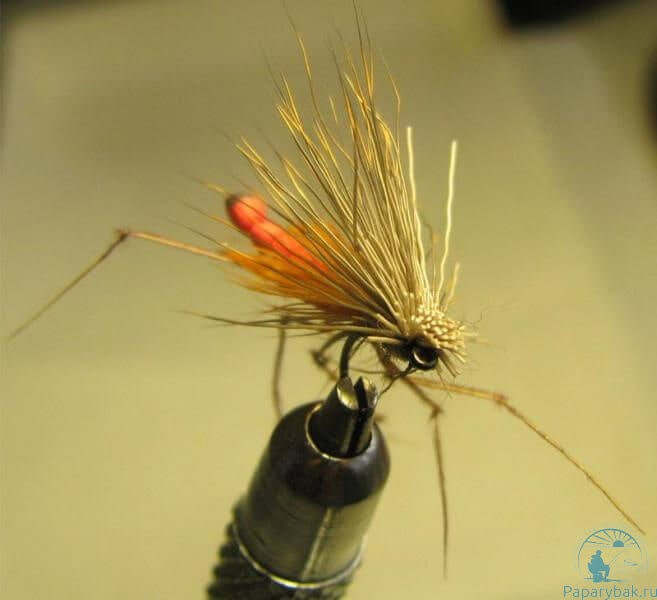

A dry fly that imitates a mosquito often helps when fish activity is low.
Fishing with dry imitations is the most spectacular, since the bite occurs in front of the angler’s eyes. For fishing with such baits, a floating line and undergrowth are used. If the fish is cautious, it is advisable to use a leash with neutral buoyancy, which will be under the surface film of water during the fishing process.
Large dry baits in the form of beetles and cockroaches are often used when fishing with light spinning tackle. In this case, the trophies are usually chub and asp.
Wet flies
Wet fly fishing flies imitate insects that have fallen into the water and choked, slowly sinking into the water column. When making baits of this type, it is important to pay attention to the smallest detail. The resulting imitation should be as similar as possible to its natural prototype. This is due to the fact that before attacking the fish visually studies the fly.
Wet fly types work well throughout the warmer months. They get bitten consistently:
- grayling;
- trout;
- chub;
- roach;
- ide;
- perch;
- rudd.
On a note! For fishing with wet imitations, a floating line is usually used in combination with sinking leaders and leaders.

Wet - so that you would drown
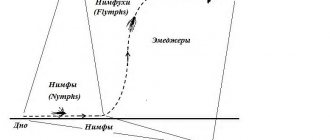
Nymphs
Nymphs imitate aquatic or aerial insect larvae. Fishing with them can be successful throughout the entire period of open water. When fishing with these baits, the fly fisherman's trophies are:
- roach;
- perch;
- ide;
- chub;
- dace;
- grayling;
- trout.
The nymph is usually fed in the bottom layers of water. The most universal bait is considered to be an imitation of a free-living caddisfly larva.
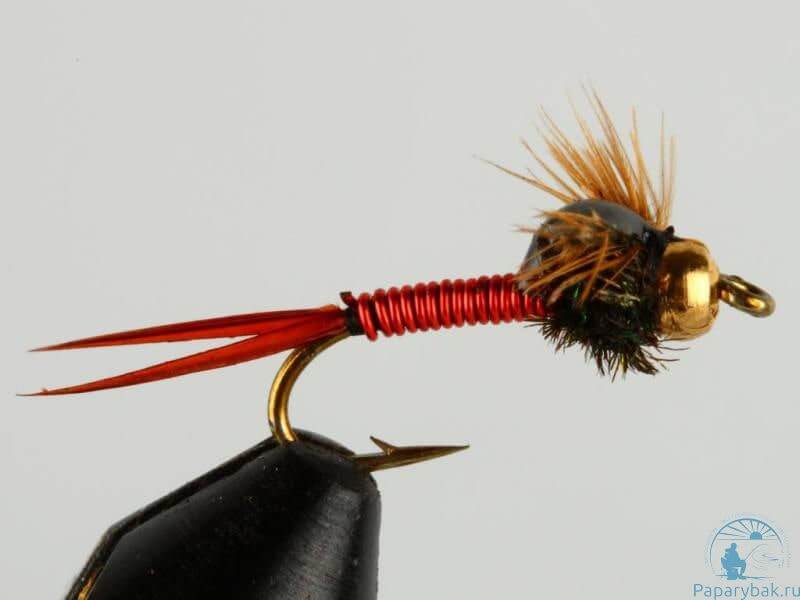

Nymphs with a small body and a tungsten head work well in strong currents.
When fishing for a nymph, a sinking line is often used. The leader and leader must also have negative buoyancy. When making a fly, the fly fisherman should try to give the imitation as natural a look as possible.
Pike streamer
A pike streamer is a large fly 10–15 cm long, imitating a fry. The bait belongs to the sinking class and, depending on the fishing conditions, can be fed in different layers of water. The fly is equipped with 1 or 2 single hooks.
The pike streamer is carried out with sharp pulls of 15–25 cm, which are alternated with short pauses. Bites occur more often when the bait is stopped. When the fish activity is low, a uniform retrieve with smooth swaying of the rod tip works well.
For streamer fishing, fly rods of class 8–10 are used. The degree of buoyancy of the line and undergrowth is selected depending on the depth at the fishing site. To avoid cutting off the bait with sharp pike teeth, you need to include a short metal leash about 10 cm long in the rig.

Pike sinking
Emergers
Emergers imitate a pupa emerging from the water at the stage of transformation into an imago or an adult insect that lays larvae in the water. This type of fly fishing is especially effective in the spring, when there is an active emergence of aeroplankton.
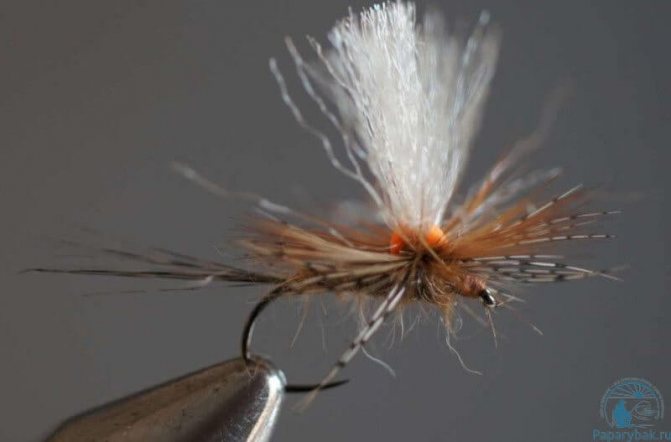

The white tuft of fur at the top of the emerger allows the fly fisherman to visually control the bait when retrieving.
The fly is tied in such a way that its lower part is under water, and the upper part remains on the surface film. The following are successfully caught on emergers:
- chub;
- trout;
- grayling;
- rudd;
- bleak.
When fishing for emergers, correct presentation of the bait is extremely important. To make a fly fishing that attracts fish, the fly fisherman must have an idea of the behavior of a particular insect during the period of leaving the water or laying eggs.
Asp Vabik
The asp wabik can be made in both fly fishing and spinning formats. In the first version, the bait is a classic streamer knitted from goat hair. The fly also has a painted epoxy resin head, as well as additional elements in the form of lurex winding and bright feathers. Fly fishing is carried out in the upper layers of water using a jerk retrieve.
The spinning version of the asp wabik is crocheted on a double or triple hook and is a beard made of goat hair. When fishing in the bottom layers, the bait is mounted on a Cheburashka sinker. If we are talking about fishing near the surface, the fly is tied in front of the spoon on a short leash.

For asp fishing
Small perch flies
Perch flies usually have bright, provocative colors. They can imitate both fry and various insects. For their manufacture use:
- multi-colored beads of bright color;
- Lurex;
- bright mounting thread;
- multi-colored synthetic threads.
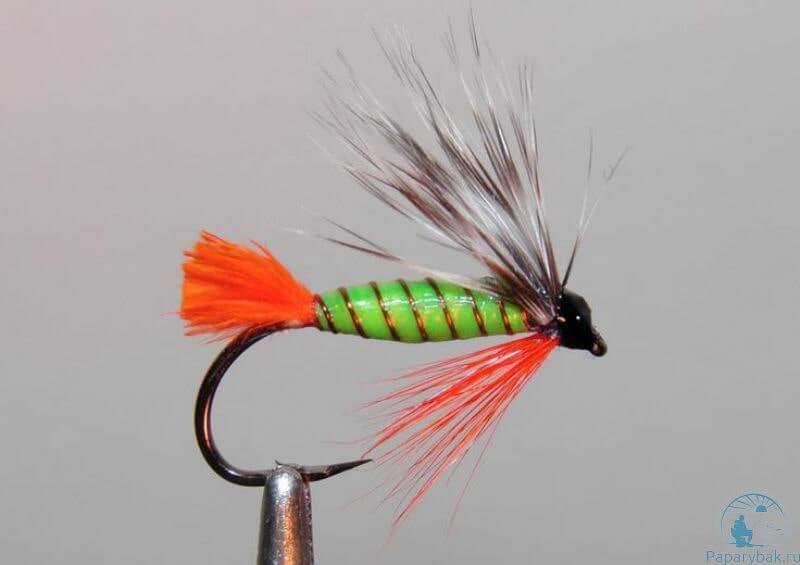

When fly fishing, such baits are used with sharp, short jerks. Perch flies are also used for ice fishing. In this case, they are tied on a short leash, 10–15 cm above the vertical spoon.
Fantasy
Fantasy flies (attractors) do not imitate any insect. They are baits that arouse the interest of fish with their unusual appearance and non-standard behavior when retrieved. The following models are good for catching:
- perch;
- ide;
- chub;
- rudd.
Fantasy group imitations usually have bright colors and are presented in an “aggressive” wiring style. They work better when the fish are active.

Fantastic
Large trout bugs
Large trout bugs work well from May to September, when the predator is actively collecting food from the surface of the water. To make such imitations, they usually use:
- polyurethane foam;
- rubber flagella;
- rooster or pheasant feathers.
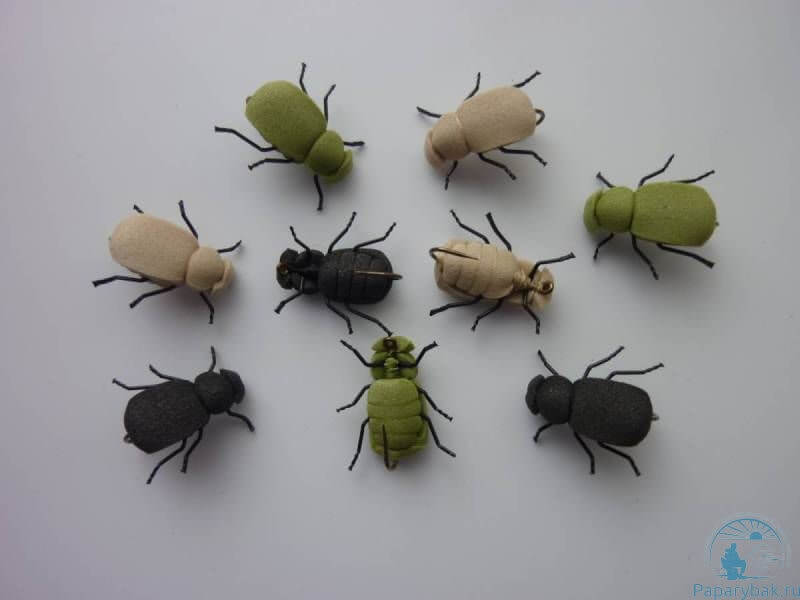

When fishing for trout, the color of the artificial beetle does not play a decisive role. The main thing is that the imitation is clearly visible to the fisherman.
The process of tying a trout bug is quite simple, so even a novice fly fisherman can make such a fly. When fishing, the bait does not require additional animation and simply floats downstream. In addition to trout, chub respond well to this insect imitation.
Spoon fly
Spinner flies are successfully used in spinning fishing. It consists of a crocheted body made of bright elements. A petal from a rotating spoon is attached to the shank of the hook (via a swivel). People willingly bite on this bait:
- perch;
- pike;
- chub;
- ide;
- rudd;
- asp.
The spinner fly can be tied on single, double and triple hooks. The most effective is considered to be uniform wiring with periodic slowdowns.

with petal
"Ant"
The fly called “ant” can be in a sinking or floating version. It is most effective in the summer. For its production the following are used:
- epoxy resin;
- polyurethane foam;
- bird feathers;
- synthetic threads.

This fly works better on forest rivers, along the banks of which coniferous trees grow. When the fish is active, it is easier to catch it with the “Chernobyl ant” bait, which is large in size.
"Fly"
The classic fly is designed to imitate a horsefly or a dung fly that accidentally fell into the water. The model is usually made in a dry version and floats on the surface during fishing.
When retrieving the “fly,” you just need to float it downstream, constantly monitoring so that the speed of the bait does not exceed the speed of the water flow. Floating synthetic materials are used to make this model. The main trophies are chub and rudd.

like real flies
"Mole"
The moth fly also belongs to the group of floating fly fishing lures. It is made from the following materials:
- deer wool;
- synthetic dubbing;
- light feather of a rooster.
“Mol” shows stable results when fishing for grayling in coastal pools. Does not require additional animation.

Moths often fall into the water
"Mayfly"
Mayfly imitation is considered one of the best baits for catching grayling in the spring. It is performed in a dry version and differs:
- thin body made of synthetic dubbing;
- long tail unit;
- voluminous brush in the head part.

Such characteristics allow the bait to remain on the surface for a long time even without treatment with flotants. The fly is crocheted on a thin hook No. 18–16. The coloring of the imitation is dominated by gray and light brown tones.
"Palmer"
“Palmer” is a fly fishing fly that imitates a caterpillar that has fallen into the water. Works well when fishing for lenok and grayling. The bait is distinguished by a thin green dubbing body, as well as many rooster feather hairs, allowing the fly to stay afloat.
If you want to make a sinking version of the “palmer”, a tungsten bead is attached to the head of the fly. The bait works well in the summer months.

What's not a caterpillar
Silk and wool threads for knitting artificial flies
Silk and wool threads of different colors and shades are used to make the body of an artificial fly. You can use natural and synthetic silk threads for embroidery or pull the thread from silk ribbon, braid, or fabric. It is better to first unravel the twisted thread into separate strands, since when knitting in strands, a smoother body is obtained, and the fly retains its shape longer.
Silk threads are stored on spools, separately by color (Fig. 4). Two holes are made in each bobbin, in one of which the end of the thread is attached, and through the second its working part is passed. This design prevents the thread from unraveling when knitting, without requiring special fastening during operation.
For woolen threads, use ordinary knitting wool of different numbers and colors; They are stored in the same way as silk. Before use, the thread is divided into separate strands.
Materials and tools for manufacturing
To make flies, an angler will need a set of specific materials, which include:
- classic and curved hooks;
- wool;
- dabbing;
- polyurethane foam;
- bird feathers;
- mounting thread;
- Lurex;
- glue;
- waterproof varnish.
For some models of flies, classically shaped hooks are suitable, used when fishing on float tackle. To make a nymph or emerger, you will need curved fly hooks to ensure the correct position of the bait in the water.

A fly fisherman must have mounting threads of various colors in his arsenal.
The vast majority of models are made from deer or goat hair. The body of the bait is made from dabbing. Polyurethane foam is used to create large floating flies. Additional elements in the form of wings and legs are made from rooster or pheasant feathers.
The mounting thread is used to fix the elements on the hook. Its color is selected depending on the type of fly. Lurex is an additional attractive element and is more often used to create fantasy-type imitations.
When creating fly and spinning flies, it is better to use regular superglue. It has good adhesion and dries quickly.

For the convenience of tying flies, the fisherman will need a set of specialized tools, which includes:
- nail scissors;
- tweezers;
- mortar for fur;
- knotweed;
- feather clip;
- dabbing needle;
- knitting vice;
- bobbin holder;
- threader
This set of tools will greatly simplify the process of tying flies and make it faster. Once a certain amount of experience is gained, the angler will be able to make the bait he needs in a few minutes.
Fly tying hooks

When choosing a hook, you need to pay attention to the following:
- strength;
- pungency;
- quality of material.
If you use old hooks, you won't be able to catch fish.
Important: a leash is attached to the hook, so it must have a ring.
The experience of many fishermen suggests that to make a “dry insect” it is best to use a hook with a ring bent inward. This bait looks natural and fits naturally on the water surface.
It is best to use a hook with the ring bent upward as the basis for a wet fly. This gives the impression that the insect has fallen into the water. If you tighten the line, the bait will rise to the top.
In fact, the type of ring on the hook does not play a huge role. It is best to pay attention to the thread used to weave the fly.
Build process
The classic process of tying fly fishing and spinning flies is divided into several stages:
- The mounting thread is wrapped several times near the eye of the hook and secured with a knot;
- The hook is spooled with dabbing;
- During dabbing, segments of the fly's body are formed;
- The fur forms the body;
- Using a mounting thread, the tail part of the feathers is fixed;
- Individual elements of the feather are wound to the body of the future bait, imitating the legs or hairs of an insect;
- Using a mounting thread, an imitation of insect wings made of feathers is attached to the resulting workpiece;
- A head is formed from a thread near the eye of the hook, which is soaked in superglue;
- The head is coated with a waterproof, transparent varnish.

When making a fly, it is better to clamp the hook in a vice through a paper or plastic spacer.
The stages of the front sight assembly process may all depend on the design features of a particular model.
Manufacturing rules
When tying flies, you need to make sure that they look like the original, that the proportions and sizes are respected.
Everything must be tightly connected, otherwise the bait will fly off the hook when casting. Its color should not change from getting wet. That is, the material used must be of high quality. The hooks must be massive for optimal immersion in the water.
All the bristles on the body are strengthened with varnish and it is necessary to ensure that they are at the right angle.
For production we take:
- hooks of different sizes;
- silk or mounting threads;
- feathers;
- Lurex;
- wool;
- dabbing (wool or synthetic thread);
- varnish;
From the tools:
- a vice is needed to securely fix the hook;
- pen holder;
- sharp scissors;
- bobbin holder;
- needles;
- threader;
- knotweed;
- tweezers;
- varnish brush;
- magnifying glass;
- mirror;
- lamp;
It is the body that attracts fish most of all.
When making an analogue of an insect, it is desirable to accurately copy the original. A fly has a head, abdomen, chest, wings, bristles, and legs.
Taurus must be given a bright color. This can be achieved using different materials, which should be tested to see if they get wet and whether they will change color.
To better resemble a natural insect, plates and bristles are attached to the body. The end of the body is made of thin wire. The head is made massive and varnished.
The legs should be made so that the bait can easily float on the water. The suitable material for them is thin chicken feathers.
Wings are most often made from terry feathers of various birds. They must be the same size. Duck breast feathers work best.
Subsequence:
- The hook is secured with a vice. Preferably from size 8 to 28.
- The next stage is to fix the mounting thread and wind it along the bend of the hook. The excess is cut off.
- A woolen thread attached to the middle of the fore-end forms the base of the body, gradually thickening.
- Making bristles from wool. To do this, you will need to roll the fibers around the mounting thread. After which, all this is wound around the body of the fly, secured with a knot and coated with varnish.
- When everything is dry, the bristles are wrapped in lurex in the opposite direction from the angle of the fur. The end of the thread is fixed. The fibers are cut to the required length.
- The legs are made from the spine of a feather, half a centimeter long. The feather is placed on the head of the fly and strengthened with varnish. After a few minutes, the feathers gather to form the insect's head. The excess is directed towards the sting and carefully trimmed.
DIY dry fly
Making a classic dry bait that imitates a horsefly or fly is quite simple. The process consists of several stages:
- A black mounting thread is wound around the shank near the eye of the hook;
- A dumbbell-eye is attached near the ear;
- At the bend, a strip of black polyurethane foam is tied to the fore-end;
- The thread is returned to the eye;
- The dabbing is used to form the body;
- The wound strip of foam is bent and secured at the end of the dabbing turns;
- A small strip of polyurethane foam is attached in the middle of the future bait and secured with a half-knot;
- The black strip of polyurethane foam is folded back;
- The dabbing is screwed onto the forend up to the dumbbell;
- Strips of raffia are tied to the body, imitating insect wings;
- Raffia is carefully trimmed with scissors to a natural look;
- Next to a strip of black polyurethane foam, the beards of a black rooster feather are fixed;
- The beards of the feather are pulled back with a thread;
- The dubbing is formed into a breast;
- The breast is covered with a strip of black foam;
- Fix the polyurethane foam with a mounting thread at the dumbbell;
- Excess foam is trimmed off.

Next, a head is formed from the mounting thread, which is impregnated with superglue.
At the final stage, the head of the bait is coated with a thin layer of transparent varnish.
Gadfly fly
Materials:
- hook;
- mounting thread;
- chenille;
- foam;
- refined wax;
- feather for legs;
- mesh for fly wings, burning mold;
- varnish
So, how to make a fly for fishing at home:
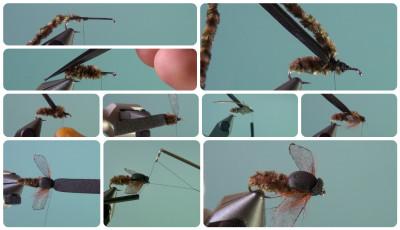
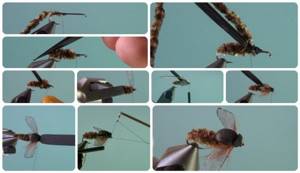
We wrap the hook shank with mounting thread in the direction of the bend.- At the bend we attach chenille, a color similar to that of the gadfly , and we tie it to the fore-end (we do not cut off the remaining part, we will still need it for the breast).
- We cut off some of the hairs at the bend of the hook, giving the body a cone shape.
- On the side of the loop (at a distance of 1/3 to the tail) we attach 2 mm in thickness and 6 mm in width.
- From the chenille that remains after the formation of the body, we make a breast. We cut off excess material.
- We rub the thread with cleaned wax so that the wings do not slide on it (there should be no lumps of wax on the thread).
- We create wings from mesh, burning them on a special form.
- We attach the wings one by one to the body of the gadfly.
- We tie a feather under the place where the wings are attached to make legs out of it.
- Wrap the feather 3 times . We press the resulting brush with a thread: it should not puff up.
- We press the foam onto the breast from above, wrap it with a thread next to the loop and cut it off, leaving a millimeter of material after the breast.
- Using a knotter we form a head for the gadfly.
- Apply varnish to the head.
Larger picture
.
Botflies often end up in the water at cattle watering holes.
Cows use their tails to drive them away, often knocking the insects into the river.
The ideal place for catching chubs and other fish with gadflies is near a watering hole downstream.
Below are video step-by-step instructions for knitting a fly for fishing with your own hands.
DIY streamer
Even an angler with no experience in fly tying can make a simple streamer model on his own. For this you will need:
- Take a bunch of synthetic yarn or natural wool about 20 cm long;
- Attach the bundle to the hook so that its middle is near the eye;
- Secure the material with a mounting thread near the eyelet;
- Fold the yarn in half towards the bend of the hook;
- Form a head from the mounting thread;
- Coat the head of the bait with varnish or epoxy resin.
Despite the simplicity of manufacture, such a fly works great when fishing for pike at a depth of up to 2 m. The bait should be jerked.
How to tie your first fly?
The first thing every fisherman needs to consider before starting to make a fishing bait is the shade of the material. Therefore, if you don’t have colored or shiny synthetic threads on hand, they should be painted with aniline-based paints. Contains stable pigments.
You should start knitting not from the top or the end of the hook itself, but from its middle. After the thread is secured, it must be wrapped around the shank of the hook from top to bottom twice.
Only after this will it be possible to begin attaching the tail and wings of the front sight. To make it easier to glue other elements to the hook shaft, you need to additionally glue wool thread or bird feathers on top of the fishing line.
Next, small fastenings in the form of knots are made on the sides of the product. Once the body of the insect is ready, you can begin making the upper part.
Pros and cons of making your own
The advantages of making your own fishing flies include:
- low cost of bait;
- the ability to make a fly that works better on a specific body of water;
- the opportunity to experiment with color, size and modification of the front sight, choosing the best option.
Having learned how to quickly make various types of fishing flies, an angler will be able in a few minutes to create a catchy imitation of the insect that the fish is feeding on at a given time.

Large streamers designed for fishing at great depths are equipped with a lead head.
The downside to tying flies yourself is the time spent making them. However, with the advent of experience, this disadvantage disappears.
Adviсe
Fly fishers and spinners planning to start making fishing flies and fishing with these baits can be given some advice:
- At the initial stage of mastering the tying of artificial flies, you should not take on the production of complex models;
- It is advisable to install a table lamp at the knitter’s workplace that provides the best possible lighting;
- When going fishing, you should take with you the tools and materials necessary for tying flies - this will allow you to create imitations of insects that are present in the diet of fish at a particular moment;
- When fishing, it is advisable to have a set of permanent markers of different colors with you, which will allow you to quickly change the color of the bait.
To achieve stable results when fishing with flies made by himself, the angler must constantly improve his tying technique and not be afraid to experiment.
Which insect should I tie?
Information on how to tie a fly can be found in specialized literature or on the Internet. During its production, the insect figurine should have more pronounced features of a real bait.

Since the catch will largely depend on the quality of the fly made.
To catch large fish, you can think of the following types of insects:
- Grasshopper.
- Bug.
- Dragonfly.
- Gadfly.
- Fly.
For smaller fish:
- Ant.
- Butterfly.
- Butterfly caterpillar.
- Hairy insect larvae.
In fact, this list can have a huge variety of insects, it all depends on what types of materials are available and what can be invented from them.