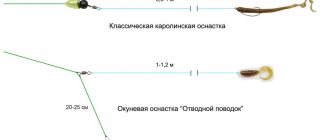
The fly rod is considered the most effective float rod for catching small fish of all types. This is achieved by the speed of casting and pulling out the equipment. And the only thing inferior in terms of control over equipment is the plug.
Fly rods are universal gear that can be used for different fishing methods and different types of fish: crucian carp, white bream, ide, roach, rudd. According to the type of connection, they can be divided into:
- plug;
- telescopic.
Fishing is usually carried out only in the coastal zone of a reservoir at medium and short distances. The fishing process is short, depending on the length of the rod, guiding the equipment through the water, followed by its control: holding and stopping. When the rod has a light weight, it is easier to make repeated and accurate casts over a long period of time. The main advantage of this kind of fishing is the ability to quickly recast, which is especially important when there is a strong bite.
Types of fishing rods
They have a fairly wide range of applications, and therefore are endowed with many different modifications. Each of which has its own unique characteristics.
There are 3 main varieties:
- Classic . The most common length is up to 13 m. Very powerful, thanks to its design and the flexibility of the material used, you can easily pull out a trophy weighing 5 kg.
- Ukleichnoe . They received this name after repeated sporting competitions where they caught bleak on them. The length reaches 4 m. They are quite light and thin. The handle is made of high-quality materials and has a slight thickening of up to 30 cm. This thickening is made to increase comfort.
- Karpovoe . They are not widely used due to their very large size: from 7 to 14 m. They are quite heavy, so they usually catch fish from special stands.
Criterias of choice
Select according to the following criteria:
- The rod's legs should be long.
- The more joints, the heavier it is and, therefore, the worse the structure will be.
- The thinner the diameter of the butt, the higher its class will be, and, therefore, the better the action.
- You need to pay attention to the tip of the fishing rod, the thinner it is, the better.
Material
Nowadays it is mainly used: composite, fiberglass, carbon fiber.
Fiberglass is the most budget option, and this is probably why it is not very successful, it has:
- large mass;
- insufficient elasticity and strength.
The composite consists of a mixture of fiberglass and carbon fiber. Strength and rigidity will depend on the content of all components. These form data will reduce its weight, while proportionally increasing the price. Not a bad option at all, which will combine certain characteristics of top models and affordability of purchase.
Carbon fiber (carbon) is the most successful, which differs:
- weightlessness;
- good strength;
- excellent elasticity;
- reliability;
- durability.
Thanks to the fiber, it has a low specific gravity and high tensile strength.
Graphite has a variety of markings, the best swings are made using graphite - IM-9, with a length of up to 11 m. The rather long length gives great advantages to the owners, and ease of use will help you enjoy fishing to the fullest. It has the only drawback - great fragility.
Test
The test is the range of weight sent in casting that will be comfortable for the fisherman. An ideal test will provide:
- correctness of the throw;
- required range.
And the inconsistency of this test, its great exaggeration, can result in the form breaking.
Build
The structure of the rod directly depends on the rigidity indicator. It happens:
- slow;
- fast.
The level of rigidity depends on the following indicators:
- material;
- strength of connections.
The fewer legs, the more accurate its action will be: the dimensions of this form must be proportional to the number of legs, for example, a 5-leg blank will be 10 m long. A rod with an excellent fast action will not sag or sag. When the fishing rod has an excellent action, it will be able to hook a fish with one movement of the whip.
Length
Will vary from 3 to 14 m, divided into 4 categories:
- Short - from 2-4 m, weight from 250-450 g.
- Medium - from 4-7 m, weight no more than 1.5 kg. This is a particularly popular category.
- Long - from 8-11 m, for fishing, no more than 3 kg. They are in little demand, and only for fishermen with extensive experience.
- Extra long - from 11-14 m, used mainly for competitions.
Weight
Weight should be as minimal as possible. This will allow fishermen to easily manipulate the whip.
Optimal characteristics:
- length 2-4 m.
- weight 110-130 g.
- weight 160-280 gr.
Balance
The basic sensations of hooking, catching, casting and holding are determined by knowing its balance. It must correspond to the dispersion of the mass of the form over its length, and create a center of gravity at a certain point.
The dynamics of casting are also important; the smaller the residual vibrations, the better. If the center of gravity is near the handle, then the rod is of high quality.
Power
Power parameters are quite rarely taken as separate characteristics.
By power they are divided into:
- medium-power;
- ultra-light;
- powerful;
- lungs;
- medium-light.
Vershinka
The last link of the rod is called the “top” - this is the most bendable part of the blank, which plays the main role in hooking. They are made from elastic composites of different compositions, and in various modifications.
They produce it in 3 types:
- reinforced;
- hollow;
- hybrid.
The most acceptable option is a solid reinforced whip.
Bottom knee
The length of the main leg is important especially when transporting it. If we proceed directly from the thickness of the butt, then the form can be different, it all depends on the material used: for carbon fiber ones, for example, the base section is equipped with a diameter of about 4 cm.
When ergonomic holders specially designed for this purpose are placed on the butt, this significantly eases the pressure and improves its grip.
Selecting a shock absorber and installing a connector
The rubber in the rig plays a key role; when biting a large specimen, it is the only thing that separates the fisherman from catching it. You can assemble the tackle with your own hands; to do this, one end of the shock absorber is attached to the connector sleeve, and the other is passed through the rod from the inside and removed from the hole in the whip. The free segment is tied with a loop to the second part, which is installed in its place.
The diameter of the elastic is the main criterion. When catching small fish weighing no more than a kilogram, use a shock absorber up to 1.2 mm thick. Large individuals require an increase in this parameter. The length of the shock absorber directly affects the quality of the development of mining jerks - the shorter the element, the stiffer it is and the less it stretches. That is why you should install longer tires, which will have a reserve reserve when fishing. The thinnest models are built into the first two legs of the rod, and the thickest ones, such as carp ones, are built into three or four segments. Difficult choice of tires causes beginners to make mistakes, so at the initial stage you should consult with more experienced comrades, and also look for information on your own.
Basic elements of gear
For assembly you will need:
- connector;
- fishing line of various thicknesses;
- set of hooks;
- set of weights;
- several floats;
- fishing line for a leash;
- float mount.
Form
A high quality fishing rod:
- handle diameter is smallest;
- knees, have a greater length, and the smallest number of knees.
The price of such models will be correspondingly very high. Because high-quality materials are used for their production, but this is a justifiable waste.
fishing line
Mostly blind equipment is used, and with a thin fishing line. The ideal fishing line thickness is 0.1-0.2 mm. The fishing line also needs to be equipped with a special leash:
- 16-20 cm long;
- with a diameter of no more than 1.3 mm.
It's even better to use monofilament. All connections must be made, completely excluding the use of swivels and special carbines.
Float
Drop floats
When choosing a float, it is necessary to take into account the current speed:
- The lower the speed, the more sensitive the float is selected.
- Intense currents require floats that are stable on the water.
A teardrop-shaped float is the best option . A special float is attached directly to the fishing line using cambrics.
Loading and hooks
The sinkers used are light, mostly rounded. The float is surrounded with small pellets, this is done for good stability. The main sinker is attached near the connection of the leader.
The leash is surrounded by a so-called underhook made of pellets, but not very heavy, almost up to the hook. Then the fish will be able to swallow the hook well.
Coil
There is no reel attached to the rod .
As a rule, small, primitive coil devices are used on medium-length forms. They mainly serve only for storing fishing line.
Fishing with a fly rod
- VK
A fly rod is a very effective method of fishing on any body of water. It allows you to present the bait to the fish on sensitive equipment accurately and accurately, and the fishing itself is interesting, productive and quite simple. Most often, such conditions occur in reservoirs and lakes, the species composition of fish and fishing in which have much in common.
FLY ROD FISHING IN RESERVOIRS
As with any fishing, one of the main tasks when fishing with a fly rod is choosing a catchable place. The task is simplified if there is preliminary information from the reservoir from fellow fishermen, which, of course, should be treated with a certain degree of criticism, especially if it is received from local fishermen. Usually they fish not in places interesting for fish, but where it is more convenient for them or closer to home. Often this tactic is justified, since the fish are suitable even for an unpromising, but constantly fed place. Of course, the most valuable is your own experience gained through the use of individual fishing techniques and specific bait.
But there are often situations when you have to choose a place on an unfamiliar body of water, then you can only rely on your experience and observation skills. In such cases, it is worth carefully examining the topography of the shore. When hunting for more or less decent specimens, you have to look for deep places. The steeper the slope approaches the water, the greater the depth you can expect near the shore. If the slope is cut by a stream or ravine, it means that in this place there is a discharge of soil into the reservoir; here a bank is formed with two slopes on the sides. Such a place is also interesting because the stream brings out additional food for the fish. Trees on the shore suggest the presence of snags at the bottom, and they always attract fish. In addition, the soil retained by snags forms smooth local shelves, convenient for fishing. However, when measuring the depth, such places should be examined very carefully: an unnoticed snag or branch will deprive you of a large number of hooks. Large reservoirs and lakes are characterized by wide coastal shallows, so you have to look for places near the confluence of rivers or large streams, near hydraulic structures (where fishing is allowed).
Particularly interesting are the dams that separate the reservoir surface from the swampy lowlands. If they are lined with stone, then, in addition to a decent depth, they attract the fish that live here with the zebra mussel shell, especially bream and large roach. And the fish are always interested in places where different soils are combined, which can be either natural or artificially created. Often there is a chance to catch excellent fish even at a shallow depth, about 2 m, of course, if there are thickets of grass or snags in which there is a lot of food, and the saving depth is not far away. Early in the morning and before sunset, most fish come out to such places to feed. At this time, even large bream can be caught from a depth of about 2 m. And fish such as roach and silver bream almost always prefer to stay at a depth of 2-3 m, especially if this is the upper edge of the riverbed.
DEPTH MEASUREMENT
On a flat bottom, a few casts of a medium-sized depth gauge (10-15 g) are enough to find out the depth. A depth gauge is convenient for quickly examining the bottom, for example, when searching for a fishing spot; it can easily determine the presence of algae, snags, and the approximate structure of the bottom (silt or sand). Lately, on stagnant bodies of water, I have been quite accurately determining the depth with a fly rod without a depth gauge. The technology is simple: I move all the sinkers to the leash, and when casting, the float clearly shows whether the sinkers are on the bottom or in the water column.
As a result, I set the depth so that the entire antenna protrudes from the water and the sinker lightly touches the bottom. I mark the depth with a marker on the rod and move the float lower by the length of the leash. In this case, the hook will touch the bottom, which is optimal for catching most fish. When hunting for bream, I only move the float slightly lower so that the main load rises a little in the water column, and the leash with the hook remains at the bottom. After this, I distribute the main weights along the fishing line, bringing the equipment into working condition. I like the method of measuring depth with a movable load because it eliminates the error due to the stretched line that occurs with the traditional method.
When measuring the depth, it is necessary to examine not only the fishing point, but also a short distance around it in order to identify the slope of the bottom and the possibility of hooks. A much more difficult task is measuring the depth on a steep slope of the bottom. Fishing on a very sloping bottom is difficult, and it is better to avoid such places, but if you manage to find a small “shelf” on the slope or even just a more level area, then a large bream may well come out from the depths to bait.
TACKLE
If you don’t set yourself the task of fishing in a specific, well-known place, then you need a pair of rods: one for fishing at close range (up to 5 m), and the other for long distance (7-9 m). A long rod came to my rescue when large fish entered shallow water but did not approach the shore. A short one can save you if there is no bite at a long distance or when large fish are inactive in the middle of the day, but you can successfully fish under the shore. It is never superfluous to feed the reserve point a little closer in anticipation of roach and silver bream. Sometimes, at a distance of a short rod, a large bleak comes out, the size of which in the reservoirs of the middle zone can be impressive: I managed to catch a bleak weighing up to 60 g. Of course, you can get by with just one rod.
The main problem with gear when fishing in still waters is current. Most often this is a wind-driven surface current, but often the entire water column moves at low speed. This usually happens after several days of windy weather, when the water begins to circulate through the reservoir, and even after the wind stops, this phenomenon continues for several days. The best option is when the current is directed against the wind. The traction force on the surface compensates for the movement of the equipment from the float to the sinker, and a certain balance is observed. If the directions of the current and wind coincide, then you have to significantly make the equipment heavier and lower some of the weights to the bottom, which reduces the drift speed. Additionally, submerging the line running from the float to the rod helps. To do this, a micro-pellet (No. 12-13) is attached in the middle of the fishing line section, which, when casting, pierces the surface of the water and sinks the fishing line, preventing it from sailing. Taking into account the fact that the stock for such fishing is at the bottom, there is no need to adjust the load. For fishing in still water, elongated floats are used, with a thin upper body; they perfectly show rising bites, of which there are many when feeding lying on the bottom. The main distribution patterns of weights are shown in the figures.
Casting light equipment even in light winds can be difficult. To do this, it is necessary to give it sufficient momentum, accelerating the rod from behind the back, for which it is pulled back and after a pause sufficient for the equipment to move further away, cast smoothly but energetically. The equipment should stretch out in a line on the surface of the water, which ensures that there are no overlaps when diving.
Casting from the side or from below with a long rod cannot be done, as this leads to tangling of the equipment, and sometimes even to breakage of the rod. It is much easier to cast light tackle with a soft rod and, thanks to good shock absorption, it is easier to land fish than a harder one. Some delay in hooking with a soft rod is more than compensated for by better bites on light tackle.
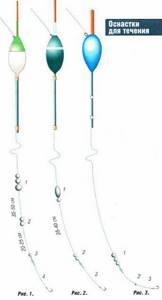
Rice. 1. Equipment for catching roach and silver bream at shallow depths: 1 - main load; 2 — additional sinker; 3 - sub-lead 0.1-0.2 g: 4 - leash 20-30 cm.
Rice. 2. Equipment for deep 1 depth or for catching bream from the bottom: 1 - olive sinker: 2 - additional sinkers; 3 - additional feeding 0.1-0.2 g. 4 - additional feeding 0.05-0.1 g on a leash of 20-30 cm.
Rice . 3. Bleak equipment for fishing in the water column: 1 - sinkers; 2 - additional grazing 0.05-0.07 g; 3 - leash 10-20 cm.
LURE
The basis of the bait is loose mixtures. Its composition must be selected for a specific body of water and fish. This composition is very different in effectiveness from the crackers and cereals that many fishermen feed. In addition, the fish completely eats this bait and it does not sour at the fishing site. The amount of soil added to the bait depends on the season and water temperature.
In spring and autumn it can be up to 50% of the volume of the mixture. This amount of soil greatly reduces the nutritional value of the bait and does not allow the fish to quickly become saturated.
In summer, when fishing in standing reservoirs, the soil is used mainly as ballast to weigh down the bait balls, and the fish are interested in the active aromatic mixture. But no matter what bait you choose, you definitely need to check its operation: a small ball of bait should disintegrate in the water within 1-10 minutes. Denser balls are only suitable for attaching fish. They can be thrown in the evening so that they take effect at dawn.
I have repeatedly noticed that anglers throw bait directly to the float. This is a very common mistake. Firstly, in flight and for some time in the water, the ball has a horizontal velocity component. Secondly, fishing rarely takes place on a completely flat bottom; most often there is a slope towards the reservoir, and the ball of bait rolls down a little. As a result, he ends up at a completely different point from where the fisherman is fishing. This must be taken into account and adjustments made. Of course, you can check how much the bait balls have moved by trying to fish further away, but such fishing is tedious or requires the use of a longer rod. It is much easier when casting bait 20-50 cm not to throw it to the float. This compensates for the slight approach of the gear during fishing due to wind currents and allows for better control of the gear. Even a weak current slightly carries bait balls and bait particles along the shore; There is no need to make allowances for this, but from time to time it is necessary to try to fish a little further downstream. Often the largest specimens stand on the bait train, this behavior is especially typical for roaches.
CATCHING
Usually, soon after feeding, bites begin. Small fish quickly find bait and actively eat it. To wait for large specimens, additional feeding is necessary. The rate of supplementary feeding has to be determined anew each time. Standard practice when catching large fish is to cast rare, massive, 3-5 large balls of bait. As soon as the first noteworthy specimen is caught, the pace of bait must be changed. Large fish are usually frightened by large balls, so supplementary feeding is done in small portions, throwing balls approximately the size of a table tennis ball. To keep the fish interested, bait is thrown more often, but only if the fish is not scared. If the reaction is negative, throw in two or three lumps of bait, increasing the pause between subsequent portions. When fishing for bream, it often happens that the fish gather at a feeding point and manage to catch several specimens, but suddenly, as if on command, the bite stops. Sometimes this happens after the bream has fallen off the hook. It can be assumed that the fish scared away others nearby. Usually in such a situation the bream is replaced by roach or silver bream, but in this case this does not happen. The fisherman, deciding that the bream has not gone far and the bite will resume, continues to fish. The bream really doesn’t go anywhere, it just rises about 1 m above the bait, thereby preventing small fish from approaching, but it doesn’t bite either. It’s rare that you manage to catch a fish, but almost always it ends with a gathering and subsequent stories from the fisherman that, they say, such a bream bit from the bottom and couldn’t get it off! It is typical that in this case the leash and part of the fishing line above it end up in fish mucus. Athletes also have to face this problem, but a way to solve it has not yet been found. It may be advisable to stop fishing for a while; the fish will calm down and continue to bite, but this is unacceptable in competitions. Athletes usually prefer to try to catch fish with an extremely light falling rig, although this opportunity only arises when fishing with a pole. Sometimes bream simply waits for the feeding period, for example in the morning or evening, preferring not to swim far, but to stay close to the table set by the fisherman. Roach, fortunately, is less picky, and if you managed to collect it, then the most important thing is to maintain the pace of feeding.
It can be more difficult to catch larger specimens. This can often be done by placing a maggot, its pupa or a piece of a worm on the hook. Small fish are reluctant to take these baits, and large fish often get them. Fishing for silver bream is very interesting. In its habits, it occupies an intermediate place between the bream and roach. The silver bream responds well to bait, is much less timid than bream, and when fished it offers decent resistance. Of all the baits, she prefers maggots, colored red. The main problem when fishing for silver bream is very fast bites, during which the float only shudders, so hooking is out of the question. Maximum lightening of the gear can help, since the silver bream is kept close to the shore, within the reach of a 6-7-meter fishing rod, allowing the use of equipment weighing less than 1 g. If you have to use equipment weighing less than 0.5 g, then a simple technique can make casting easier: one knee When landing fish and re-rigging, the rods are folded inward, thereby shortening the rig, and before casting they are pulled out. This technique allows you to react faster to bites, since the length of the fishing line between the rod and the float is reduced. The main line for such fishing should be no thicker than 0.12 mm, otherwise casting is very difficult due to its windage.
Fishing with a fly rod on a reservoir does not present serious difficulties even for a novice fisherman, but it allows you to fully master the gear and count on good catches.
FISHING WITH A FLY ROD IN THE CURRENT
When fishing in the current, certain requirements are imposed on the rod: it must be as light as possible and sufficiently rigid. If everything is clear with the weight (you almost always have to hold the fishing rod in your hands, and every extra gram affects the convenience of fishing), then the rigidity should be within certain limits. In the current it is rarely necessary to use very light rigs, so medium-action rods are optimal, which are good at casting various rigs and are convenient for retrieving and holding. Unlike a soft rod, a stiffer rod behaves better in the wind, allowing you to work more efficiently with gear. But at the same time, if we compare a rod of average construction with a rigid one, the first one is somewhat lighter and obviously has a greater reserve when landing large fish, allowing, thanks to its flexibility, to absorb its jerks.
It is optimal to have a pair of rods, 4-6 and 7-9 m long: short ones are used to fish the coastal part of the river, for example, when fishing for roach, dace or bleak; It is also convenient in strong currents; and long - deep water when fishing for bream or silver bream. Floats for flow require a drop-shaped shape and a long keel - they perfectly resist the pressure of the water flow and are more stable when deployed. The stronger the current, the more the shape of the float should approach spherical. The wide upper part of such a float does not come out of the water, maintaining sufficient sensitivity of the equipment during braking. Such a float does not show bites on the rise, which, by the way, almost never happen in strong currents.
Rice. 1. For weak and medium currents (main option): 1 - main load: 2 - additional load; 3 - sub-lead 0.08-0.15 g: 4 - leash 20-25 cm.
Rice. 2. For a very strong current: 1 - main load: 2 - supplementary weight 0.2-0.5 g. 3 - leash 20-40 cm.
Rice. 3. For wire fishing: 1 - main load; 2 - sub-lead 0.1-0.3 g: 3 - leash 25-40 cm.
The distribution of sinkers on the rig varies depending on the fishing conditions. The load can be from evenly distributed along the entire length of the fishing line to concentrated at one point - in front of the leash. The greater the distance the weight of the load is distributed, the more naturally the rig moves in the water flow and the fewer kinks in the line from the float to the hook, which greatly increases the sensitivity of the rig. But such equipment has a significant drawback - it is prone to frequent tangling, so in practice it makes sense to install sinkers in three to five places. one of them serves as a shepherd.
The weight of the sinkers should increase from bottom to top, starting from the hook. This equipment is universal and has good performance characteristics (Fig. 1).
In some cases, for example, when fishing in a very strong current or with a tight hold, you can concentrate the load in one place, 40-80 cm from the hook, and install a heavy feeder weighing 0.2-0.5 g in front of the leash (Fig. 2 ). It is only important that the length of the leash (20-40 cm) be less than the distance between the underline and the main sinker; this will save you from overlapping the hook and line above the main sinker.
COMPOSITION OF BAIT FOR FISHING IN CURRENTS
In addition to the main basic components of bait, during currents you almost always need ballast - soil, which performs three functions.
Firstly, the weighting of the bait is necessary so that it reaches the bottom faster and does not get carried away by the current.
Secondly, a change in the physical properties of the bait: clay makes the bait heavier and additionally glues it together; loam (ordinary soil) makes it heavier, and depending on the concentration of sand in it, either slightly sticks it together or loosens it.
Fine (3-5 mm) gravel will help to radically make the bait heavier, almost without changing the speed of its erosion. It is not recommended to use clean sand, since when the balls at the bottom are washed out, it remains in place, gradually covering the bait. The bream, of course, is able to dig up a pile of sand to get to the food, but in this case the meaning of the action of the bait is lost, since the fish will quickly eat the offered treat. And for roach, the bait lying on the bottom ceases to exist, since it is primarily interested in particles floating with the flow and marking the feeding path.
Soil is not required when feeding with a mixture of steamed grains of wheat, city, pearl barley, hemp, etc., but such bait is still more typical for fishing with reel gear, and is rarely used in fishing with a fly rod. As for any fishing , it is highly desirable to include at least a small amount of animal components in the bait - bloodworms (small or large), maggots or cut worms. If there are few of them, you can use animal supplements, but only in the supplementary part of the bait.
FEEDING WITH THE CURRENT
There are two main feeding schemes when fishing with a fly rod.
The first option - feeding along the line of the equipment's passage - is more often used on a fairly flat bottom. Balls are thrown like this. so that the main part of the bait is opposite or slightly downstream from the angler; It is from this point that it is possible to control the gear with minimal drift towards the shore. The rest, a smaller part of the bait, is thrown along the line of movement of the equipment, taking into account its braking and displacement towards the shore. In this way, we attract some of the fish to the main bait, and some may be a little further away. This scheme works especially well when fishing for roach, silver bream and chub, which love floating food particles.
Another option is that all the bait is localized at one point. You need to cast it so that the main part falls a little lower downstream, then guiding along this point will be most effective, with a decent distance from the shore. This option is especially good when fishing for bream or crucian carp, when you need to strongly slow down the tackle at the fishing point, provoking a bite. Of course, such a scheme does not cancel free-floating fishing, which is used periodically to check the presence of fish downstream, where biting by roach and silver bream is quite possible.
When casting bait, it is extremely important not to add it slightly. If in still water this is required by the bottom topography, which allows the balls of bait to roll a little (which must be taken into account), then in the current - holding on to the tackle while retrieving it, when it moves to the shore in a certain arc under the influence of a fishing line stretched by the fishing rod. In practice, test runs monitor the degree of approach of the float to the shore, the speed of the current, the required braking force, the presence of hooks, etc. It is along this line, but upstream (taking into account drift), that the feeding point is marked. Usually the degree of lead is 1 -1.5 m to the fishing point. You can, of course, do it simpler: after feeding, look for fish in the fishing place, but in this case there is no guarantee that it will be at a point convenient for fishing. For example, if the main part of the bait lies near a stone, then the equipment will constantly cling to it. The starting part of the bait is about half of the total amount, the rest is required for supplementary feeding.
One of the most important points when fishing is to maintain the fish’s interest in the fishing point by supplementary feeding. With a small amount of food, the fish loses interest and leaves. It can be delayed for a relatively long time without bait only by exceptional bottom topography or the presence of shelter, such as snags. Therefore, constant supplementation is necessary.
The supplementary feeding scheme is close to catching large bottom-dwelling fish in still water: bream, ide or river kras. Additional feeding should be done quite rarely so as not to constantly disturb the fish, but in solid portions - three to five balls of bait the size of an orange. Since the supplementary feeding and starting balls are the same in size, the feeding point is determined simply - by a landmark on the opposite bank. This allows you to clearly control the fishing point at all times.
Constant feeding with small portions of bait (about the size of a table tennis ball) is primarily required for catching roach and silver bream. Lumps are thrown in one or two every 5-10 minutes. Thus, the fish are not disturbed by constant bait, but their interest is maintained as much as possible.
The correct rate of feeding is monitored by the reaction of the fish: if the quantity and quality of bites improve, large fish are caught, which means that the fisherman’s actions are absolutely correct. Of course, the total amount of both bait and supplementary feeding depends on the number of fish in the fishing area. If there is a lot of it, then the risk of overfeeding the fish is minimal, and if it is not enough, it is necessary to reduce the amount of bait, otherwise the bites will become weak and uncertain, and the fish, having had enough, will not be interested in the bait.
Small lumps of bait behave in water a little differently than large starting balls - they are carried away more and washed away faster by the current, and this must be taken into account. In addition, during the fishing process, the bait dries out a little, and it is necessary to either slightly moisten it with a spray bottle, or make allowances for that. that the bait becomes more active and breaks down faster at the bottom. When fishing for roach and silver bream, active bait helps fishing, but for bream it is absolutely necessary to control the degree of moisture in the bait. To ensure that the bait dries out less on a hot day, if possible, place it in the shade and cover it with a damp towel.
Fishing with a fly rod in the current involves floating the gear at one speed or another over the fishing point. The effectiveness of fishing is affected by the speed of the current and its changes, possible changes in water level, distribution of fish along the feeding line, its activity, etc.
Related articles:
Catching bersh
Spider lifts
Fishing for undermouth
Catching whiteeye
Installation of equipment
It is advisable to immediately equip them with various equipment options that will be suitable for different fishing conditions. This is done in advance and screwed onto the reel. You definitely need to have a couple of rig options, with different lengths of the main line.
Whether it is used when removing the knees of the form will depend on:
- depth of the reservoir;
- casting distance.
The tackle is made 27-35 cm less than the length of the form. This is essential for a good swing. Prepare several equipment at once: rod-shaped and equipment that is equipped with a round float.
But the most important thing is the options for loading the gear; it sets several options for equipment for a variety of fishing:
- To fish in all layers of water, equipment with a light load is constructed, and several pellets are evenly distributed along the fishing line. When casting, it goes to the bottom slowly, smoothly and as it follows, it will attract all the fish from the upper water to the lower water.
- To hunt for fish in the middle layers of water you need to: place the load with the so-called disturbed uniformity, move the pellets a little towards the under-grazing. The weight of the weights should decrease as they approach the metal hook.
- When fishing occurs in the bottom part, with a depth of about 3 m and with an intense current: install a heavy weight, with special pellets regulating it from below.
- If there is a lot of vegetation in the reservoir, then punching equipment is used: the load is placed compactly, and a special float is tied with a larger load capacity. We must not forget that very light equipment is of little use here, due to the impossibility of casting accurately.
Attaching the fishing line to the fishing rod using a connector
Fly fishing rods from most branded manufacturers have a tip without a built-in ring. It is assumed that the only and correct way to attach the fishing line will be through a special connector, which can be purchased separately at any fishing store.
The size of the connector is selected depending on the diameter (thickness) of the tip. The connector also differs in type of construction depending on whether the tip of the last bend is hollow or not. The inner one is inserted inside the tip, and the outer one is placed on top. Attach it with simple glue.
The connection is made using a loop on a fishing line, which is threaded into a special fastener. To prevent the line from slipping off, there is a special protective cap that covers the hook of the connector.
When purchasing it, you need to pay attention to the quality of workmanship. The entire surface should be perfectly smooth, without any sagging or burrs that will cause the line to fray.
Metal products are more reliable, but if they come into contact with water, they can become rusty over time.
The connector is the most popular compared to other fastening methods because it is reliable and allows you to easily change equipment.
Advantages and disadvantages of a fly rod
Advantages:
- Convenient to use.
- Has a small mass.
- Elementary equipment and lightning-fast replacement.
- Changing knees is not burdensome.
- Tangles and snags are kept to a minimum.
- Casting accuracy is high.
- Universal in use.
- It is not difficult to master the fishing technique.
- Setting up a fishing spot is also easy.
Flaws:
- The casting distance is small.
- Fragility.
- Difficulty in fishing near branches.
- At great depths, fishing is impossible.
- Large fish are impossible to catch.
Review of popular manufacturers
Light carbon fiber materials began to be used in production. The rod structure and design have been improved. In our country they are popular, especially famous
Made from carbon fiber, very durable. Equipped with a small butt diameter. With its help you can make precise casts, especially suitable for carp hunting.
- sections 6;
- weight is 430 g;
- length is 600 cm;
- transport length is 118 cm.
"Cormoran"
The telescopic fishing rod is made from composite material, therefore it has high strength and power:
- length from 3 to 6 m;
- weight: 390 gr.
Designed for fishing on lakes and small rivers for roach, carp, and crucian carp.
"Maver"
They are made using the latest technologies. She is fast in action and has good balance. Maver is used for catching large fish. Maver is in demand in sports. Main characteristics:
- the length is 5 m.
- weight is 140 g.
- transport length is 130 cm.
- test up to 18 gr.
"Trabucco"
A series of budget fishing rods from the Italian company TRABUCSO. The upper knee is combined, the tip is soft and thin. They are light and comfortable:
- footage 4 m.
- transport length 1.13 m.
- number of sections 4.
Shimano
Telescopic fishing rod, made of composite materials:
- footage: 4.9 m;
- weight: 270 g;
- has five sections;
- reel seat – classic;
- transport length – 1.43 m.
It easily casts almost any bait over a considerable distance.
Pros:
- light weight;
- excellent test;
- good strength.
Minuses:
- too high cost;
- Takes up a lot of space when folded.
"Daiwa"
The design is plug-in, quite simple and quite reliable. Made of carbon and carbon fiber. It behaves excellently with a test weight of 13 to 20 g, but it cannot be used only with heavy bait.
Pros:
- considerable length;
- quality ingredients
- reliability.
The downside is the high price.
"Black Hole"
Very compact and lightweight. Produced from graphite (grade IM 7) with high modularity. Equipped with:
- with a soft whip;
- good balance;
- performs sweeps perfectly.
"ZEMEX"
Telescopic design with 5 sections. The structure of the form is average. Made from carbon fiber material. It has:
- weight: 214 g;
- footage (cm): 500;
- length of tr. (cm): 132.
"Match"
Plug-in, composite, has a coil. They are especially successfully used for fishing in still water, medium and long distances. She has no competitors here.
"Sabaneev"
Suitable for beginner fishermen. It has good characteristics:
- excellent strength;
- good rigidity;
- ease;
- excellent balance.
Made from composite materials with a high carbon content, equipped with replaceable tips. The main advantage of this model is its excellent price. Moreover, this does not at all affect the quality.
Fishing technique and tactics
The main target of the floater is considered to be peaceful fish. Fishing with a fly rod involves a large selection of baits, feed mixtures and tactics. In the warm season, underwater inhabitants willingly take plant bait, and in early spring and autumn they prefer live food. Winter fishing is possible only in the absence of ice on the reservoirs. As a rule, rivers with strong currents freeze last. Everyone decides for themselves how to equip a fishing rod without rings, but everyone is guided by the basic rule: “thinner is better.”
Regardless of the time of year, the chosen location requires careful feeding. To do this, you can use a cup-shaped feeder, which is attached to the connector and pours out at the fishing site. The technique is used at long distances, where it is impossible to throw complementary foods by hand. In some cases, a fishing slingshot is used. To maintain the bite, two small feeding balls are thrown every half hour. The tactic is to quickly search and catch fish in a well-fed area. With the help of a long plug, you can successfully track prey in the nearest water area by adding or removing an extra pole.
Reviews from anglers
Sergey, 56 years old: “The fly rod, especially among amateur fishermen like me, is considered a very simple and favorite tackle for good reason. I have been sick with it for twenty years now. And I know the most important secret, this is short fishing. The adrenaline especially goes off scale when I pull kilogram ides or bream out of the water. So, this gear is a pretty serious weapon, I know that for sure.”
Vadim, 23 years old: “I personally think that only children and pensioners can fish with it. I made repeated attempts, but there was never any point, just small fish and nothing more. It’s just a pity for the wasted time!”