The common ide is a medium-sized fish of the carp family and a popular object of amateur and sport fishing. It belongs to the genus of dace, where it forms its own species (Leuciscus idus) from several taxa that have geographical and biological differences. The closest relatives are the Chebachok and representatives of the Dace (Siberian, Kyrgyz, Trans-Caspian, Talas, etc.). The species is characterized by significant age dimorphism, similar to bream. Fingerlings and small 2-3-year-old young animals weighing 400-800 grams are called roaches by analogy with breams. At this age, the fish are very similar to the roach (Rutilus rutilus). Adult individuals have their own characteristic exterior, which is close to another representative of cyprinids - the chub (Squalius cephalus) and to a lesser extent to the asp (Aspius aspius).
Size and lifespan
By the age of 6-10 years, the fish grows in length to 30-50 cm and gains a weight of 2.0-3.0 kg. These indicators are characteristic of trophy specimens, which are now found quite rarely. Under favorable conditions, individual individuals can live up to 15-20 years. It is in adulthood that there is a significant increase in body length (up to 80-90 cm) and maximum accumulation of mass.
The largest ide weighed 8.2 kg and was over a meter (102 cm) tall. Modern standard catches are much more modest. The average weight of fish does not exceed 0.5-1.5 kg, which indicates a significant rejuvenation of the population due to a reduction in the number of places with suitable conditions for long-term development, the growing popularity of sport fishing, and the availability of high-quality gear that can withstand high tensile loads.
Fishing
Sports and amateur fishermen are showing increased interest in catching ide, because this fish is large in size and contains many useful substances. You can catch this type of fish all year round. The meat of this fish is very tasty and healthy, it also contains all the vitamins and microelements, as well as protein necessary for the proper development of the whole organism.
Fishing methods
The ide is caught on various fishing rods; what to catch the ide with and with what, the person decides for himself. It also depends on the season when fishing takes place.
All fishing rods are suitable for catching ides; the most effective ones are listed below:
- fly float;
- wire fishing rod;
- Bolognese tackle;
- match fishing rod;
- donka;
- feeder;
- live bait fishing rod;
- fly fishing tackle;
- bombard;
- spinning;
In winter, special gear is needed to catch an omnivorous semi-predator:
- nod;
- a fishing rod with a float, which must be kept exclusively under water at all times so that the float does not freeze to the ice.

It is impossible to say when the season for catching such fish as ide opens, because it can be caught in any season. It may not bite only in severe frosts, but with minimal warming it immediately begins to please the fisherman with an active bite.
Baits and lures
The mouth of this type of fish is small, therefore the baits should be small from number 0 to 2, and the length of the spoon does not exceed 4 cm. As for the hooks, their size should be a maximum of 5. The ide is a shy and cautious fish, so you need to fish silently , and it is advisable to disguise yourself. For the tackle, a transparent fishing line is suitable, the diameter of which should be 0.22 mm, and the leashes should be 0.18 mm.
If fishing is done using a float, the following baits are used:
- grasshopper;
- caddisfly;
- muckworm;
- maggot;
- dragonfly;
- mole cricket;
- Chafer;
- bark beetle;
- mayfly;
- reed shoots;
- fry;
- wobblers;
- jig with a piece of fish;
- peas;
- dough;
- semolina;
- insect larvae;
- worms;
- bloodworm.
We suggest you read: The difference between bream and silver bream
Plant-based baits can also be used to catch ide: dried canned peas, corn, semolina, bread, etc.
To catch ides, you can use a simple bait, but always with a scent:
- vanilla;
- sunflower oil;
- birch branches.
This bait can be made at home from bread with the addition of clay. The bite is confident and at the same time fast, so the fisherman should always be on the hook. Fishing with a spinning rod is quite effective.
As for vegetation, the best recommended algae is mulberry, especially when fishing for wiring. Starting from the month of May, this bait performs better than anyone else in its fishing, and not only on ide, but also on:
- rudd;
- roach;
- ruff;
- crucian carp
Such algae can be found on stones at a depth of 30 cm, as well as on driftwood and concrete structures (bridges, piers, slipways).
For bottom gear they use live bait from small fish: dace, bleak, gudgeon and small toads. The ide is a picky fish, it picks at its food, but it never refuses bark beetles (larvae) and dragonflies.
Catching ide, if you know the places where it prefers to stand and feed, as well as the right bait, is not particularly difficult.
In the basins of some Siberian rivers, ide forms fairly dense populations - there its share in commercial catches is up to 40% or more.
Mostly ide is caught with a float rod and a donk. On the rivers of the Urals, fishing for this fish is also practiced. The bait is usually used of animal origin - worms, bloodworms, maggots, wood-boring beetle larva or May beetle. Ide also bites well on bread, barley and steamed peas.
Somewhat less often than with a fishing rod, ide is caught with a spinning rod (small wobblers and spinners). It is also caught using surface gear (fly fishing, boat, tug) during the period of insect flight, when the fish hunts in the upper layers of water. In addition to artificial flies, the bait used is a grasshopper or grasshopper, horsefly, housefly, dragonfly, small frog or fry.
A fishing rod with a side nod also shows good results when fishing for ide - both with a nozzle and in the nozzle version - with the right game.
Reelless tackle or a jig with an attachment - a bloodworm, a worm or a bark beetle larva - are very effective. During the thaw, ide can also peck on vegetable attachments - bread or semolina. Some anglers are quite successful in catching ide using small winter spinners and even balance beams. There is information about catching this fish using girders—small live bait.
Ide fishing calendar
A hungry ide takes the bait confidently - it drowns the float or noticeably pulls on the line of the donkey. A well-fed one can behave like a crucian carp - pinching the bait with the tips of its lips, while the float stands still and sways; it is necessary to hook only when it goes under the water.
Once on the hook, the ide stubbornly resists and pulls to depth - at this moment the line must be kept moderately taut, avoiding breakage or sagging. However, he gets tired quite quickly (especially if you give him a breath of air), after which the ide can be safely brought to the shore or boat. Excessively intense fishing may result in a death, as the fish has weak lips.
Fishing for large ides is many times more difficult than for small roaches; they are very strong and stubborn - sometimes you have to bring them in and let them go several times. These are best removed from the water using a landing net. At the same time, you need to be careful - at the very last moment the fish may make a sharp jerk and break the fishing line or jump off the hook. Also, do not forget about the ability of the ide to jump - it can easily jump out of the cage.
Our observations
In our fishing practice, we have repeatedly caught and observed ides in three rivers - Chusovaya, Bolshoi Shishim and Ufa. In the first of them, it is numerous only in those places where all the necessary conditions exist for it - slow currents, great depths and a muddy bottom. This is an area with dams after the discharge of the Volchikha reservoir (within the boundaries of Revda and Pervouralsk).
After the Sazhinsky Bridge, Chusovaya becomes smaller and faster. Below this dam, ide is regularly caught mainly in the spring - when it rises to spawn, but is rarely caught the rest of the year. However, it is in the middle reaches of the Chusovaya that you can catch a trophy specimen of this fish.
One of these ides, weighing about two kilograms, was observed while fishing in the area of the village of Staraya Treka - on a small rift bordering a deep hole. It was actively feeding at dawn, making impressive leaps after insects flying over the water. The ide made one of these jumps a few meters from the fisherman - so that he was able to clearly see the fish and identify it by the color and shape of the fins, as well as the silhouette of the body and the characteristic shine of the scales.
Fishermen I know, who also practice boat fishing, came across ide in Chusovaya while fishing for chub, but this happened extremely rarely.

On the Ufa River, ide fishing turned out to be more productive. There is noticeably more of it there than on neighboring large rivers, although roaches are most often found, but large individuals are quite rare in fishermen’s catches. However, if you know the places, you can catch ide in Ufa on purpose.
Our companions came across this fish in Ufa when fishing from the shore with a float rod - on sharp drops into the depths. Also, a fairly decent (under a kilogram) ide was caught during night fishing - on a boat. The fish bit on a small filly.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with: Roach (roach) fish: where it lives, what it is caught with
What does ide fish look like?
Small, dense roaches with an elongated snout are characterized by an overall light silver color, pale fins and golden eyes. This description is enough not to confuse young Leuciscus idus with a roach, which has a dark back with a greenish tint, lower mouth, reddish irises and ventral ray feathers, and strongly compressed sides.
An adult ide has other unique external characteristics:
- a thick body with a pronounced arch of the ridge in turquoise and olive tones;
- snow-white belly with a clearly visible keel;
- orange-purple color of the chest, tail and ventral plumage;
- an oblique terminal mouth that does not reach the line of medium-sized eyes with a darkened yellow iris and a large pupil;
- shortened head, behind which there are large gill covers;
- copper-golden sides;
- medium-sized, tightly fitting scales of the cycloid type.
Depending on the characteristics of the habitat, the color scheme of the body may change, but the tiered contrast of shades in the direction from a darker top to a very light bottom is maintained.

Age and spawning
Ides live for 15-20 years, and at the time of sexual maturity, depending on the food supply of the reservoir, ides reach the age of three to five years. Ides are among the first to spawn among carp fish. The spawning of these beauties occurs when the water temperature warms up to 6-8 degrees Celsius, at which time the birch trees are slightly shrouded in the greenish fog of the budding buds.
In central Russia and Siberia, ide spawning occurs in mid-to-late April, in the southern regions - at the end of March.
Like many other fish, ides rise to spawning grounds upstream and choose shallow, 50-80 centimeters, areas of the bottom with last year’s grass or higher aquatic plants: reeds, cattails or reeds, on the stems of which the eggs adhere. On rivers, spawning sites are often pebble riffles with individual clumps of grass; in addition, the fish spawns part of its eggs onto snags or piles of hydraulic structures during the spawning run.
Fish of all ages take part in the spawning process, but families are divided by age. Usually one female is accompanied by 2-3 males. The number of eggs depends on the age and size of the fish; the largest “mothers” spawn over 120 thousand eggs, the diameter of which is about two millimeters.
The rudd reaches sexual maturity in the fourth year of life. The fish grows slowly, and readiness for reproduction begins at a height of about 12 cm. Before spawning, the color of the rudd becomes brighter, and noticeable growths appear on the males on the head and part of the back.
Spawning of rudd has its own characteristics. Spawning grounds are places located close to habitats. The pre-spawning run of fish is difficult to notice. Rudds move to spawning grounds in small groups: a small group of males, and then a small group of females. And so it goes on and on.
The rudd spawns in portions. Before the start of spawning, females ripen 2 portions of eggs, and the third - already during the spawning period. Rudds are characterized by high fertility. One female, depending on its size, can lay from 10 to 130 thousand eggs. Spawning begins after the water temperature has stabilized from 15o.
The female lays eggs on plants, and some of the eggs fall on the bottom surface. The diameter of the caviar is about 1 mm. The incubation period is 3-4 days. Despite high fertility, rudd populations remain small. Some of the eggs remain unfertilized, since females can spawn without males. A large number of eggs and fry are eaten by other fish.
Rudd fry grow slowly. During the first year of life they grow to several centimeters. The main food of juvenile rudd is zooplankton. As fish grow older, their diet becomes more varied.
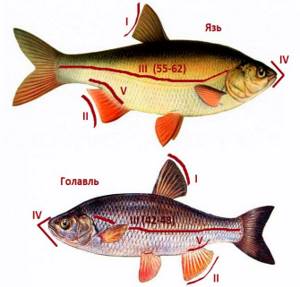
Ide and chub - the difference in appearance
The problem of identifying related species due to their similarity is typical only for inexperienced anglers. Knowledgeable people can easily determine where each fish is, focusing on just a few external signs. This does not take into account the basic color nuances of the color, which can be almost the same in one river or lake.
If you do not know how to distinguish an ide from a chub, use the comparative information in the table below.
| No. | External sign | Ide | Chub |
| I | Shape of the outer rib of the dorsal fin | Straight, often concave inward | Convex outward |
| II | Shape of the outer edge of the anal fin | Concave inward | Convex outward |
| III | Size and number of scales in the lateral line | Not large. 55-62 pieces | Large. 42-48 pieces |
| IV | Mouth section | Narrow. Looks straight. | Wide. Looks up. |
| V | Keel on belly | Expressed | Smoothed |
| VI | Body Shape | High | Moderate |
| VII | Head size (relative to body) | Small | Big |
To accurately identify a particular species, it is enough to remember the first three comparative characteristics. Despite the external resemblance to the asp, the ide is easily recognized by its huge mouth, elongated head and pointed fins.
How are ide bred and grown?
The ide is the most popular fish for breeding in the pond; the golden ide stays well on the water, hunting insects. In a large pond, fish can reach 50 cm in length; the fry feed on both plant and live food.
If there are enough plants in the pond, then growing ides is easy and effective. In the third year of life, pond ide can weigh 500 grams. Breeding does not require special equipment, and it feeds on what the carp refuses.
Ide - habitats
The species' range occupies almost all of Europe with the exception of the extreme south and south-eastern territories. In Russia, the fish lives in the central part, in the Urals, Siberia and even in the Sokha Republic. The taxon is characterized by sufficient thermal stability against the background of poor tolerance to heated water with a low oxygen content and too cold or fast-flowing streams, characteristic of mountain rivers and lakes. The largest populations live in the rivers of the Azov, Baltic, Caspian and Black Sea basins (with the exception of Crimea).
Despite its freshwater status, the fish adapts well to slightly salted water, and therefore is often found in estuarine areas and bays. Under natural conditions, it prefers flowing deep reservoirs with a slow current and a moderately hard or silted bottom (steppe rivers, lakes, reservoirs, large sewage ponds). A popular fishing object in the riverbed and tributaries of the Volga, Lena, Kuban, Ob, and Ural. The species was also introduced into the United States, where it has successfully established itself in the northeastern states, especially in Connecticut.
Useful properties of meat
As a member of the Karpov family, ide has tasty meat. In the simplest preparation (boiled or baked), it is a valuable nutrition - systems for weight loss, gastroenterological diets and general health include it as a necessary product.
Vitamins (content per 100 g of ide meat):
- PP (nicotinic acid), B3 - 6.6 mg, 3 mg. Stimulates liver function and reduces blood sugar levels.
- B1 - 0.6 mg. Promotes the absorption of proteins and fats, stabilizes the functioning of the nervous system.
- B9 - 5.3 mg. Improves the functioning of the immune system, increases the number of active sperm in men.
- B12 - 1 mg. Increases stress resistance and performance.
- E - 0.9 mg. Slows down the aging of the body.
Minerals:
- Potassium - 265 g. Ensures proper functioning of the heart and kidneys.
- Calcium - 35 g. Together with vitamin D, it supports bone, muscle tissue and blood functions.
- Magnesium - 25 g. Its presence reduces irritability and stabilizes heart rate.
- Phosphorus - 210 g. Stimulates brain function.
- Iron - 0.8 g. Stabilizes metabolism.
The nutritional value of this fish is high: 19 and 4.5%, respectively, are proteins and fats; carbohydrates are found in small quantities only in caviar (there are no carbohydrates in meat at all). The product is easily digestible, therefore it is recommended for nutrition of people with diabetes, gastritis and diseases of the heart system.
There are two dangers - a lot of small bones that a person can choke on and parasites that often live in the ulcer, so it is important to heat-treat the fish before cooking.
The ide is a hardy fish and can live for a long time in water bodies polluted by industrial production, where heavy metals, pesticides, herbicides and various wastes are present. In this regard, before fishing, you should make sure that the fish is safe.
Lifestyle and nutritional habits
Ide remains biologically active throughout the year, without going into real hibernation. Only a pronounced “deaf season” with severe February frosts, windy weather and thick ice becomes the cause of short-term suspended animation in free deep holes. The constant “partner” in the forced feeding downtime is another all-season glutton – perch, whose life processes slow down under similar external factors.
Young roaches stay in large flocks near the coastal zone. Areas with dense aquatic vegetation, a complex bottom with plenty of shelter, and snags are selected as permanent locations. Large individuals are very cautious, afraid of noise, and love safe, wide reaches with a slow current and considerable depth. At the same time, they avoid walls made of reeds and “windows” among water lilies, avoiding encounters with large pike.
Beginner fishermen are interested in knowing whether the ide is a predator or not in order to select a catchable bait. Among peaceful carp representatives, only the asp has the exceptional status of a carnivorous “white crow”, which in the gastronomic aspect gives preference to the grown-up fry and underyearlings of its own and other species. During the hunt, the fast-moving fish quickly catches up with a medium-sized prey, crushes it with a blow of its tail and instantly swallows it thanks to its huge mouth.
The ide is a universal eater with a semi-carnivorous lifestyle, which, depending on the seasonality and characteristics of the food supply, can behave as a benthophage or planktonophage, feeding from the bottom or surface, respectively.
The main diet includes:
- zooplankton, rotifers, daphnia, brine shrimp (at the young roach stage);
- crustaceans, mollusks, leeches, tadpoles;
- cereal grains and legumes, corn, young shoots (in warm water);
- worms, bloodworms, chironomid larvae, dragonflies and caddisflies;
- mayflies, beetles, grasshoppers, hymenoptera and other insects falling into the water.
At a body length of 15-20 cm, moderately predatory tendencies begin to appear. The object of the hunt is the fry of gudgeon, bleak, roach, and crucian carp. Thanks to such an energy-efficient food additive, fish are freed from a key behavioral disadvantage characteristic of herbivorous representatives of the ichthyofauna - a constant feeling of hunger amid a round-the-clock search for food.
Description and dimensions
Ide is a very beautiful fish. Its scales have a golden sheen, especially a lot of yellow on the gill covers, while the back is black and blue, and the belly is silver. This fish looks most elegant during spawning; adult specimens are much brighter in color than roaches.
When done, the head looks small and has a slanting mouth at the bottom. The eyes have a yellow iris with a greenish tint. The fins are colored red, the anal and ventral ones are especially bright. The average weight of an adult ide is from one and a half to two kilograms with a body length of forty to fifty centimeters, although record specimens reach the six-kilogram mark.
Ide is often confused with other representatives of carp fish, especially with species such as chub and roach.
When our hero is caught in the bycatch with the specified fish, the differences are still visible to the naked eye, for example, the ide differs from the chub in the following ways:
- taller body;
- less wide head;
- small mouth;
- small scales.
The differences from roach are also very obvious:
- yellow eyes;
- small scales;
- light back.
Subspecies of ide
The basic, “common” taxon is Leuciscus idus. It is he who inhabits all favorable bodies of water and determines the characteristic appearance of the fish. There are also several unique forms that arose under the influence of humans or climatic and geographical features:
- Orfa, or golden ide (Leuciscus idus var. Orfus) is an artificially bred variety for pond fish farming and decorative keeping in home reservoirs. It has a dorsal fin with an increased number of rays - 10-12 versus the standard 8-9. In the cold season it is inactive. Overwinters in pits along with carp and carp. It is distinguished by a pronounced golden or red color, often with pinkish or scarlet tints. It grows up to 50 cm in length and weighs 1.5-2 kg.
- Turkestan (Leuciscus idus oxianus) is a small subspecies that lives in the Aral Sea basin. It is found in the middle reaches and lower reaches of the Amu Darya and Syr Darya. The body length does not exceed 25-30 cm and weighs 700-900 grams. It has small scales - 52-55 pieces in the lateral line. The main color corresponds to the base taxon.
Reg.: 10/06/2005 Threads / Messages: 9 / 427 From: Moscow, Perovo Age: 40 Car: MitsPajeroSport 2002
Reg.: 12/09/2004 Threads / Messages: 9 / 977 From: St. Petersburg Kolomyagi Age: 49 Car: 214 May 11, A6 Avant 12 and Kalina 2008
Reg.: 10/06/2005 Threads / Messages: 9 / 427 From: Moscow, Perovo Age: 40 Car: MitsPajeroSport 2002
canek.spb
Why such effort, thanks in advance
I'm so simple. out of curiosity. I just caught a roach at 800g once, but maybe it was an ide. This is how I have been suffering since the summer. in conjecture.
Reg.: 05.27.2005 Threads / Messages: 3 / 929 From: Moscow Age: 42 Car: VAZ 21213. 2002
questions)? in PM
Reg.: 04/27/2005 Topics / Messages: 1 / 291 From: Moscow, Zelenograd Age: 33 Car: 2131 amulet (dark green ME) 1.8-carb 2004, s/k-Sheriff
The roach has red eyes, a narrow horizontal mouth, a blue back, and fairly large scales.
The ide has a narrow mouth and is slightly directed upward, the scales are smaller, and the back has a greenish-gray tint.
Reg.: 10/06/2005 Threads / Messages: 9 / 427 From: Moscow, Perovo Age: 40 Car: MitsPajeroSport 2002
Spawning of ides
Sexual maturity of males occurs at 2 years, when their size reaches 25 cm and weighs 250 grams. In the North, sexual maturity occurs 1-2 years later. Spawning of ides occurs faster than others, as soon as the ice melts and the water warms up to 7 degrees.
At this time, the inhabitants are divided into certain groups, each of which contains fish of the same age. Then they swim to the surface of the water and look for a suitable place to mate. If the ides lived in large rivers, then during spawning they swim into small tributaries and swim up to the stones; the depth of the tributary does not exceed 50 cm; last year’s vegetation will serve as a substrate for them.
During the spawning period, males jump to the surface and swim there. In ides it is fleeting and lasts up to three days, and is carried out in 1 step: the old people go first, and the young ones go last. At the end of the spawn, the river inhabitants return to their original places.
After a week, larvae appear and hang motionless for 3 days, glued to stones or vegetation using an adhesive substance produced by cement glands. After which, they peel off, swim and feed on their own, learning to survive on their own. They live in the same place for 3-5 days, and then swim to safe coastal areas.
Yazi that live in the lake during spawning move to nearby river mouths or to shallow waters where there are reed thickets. At the end of spawning, they go to depth, and after 3 days they emerge and actively feed, making up for lost calories.
Appearance
Let's figure out what ide looks like? The length of the thick body of an adult fish varies from 35 to 50 cm, and especially large individuals can reach a length of 90 cm. At the same time, the average weight is up to 3 kg , but there are also record holders, ides up to 8 kg! Moreover, representatives of the species in central Russia weigh about 1.5-2 kg. But in clean and oxygen-rich artificial reservoirs, the fish reaches very impressive sizes.
You can recognize a fish by the following signs:
- Thick body.
- Shortened head.
- Small slanted mouth.
- Large eyes.
- Usually gray in color
The body color of the ide may vary depending on the time of year or the age of the individual.
Adult individuals have a gray, metallic body color with golden “cheeks” and head. At the same time, in the sun, the color can change , becoming either completely dark or silvery-golden. The sides are close in color to white, creamy yellow, the back is black with a blue tint. The reddish-crimson color is characteristic of the lower fin, less often – the caudal and upper fin. Some fish have a much darker dorsal and caudal fin - silver-gray with a purple tint. The scales are medium in size.
The color of the eyes is yellow or yellow with a tint of green, the shell of the eyes is a characteristic bright orange color.
Young individuals , which are usually called roaches, are distinguished by a lighter body color, silver, and their fins are much paler. The older the fish gets, the more contrasting color its body acquires.
Let's figure out how to distinguish the ide fish from the chub, which is similar in appearance. The chub is a freshwater representative of the carp family, with a flattened massive head and large scales. The following signs will help you distinguish ide from chub:
- Lighter color on the back.
- Narrower head. In the ide it is slightly pointed, in the chub it is more blunt.
- The scales are smaller in size.
- The mouth is narrow.
- The chub has a larger mouth.
- The body of the ide is somewhat flattened on the sides, which is not the case with the chub.
Also, the ide fish, the description of which is presented above, has several similar characteristics with the roach, but differs from the latter in its lighter back, yellow eyes and scales - they are smaller in the ide.
There are a number of differences between chub and asp that will help the fisherman avoid making an annoying mistake:
- The asp has a lighter silver-gray color.
- The anal fin of the asp is wide, while that of the chub is convex and narrow.
- A prominent lower jaw characterizes the asp, while in the chub both jaws are identical.
Knowing these signs will allow you to correctly identify the caught fish.
Ide
The ide fish is from the carp family. At a young age, its representatives are called roaches.
Description and lifestyle of ide
Spreading
This fish is present in varying degrees of concentration in almost all reservoirs of Europe. The exception is its southern and southeastern regions. In Russia, fish are found throughout most of the territory. Absent only in the region of Yakutia and the eastern part of the country.
Ide inhabits the rivers of the northern part of the Caspian basin (Volga, Emba, Ural). Fish live in rivers that flow into the Black Sea (from the Kuban to the Danube). True, it does not occur in Crimea. Through introduction, the species was brought to the United States, where it took root in the reservoirs of Connecticut.
The ide fish is a freshwater species. Although it easily tolerates brackish water and can live in sea bays. Distributed in hand ponds, rivers, and flowing lakes. Does not like fast, cold, mountain rivers. Prefers slow currents and deep places. It is easy to find near holes, whirlpools, bridges, bushes hanging over the water near the shores.
Fish do not hibernate. In winter it easily tolerates significant temperature changes. It is a very hardy species among its relatives.
Appearance
The length of adult individuals reaches 35...63 cm, their weight is usually 2.8...2.0 kg. Although the largest ide caught by fishermen is known, its length was 90 cm and its weight reached 8...6 kg. The fish lives 15...20 years.
The body of the fish is thick, with a short head. The mouth is oblique and small. In different habitat conditions, depending on the period of the year, age, fish may have pronounced or not very pronounced differences from each other.
In spring, the body of the fish gives off a metallic sheen. The gill covers and head of the fish appear golden. The colors change quickly when the carcass is rotated under the sun's rays. They can be golden, silver and almost dark tones.
The lower fins are reddish. Sometimes the tail and top have the same color. The back is black-bluish, the belly is silvery, the sides are whitish. The eyes are yellow or greenish-yellow, with a dark spot located at the top.
Adults are more intensely and brightly colored compared to roaches.
Differences between ide and chub
The ide is very similar in appearance to the chub. Differences are expressed in a lighter color of the back, a flattened body, a narrow head and mouth, and small scales.
The fish also strongly resembles a roach. Although it has smaller scales, a light back and yellow eyes.
Nutrition
The ide fish is an omnivorous type. Feeds on animal and plant foods. Its diet includes insects, their larvae, worms, mollusks, and aquatic higher vegetation. Feeding time is night and twilight. Location – areas with increased flow speed.
Reproduction
Ides become sexually mature at 3…5 years of age. Fish spawning usually occurs in the spring, in its second half. After the ice melts, schools of fish rush to their traditional spawning grounds. During this period, the body of males is covered with yellowish small warts. There are about 2 times more females in the spawning herd.
The beginning of spawning in ides coincides in time with pike and perch. The water temperature reaches 2°С…13°С. The duration of the spawning period is 1…2 weeks.
Eggs are deposited at a depth of approximately 0.80 m, on the roots of various underwater plants and last year's bushes of herbaceous vegetation. Spawning is instantaneous.
Fish eggs are round, 2.0...1.5 mm in diameter. Their number in a fish depends on its age, size and reaches 130 thousand pieces.
Catching ide
Where to catch ide
The areas of reservoirs where it is preferable to catch ides are different at different times of the year. In spring, these are places with a rocky bottom, fairly fast currents, and shallow depths. By the end of May, the fish roll into deep holes, where you should look for them until the fall.
The best time to catch ide is in the evening, after sunset, and in the early morning, when the sun is still far away from sunrise.
What to catch ide with
When catching ides, they use insects, black bread, crayfish, worms, and sometimes small frogs as bait. It is better to catch ide with dung and earthworms at the beginning of the season, in the spring. From May, bread balls, which are about the size of a hazelnut, are better.
When flying insects appear, the fish begins to “neglect” the indicated baits and prefers large nocturnal butterflies, bread bugs, grasshoppers, and various insects that fly near the water.
Steamed bread grains work well as bait. The effect increases when adding hemp pulp (cake) and kvass grounds to them.
Fishing with bait made from steamed peas and wheat grains is always successful. Especially if you use bait made from steamed rye crackers.
Tackle and methods of catching ide
When fishing, various gear is used: float, spinning, fly, bottom. The fish grabs the bait quite tightly. The hook must be done immediately and decisively, but not abruptly. When fished, the ide resists strongly.
Catching ide with a float rod
When fishing with any bait other than insects, fishing rods are equipped with thick fishing line and medium-sized hooks.
The best way to fish with a float rod is to fish in sections of rivers with a current. It is performed from a boat, or from the shore (on a small body of water). With this method, bait is necessarily used. The best guided hunting occurs from dawn until 9-00 am.
Catching ide on a donk
They also successfully catch ides using bottom gear. For example, ide is more often found on the feeder at night, from dawn to dusk. The middle of the night is usually characterized by no biting.
When using bottom gear, millet porridge, bread, lamprey larvae, crayfish meat, crawling fish, dung and earthworms are used as bait. To attract fish, bait is used, which is scattered in balls in bulk.
Catching ide with a spinning rod
Tackle
To catch this fish, the gear used for perch hunting is used. A rod with a medium or fast action, with a weight of no more than 25 g. A leash is not necessary if pike do not often attack the bait. To increase sensitivity, it is better to use braided wire.
You can use a standard coil, size 2500...3000. Polarized glasses will help you better navigate the situation.
Lures
You can catch ide with a spinning rod using a wobbler, spinners and even poppers. Among them, the best spinners are the “Long” and “Comet” types. A special requirement for the quality of spinners is that they should start working at low reel speed.
Considering that the fish has a small mouth, use rotators up to No. 2. Although in the presence of large individuals, products No. 3...4 will be suitable and will give good results.
Particular attention must be paid to the condition of the hook in the nozzle. Its sting must be very sharp. This is important, since ide, unlike, for example, pike, must always be hooked when biting.
Tactics and fishing techniques
It is necessary to fish in mid-water, at depths of no more than 2 m. Depths of 1.0...0.5 m are considered optimal among fishermen.
The spinner is retrieved at an average speed, often on the verge of “breaking”. Even after finding a place where the ide feeds, you should not expect a quick bite. Fish, unlike, for example, pike, can attack the spoon after 5...10 empty casts.
It is important when fishing with a spinner to often change the speed of the retrieve and its type. Changing attachments by size, color, type helps. When fishing, you should remain quiet.
Fly fishing for ide
Tackle
On small rivers it is more convenient to fish with a one-handed rod of class 5...9. The cord is better than the “rocket head” type, floating, dark in color (dark green, black). The backing must also have a dark color, the length of which cannot be less than 60...70 m.
The type of suspension is not important. The leash must be approached responsibly, especially in terms of color. In August, for example, green is suitable, during spring floods - brown, in summer - colorless. The diameter of the fishing line is preferably 0.15 mm and above with a breaking load of over 4 kg. The length of the leash must be at least 3 m.
Fly fishing for ide in spring
You can start fly fishing for ide in the spring immediately after the reservoir is freed from ice. Fishing can be done all day; periods of calm and cloudy weather are especially good. It is worth looking for prey in sections of rivers where there is a fast current, especially in the opposite direction. Fishing areas include bottom holes, behind rocks, in snags, near bridge piles and hydraulic structures.
One of the best baits at this time is an ant imitation. It can be black, red, dry or wet. Later, a fly made in the shape of a caddisfly larva becomes catchy. On rivers where there are no chub, an excellent bait is an imitation of the cockchafer (during its natural emergence).
Fly fishing for ide in summer
In summer, only early morning and late evening hours become catchable. During the day, ide is practically not caught by fly fishing. Cloudy, windless weather is also more promising. The most catchy baits are flies that imitate the adult form of mayflies (dry only).
From mid-June until the onset of autumn, a caddisfly-shaped nozzle becomes relevant. Moreover, it should be knitted on size 12...15 hooks and in dry and wet variants.
Fly fishing for ide in autumn
In autumn, ide again switches to feeding during the day, which is why it is caught at this time. You should look for fish near the main streams of the current, but not on them. Promising places are under the hanging branches of bushes and trees.
The most popular attachment is a small-sized streamer. Flies tied to look like a grasshopper, cricket, butterfly, caterpillar, or small midge can bring a good catch. Moreover, the latter are effective only in the evening.
In late autumn, the only bait that gives a catch against ide is a dragonfly fly.
Recipes for cooking dishes from ide
Use of ide in cooking
The meat is white or yellowish in color. Its taste is high, but it has a lot of bones.
You can prepare various dishes from ide. In this case, the fish is boiled, salted, smoked, baked, fried, salted. Meat is used as a filling in the manufacture of canned food and pies.
Unlike other types of fish, ide is processed at higher temperatures and for a longer time. This is done more due to the fact that its meat is considered to be contaminated with various parasites more.
The taste of the meat depends on the time the fish was caught. For example, in summer it smells like mud, so before cooking it is soaked in salted water.
Calorie content of ide
The calorie content of ide meat is low, it does not exceed 116.5 kcal. The product contains vitamin PP, proteins, fats, microelements (iron, chromium, fluorine, nickel, molybdenum).
How to salt ide
For salting “Under salmon”, 200 g of salt, 100 g of sugar, various spices (coriander, crushed allspice) are used per 1 kg of fish.
The fish is opened along the back with a sharp knife. The tail and head are cut off and used later for fish soup. Remove the insides and wipe with a dry cloth. The spine and ribs can be removed.
The inside of the fish layers is sprinkled moderately with salt, sugar, and spices. Fold in halves and place under pressure. Keep in the cellar, in the refrigerator for 2 days.
The resulting fish resembles young salmon. It can be consumed immediately or further smoked.
Baking ide in the oven
Fish can be baked in the oven in pieces or as a whole carcass. In the latter version, the ide is cleared of scales, gills and entrails are removed. The fins are cut off and washed well. To remove the smell of mud, place it in a weak salt solution for 2 hours.
Prepare minced meat from finely chopped 2 onions, the juice of half a lemon, salt, red and black pepper. They stuff the fish carcass from the inside.
From the outside of the body, transverse incisions are made down to the bones. Rub with a mixture of salt and pepper (red and black). Thin lemon rings are inserted.
Pour vegetable oil onto a baking sheet and place onion rings on the surface. The prepared ide carcass is placed on top. Coat generously with sour cream.
Next, cover the baking sheet tightly with foil and place it in the oven on top. Place another baking tray with water underneath. Oven-baked ide is prepared at a temperature of 180°C and 1 hour. A quarter of an hour before the end, the foil is removed.
Ide baked in sesame crust
To prepare the dish you will need: an ide carcass, 2 onions, 2 tomatoes, 150 g of flour, 100 g of sour cream, a glass of vegetable oil, half a lemon, 2 cloves of garlic, a little “Goldfish” spice mixture, 10 g of sesame seeds.
First you need to prepare the fish: clean, gut, cut off the fins, wash. Next, transverse cuts are made on the sides of the carcass down to the bones in increments of 1.5 cm. Rub with the “Goldfish” mixture outside and inside, pour over lemon juice, and insert its slices into the cuts. The fish is wrapped in film and left to marinate for half an hour.
Cut the onion into rings and stew it. Separately, chop the garlic and chop the tomatoes.
The water formed after pickling is drained from the ide. Garlic is stuffed inside the carcass into the slits. The fish is then dredged in flour.
The fish is placed on foil. Place a layer of stewed onions on top, then a layer of tomatoes mixed with sour cream. Sprinkle everything on top generously with sesame seeds.
The fish is covered tightly with foil and placed in an oven preheated to 180°C for 1 hour. Vegetables and herbs are better suited as a side dish.
Habitat area
It has a wide distribution area:
- Most countries in Europe (except the south and southeast).
- The Arctic Ocean basin (from the White Sea rivers to the Lena).
- Bays of the Baltic Sea.
- Basin of the Aral Sea.
- The main territory of Siberia.
- Black Sea basin.
- Northern section of the Caspian basin (Volga and Ural rivers).
- North America (Connecticut in the USA).
Ide is very widespread in Ukrainian reservoirs , where it is found in almost all lakes, reservoirs and rivers.
Features of reproduction
The spawning period begins late (late April - June) at a water temperature of 16-17°C. Eggs are laid in 2-3 portions in very shallow areas (15-50 cm) with an abundance of bottom vegetation. Sexual maturity occurs at 2-4 years with a height of 10-12 cm. For its small size, the rudd is very prolific, even small females lay more than 10 thousand eggs per season.
We suggest that you familiarize yourself with which platbands are better, telescopic or conventional
A large individual weighing up to 300 g (20-23 cm) is capable of giving birth to hundreds of thousands of fry. But usually only a small part of the young survive. A huge number of eggs and hatched larvae die on greatly shallowed floodplain spawning grounds. The late timing of spawning also has an effect - during this period, many fish completed the breeding process and began active feeding, massively exterminating clutches and young rudd.
The incubation period of eggs lasts 3-4 days. When a fry swims, it immediately hides in the vegetation near the surface of the water, where it feeds on zooplankton all summer. As autumn approaches and most of the floating flora disappears, the young animals move to shallow areas or closer to the shore in search of shelter in reed thickets.
Habits
The fish is a cautious fish, preferring to live in schools, often large ones. But large individuals prefer to live alone. Young roaches choose coastal zones to live , while adults prefer to live in the depths. The ide fish spends the winter at depth, hibernating together with the perch. Under the ice in spring, fish gather in schools and begin to approach the shores. When the river opens up, the flocks rise upstream, staying near the banks, without leaving the riverbed into the floodplain, except in floodplain lakes connected by channels with the river.
Lures for ide

The mouth of the ide is small, so it is best to use small spinners, oscillating spoons or wobblers up to four centimeters long as bait.
For float gear, you can use bait of plant origin. It is best to take canned peas, slightly air-dried, boiled corn, bread crumb, dough and others. Vanilla or sunflower oil is added to the bait.
Filamentous algae are also used as bait. From the end of spring, you can catch not only ide, but also other types of fish using mulberry. This bait is especially relevant on hot days. Young parts of the plant, up to 10 cm long, are suitable for this purpose. The shoot is tied to the shank of the hook and braided around it. Only a small tip of the shoot is left free. Such algae grow on rocky surfaces, driftwood, piles or concrete surfaces.
Also used as bait for ide are grasshoppers, caddis flies, larvae or adults of May beetles, bark beetles, and mole crickets. In winter, fish can be caught using bloodworms or worms.
Small tadpoles or frogs and small tenacious fish are used as bottom equipment.
The ide is very capricious and often neglects bait. The only thing he cannot refuse are bark beetle larvae and dragonfly nymphs.
Nutrition
Ide is not a gourmet; his diet is quite varied and may include elements of plant and animal foods:
- worms;
- shellfish;
- insects;
- larvae of stoneflies, caddisflies, chironomids;
- juveniles of other fish.
That is why fish are classified as euryphages , that is, omnivores. But the diet of ides varies by season: in the spring it consists mainly of animal food, and in the summer and autumn - of plant food. The ide begins to feed heavily after spawning. The ide is not picky about food, consuming the food that can be found in the reservoir.
What does ide eat in nature?
Ide is a fish that eats everything, it can be both plant and non-plant food. They even like small fish, crayfish and frogs. Semi-carnivorous fish, such as ide, can feed only once a day compared to carnivorous fish, which can go hungry for quite a long time. But if you compare semi-predators with fish that eat only vegetation, you need to eat twice a day; ides only have one snack.
The greatest importance for river inhabitants is food; it depends on precipitation, melting of ice at the end of winter, and the opening of floodgates. When the current intensifies, a lot of plant food comes to the fish, which is enough for all sea and river inhabitants.
During this period, the ide stays on the watercourse, since the main food is found in this place. Lake ides do not depend on floods, but rain is important for life; it not only fills the lake with clean water, but also with food. All ides, regardless of their habitat, feed on neighboring shallows, but do this in the daytime; sometimes they can go hunting at night.
Feeding the fry
The main food for fry are small crayfish, crabs, lobsters and insect larvae. When their length reaches 20 cm, the babies begin to devour small fish, tadpoles, and leeches. In addition, their diet begins to include small algae and other aquatic vegetation.
Reproduction
The ide fish becomes ready for reproduction at the age of five , with a body length of up to 30 cm and body weight of 600 grams. Spawning of ides is early, occurring at the end of May - beginning of June, the water temperature does not exceed 6 °C. Spawning most often occurs in the evening, much less often in the morning, eggs are laid in one go. During the life of an individual, spawning occurs several times; the number of eggs from one spawning depends on the size and age of the ide and can reach more than one hundred and thirty thousand.
The duration of spawning in favorable weather is no more than three days; in deteriorating weather conditions it can take up to 10 days. If the weather changes sharply, then reproduction may be delayed until the thaw. Eggs are deposited on branches and vegetation that have been in the water since the previous year, on stones and woody debris.
The color of the caviar of this large fish is yellowish, the size is small, about the size of a small grain, and is not much different from the caviar of other fish.
Embryos develop within 15-30 days; for best development, the water temperature should be around 10°C. The larvae appear in the second week of June, weigh up to 2 mg and body size up to 8 mm.
Fishing for ide begins in small reservoirs in early spring after the melt water has subsided until it clears. Fishing is also possible in winter during thaw periods.
Methods of catching ide

This type of fish is very shy and cautious. When fishing, you should behave as quietly and inconspicuously as possible. Also, camouflage will not be superfluous.
To catch ide, a monofilament line with a thickness of 0.22 mm and a leash with a diameter of 0.18 mm are used.
Ide can be caught using a float, spinning rod, fly fishing and bottom gear. The method depends on the season and the preferences of the fisherman.
Ways to catch ide:
- live bait fishing rod;
- spinning;
- Bolognese tackle;
- frieder;
- donka;
- bombard;
- match fishing rod;
- fly float;
- fly fishing tackle;
- wire rod.
In winter, when reservoirs are covered with ice, ide can be caught with a float or nod fishing rod. Also, for winter fishing, special floats are used that are immersed in water and do not freeze to the surface.
The ide bite is very fast and swift. The float simply disappears under water.
The fishing season lasts almost all year round. The fish do not bite only during severe frosts.
Intense biting of ide is observed during the post-spawning and autumn feeding season. At this moment, the fish loses its vigilance, and it is easiest to catch it. The spring zhor begins after spawning, when the first leaves begin to appear on the birch tree. In autumn, the zhora period begins after the first cold snap, when the leaves begin to fall. This period lasts up to three weeks.
Despite the fact that in natural conditions this fish seems slow and lazy, when hooked this fish begins to jump out of the water and actively spin. In this case, the ide often cuts the fishing line with the help of its dorsal fin. To avoid such situations, do not loosen the line when fishing.
{banner_vnutri-kontenta-3}
How to distinguish ide from chub
4 minutes Author: Konstantin Pavlov 0
Ide belongs to the carp family, just like the chub and asp. Therefore, these types of fish are very similar to each other, which is why they are quite easy to confuse. Often passions flare up on fishing forums in discussions about what kind of fish this or that person caught, because they are so easy to confuse. However, there are still differences between ide, chub and asp, and if you study them well, you can understand at first glance what kind of fish is in front of you.
Features of asp
Asp is the largest representative of the carp family. Its second name is sheresper. Its body reaches 80 centimeters in length; this fish weighs on average 10–12 kilograms. The eyes of the Sheresper are always bright, pure yellow with a small green stripe.
An interesting feature of the asp is its way of life. Unlike its two brothers, this is a daytime fish. This means that he sleeps at night and you definitely won’t catch him during night fishing. These fish go hunting exclusively during the day. The most distinctive feature of the asp is its anatomical feature - a blunt rib that is located on the belly between the fins.
The difference between asp and ide and chub
- Scales. The first noticeable difference between these fish is the color of their scales. In the asp it is dark and has a bluish tint, but in the chub it is golden-green. There is also a difference in its size. The sheresper has small scales, the ide has slightly larger scales, and the chub has the largest scales.
- You can also notice the difference between the fins, namely the anus. In an asp, this part of the body is quite wide, while the chub’s fin is narrower and slightly convex. There is also a difference between the color of the fins, since if you compare them in these three species of fish, it turns out that the sheresper has the lightest, slightly reddish, as well as a gray, slightly bluish tail.
- The eyes distinguish ide from asp. The latter ones are small. These three fish also differ in their jaws. Sheresper has a prominent lower jaw, but the other two species of fish have jaws of the same size.
Tackle for rudd
The fish feeds at mid-water, which limits the number of equipment suitable for fishing. The most versatile is a float rod with a blank of 4-6 meters, which allows you to accurately cast the bait into a “window” among the vegetation. It is important to take into account the high probability of snagging, so a fishing line with a thickness of 0.15-0.2 mm with a tensile test of 2-3 kg is used.
If it is necessary to give additional buoyancy to a hook with a nozzle, a foam ball is placed on the fore-end. For catching rudd at a considerable distance from the shore (20-30 m), a long fast action Bolognese rod equipped with rings and a small spinning reel is well suited. If fishing involves fishing in open water at the border with vegetation, it is effective to use a sbirulino float (bombard) or a light spinning rod.
It is necessary to take into account the excellent sense of smell of the rudd, which is able to smell food at a considerable distance. If you choose the right bait, you can not only lure and hold a lot of fish, but force it to leave the overgrown area into an open place. For this purpose, dusty and strongly flavored, but not satisfying mixtures are used. Excellent results are demonstrated by bait for rudd, which includes:
- boiled corn (1 kg);
- vanilla (3-4 bags);
- honey (5 tablespoons);
- semolina or ground crackers (3 cups);
- steamed millet (0.3 kg);
- anise oil (10-15 drops).
Winter rudd is an inactive fish, which is characterized by a slowdown in life processes in a cold environment (anabiosis). But in shallow water areas covered with thickets of reeds or reeds, successful fishing is possible using nodding tackle with dark jigs (size 3-4 mm). Burdock fly larva, bloodworms or maggots are used as bait.
The best time to catch rudd from the ice is the first half of the day. The intensity of the bite is also affected by temperature - in severe frost the fish completely stops feeding, and vice versa - it actively looks for food on sunny days with a thaw and responds well to food turbidity. To do this, a little flour, porridge, and crackers are regularly thrown into the hole.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Ingredients for Shawarma
Ide in cooking
There are quite a few ways to prepare ide fish. Protein-rich meat is quite high in calories; the raw product contains about 116 kcal per 100 g. But it should be remembered that depending on the methods of heat treatment, the calorie content of the finished product also changes.
Fish meat is a source of complete protein and a wide group of vitamins; it is also rich in potassium, phosphorus, calcium, magnesium and many other substances beneficial to the human body.
The product is easily and quickly digestible. Due to this, it is highly valued in dietary nutrition.
The beneficial effect of eating ide meat on patients with cardiovascular diseases, gastritis and stomach ulcers has been scientifically proven.
The main value is the content of unique amino acids: tryptophan, lysine, methionine, taurine.
Due to the phosphorus and calcium content, eating this fish is an excellent preventive measure against osteoporosis and serves as a natural strengthener of teeth and bones.

Ukha prepared from ide is an excellent stimulant for the production of gastric juice and pancreatic enzymes, which helps improve the digestion process.
One of the original recipes is salted ide for “salmon”.
List of ingredients:
- fresh ide – 2 kg;
- table salt – 400 g;
- granulated sugar – 200 g;
- spicy seasonings to taste: coriander, allspice, etc.
To prepare, the carcass is cleaned of scales, the head, tail and fins are cut off. The peritoneum is opened and the intestines are cleaned out. The cleaned semi-finished product is opened along the back and the spine and rib bones are removed.
Then the inside of the layers is sprinkled with salt, sugar and spices. Having combined the halves treated with spices, put them in a container and put oppression on top. Then put it in the refrigerator for two days.
After the required time has passed, the product is ready for use. Its taste is reminiscent of young salmon. Additionally, the meat can be lightly smoked.
Ide fish, its difference from the chub and where it lives
Ide, like asp, belongs to the carp family, representing one of the most interesting species of the ray-finned family.
This representative of cyprinids is a freshwater species, but can also tolerate slightly salty water of sea bays. The main places where this fish lives are rivers, river ponds and flowing lakes. But you won’t find it in mountain rivers with fast and powerful currents or in cold reservoirs. The ide fish is one of the hardiest river inhabitants and can easily tolerate temperature changes, including sudden ones. At the same time, the most comfortable body of water for it is a clean, deep river with a moderate current and a silted clay bottom. It can also live in reservoirs, preferring deep places, avoiding rocky and sandy areas.
The lifespan in natural conditions ranges from 15 to 20 years. But as a rule, an ide rarely manages to live to see its 10th birthday.











