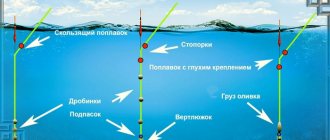
Carp represents one of the forms of carp. It can be seen in shallow bays, lakes and ponds. There are pond and river ones. Pond carp has a humpbacked and roundish body, covered with large scales.
River carp, on the contrary, has fractional scales, but the body, when compared with pond carp, is much more massive and the color is lighter. The only thing they have in common is the mustache located on both sides of their heads. They are caught in large numbers, which directly depends on their spawning.
What does carp spawning depend on?
Carps are very hardy fish; in order to reach the place where eggs are laid, they overcome a difficult path. On their way there are dams and low dams, but this is not a hindrance for them. The ability to jump out of the water up to two meters helps them achieve their goal.
Spawning grounds are chosen in places:
- overgrown with reeds and water lilies;
- bottom driftwood.
This happens so that you can protect your “descendants”, that is, hide them. For them, such fates are considered successful.
After feeding and a good meal, all holders of the carp title begin the spawning process. In several flocks, partners chase their “producers”.
There are approximately five to six individuals in one group. An interesting fact is that females themselves choose several partners and... The female is slightly larger and thicker than the males.
When do carp bite after spawning?
Most often, biting begins 15-20 days after the main phase of egg laying. However, it is difficult to say exact numbers due to the fact that the process itself can last more than a month for the entire species.
It is worth considering other features. For example, in colder regions the bite may begin earlier, within a week.
In general, it is extremely difficult to determine the exact time, but it is still possible to approximately calculate it. The main spawning activity occurs in late May and early June. It’s better not to fish at this time, and in mid-June. A good bite begins closer to the mid-twenties of June and returns to normal closer to early-mid July.
Rest after spawning
Such rest manifests itself as a strong decrease in the activity of individuals. They become a little childish and don't want to do anything, not even take the bait. Master fishermen still manage to catch them during such periods, but it is difficult to do.
Let's celebrate! Fish most often rest in quiet places where there is no strong current. Also often close to tree roots or in thickets of thick grass. Every day the activity increases, and the fish begins to lead an increasingly ordinary lifestyle.
At what temperature does carp spawn?
When the flood begins, the carp goes “to play” along with the water. Carps that live in ponds and lakes rub faster than river ones, since running water warms up faster than standing water.

There is a belief that the spawning of fish coincides with the flowering of wheat, this is due to the fact that at this time there is intense heat. Favorable temperatures range from 18 to 20 degrees.
In very cold water and steamy water, like milk, fish do not spawn. At such moments, they are inactive and behave calmly, not playfully, they just swim for themselves, and that’s all.
A large river flood is not a suitable place, because adult fish move far from the riverbed, and the spawned eggs attach to the walls of cliffs and leaves of plants. Over time, the water gradually begins to recede, the eggs are left to dry in the sun or become food for birds. Despite all this, small carp are eaten by their neighbors, such as perch and pike.
Caviar is mostly stored in:
- pits;
- bays.
It is difficult for other fish species to get there and there is a possibility that some will survive. River spawning is sometimes carried out in cold water.
When does carp spawn in the middle zone?
Carp spawning is a little different from many other fish. The fact is that in the middle zone, carp spawning can actively begin as early as the 20th of April. Closer to May, this phenomenon becomes more common, and the peak occurs at the beginning of June.
In general, the spawning of some individuals can continue until mid-August, although these are rather exceptional cases that should not be taken into account.
Let's celebrate! Most individuals begin to spawn when the temperature becomes warm and constant, and the nights are no longer so cold. Most often this occurs in early summer, although depending on specific weather conditions, spawning can begin earlier or later.
How long does it take for carp to spawn?
Typically, carp spawning lasts one month. True, this phenomenon is not chaotic and can often drag on for a longer period. The fact is that this fish has a clear hierarchy. The youngest fish spawn first, and then it’s time for older and larger individuals.
Good to know! Despite the average duration of a month, the process may take a long time. For example, this may be caused by a sudden cold snap. In this case, the fish can “postpone” the process of spawning until more favorable conditions.
If we talk about a specific time of day, then everything starts before dawn and ends closer to noon.
Features of carp spawning
The spawning process occurs mainly in the morning, especially as soon as the sun rises. When the sun just rises, the fish begin to visibly squirm, as if preparing themselves for spawning. By noon everything stops.
Females are accompanied by two to four small moloshniks. They take a long time to choose a suitable place for spawning and look for grass thickets. Sometimes females stop in areas where there is very little water, this happens in order to better fit themselves in this place. But as the water recedes, the fish dies; it is unable to get out to its native abode.
Carp breeding
full-fledged producers in the conditions of cultural pond breeding of carp . In the southern regions, sexual maturity of carp occurs much earlier: in the Krasnodar Territory, for example, at the age of three. In Indonesia, carp spawn when they are one year old.

Pictured is a scaly carp
The process of spawning in carp fish is repeated annually and usually occurs at a water temperature of 18 ° C. However, when the eggs of the carp are ripe, spawning is possible at a lower temperature. In practice, there have been cases when carp, planted for spawning, did not spawn even at temperatures of 20°C and above. When the time comes, sexually mature females approach the spawning grounds, spawn eggs, and male carp fertilize them with milt. Some of the milk penetrates the eggs, and the rest die after about a minute. Unfertilized eggs also die, which after 10 hours acquire a whitish-cloudy color and then quickly decompose. The carp spawns eggs in 2-3 portions. The eggs are sticky, 1.4-1.5 mm in size, and stick to the vegetation of the reservoir.
The success of fish reproduction largely depends on spawning conditions. Carp, for example, in the absence of meadow vegetation or in the presence of vegetation that has been under water for a long time, often does not spawn. The same thing happens in the presence of an acidic environment in spawning ponds.
To obtain a large number of offspring (juveniles), special conditions for breeding carp are created in spawning ponds that correspond to the biological characteristics of the fish of this species. In pond farms, isolated spawning is organized (planting fish of the same species in spawning ponds), guaranteeing the preservation of the largest possible number of eggs and juveniles.
Based on the type of spawning, carp are classified as schooling carps - they gather in large herds to spawn. In the conditions of pond breeding of carp, the following types of reproduction are distinguished:
Types of carp reproduction
- Pair propagation is used in the breeding of carp or carp.
- Nest breeding, the most common, is used for both carp and other fish. Typically, a nest is formed from 1 female and 2 males.
- Group breeding of carp. Common when breeding carp, silver crucian carp, and tench. Several females and males are planted for spawning.
Experience shows that obtaining a high yield of juveniles per 1 kg of female carp weight is possible both during group and nest spawning.
The advantages of group spawning are that with this method, greater selectivity of fertilization is achieved, reducing by 2 times the number of males in the farm, since not two, but one male can be released for each female. For group spawning, the area of each spawning pond should be 0.15-0.20 hectares (at the rate of 0.05 hectares per female), and the planting should be 3-4 nests or 3-4 pairs of breeders.
In large farms for group spawning, spawning ponds with an area of 0.3 hectares are allowed, with six pairs of spawners planted in each pond at the rate of 0.05 hectares for each pair. Large-area spawning ponds are more preferable not only because their construction requires less capital investment, but also because it is easier to use mechanization in them for liming, fertilizing, harrowing in the spring, as well as mowing vegetation in the summer. Obtaining high practical fertility largely depends on the skill of the fish farmer.
| On a note. A fish farmer from the Belgorod region used mowing of vegetation in spawning ponds. With group spawning, based on planting one female per 0.05 hectares of pond, he received 160-190 thousand eight-day-old fry from each female Kursk carp. He left only a strip 1-4.5 m wide near the dam unmowed. Farmed carp laid their eggs on this strip of vegetation, and the larvae emerged into open water to feed. |
Drawing of Kursk scaly carp
In practice, the fertility and yield of commercial fry from one female also largely depends on the rearing conditions of the producers. From four-year-old first-spawning females of Kursk carp weighing 2.5 kg each, raised in good conditions, during group spawning in wintering ponds, from 127 to 192 thousand fry per female were obtained, or from 28.2 to 42.6% of absolute fecundity.
Spawning period of carp

At this crucial moment, the males try to swim near the females, creating a splash of water. In calm weather, their playing can be heard at a distance of up to a kilometer. During this wonderful period, the scales of males become covered with small tubercles, from which the reproductive product then comes out more easily.
The female scatters the eggs with her tail so that they stick evenly and well to the grass. The male comes next and, like a “real father,” covers her with his milk, which is released very quickly. A small part of the milk is enough to fertilize it; it only superficially covers the eggs.
Carp eggs stand out noticeably against the background of other fish eggs, the yolk is covered with small dots of a mucous substance, there are no currents. This is why several “partners” are needed for fertilization.
Duration
The spawning period directly depends on weather and climatic conditions, and the age of the individual. As a rule, carp spawning lasts no more than a month. All fish are conventionally divided into age groups, each of which spawns for 10-12 days.
An interesting feature of the carp is that the fish does not immediately release its eggs, spawning them in stages. There are cases where fishermen caught large adult specimens with eggs even in mid- and late August. The duration of spawning depends, among other things, on the temperature of the water in the river or lake. In warm, heated water, carp spawn much faster.
Note! Pond and lake carp go to spawn much earlier than river ones, since the standing water of these reservoirs heats up faster than running water.
Such unstable spawning periods allow experienced fishermen to unwittingly “bypass” the fishing ban by fishing for carp with eggs in late June and early July.
Average data
The transformation of eggs into young eggs depends on the heating of the water. At 18-20 degrees the duration is up to ten days, at lower temperatures it takes twenty-one days, or even more.
Well, if the water is very cold, then, unfortunately, no one survives. According to statistics, out of three hundred thousand eggs, on average, only three thousand survive, after about one year there are even three hundred individuals. In the first days of life, the fry feed exclusively on zooplankton.
During their first year, small carp grow quickly, although they lie down for the winter. This happens because carp are omnivorous fish. And she has enough food for the entire time until it gets warmer. It is also popularly called the “water pig”, which eats plant and animal matter.
What are the peculiarities of spawning?
- With the arrival of spawning, carp change their previous habitat and head towards shallow water. They like different water bays, tiny wells or just puddles. Thus, the carp breed tries to protect its future offspring from freezing. Because it is in these places of the reservoir that the water is best heated. But this distinctive feature of carp spawning can “play a cruel joke” on them. Because during a particularly hot summer, the water in such puddles can dry out, causing certain death of the offspring.
- But not all the carp family chooses shallow waters for spawning. Wild carp, in other words, carp, prefer to spawn directly in the riverbed.
- Another feature of carp spawning is that the fish spawn in a clear sequence. At the beginning, the small individual spawns, then the medium one, and only then does it come to the largest fish. Moreover, the grater of any of the groups of the carp family does not last more than ten days.
- Carp spawn in portions, two to three times. Moreover, in the first pass the main part of the caviar comes out. It is also interesting that one individual (female carp) can lay more than one million eggs. And with age, this number will only increase.
- The grating of the carp family occurs exclusively at dawn. It is at this time of day that fish feel most protected and safe in shallow water.
- Practice shows that in a flock there are two males per female. A distinctive feature of the latter is their shorter body length than that of females, including differences in other proportions. The female carp is superior in both width and height to its male.
- It is interesting that in the world there are sterile individuals of the carp family. They can be distinguished from other fish, since such an individual is distinguished by its enormous size and thick belly. Her lips are protruding, and her tail is much shorter than the others.
Carp spawning time is usually in the morning. By lunchtime the game process stops. Female individuals spend a long time choosing an area for spawning. Basically, their choice is vegetative terrain. It also happens when the female lays eggs in a place where there is little water. This is fraught with the fact that in the future, due to the decrease in water, the carp will not be able to swim out and will die, unable to return to deeper water.
Special carp
In nature there are carps that cannot reproduce; these are considered sterile. They have milk on one side and a caviar sac on the other.
Such fish is often found on household tables and is considered the most delicious and fatty. If you have the opportunity, be sure not to miss the chance to try and enjoy such carp.
From spawning to maturity, fish go through a long and dangerous path:
- dry out when exposed to sunlight;
- birds and their relatives eat.
But this is how nature works and nothing can be done about it. So, let's at least show a little conscientiousness and not catch any more small fish that are not fully mature. Let it take some time to catch a great trophy later. Catching fish during the spawning period is strictly prohibited!
Is carp caught during spawning?

In most cases, fishing during spawning is prohibited . But fishermen simply limit their fishing gear to fishing, and then only for a short time. Active carp fishing continues as usual. In order to catch fish during spawning, it is necessary to calculate the possible routes of movement of the bulk to the spawning ground. All the fish are going to move to one place, so the chances of catching a big catch in such places are high.
Peculiarities of carp behavior in sultry heat
Despite the fact that carps are very heat-loving creatures, they do not like heat. When the water temperature begins to approach +20 degrees Celsius, the fish increasingly hides in “burrows” (for example, in “shelters” under the roots). If it gets even hotter, she moves to a cold spring or goes to the pools. In the absence of such in the reservoir, the carp can simply stand for a long time and motionless on the bottom, completely burying its head in the silt (or lying algae).
Thanks to a very developed lateral line, he can sense a threat even without a head (i.e. without sight and hearing). At the slightest suspicion of “trouble/danger,” the carp suddenly take off and quickly leave. At the same time, literally in seconds, changing the direction of its movement several times. At the moment of the jerk itself (with the help of a swim bladder), they emit a low-frequency “clicking” sound, a kind of “general alarm signal” for their relatives. Further, in the process of “escape,” the external glands of the carp release special hormones into the water (the so-called “fear hormones”), the smell of which warns all fish in the area about the approaching danger.